Ted Gioia outlines the dismal state of the “macro” culture — television, movies, newspapers, book publishing and all the big corporations that control them — with the dynamism of the “micro” culture:
In the beginning, all culture was microculture.
You knew what was happening in your tribe or village. But your knowledge of the wider world was limited.
So you had your own songs and your own stories. You had your own rituals and traditions. You even had your own language.
But all these familiar things disappeared when you went off into the world. That was dangerous, however. That’s why only heroes, in traditional stories, go on journeys.
You learn on the journey. But you might not survive.
But all that changed long before I was born.
In my childhood, everything was controlled by a monoculture. There were only three national TV networks, but they were pretty much the same.
When I went to the office, back then, we had all watched the same thing on TV the night before. We had all seen the same movie the previous weekend. We had all heard the same song on the radio while driving to work.
The TV shows were so similar that they sometimes moved from CBS to NBC, and you never noticed a change. The newscasters also looked pretty much the same and always talked the same — with that flat Midwestern accent that broadcasters always adopted in the US.
The same monoculture controlled every other creative idiom. Six major studios dominated the film business. And just as Hollywood controlled movies, New York set the rules in publishing. Everything from Broadway musicals to comic books was similarly concentrated and centralized.
The newspaper business was still local, but most cities had 2 or 3 daily newspapers — and much of the coverage they offered was interchangeable. Radio was a little more freewheeling, but eventually deregulation allowed huge corporations to acquire and standardize what happened over the airwaves. [NR: I suspect the “freewheeling” went away once the government started imposing regulations, and the corporate consolidation was enabled when they “deregulated” the radio licensing regime several decades later.]
When I went to work in an office, back then, we had all watched the same thing on TV the night before. We had all seen the same movie the previous weekend. We had all heard the same song on the radio while driving to work.
And that’s why smart people back then paid attention to the counterculture.
The counterculture might be crazy or foolish or even boring. But it was still your only chance to break out of the monolithic macroculture.
Many of the art films I saw at the indie cinema were awful. But I still kept coming back — because I needed the fresh air these oddball movies provided. For the same reason, I read the alt weekly newspapers and kept tabs on alt music.
In fact, whenever I saw the word alt, I paid attention.
That doesn’t mean that I hated the major TV networks, or the large daily newspaper, or 20th Century Fox. But I craved access to creative and investigative work that hadn’t been approved by people in suits working for large organizations.
The Internet should have changed all this. And it did — but not much. Even now the collapse in the monoculture is still in its early stages.
But that’s about to change.
If you don’t pay close attention, the media landscape seems pretty much the same now as it did in the 1990s. The movie business is still controlled in Hollywood. The publishing business is still controlled in New York. The radio stations are still controlled by a few large companies. And instead of three national TV networks plus PBS, we have four dominant streaming platforms — who control almost 70% of the market.
So we still live in a macro culture. But it feels increasingly claustrophobic. Or even worse, it feels dead.
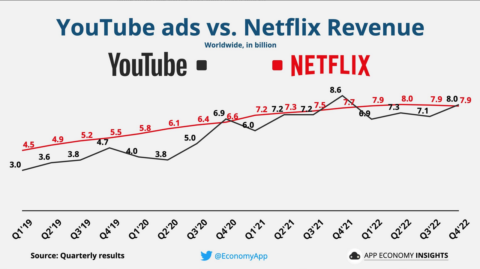
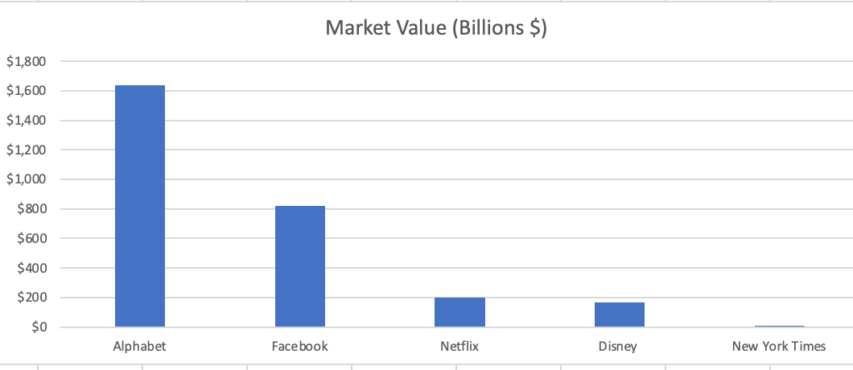
Meanwhile, a handful of Silicon Valley platforms (Google, Facebook, etc.) have become more powerful than the New York Times or Hollywood studios or even Netflix. It’s not even close — the market capitalization of Google’s parent Alphabet is now almost ten times larger than Disney’s.
But here’s the key point — these huge tech companies rely on the microculture for their dominance.
Where is Facebook without users contributing photos, text and video? Where is Google’s YouTube without individual creators?
In terms of economic growth or audience capture, the microculture has already won the war. But it doesn’t feel that way.
Why not?
First and foremost, Silicon Valley is a reluctant home for the microculture. To some extent Alphabet and Facebook are even going to war with microculture creators — they try to make money with them even while they punish them.
- So Mark Zuckerberg needs creators, but won’t even let them put a live link on Instagram and limits their visibility on Facebook and Threads.
- Alphabet needs creators to keep YouTube thriving, but gives better search engine visibility to total garbage that pays for placement.
- Twitter also claims it wants to support independent journalists — but if you’re truly independent from Elon Musk, your links are brutally punished by the algorithm.
This tension won’t go away, and next year it will get worse. The microculture will increasingly find itself at war with the same platforms they rely on today.
And legacy media and non-profits are even more hostile to emerging media. Go see who wins Pulitzer Prizes, and count how many journalists on alternative platforms get honored.
I’ll save you the trouble. They don’t.