Polyus Studios
Published 14 Jul 2018The program that developed the CL-84 lasted for almost 20 years and produced one of the most successful VTOL aircraft ever, as far as performance. Canadair produced four Dynavert’s over those 20 years and two of them crashed. In fact one crashed twice. The story of the great CL-84 is one of perseverance and missed potential.
(more…)
November 25, 2022
Canada’s all-purpose VTOL transport that could have changed everything; the Canadair CL-84 Dynavert
November 11, 2022
In memoriam
A simple recognition of some of our family members who served in the First and Second World Wars:
The Great War
 Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
Private William Penman, Scots Guards, died 16 May, 1915 at Le Touret, age 25
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)- Private Archibald Turner Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, mortally wounded 25 September, 1915 at Loos, age 27
(Elizabeth’s great uncle) - Private David Buller, Highland Light Infantry, died 21 October, 1915 at Loos, age 35
(Elizabeth’s great grandfather) - Private Harold Edgar Brand, East Yorkshire Regiment. died 4 June, 1917 at Tournai.
(My first cousin, three times removed) - Private Walter Porteous, Durham Light Infantry, died 4 October, 1917 at Passchendaele, age 18
(my great uncle) - Corporal John Mulholland, Argyll & Sutherland Highlanders, wounded 2 September, 1914 (shortly before the First Battle of the Aisne), wounded again 29 June, 1918, lived through the war.
(Elizabeth’s great uncle)
The Second World War
- Flying Officer Richard Porteous, Royal Air Force, survived the defeat in Malaya, was evacuated to India and lived through the war
(my great uncle) - Able Seaman John Penman, Royal Navy, served in the Defensively Equipped Merchant fleet on the Atlantic convoys, the Murmansk Run (he may have been on a ship in convoy PQ-17, as we know he spent a winter in Russia) and other convoy routes, was involved in firefighting and rescue efforts during the Bombay Docks explosion in 1944, lived through the war
(Elizabeth’s father) - Private Archie Black (commissioned after the war and retired as a Major), Gordon Highlanders, captured during the fall of Singapore (aged 15) and survived a Japanese POW camp (he had begun to write an autobiography shortly before he died)
(Elizabeth’s uncle) - Elizabeth Buller, “Lumberjill” in the Women’s Timber Corps, an offshoot of the Women’s Land Army in Scotland through the war.
(Elizabeth’s mother) - Trooper Leslie Taplan Russon, 3rd Royal Tank Regiment, died at Tobruk, 19 December, 1942 (aged 23).
Leslie was my father’s first cousin, once removed (and therefore my first cousin, twice removed).
My maternal grandfather, Matthew Kendrew Thornton, was in a reserved occupation during the war as a plater working at Smith’s Docks in Middlesbrough. The original design for the famous Flower-class corvettes came from Smith’s Docks and 16 (including four intended for the French Marine National) of the 196 built in the UK during the war (more were built in Canada).
For the curious, the Commonwealth War Graves Commission the Royal British Legion, and the Library and Archives Canada WW1 and WW2 records site provide search engines you can use to look up your family name. The RBL’s Every One Remembered site shows you everyone who died in the Great War in British or Empire service (Canadians, Australians, New Zealanders, South Africans and other Imperial countries). The CWGC site also includes those who died in the Second World War. Library and Archives Canada allows searches of the Canadian Expeditionary Force and the Royal Newfoundland Regiment for all who served during WW1, and including those who volunteered for the CEF but were not accepted.
In Flanders fields the poppies blow
Between the crosses row on row,
That mark our place; and in the sky
The larks, still bravely singing, fly
Scarce heard amid the guns below.We are the Dead. Short days ago
We lived, felt dawn, saw sunset glow,
Loved and were loved, and now we lie
In Flanders fields.Take up our quarrel with the foe:
To you from failing hands we throw
The torch; be yours to hold it high.
If ye break faith with us who die
We shall not sleep, though poppies grow
In Flanders fields.Lieutenant Colonel John McCrae, MD Canadian Army Medical Corps (1872-1918)
November 5, 2022
A working flight simulator, no computers necessary
Tom Scott
Published 4 Jul 2022There are only a few working Link Trainers left in the world: but before microprocessors, before display screnes, half a million pilots learned the basics of instrument flying inside one. More: https://www.most.org/explore/link-fli…
(more…)
October 24, 2022
An overview of strategic airpower
Bret Devereaux wants to provide a basic idea of what we mean when we use the military term “strategic airpower”:

USAF B-52 Stratofortress near the North Pole on 31 July, 2016 during the Polar Roar exercise.
Detail of original USAF photo by Senior Airman Joshua King via Wikimedia Commons.
This week, I’m going to offer a fairly basic overview of the concept of strategic airpower, akin to our discussions of protracted war and nuclear deterrence. While the immediate impetus for this post has been Russian efforts to use airpower coercively in Ukraine, we’re going to focus more broadly on the topic: what is strategic airpower, where did the idea come from, how has it been used and does it actually work? As with nuclear deterrence, this is a much debated topic, so what I am going to present here is an overview of the sort I’d provide for an introductory class on the topic and then at the end we’ll cover some of the implications for the current conflict in Ukraine. That said, this is also an issue where I think most historians of the topic tend to part ways with both some things the public think they know about the topic and some of the things that occasionally the relevant branches of the military want to know about the topic; in any case I am going to try to present a fairly “down the middle” historian’s view of the question.
Before we dive in, we need to define what makes certain uses of airpower strategic because strategic airpower isn’t the only kind. The reason for the definition will emerge pretty quickly when we talk about origins, but let’s get it out of the way here: strategic airpower is the use of attack by air (read: bombing) to achieve “strategic effects”. Now that formal definition is a bit tautological, but it becomes clarifying when we talk about what we mean by strategic effects; these are effects that aim to alter enemy policy or win the war on their own.
Put another way, if you use aircraft to attack enemy units in support of a ground operation (like an invasion), that would be tactical airpower; the airpower is a tactic that aims to win a battle which is still primarily a ground (or naval) battle. We often call this kind of airpower “close air support” but not all tactical airpower is CAS. If you instead use airpower to shape ground operations – for instance by attacking infrastructure (like bridges or railroads) or by bombing enemy units to force them to stay put (often by forcing them to move only at night) – that’s operational airpower. The most common form of this kind of airpower is “interdiction” bombing, which aims to slow down enemy ground movements so that friendly units can out-maneuver them in larger-scale sweeping movements.
By contrast strategic airpower aims to produce effects at the strategic (that is, top-most) level on its own. Sometimes that is quite blunt: strategic airpower aims to win the war on its own without reference to ground forces, or at least advance the ball on winning a conflict or achieving a desired end-state (that is, the airpower may not be the only thing producing strategic effects). Of course strategic effects can go beyond “winning the war” – coercing or deterring another power are both strategic effects as well, forcing the enemy to redefine their strategy. That said, as we’ll see, this initially very expansive definition of strategic airpower really narrows quite quickly. Aircraft cannot generally hold ground, administer territory, build trust, establish institutions, or consolidate gains, so using airpower rapidly becomes a question of “what to bomb” because delivering firepower is what those aircraft can do.
As an aside, this sort of cabined definition of airpower and thus strategic airpower has always been frustrating to me. It is how airpower is often discussed, so it’s how I am going to discuss it, but of course aircraft can move more than bombs. Aircraft might move troops – that’s an operational use of airpower – but they can also move goods and supplies. Arguably the most successful example of strategic airpower use anywhere, ever is the Berlin Airlift, which was a pure airpower operation that comprehensively defeated a major Soviet strategic aim, and yet the U.S. Air Force is far more built around strategic bombing than it is around strategic humanitarian airlift (it does the latter, but the Army and the Navy, rather than the Air Force, tend to take the lead in long-distance humanitarian operations). Nevertheless that definition – excessively narrow, I would argue – is a clear product of the history of strategic airpower, so let’s start there.
And once again before we get started, a reminder that the conflict in Ukraine is not notional or theoretical but very real and is causing very real suffering, including displacing large numbers of Ukrainians as refugees, both within Ukraine and beyond its borders. If you want to help, consider donating to Ukrainian aid organizations like Razom for Ukraine or to the Ukrainian Red Cross. As we’re going to see here, airpower offers no quick solution for the War in Ukraine for either party, but the recent Russian shift to air attacks on civilian centers sadly promises more suffering and more pressing need for humanitarian assistance for Putin’s many victims.
Finally, a content warning: what we’re discussing today is largely (though not entirely) the application of airpower against civilian targets because it turns usually what “strategic” airpower ends up being. This is a discussion of the theory, which means it’s going to be pretty bloodless, but nevertheless this topic ought to be uncomfortable.
On with our topic, starting with the question of where the idea of strategic airpower comes from.
October 22, 2022
Battle of the Bulge 1944: Could the German Plan Work?
Real Time History
Published 21 Oct 2022Sign up for Nebula and watch Rhineland 45: https://nebula.tv/realtimehistory
The Battle of the Bulge was one of the last German offensives during the Second World War. It caught the US Army off guard in the Ardennes sector but ultimately the Allies prevailed. But did Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein (“Operation Watch on the Rhine”) ever have a chance to succeed and reach Antwerp?
(more…)
October 19, 2022
South Atlantic D-Day: Battle of San Carlos – Falklands War
Historigraph
Published 15 Oct 2022On May 21st 1982, the United Kingdom landed thousands of troops at San Carlos Water in the Falkland Islands, to begin their recapture from Argentina. But only hours after arriving, British forces were under intense attack, as the Argentine air force attempted to push the troops clambering ashore back into the sea. This was the Battle of San Carlos.
0:00 – Intro
0:37 – Britain’s Invasion Plans
2:59 – Bespoke Post
4:16 – The Argentine Onslaught
8:46 – Attack on Coventry and Conveyer
(more…)
October 11, 2022
A tribute to the F-101 ‘Voodoo’ Fighter
Matsimus
Published 4 Jun 2022The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF).
Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a penetration fighter) for the USAF’s Strategic Air Command (SAC), the Voodoo was instead developed as a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber for the USAF’s Tactical Air Command (TAC), and as a photo reconnaissance aircraft based on the same airframe. An F-101A set a number of world speed records for jet-powered aircraft, including fastest airspeed, attaining 1,207.6 miles (1,943.4 km) per hour on 12 December 1957.[1] They operated in the reconnaissance role until 1979.
Delays in the 1954 interceptor project led to demands for an interim interceptor aircraft design, a role that was eventually won by the B model of the Voodoo. This required extensive modifications to add a large radar to the nose of the aircraft, a second crew member to operate it, and a new weapons bay using a rotating door that kept its four AIM-4 Falcon missiles or two AIR-2 Genie rockets hidden within the airframe until it was time to be fired. The F-101B entered service with USAF Air Defense Command in 1959 and the Royal Canadian Air Force in 1961. US examples were handed off to the USAF Air National Guard where they served until 1982. Canadian examples remained in service until 1984.
(more…)
September 22, 2022
RAF Coastal Command vs U-Boats
The History Guy: History Deserves to Be Remembered
Published 5 Oct 2020The contest between aircraft and U-Boats during the Second World War was one of competing technological innovations, culminating with a decisive struggle in the summer of 1943. The History Guy tells the forgotten story of the development of anti-submarine warfare and the contest between the aircraft of RAF Coastal Command and U-Boats of the Kriegsmarine in the Bay of Biscay.
(more…)
September 18, 2022
“King Eeyore”
In the latest edition of the SHuSH newsletter, Kenneth Whyte recounts some of the anti-Carolean gossip from the early years of King Charles:
My library of royalist literature is thin, but I did find Tina Brown’s The Palace Papers on the shelf. Published last spring, it chronicles the recent history of the House of Windsor and while it treats the whole cast of characters — Elizabeth, Philip, Margaret, Charles, Anne, Andrew, Edward, William, Kate, Harry, Meghan — much is revealed about the new king.
Charles, writes Brown, the former Vanity Fair and New Yorker editor, was never a happy fellow. She calls him “Prince Eeyore”. He “felt bruised by his childhood and miserable school days, misunderstood by his domineering father, and deprived of an emotional connection with his mother”. Among the “brutalities” he endured in his youth: his schoolmates at Gordonstoun beat him with pillow because he snored.
Although an indifferent student, he attended Cambridge where he read anthropology and archaeology. In 1969, a year before graduating, his mother crowned him Prince of Wales. He spent his early twenties in the Royal Air Force and the Royal Navy, distinguishing himself in the latter service by lowering an anchor without noticing on his chart the presence of a telecommunications cable linking Ireland and Britain. “It was snagged,” writes Brown, “and the two divers send down to dislodge it nearly drowned.” Charles earned a “stern rebuke”.
Having done his military duty, he devoted himself to polo, windsurfing, and test-driving prospective wives. Charles’s royal status made him an obvious catch, writes Brown, who judges that his “Dumbo ears were offset by his excellent tailoring and debonair polo prowess.”
Finding a wife proved difficult, not least because of his affinity for married women. At one point he was sleeping with both Camilla Parker Bowles, wife of Andrew Parker Bowles, and Dale “Kanga” Harper, wife of his buddy, Lord Tyron. “In the mid-seventies,” says Brown, “both married women were on call for the Prince while their husbands looked the other way.”
That’s not exactly true. Both men seemed pleased to lay down their wives for their country, as the joke went at the time. Charles was godfather to Tom Parker Bowles, son of Andrew and Camilla Parker Bowles, and also to a middle child of the Tyron’s who, naturally, was named Charles.
What Camilla and Kanga had in common were game personalities and maternal instincts that accommodated the Prince’s “sentimentality and tantrums, and needs to be soothed and amused”.
It wasn’t until 1981, at the age of 32, that the Prince of Wales made his choice of a bride. It was famously awful for all concerned. He married twenty-year-old Diana Spencer who bore him an heir, William, in 1982, and a spare, Harry, in 1984. Brown reports that Charles behaved properly in the marriage until the birth of Harry who, to his disappointment, was not a girl. “Oh God,” he said, “it’s a boy … and he’s even got red hair.”
He was back with Camilla in no time. Diana ratted him out to the author Andrew Morton in 1992 and Charles unwittingly confirmed his infidelity the next year in a notorious telephone conversation with Camilla in which he said that he wanted to “live inside your trousers or something”. You know the rest.
September 9, 2022
The Velvet Glove and Sparrow II missiles; A Beginners Guide To Post-War Bomber Interception Tactics
Polyus Studios
Published 14 Jul 2018The Velvet Glove was a semi-active guided missile system developed by the Canadian Armament Research and Development Establishment. Its successor, the Sparrow II, was developed by Canadair in association with the US Air Force. This is the story of the development of the missiles in the context of contemporary weapons systems.
(more…)
August 26, 2022
Bristol/Magellan CRV7 Ground Attack Rockets; Simply The Best
Polyus
Published 19 Aug 2022Sometimes a weapon is produced that no one can ignore. Something so much better than anything else on the market that it becomes the de facto standard. Winnipeg, Manitoba’s Bristol Aerospace created such a weapon in the early 1970s. It combined high speed and long range with a powerful knockout punch. It was the CRV7 rocket and it would eventually become ubiquitous among western aligned armed forces.
(more…)
August 24, 2022
Serbia ensures that we still have fresh concerns this summer
CDR Salamander on yet more potential trouble in the Balkans that has drawn some serious attention from the US Air Force:

USAF B-52 Stratofortress near the North Pole on 31 July, 2016 during the Polar Roar exercise.
Detail of original USAF photo by Senior Airman Joshua King via Wikimedia Commons.
I know everyone is busy and all … but you need to keep an eye on the usual problem areas.
You would think one war in Europe at a time would be enough, but you should never underestimate the Serbs.
As with most of us who were on active duty in the 1990s, I have more than a passing interest in the former Yugoslavia — and invested my quota of effort in its wars.
Later in my career I later served in NATO with Slovenes, Croatians, and N. Macedonians. I’ve vacationed a few times in Slovenia and Croatia. One of my daughters has studied, twice, in Serbia.
I keep an eye on it … and thankfully so are some smart people in The Pentagon.
The Balkans is always on the edge and has been for centuries, so it is only natural that now and then it bubbles over.
You may have missed with all the other news that the frozen conflict in Kosovo was throwing sparks again. That is why on Friday I tilted my head a bit with this announcement;
Two U.S. Air Force B-52 Stratofortress aircraft assigned to the 23rd Bomb Squadron currently operating out of RAF Fairford, United Kingdom, will conduct low approach flyovers over Southeastern Europe scheduled on August 22.
The purpose of each flyover is to demonstrate U.S. commitment and assurance to NATO Allies and partners located in Southeastern Europe. Additionally, this will provide citizens an opportunity to take photos, videos, and enjoy the aircraft flying overhead.
That told me that the Balkans desk has run their concerns up the chain and whatever they briefed was enough to greenlight a not insignificant display.
Sure enough, off it went Monday;
A pair of U.S. Air Force B52 strategic bombers on Monday flew low over the Croatian resort of Dubrovnik and three other NATO-member states in the region as a sign of support amid the Russian aggression in Ukraine.
In addition to the walled Croatian tourist resort of Dubrovnik, the aircraft flew over the government headquarters in Skopje, North Macedonia, the downtown Skanderbeg Square in the Albanian capital, Tirana, and up the Adriatic coast of Montenegro.
The Balkans and the Adriatic Sea have lately seen increased military, intelligence and propaganda activity by Moscow, which considers the region of its strategic interest because of its access to the Mediterranean.
Serbia is about Russia’s last friend in Europe and make no mistake … the Serbs do not consider borders settled anywhere — they are just waiting for the moment to be ripe.
August 1, 2022
Hamburg’s Citizens Burnt Alive – WAH 071 – July 31, 1943
World War Two
Published 31 Jul 2022In Italy the Fascists fall from power in a peaceful coup, while in Germany the RAF and USAAF bring down a rain of fire of biblical proportions in Operation Gomorrah, launching the Firestorm of Hamburg.
(more…)
July 17, 2022
Who Let the Dogs Out?! – The Invasion of Sicily – WW2 – 203 – July 16, 1943
World War Two
Published 16 Jul 2022The Allies have begun their fight to take back Western Europe with Operation Husky. That’s not the only news though. They are also trying to extend their foothold in the Solomons, and Germany and the USSR continue smashing into one another at Kursk.
(more…)
July 5, 2022
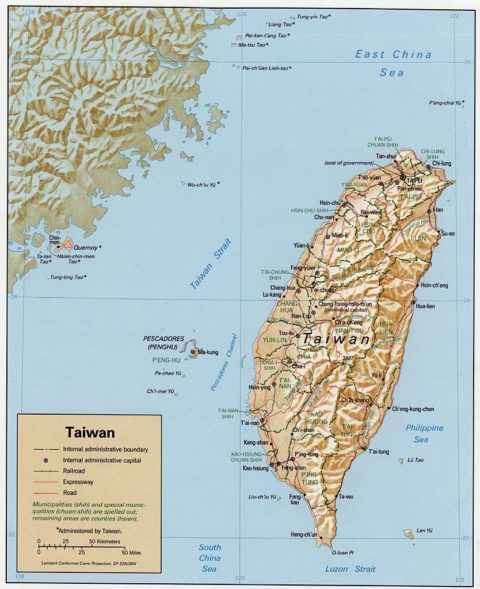
The Republic of China’s “Porcupine strategy”
Originally published in the New York Sun and reposted by the New English Review, Conrad Black believes any attempted amphibious invasion of Taiwan will become the worst invasion outcome since the Athenians assaulted Syracuse in 414-413 BC:
There has for some time been a good deal of flippant talk about a Communist Chinese invasion of the Republic of China on Taiwan, as if that would be a simple military undertaking. It seems to be inadequately appreciated that Taiwan has thought of little else for many years, and is, unlike Ukraine, a very prosperous and technologically sophisticated country that is armed to the teeth with the most advanced American weaponry, and has plotted out a defense in depth that is called its “porcupine strategy”.
Though it is probably accidental, “porcupine” is the word applied to Switzerland by Adolf Hitler in 1941, when, after careful analysis by the German General Staff, he concluded Swiss defenders would inflict a much larger number of casualties on a German invasion force than could possibly be justified by the occupation of the country. (It can be lamented that more recent Western strategists did not apply the same test to Afghanistan.)
Comparisons with Ukraine are inapplicable, other than the fanatical determination of the defenders. Most obviously, Taiwan is not only an island but the Formosa Straits are three to four times as wide as the English Channel from the southern British ports to the beaches of Normandy. The People’s Republic of China would have no choice but to attack amphibiously as they could not possibly imagine success with fewer than 500,000 combat soldiers and no force remotely as large could be parachuted onto Taiwan.
A strike force of 500,000 would probably have to be supplemented by a follow-up force at least as large, all conveyed in a huge armada of slow and vulnerable craft. Taiwan has been supplied with the precise ground and air-launched missiles that the Ukrainians have used to such deadly effect in the Black Sea, including the sinking of the Russian flagship, the heavy missile cruiser Moskva.
Taiwan has a front-line Air Force of about 300 of the latest fully equipped fighter and interceptor aircraft that along with shore batteries could rain a dense and prolonged fire of missiles upon any invasion fleet. Such a fleet, even in the best of weather, would plod through open water for at least ten hours. They would be sitting, or at least slowly moving, ducks throughout that journey. It brings to mind the conclusion of one of Churchill’s Demosthenean addresses in the autumn of 1940: “We are still awaiting the long-promised invasion; so are the fishes.”