BFBS Forces News
Published 14 Aug 2025Ahead of VJ Day — go behind the scenes for a rare glimpse into the private collection of Field Marshal Slim’s wartime artefacts.
In this exclusive film, Tim Cooper visits Viscount Slim — grandson of the legendary Second World War commander — for an intimate look at a treasure trove of historical items. From a razor-sharp Japanese sword surrendered in 1945, to the pen that signed peace, and even the stark telegram announcing Britain’s entry into war, each item tells a powerful story.
(more…)
August 15, 2025
The pen that ended WWII: Inside Field Marshal Slim’s hidden collection
July 3, 2025
Bill Slim, the most forward-looking British commander of WW2
At The War Room, Dr. Robert Lyman explains how and why General (later Field Marshal) William Slim was able to turn around British and allied military fortunes in Burma and drive the Japanese out of India to their eventual defeat:
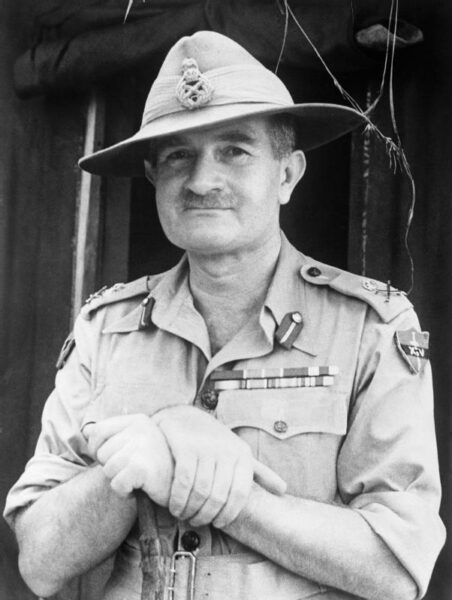

Field Marshal Sir William Slim (1891-1970), during his time as GOC XIVth Army.
Portrait by No. 9 Army Film & Photographic Unit via Wikimedia Commons.
“Burma and the Birth of Modern Warfare” is the subtitle to my 2004 book and PhD about General Slim’s command of the 14th Army in Burma during the last war, titled Slim, Master of War, a use of Sun Tzu’s description of a “heaven-born” commander. It may appear a rather grand claim, and perhaps it is, but the purpose of the subtitle reflects that fact that Slim’s conduct of operations in India and Burma in 1944 and 1945 represented an entirely new style of warfighting to that experienced by the British Army during the war. Instead of looking back to the lessons of World War One, Slim’s conduct of operations looked forward to reflect a style of warfare that would only be adopted as formal doctrine by the British Army in the 1980s. In the mid-1940s it remained alien to the vast bulk of similar British military experience and understanding.
My argument wasn’t that Slim was the best general who had ever commanded men in the history of warfare. That may or may not be true, but for the sake of my argument is irrelevant. My proposition, rather, is that:
Slim was the foremost British exponent in the Second World War of the “indirect approach” and that in his conduct of operations in 1944 and 1945 he provided a clear foreshadowing of “manoeuvre warfare”.
My idea, which first saw expression in my 2004 book, has been developed since then in my subsequent writings, including that of Japan’s Last Bid for Victory, which deals with the great events in the Assam and Manipur in 1944 (2011) and A War of Empires (2021). A major reason for the continuing amnesia in British military thinking about the warfighting characteristics of the Burma Campaign – apart from the fact that it is a long way to go for a staff ride – seems to be the fact that Slim’s style of warfighting remained largely alien to the British Army’s doctrinal precepts until the late 1980s. Until then, Slim’s strategic conceptions had been considered an aberration, and Slim himself regarded merely as the epitome of a fine military leader, and nothing more. Then, in a doctrinal revolution which began in the 1980s, the old firepower-based foundations – which themselves were largely a product of Montgomery’s approach to war in 1944 and 1945 – in which the supreme military virtue was the effective and coordinated application of force, were replaced. This revolution in doctrine and thinking about warfighting exchanged the old foundations with new ones based on an entirely different conception, that of manoeuvre at the operational level of war, in which notions of subtlety, guile and psychological dislocation came to be emphasised in an entirely new and refreshing way. My belief is that it was the effective and pragmatic employment of manoeuvre at the operational level of war by Slim in Burma that was the direct cause of the extraordinary victories the 14th Army achieved in 1944 and 1945 and which led to the two greatest defeats the Japanese Army suffered in the field in the Second World War, the first at Imphal-Kohima in India in 1944 and the second at Mandalay-Meiktila in Burma in 1945. My argument I suppose is that Slim’s exercise of command in Burma makes him not merely a fine example of a “manoeuvrist” commander but in actuality the template for modern manoeuvrist command.
[…]
First, the 14th Army was the only truly joint formation in the British armed forces during WW2. Nothing else, in North Africa, Italy or North-West Europe came close to it. Slim insisted on nothing less than full integration. Not only were headquarters joint, but operational and tactic delivery was also joint. At every level of command air and land headquarters were completely interlinked. I became convinced of this fact when I discovered that the RAF and the Army even shared messes! Strategic air transport, winning the air war, the operational reach and flexibility provided by air power underwrote Slim’s conception of battle, to the extent that the senior RAF officer in the theatre ruefully concluded in 1945, and I quote, that:
Slim was quicker to grasp the potentialities and value of air support in the jungles of Burma than most Air Force officers.
There was no snobbery and no shibboleths with Slim: if it worked, it was pressed into action.
[…]
Professor Dixon argues [in On the Psychology of Military Incompetence] that, unusually for a senior commander of his ilk in WW2, Slim was non-ethnocentric. He had no intrinsic prejudices about the virtues of one race over another. Slim, after all, was an officer of the Indian Army, and I have yet to come across any evidence that British regimental officers of the Indian Army regarded their soldiers in any way inferior to themselves. He was commonly known to those who served under him as “Uncle Bill” from the special affinity British troops had to him: the remarkable fact, however, was that at least 87% of his Army of several hundred thousand men recalled him as “Cha Cha Slim Sahib”: 14th Army was, after all, very largely Indian, Gurkha and West and East African. I certainly cannot think of any other Indian Army general who had such an impact on British troops. He became, of course, Chief of the Imperial General Staff following Field Marshal Montgomery, in 1948, which securely establishes this feat. On that note, I cannot conceive of “Uncle Bernard” when referring to Field Marshal Montgomery!
The Burma campaign was as much a struggle for mastery of logistics as it was a struggle for mastery on the battlefield, and it was about risk as much as it was about adherence to logistical principles. Slim had an implicit understanding of the constraints placed on warfare by the demands of logistics. Great efforts were made to increase the quantity of supplies to Burma. Railways were extended, roads built and surfaced, sunken ferries refloated and repaired, barges and rafts built for use on the numerous waterways. In this regard Archibald Nye, the VCIGS under Alan Brooke, regarded Slim’s mastery of logistics to be the most significant measure of his greatness as commander of 14 Army in Burma:
He never had enough to do what he had to do and this … is the measure of his greatness.
The practice of war in Burma by Slim was so startling in its modernity, and unlike any other pattern of warfighting by operational level British commanders in the war. My view of Slim as a commander can be interpreted at two levels. He was, first of all, a great commander and leader. Being a master of strategy, of logistics, of technical proficiency and so on are important in themselves when considering the nature of leadership in war, but by themselves they remain insufficient. Successful military command requires someone who can, through dint of personality and inspirational leadership, wield all of the components of fighting power together so that an extraordinary result transpires. What marks Slim out from the crowd was much more than just his winning of a succession of extraordinary battles. His strength lay in his ability to produce a decisive effect from scratch; to mould thousands of disparate individuals together into a single team with a single goal; to persuade a defeated army that it had the potential to turn the tables on their enemies; to master the complexities of terrain, climate and administrative deficiency so that self-help, resourcefulness and ingenuity could become as much prized as fighting skill. In these individual areas, and more, Slim proved the master. His genius for war was the consequence of his ability to bring together all of these elements to create an extraordinary result, the visible sign of which was the greatest defeat suffered by the Japanese on land during the Second World War.
June 2, 2025
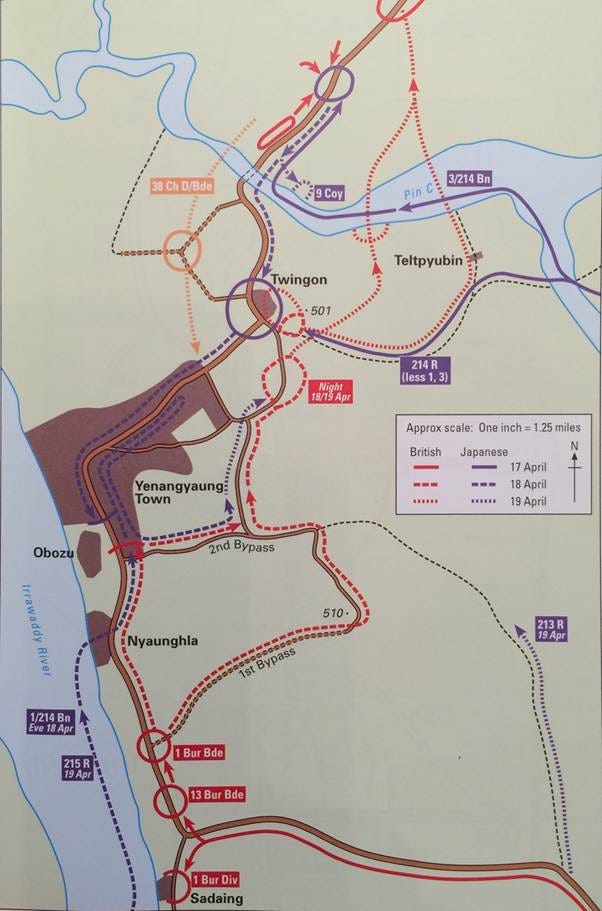
Fighting at Yenangyaung, 17-19 April 1942
Dr. Robert Lyman on the battle at Yenangyaung between 17-19 April 1942 early in the Burma campaign:
… the Yenangyaung battle is a fascinating one, with its own small degree of controversy, I decided to lay it out in this post. A mystery of the battle is the differing accounts of the Chinese attacks on the 19th April. In the British accounts (including Bill Slim’s in Defeat into Victory) the Chinese are blamed for failing to attack in the morning as they had promised, adding further jeopardy to the fate of the encircled 1st Burma Division. But was this true? The Japanese, Chinese and American accounts differ, so I thought I’d lay out the story to allow you, dear reader, to come to your own conclusion.
The scrap at Yenangyaung was the final Corps-sized battle before the order to evacuate Burma Corps was given in early May. The Japanese had pushed out of Rangoon in mid-March, driving up the Irrawaddy on the left and against Toungoo on the right. Allied plans for the defence of Burma were inadequate, both Chinese (on the right) and Slim’s Burcorps (on the left) effectively fighting separate battles. Attempts by General Harold Alexander, the Army Commander, to control the battle and constrain the advancing Japanese ultimately came to naught. Alexander, Slim and Lieutenant General Joe Stilwell, nominally commanding the Chinese 5th Army, tried every trick in the tactical rule book to bring a halt to the relentless Japanese advance, and to destroy them in battle. After a month of fighting in which the Chinese were pushed out of Toungoo, the British lost control of Prome and an attempt to consolidate a defensive line across the country failed, the Japanese moved up the Irrawaddy in an attempt to turn the British flank, breaking in at the oilfield town of Yenangyaung on 17 April. At the time Slim’s Burma Corps was attempting to withdraw to the north from Allamyo. The Japanese infiltration into Yenangyaung cut the British in half. The 1st Burma Division was now cut off in Yenangyaung. The battle by the already weakened division (amounting to probably no more than 4,000 troops) into the Yenangyaung pocket over the period 17 and 19 April proved to be the severest trial yet faced by British troops in the short Burma campaign, the pressure applied by the Japanese exacerbated by the intense heat and the lack of water.
It was critical that Slim defeated this Japanese infiltration, rescue the 1st Burma Division from encirclement and retain the integrity of his Corps. If Yenangyaung were lost the Japanese would be free to sweep north to threaten Mandalay. It was crucial therefore that the divisional commander – Major General Bruce Scott – held on for as long as he could. But Slim had no reserve. The only hope of relief lay in assistance from the Chinese far to his right. He concluded that if he could engineer a attack into the pocket by the Chinese, across the Pin Chaung, combined with a breakout attack by 1st Burma Division, they might have a chance of escape. Nothing else looked likely to succeed.
When asked, Stilwell agreed to Alexander’s request for help to be provided to Slim, and gave him Lieutenant General Sun Lijen’s 38th Division – responsible for the defence of Mandalay – for the task. Chiang Kai-shek had given Sun responsibility for defending Mandalay. At midnight on 16 April Sun received an order from General Lo Cho-yin, “to dispatch his 113th Regiment to Kyaukpadaung, there to be commanded by the British General Slim …” Sun’s friend, Dr Ho Yungchi, recorded that by 3 a.m. he had arrived at Lo’s HQ at Pyawbe to discuss the order. Lo explained that the British were in serious trouble “in the oil town of Yenangyaung and had sent repeated requests for help”. By 6.30 a.m. it was agreed that Sun would personally take command of the 113th Regiment, while the two remaining regiments stayed to defend Mandalay. Sun and 1,121 men of 113th Regiment (commanded by Colonel Liu Fang-wu) arrived at Kyaukpadaung on the morning of 17 April.
Slim recalled: “The situation was not encouraging, and I was greatly relieved to hear that 113 Regiment of the Chinese 38th Division was just arriving at Kyaukpadaung. I dashed off in my jeep to meet their commander and give him his orders … this was the first time I had had Chinese troops under me … I got to like all, or almost all, my Chinese very much. They are a likeable people and as soldiers they have in a high degree the fighting man’s basic qualities – courage, endurance, cheerfulness, and an eye for country.”1
At Yenangyaung, Slim’s plan was for Sun’s 38th Division to attack from the north on the morning of 18th April while the 1st Burma Division, within the pocket, fought its way out. As Slim and Sun Lijen talked, discussing the details of the attack planned for the following morning Slim decided that he would place the Stuart tanks of the 7th Armoured Brigade directly under Sun’s command. It was only a move a man confident in the capabilities of his allies could make. Slim commented that “I was impressed by Sun and it was essential to gain his confidence. His division had no artillery or tanks of its own, and I was therefore arranging that all the artillery we had this side of the Pin Chaung and all available tanks should support his attack.” The commander of the British armoured brigade – Brigadier John Anstice – accepted this arrangement and according to Slim “he and Sun got on famously together”. What’s more, the soldiers worked well together too, Slim recording that the “gunners and tank crews, as is the way of British soldiers, soon got on good terms with their new comrades, and, in spite of language difficulties of an extreme kind, co-operation was, I was assured by both sides, not only close but mostly friendly.”2 Accordingly, at 6.15 a.m. on 18 April, Major Mark Rudkin of 2nd Royal Tank Regiment (2RTR) reported as instructed by Anstice to 38th Division HQ:
There was little activity except for the cooking of breakfast and it seemed most unlikely that the attack could start on time. I asked the British liaison officer with the Chinese what was happening and he informed me that as the Chinese realized that they would not be ready to attack at 0630 hours, they had put their watches back one hour, so that officially they were still attacking at 0630 though the time would in reality be 0730. They had, therefore, not lost “face” by being late.
The plan was that a troop of tanks would follow the leading troops of the leading Chinese battalion and give what support it could. Another troop was to follow the leading infantry battalion and assist the leading troop if required. The tanks would be almost entirely road bound owing to the going off the road.
At 0730 the assaulting Chinese moved forward off the ridge on a front of about four hundred yards, the leading troop keeping very close behind on the road. On foot near the tanks was a Chinese interpreter who carried out liaison between the tanks and infantry.
After advancing about half a mile the leading tank was hit by a Japanese 75-mm gun situated on the road just north of the Pin Chaung which was firing straight up 300 yards of road. The tank was disabled but there were no casualties.
The Chinese advance continued and by afternoon had almost reached the line of the ford on the Pin Chaung which was still held by the enemy. The Chinese had had heavy casualties, especially amongst officers, as it was the custom for Chinese officers to lead, whatever their rank. It was finally decided to hold positions about half a mile north of the crossing and continue the attack next day.3
With the first attack a failure, the Japanese retained their grip on both the ford and the village of Twingon. The situation for the surrounded remnants of the 1st Burma Division was desperate; the Japanese close to achieving a complete victory. Slim and Sun then worked through a plan for another attempt to be made the following morning, 19th April. This day also began badly, however. The Chinese attack was scheduled to begin at 7 a.m. British accounts subsequently recorded that a Chinese attack did not materialise at this time. Slim subsequently recorded in Defeat into Victory that the failure to attack must have been a function of the administrative difficulties faced by the Chinese. He wrote that with the Chinese “lack of signalling equipment, of means of evacuating wounded and of replenishing ammunition, and their paucity of trained junior leaders it was not surprising that to sort themselves out, reform, and start a fresh attack took time”.4 Slim was invariably impressed with what he saw of the Chinese soldier in action, but considered their support and command functions to be shockingly poor and a source of constant frustration to themselves, and to all who had occasion to operate with them.
Slim, and most other British published accounts, including the Indian and British Official Histories, record that the attack finally went in at 3 p.m., when Colonel Liu’s 113th Regiment successfully captured the ford and penetrated into Yenangyaung.5 “When the Chinese did attack they went in splendidly” wrote Slim in admiration. “They were thrilled at the tank and artillery support they were getting and showed real dash. They took Twingon, rescuing some two hundred of our prisoners and wounded. Next day, 20th April, the 38th Division attacked again and with tanks penetrated into Yenangyaung itself, repulsing a Japanese counter-attack. The fighting was severe and the Chinese acquitted themselves well, inflicting heavy losses, vouched for by our own officers.”
1. Slim, Defeat into Victory (1956), p. 63.
2. Ibid., p. 65.
3. Bryan Perrett, Tank Tracks to Rangoon: The Story of British Armour in Burma (London: Robert Hale, 1978)
4. Slim, op. cit., p. 70.
5. Bisheshwar Prasad (ed,) The Retreat from Burma 1941 – 42 (Calcutta, Combined Inter-Service Historical Section, 1954), p. 296.
February 20, 2025
Retaking Burma with the Fourteenth Army in 1945
Dr. Robert Lyman discusses the start of the campaign to reconquer Burma from the Japanese led by Lieutenant General Bill Slim and the Fourteenth Army:
Why Burma? Because in Burma in 1945 a series of marvellous military miracles (is there a synonym starting with “m” for concatenation?) engineered by General Bill Slim and his mighty 14th Army, broke the back of the Japanese Burma Area Army and smashed forever Tokyo’s dreams of an empire in South East Asia. 1945 is worth celebrating!
Even today, few people are aware of just how dramatic these events were, and just how spectacular was the victory wrought by the Indian, British, African, US and Chinese forces in the country.
Indeed, at the start of 1945 few people would have predicted the extraordinary outcome of the developing campaign. If Lieutenant General Sir Bill Slim (he had been knighted by General Archibald Wavell, the Viceroy, the previous October, at Imphal) had been asked in January 1945 to describe the situation in Burma at the onset of the next monsoon period in May, I do not believe that in his wildest imaginings he could have conceived that the whole of Burma was about to fall into his hands. After all, his army wasn’t yet fully across the Chindwin. Nearly 800 miles of tough country with few roads lay before him, not the least the entire Burma Area Army under a new commander, General Kimura. The Arakanese coastline needed to be captured too, to allow aircraft to use the vital airfields at Akyab as a stepping stone to Rangoon. Likewise, I’m not sure that he would have imagined that a primary reason for the success of his Army was the work of 12,000 native levies from the Karen Hills, under the leadership of SOE, whose guerrilla activities prevented the Japanese from reaching, reinforcing and defending the key town of Toungoo on the Sittang river. It was the loss of this town, more than any other, which handed Burma to Slim on a plate, and it was SOE and their native Karen guerrillas which made it all possible.
The potential of a Karenni-based resistance raised the possibility, long argued by old Burma hands, of a British armed and trained fifth column operating behind Japanese lines for the purpose of gathering battlefield intelligence and undertaking limited guerrilla action. Slim had long complained about the poor quality of the battlefield intelligence (as opposed to the signals intelligence, about which he was well provided) that he and his Corps commanders received. He was concerned, among other things, about knowing “what was on the other side of the hill”, the product of information provided – where it existed – by effective combat (ground and air) reconnaissance. There was no shortage of organisations attempting to assist in this task – at least twelve – but their coordination was poor and most reported to SEAC or parts of India Command, rather than to 14 Army. Slim dismissed most of these as “private armies” which offered no real help to the task of defeating the enemy on the battlefield. One of the groups, part of Force 136 (i.e. Special Operations Executive, or SOE), which had operated in front of 20 Indian Division along the Chindwin between 1943 and early 1944 under Major Edgar Peacock (and thus known as “P Force”) did sterling work with local Burmese and Karen agents reporting on Japanese activity facing 4 Corps. Persuaded that similar groups working among the Karens in Burma’s eastern hills – an area known as the Karenni States – could achieve significant support for a land offensive in Burma, Slim (to whom Mountbatten transferred responsibility for Force 136 in late 1944 for this purpose) authorised an operation to the Karens. Its task was not merely to undertake intelligence missions watching the road and railways between Mandalay and Rangoon, but to determine whether they would fight. If the Karens were prepared to do so, SOE would be responsible for training and organising them as armed groups able to deliver battlefield intelligence directly in support of the advancing 14 Army. The resulting operation – Character – was so spectacularly successful that it far outweighed what had been achieved by Operation Thursday the previous year in terms of its impact on the course of military operations in pursuit of the strategy to defeat the Japanese in the whole of Burma. It has been strangely forgotten, or ignored, by most historians ever since, drowned out perhaps by the noise made by the drama and heroism of Operation Thursday, the second Chindit expedition. Over the course of Operation Extended Capital some 2,000 British, Indian and Burmese officers and soldiers, along with 1,430 tons of supplies, were dropped into Burma for the purposes of providing intelligence about the Japanese that would be useful for the fighting formations of 14th Army, as well as undertaking limited guerrilla operations. As historian Richard Duckett has observed, this found SOE operating not merely as intelligence gatherers in the traditional sense, but as Special Forces with a defined military mission as part of conventional operations linked directly to a strategic outcome. For Operation Character specifically, about 110 British officers and NCOs and over 100 men of all Burmese ethnicities, dominated interestingly by Burmans (which now also included 3-man Jedburgh Teams) mobilised as many as 12,000 Karens over an area of 7,000 square miles to the anti-Japanese cause. Some 3,000 weapons were dropped into the Karenni States. Operating in five distinct groups (“Walrus”, “Ferret”, “Otter”, “Mongoose” and “Hyena”) the Karen irregulars trained and led by Force 136, waited the moment when 14 Army instructed them to attack.
February 17, 2025
Forgotten War Ep 9 – Kohima – Hell in the Hills
HardThrasher
Published 16 Feb 2025The Battle of Kohima.
Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
February 6, 2025
Forgotten War Ep 8 – Imphal 44 Pt2 – Edge of Chaos
HardThrasher
Published 4 Feb 2025A video discussing the Battles of Imphal and Kohima at the start of 1944.
Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
January 13, 2025
Forgotten War – Ep 7 – Imphal ’44 Pt1 – Planning Prevents
HardThrasher
Published 12 Jan 2025DO NOT PANIC IF YOU HAVEN’T WATCHED THE OTHER VIDEOS IN THIS SERIES YOU CAN START HERE
A video discussing the planning phase of the Battles of Imphal and Kohima at the start of 1944
Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
January 2, 2025
Forgotten War – Ep 6 – The Battle of the Admin Box – Feb. 1944
HardThrasher
Published 1 Jan 2025A short video on the highlights of the Battle of the Admin Box, and its build up DO NOT PANIC IF YOU HAVEN’T WATCHED THE OTHER VIDEOS IN THIS SERIES
Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
November 30, 2024
Forgotten War Ep 5 – Chindits 2 – The Empire Strikes
HardThrasher
Published 29 Nov 202402:00 – Here We Go Again
06:36 – Perfect Planning
13:16 – Death of a Prophet
14:51 – The Fly In
18:56 – Dazed and Confused (in the Monsoon)
20:40 – Can’t Fly in This
31:54 – Survivor’s ClubPlease consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
November 7, 2024
Forgotten War Ep4 – Rise of the Chindits
HardThrasher
Published 4 Nov 2024Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
September 23, 2024
Forgotten War Ep3 – Death in the Arakan
HardThrasher
Published 18 Sept 2024Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 — https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
August 31, 2024
Forgotten War Ep2 – You Walk, You Walk Or You Die Mate
HardThrasher
Published 30 Aug 2024Please consider donations of any size to the Burma Star Memorial Fund who aim to ensure remembrance of those who fought with, in and against 14th Army 1941–1945 – https://burmastarmemorial.org/
(more…)
August 17, 2024
Forgotten War Ep1 – Witness the Rising Sun
HardThrasher
Published Aug 14, 2024In January 1942 the Japanese Army poured over the border with Burma, and pushed back the Indian and British Armies to the border with Burma. Today we look at how that disaster came about, why and the first phase of the campaign
(more…)
July 31, 2024
The Korean War Week 006 – Stand or Die! – July 30, 1950
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 30 Jul 2024The UN Forces have been pushed back ever further, but this week, US 8th Army Commander Walton Walker issues the order to “stand or die”; he sees no other options. American reinforcements are finally getting into the actual fight, though, and Britain has decided they will send in ground troops, so things might turn around … if they can hold out long enough for those troops to arrive, because a brilliant North Korean strategy might win the war and soon.
(more…)
May 5, 2024
Allied Victory in Berlin, Italy, and Burma! – WW2 – Week 297 – May 4, 1945
World War Two
Published 4 May 2024So much goes on this week, and this is the longest episode of the war by like 15 minutes. But there’s so much to cover! The Battle of Berlin ends; the war in Italy ends; the war in Burma ends- well, it ends officially, though there are still tens of thousands of Japanese soldiers scattered around Burma. And there’s a whole lot more to these stores and a whole lot more stories this week in the war. You can’t miss this one.
01:27 The End of the War in Italy
03:40 Western Allied Advances
07:02 Relief Operations in the Netherlands
15:45 Hitler’s Death and the Surrender of Berlin
24:20 Walther Wenck’s Retreat
28:00 The Polish Situation
31:09 What About Prague?
32:44 The End of the Burma Campaign
36:04 THE FIGHT FOR TARAKAN ISLAND BEGINS
37:24 Okinawa
40:11 Other Notes
41:04 Summary
41:43 Conclusion
(more…)