In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes explains why the steam engine patent of James Watt didn’t immediately lead to Watt and his partner Matthew Boulton building a factory to create physical engines:
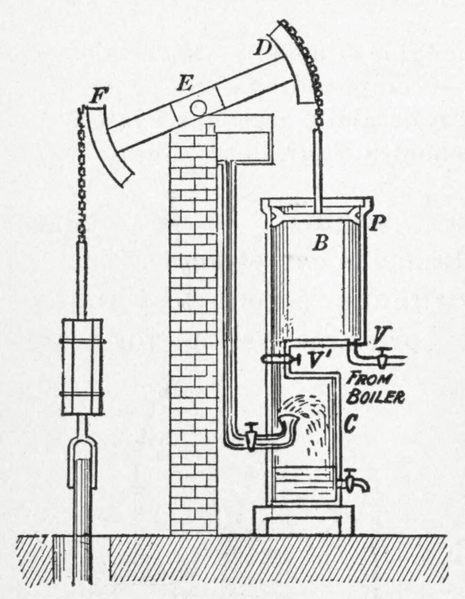
Diagram of a Watt steam engine from Practical physics for secondary schools (1913).
Wikimedia Commons.
… one of the most famous business partnerships of the British Industrial Revolution — that between Matthew Boulton and James Watt from 1775 — was originally almost entirely based on intangibles.
That probably sounds surprising. James Watt — a Scottish scientific instrument-maker, chemist and civil engineer — became most famous for his improvements to the steam engine, an almost archetypal example of physical capital. In the late 1760s he radically improved the fuel efficiency of the older Newcomen engine, and then developed ways to regulate the motions of its piston — traditionally applied only to pumping water — so that it could be suitable for directly driving machinery (I’ll write more on the invention itself soon). His partnership with Matthew Boulton, a Birmingham manufacturer of buttons, candlesticks, metal buckles and the like — then called “toys” — was also based from a large, physical site full of specialised machinery: the Soho Manufactory. On the face of it, these machines and factories all sound very traditionally tangible.
But the Soho Manufactory was largely devoted to Boulton’s other, older, and ongoing businesses, and it was only much later — over twenty years after Boulton and Watt formally became partners — that they established the Soho Foundry to manufacture the improved engines themselves. The establishment of the Soho Foundry heralded James Watt’s effective retirement, with the management of this more tangible concern largely passing to his and Boulton’s sons. And when Watt retired formally, in 1800, this coincided with the full depreciation of the intangible asset upon which he and Boulton had built their business: his patent.
Watt had first patented his improvements to the steam engine in 1769, giving him a 14-year window in which to exploit them without any legal competition. But his financial backer, John Roebuck, who had a two-thirds share in the patent, was bankrupted by his other business interests and struggled to support the engine’s development. Watt thus spent the first few years of his patent monopoly as a consultant on various civil engineering projects — canals, docks, harbours, and town water supplies — in order to make ends meet. The situation gave him little time, capital, or opportunity to exploit his steam engine patent until Roebuck was eventually persuaded to sell his two-thirds share to Matthew Boulton. With just eight years left on the patent, and having already wasted six, Boulton and Watt lobbied Parliament to grant them an extension that would allow them to bring their improvements into full use. In 1775 Watt’s patent was extended by Parliament for a further twenty-five years, to last until 1800. It was upon this unusually extended patent that they then built their unusually and explicitly intangible business.
How was it intangible? As Boulton and Watt put it themselves, “we only sell the licence for erecting our engines, and the purchaser of such licence erects his engine at his own expence”. This was their standard response to potential customers asking how much they would charge for an engine with a piston cylinder of particular dimensions. The answer was, essentially, that they didn’t actually sell physical steam engines at all, so there was no way of estimating a comparable figure. Instead, they sold licences to the improvements on a case-by-case basis — “we make an agreement for each engine distinctly” — by first working out how much fuel a standard, old-style Newcomen engine would require when put to use in that place and context, and then charging only a third of the saving in fuel that Watt’s improvements would provide. “The sum therefore to be paid during the working of any engine is not to be determined by the diameter of the cylinder, but by the quantity of coals saved and by the price of coals at the place where the engine is erected.” They fitted the licensed engines with meters to see how many times they had been used, sending agents to read the meters and collect their royalties every month or year, depending on the location.
This method of charging worked well for refitting existing Newcomen engines with Watt’s improvements — in those cases the savings would be obvious. It also meant that Boulton and Watt incentivised themselves to expand the total market for steam engines. The older Newcomen engines were mainly used for pumping water out of coal mines, where the coal to run them was at its cheapest. It was one of the few places where Newcomen engines were cost-effective. But for Watt and Boulton it was at the places where coals were most expensive, and where their improvements could thus make the largest fuel savings, that they could charge the highest royalties. As Boulton wrote to Watt in 1776, the licensing of an engine for the coal mine of one Sir Archibald Hope “will not be worth your attention as his coals are so very cheap”. It was instead at the copper and tin mines of Cornwall, where coal was often expensive, having to be transported from Wales, that the royalties would be the most profitable. As Watt put it to an old mentor of his in 1778, “our affairs in other parts of England go on very well but no part can or will pay us so well as Cornwall”.





