Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 20 Sep 2022
(more…)
September 21, 2022
The Medieval Saint Diet
September 20, 2022
The Byzantine Empire: Part 4 – Justinian, The Hand of God
seangabb
Published 1 Jan 2022Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or The Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
The purpose of this course is to give an overview of Byzantine history, from the refoundation of the City by Constantine the Great to its final capture by the Turks.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the history of Byzantium. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
September 19, 2022
City Minutes: Crusader States
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 13 May 2022Crusading is one thing, but holding your new kingdoms is a much trickier business. See how the many Christian states of “Outremer” rolled with the punches to evolve in form and function over multiple centuries.
(more…)
September 16, 2022
The Byzantine Empire: Part 3 – The Age of Justinian – Cashing in the Gains of the Fifth Century
seangabb
Published 7 Dec 2022Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or the Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
The purpose of this course is to give an overview of Byzantine history, from the refoundation of the City by Constantine the Great to its final capture by the Turks.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the history of Byzantium. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
September 14, 2022
QotD: The Wars of Religion and the (eventual) Peace of Westphalia
Thomas Hobbes blamed the English Civil War on “ghostly authority”. Where the Bible is unclear, the crowd of simple believers will follow the most charismatic preacher. This means that religious wars are both inevitable, and impossible to end. Hobbes was born in 1588 — right in the middle of the Period of the Wars of Religion — and lived another 30 years after the Peace of Westphalia, so he knew what he was talking about.
There’s simply no possible compromise with an opponent who thinks you’re in league with the Devil, if not the literal Antichrist. Nothing Charles I could have done would’ve satisfied the Puritans sufficient for him to remain their king, because even if he did everything they demanded — divorced his Catholic wife, basically turned the Church of England into the Presbyterian Kirk, gave up all but his personal feudal revenues — the very act of doing these things would’ve made his “kingship” meaningless. No English king can turn over one of the fundamental duties of state to Scottish churchwardens and still remain King of England.
This was the basic problem confronting all the combatants in the various Wars of Religion, from the Peasants’ War to the Thirty Years’ War. No matter what the guy with the crown does, he’s illegitimate. It took an entirely new theory of state power, developed over more than 100 years, to finally end the Wars of Religion. In case your Early Modern history is a little rusty, that was the Peace of Westphalia (1648), and it established the modern(-ish) sovereign nation-state. The king is the king because he’s the king; matters of religious conscience are not a sufficient casus belli between states, or for rebellion within states. Cuius regio, eius religio, as the Peace of Augsburg put it — the prince’s religion is the official state religion — and if you don’t like it, move. But since the Peace of Westphalia also made heads of state responsible for the actions of their nationals abroad, the prince had a vested interest in keeping private consciences private.
I wrote “a new theory of state power”, and it’s true, the philosophy behind the Peace of Westphalia was new, but that’s not what ended the violence. What did, quite simply, was exhaustion. The Thirty Years’ War was as devastating to “Germany” as World War I, and all combatants in all nations took tremendous losses. Sweden’s king died in combat, France got huge swathes of its territory devastated (after entering the war on the Protestant side), Spain’s power was permanently broken, and the Holy Roman Empire all but ceased to exist. In short, it was one of the most devastating conflicts in human history. They didn’t stop fighting because they finally wised up; they stopped fighting because they were physically incapable of continuing.
The problem, though, is that the idea of cuius regio, eius religio was never repudiated. European powers didn’t fight each other over different strands of Christianity anymore, but they replaced it with an even more virulent religion, nationalism.
Severian, <--–>”Arguing with God”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-01-20.
September 12, 2022
The Lord of the Rings and Ancient Rome (with Bret Devereaux)
toldinstone
Published 10 Sep 2022In this episode, Dr. Bret Devereaux (the blogger behind “A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry”) discusses the relationships between fantasy and ancient history – and why historical accuracy matters, even in fiction.
(more…)
September 9, 2022
The Byzantine Empire: Part 2 – Survival and Growth
seangabb
Published 15 Oct 2021Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or The Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
The purpose of this course is to give an overview of Byzantine history, from the refoundation of the City by Constantine the Great to its final capture by the Turks.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the history of Byzantium. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
September 3, 2022
The Byzantine Empire: Part 1 – Beginnings
seangabb
Published 1 Oct 2021Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or The Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
The purpose of this course is to give an overview of Byzantine history, from the refoundation of the City by Constantine the Great to its final capture by the Turks.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the history of Byzantium. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
August 28, 2022
Church and state, British-style
In The Critic, David Scullion reviews Catherine Pepinster’s book Defenders of the Faith: The British Monarchy, Religion, and the Next Coronation:
The longevity of Elizabeth II has (mostly) allowed us to avert our attention from the question of the relationship between church and state for a very long time. Given that her 70 years on the throne have seen the relentless rise of the forces of philistine secularism and constitutional vandalism, one cannot help but feel grateful for the benign obscurity that her reign has cast over such issues. Alas, this cannot be the case for much longer.
During her coronation in 1953, the Queen made solemn oaths to maintain the “true profession of the Gospel”, “the Protestant Reformed Religion established by law” and the Church of England. She was anointed with holy oil as the chosen ruler of God in a ceremony that owes its ultimate origins to the monarchy of Israel, and which can be traced back in England to at least the coronation of Edgar in 973 AD.
In 1953 this solemn ceremony was received with little in the way of controversy, except in terms of the debate over whether it should be televised. In the end it was, but with the most holy part of the rite — the coming of the Holy Spirit and God’s blessings in the sacred moment of anointing — kept away from the nation’s prying eyes.
If the next coronation is similar, one can only imagine the chorus of outraged, irreverent squawking that will sound from the amassed ranks of secular-liberal opinion-formers. Despite this unappetising prospect, it seems reasonable to discuss what form it should take now, given that 70 years have elapsed since the last one — a task that Catherine Pepinster’s new book purports to undertake.
I say “purports to undertake”, because in fact the vast majority of it is taken up with a rather pedestrian rehearsal of British religious and monarchical history since the Reformation, followed by long and dull accounts of what little we know about the spiritual lives of HM the Queen, Prince Philip and Prince Charles.
These central six chapters of the book are overwhelmingly preoccupied with a topic which clearly concerns the author more than any other: the nature of the relationship between Roman Catholicism and the monarchy, which seems like a rather odd focus given that the British monarchy has not been in communion with the Church of Rome since the 16th century.
She spends a large proportion of the book bewailing the historical inequities perpetrated against Ms Pepinster’s co-religionists by the British establishment, and demonstrating how recent decades have seen a real — albeit cautious — rapprochement between the monarchy and Roman Catholics. She goes on to make a series of commonplace observations about the country’s growing secularism, the rise of religious and cultural diversity, and the decline of Anglican congregations since 1953.
If one wants to know what the equivocating Ms Pepinster thinks the implications of all these trends are for the next coronation and relations between church and state, then one will have to read between the lines. Although her account of the various possibilities is a useful summary, working out what she actually favours is like trying to staple a jellyfish to wet soap.
August 20, 2022
QotD: The improbable survival of the Byzantine empire
The [Eastern Roman] Empire was faced by a triple threat to its existence. There were the northern barbarians. There was militant Islam in the south. There was an internal collapse of population. Each of these had been brought on by changes in the climate that no one at the time could have understood had they been noticed. It would not be until after 800 that the climate would turn benign again. In the meantime, any state to which even a shadow of Lecky’s dismissal applied would have crumpled in six months. Only the most courageous and determined action, only the most radical changes of its structure, could save the Empire. And saved the Empire most definitely was.
The reason for this is that the Mediaeval Roman State was directed by creative pragmatists. Look for one moment beneath its glittering surface, and the Ancient Roman Empire was a ghastly place for most of the people who lived in it. The Emperors at the top were often vicious incompetents. They ruled through an immense and parasitic bureaucracy. They were supreme governors of an army too large to be controlled. They protected a landed aristocracy that was a repository of culture, but that was ruthless in its exaction of rent. Most ordinary people were disarmed tax-slaves, where not chattel slaves or serfs.
The contemporary historians themselves are disappointingly vague about the seventh and eighth centuries. Our only evidence for what happened comes from the description of established facts in the tenth century. As early as the seventh century, though, the Mediaeval Roman State pulled off the miracle of reforming itself internally while fighting a war of survival on every frontier. Much of the bureaucracy was shut down. Taxes were cut. The silver coinage was stabilised. Above all, the senatorial estates were broken up and given to those who worked on them, in return for service in local militias. Though never abolished, chattel slavery became far less pervasive. The civil law was simplified, and the criminal law humanised – after the seventh century, as said, the death penalty was rarely used.
The Mediaeval Roman Empire survived because of a revolutionary transformation in which ordinary people became armed stakeholders. The inhabitants of Roman Gaul and Italy and Spain barely looked up from their ploughs as the Barbarians swirled round them. The citizens of Mediaeval Rome fought like tigers in defence of their country and their Orthodox faith. Time and again, the armies of the Caliph smashed against a wall of armed freeholders. This was a transformation pushed through in a century and a half of recurrent crises during which Constantinople itself was repeatedly under siege. Alone among the ancient empires in its path, Mediaeval Rome faced down the Arabs, and kept Islam at bay for nearly five centuries. Would it be superfluous to say that no one does this by accident?
Sean Gabb, “The Mediaeval Roman Empire: An Unlikely Emergence and Survival”, SeanGabb.co.uk, 2018-09-14.
August 19, 2022
QotD: How pre-modern polytheistic religions originated
… normally when you ask what the ancients knew of the gods and how they knew it, the immediate thought – quite intuitively – is to go read Greek and Roman philosophers discussing on the nature of man, the gods, the soul and so on. This is a mistake. Many of our religions work that way: they begin with a doctrine, a theory of how the divine works, and then construct ritual and practice with that doctrine as a foundation.
This is exactly backwards for how the ancients, practicing their practical knowledge, learn about the gods. The myths, philosophical discussions and well-written treatises are not the foundation of the religion’s understanding of the gods, but rather the foaming crest at the top of the wave. In practice, the ruminations of those philosophers often had little to do the religion of the populace at large; famously Socrates’ own philosophical take on the gods rather upset quite a lot of Athenians.
Instead of beginning with a theory of the divine and working forwards from that, the ancients begin with proven methods and work backwards from that. For most people, there’s no need to know why things work, only that they work. Essentially, this knowledge is generated by trial and error.
Let’s give an example of how that kind of knowledge forms. Let’s say we are a farming community. It is very important that our crops grow, but the methods and variations in how well they grow are deep and mysterious and we do not fully understand them; clearly that growth is governed by some unseen forces we might seek the aid of. So we put together a ritual – perhaps an offering of a bit of last year’s harvest – to try to get that favor. And then the harvest is great – excellent, we have found a formula that works. So we do it next year, and the year after that.
Sometimes the harvest is good (well performed ritual there) and sometimes it is bad (someone must have made an error), but our community survives. And that very survival becomes the proof of the effectiveness of our ritual. We know it works because we are still here. And I mean survival over generations; our great-great-grandchildren, for whom we are nameless ancestors and to whom our ritual has always been practiced in our village can take solace in the fact that so long as this ritual was performed, the community has never perished. They know it works because they themselves can see the evidence.
(These sorts of justifications are offered in ancient works all the time. Cicero is, in several places, explicit that Roman success must, at the first instance, be attributed to Roman religio – religious scruples. The empire itself serves as the proof of the successful, effective nature of the religion it practices!)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Practical Polytheism, Part I: Knowledge”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-10-25.
August 12, 2022
Testing the old saying about those who believe in nothing will believe anything
At Astral Codex Ten, Scott Alexander considers the old saying — often mis-attributed to G.K. Chesterton or C.S. Lewis:
There’s a popular saying among religious apologists:
Once people stop believing in God, the problem is not that they will believe in nothing; rather, the problem is that they will believe anything.
Big talk, although I notice that this is practically always attributed to one of GK Chesterton or CS Lewis, neither of whom actually said it. If you’re making strong claims about how everybody except you is gullible, you should at least bother to double-check the source of your quote.
Still, it’s worth examining as a hypothesis. Are the irreligious really more likely to fall prey to woo and conspiracy theories?
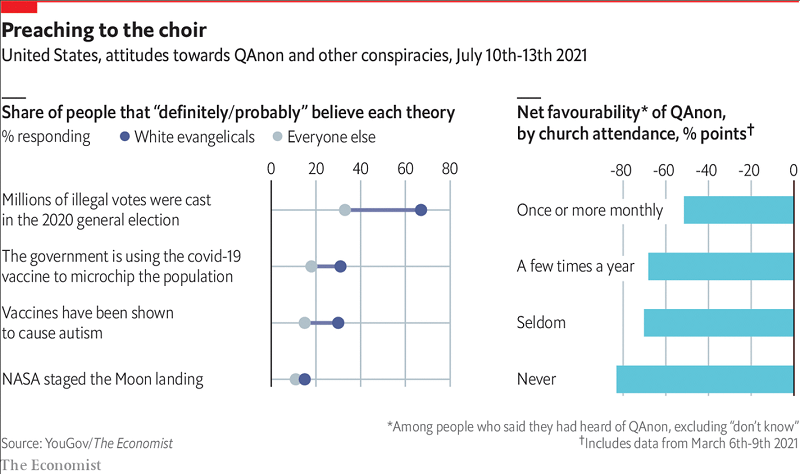
This Economist article examined the question and concluded the opposite. See especially this graph:
“White evangelicals” are more likely to believe most measured conspiracy theories, and churchgoers were more likely to believe in QAnon in particular.
There’s an obvious confounder here: the authors are doing the usual trick where they cherry-pick right-wing examples of something bad, show that more right-wingers are in favor of them, then conclude that Science Has Proven Right-Wingers Are Bad. QAnon, illegal votes, and COVID microchips are inherently right wing conspiracy theories; vaccines/autism has probably become right-coded post-COVID. Only the moon landing seems politically neutral, and it’s hard to tell if there’s a real difference on that one. So this just tells us that white evangelical church-goers are further right than other people, which we already know.
These data still deflate some more extreme claims about religion being absolutely protective against conspiracy theories. But I was interested in seeing how people of different faiths related to politically neutral conspiracies.
August 10, 2022
Coca de Sant Joan & the Fires of Saint John’s Eve
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 22 Jun 2021
(more…)
August 8, 2022
Barbarian Europe: Part 6 – The Birth of England
seangabb
Published 4 Aug 2021In 400 AD, the Roman Empire covered roughly the same area as it had in 100 AD. By 500 AD, all the Western Provinces of the Empire had been overrun by barbarians. Between April and July 2021, Sean Gabb explored this transformation with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
July 24, 2022
Still no actual evidence of unmarked graves for Residential School children
In Quillette, Jonathan Kay updates the year-old sensational stories about First Nations children being buried in unmarked (in more unhinged reporting it might have been “mass”) graves on the grounds of former Residential Schools in Canada:
Canada’s unmarked-graves story broke on May 27th, 2021, when the Tk’emlúps te Secwépemc First Nation reported the existence of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) data that indicated regularly spaced subterranean soil disturbances on the grounds of a former Indigenous Residential School that had operated in Kamloops, BC between 1893 and 1978. In addition, the First Nation’s leaders asserted their belief that these soil disturbances corresponded to unmarked graves of Indigenous children who’d died while attending the school.
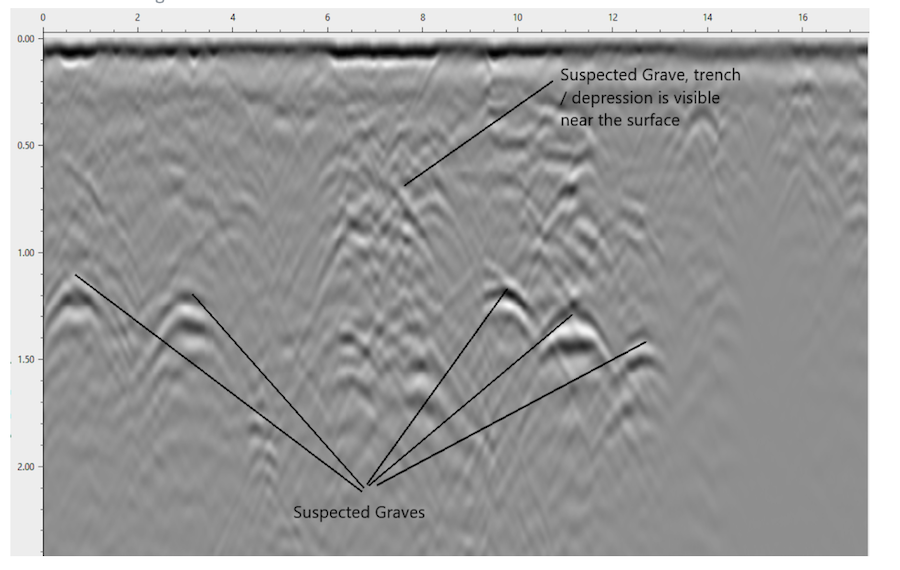
The story became an immediate sensation in the Canadian media; and remained so for months, even after the GPR expert on whom the First Nation relied, Sarah Beaulieu, carefully noted that the radar survey results didn’t necessarily indicate the presence of graves — let alone graves that had been unmarked, graves of Indigenous people, or graves of children. Contrary to what many Canadians came to believe during that heady period, GPR survey data doesn’t yield X-ray-style images that show bodies or coffins. What it typically shows are disruptions in soil and sediment. Investigators then need to dig up the ground to determine what actually lies underneath.
An explanatory image posted by GeoScan, a Canadian Ground-Penetrating-Radar service provider, showing how mapped GPR data can indicate the possible presence of graves.
Image via Quillette.But those details were swept aside during what, in retrospect, appears to have been a true nation-wide social panic. As other Indigenous groups announced that they’d be conducting their own GPR surveys, media figures confidently asserted that the original Canadian Residential-School student death-toll estimate of 3,201 would soon double or even triple. One op-ed writer went so far as to declare that “the discovery of the graves of the children in Kamloops may be Canada’s Holocaust moment.” Dramatic, tear-drenched acts of public atonement unfolded everywhere, with many July 1st Canada Day celebrations being either cancelled or transformed into opportunities for morose self-laceration.
I was one of many Canadians who initially got swept up with all of this — in large part because it seemed as if everyone in the media was speaking with one voice, including journalists I’d known and respected for many years. Looking back on the coverage, I note that headline writers mostly skipped over the technical bits about soil dislocations and such, and went straight to “bodies” and “graves”. And the stories often were interspersed with credulous recitations of dubious tales featuring live babies being thrown into furnaces or buried alive.
The whole mission of Canada’s church-run Residential School system was to assimilate Indigenous people into white Canadian society, usually against their will, while forcing children to leave their families and communities for months or even years at a time. No one disputes that many students were subject to cruel (and sometimes even predatory) treatment and substandard medical care. Certainly, the death rate for Indigenous children attending these schools was much higher than that for children in the general population. No, I never bought into the idea that there was any kind of mass-murder plot going on at these schools. But it hardly seemed far-fetched that some victims of mistreatment and neglect had been buried in unmarked graves — “off the books”, so to speak—by malevolent white teachers, school administrators, and priests seeking to evade responsibility for their actions.
The other important aspect to mention is that — like most other Canadians, I’m guessing — I believed we were only a few days or weeks from seeing real physical evidence plucked from the earth. So it didn’t much matter to me that early commentators were temporarily playing fast and loose with the distinction between GPR data and actual corpses.
Canadians were being told that the old orchard in Kamloops where the GPR data had been collected was a crime scene — a site of mass murder, and the final resting place of 215 child homicide victims. As I’ve reasoned elsewhere: If you told Canadians that, say, 215 murdered white children were buried somewhere in Toronto, or Ottawa, or Vancouver, there’d be investigators and police crawling all over the place, looking for remains that could be tested and identified. And so I naturally assumed the same thing soon would be happening in Kamloops.
But … no. Not at all, in fact.
As I wrote over a year ago, the way the story swept the media was as if the whole Residential School history was somehow new and previously unknown:
Despite being Canadian, my interest in Canadian history centres mostly on economic, naval, and military aspects, but I was certainly aware that the residential school system was a black mark on Canada’s historical dealings with First Nations and that the general outline of events — if not the gruesome details — had been known for many years. The first time I found out about it was in middle school, through what we’d now call a “Young Adult” novel about a young First Nations boy escaping from the residential school he’d been sent to and his attempts to travel hundreds of miles to get home. I read it in the early 70s and it may have been published up to a decade before then (I no longer remember the author’s name or the title of the book, unfortunately).
If I, as a schoolchild, knew something of this fifty years ago, why have people younger than me been shocked and appalled to be hearing about this widespread tragedy for the first time now?