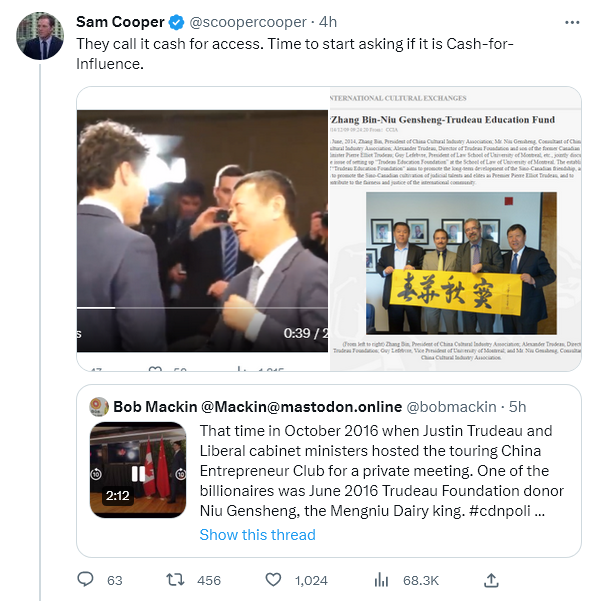
Ted Gioia provides more evidence that the scarcest thing in the world today is getting ever more scarce:
Here are some news stories from recent days. Can you tell me what they have in common?
- Scammers clone a teenage girl’s voice with AI — then use it to call her mother and demand a $1 million ransom.
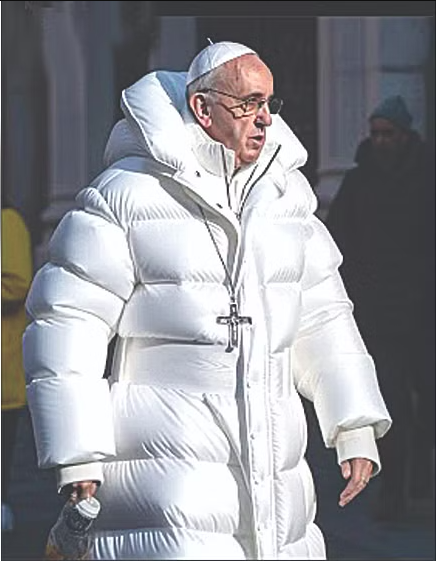
- Millions of people see a photo of Pope Francis wearing a goofy white Balenciaga puffer jacket, and think it’s real. But after the image goes viral, news media report that it was created by a construction worker in Chicago with deepfake technology.
- Twitter changes requirements for verification checks. What was once a sign that you could trust somebody’s identity gets turned into a status symbol, sold to anybody willing to pay for it. Within hours, the platform is flooded with bogus checked accounts.
- Officials go on TV and tell people they can trust the banking system—but depositors don’t believe them. High profile bank failures from Silicon Valley to Switzerland have them spooked. Over the course of just a few days, depositors move $100 billion from their accounts.
- ChatGPT falsely accuses a professor of sexual harassment — and cites an article that doesn’t exist as its source. Adding to the fiasco, AI claims the abuse happened on a trip to Alaska, but the professor has never traveled to that state with students.
- The Department of Justice launches an investigation into China’s use of TikTok to spy on users. Another popular Chinese app allegedly can bypass users’ security to “monitor activities on other apps, check notifications, read private messages and change settings.”
- The FBI tells travelers to avoid public phone charging stations at airports, hotels and other locations. “Bad actors have figured out ways to use public USB ports to introduce malware and monitoring software onto devices,” they warn.
The missing ingredient in each of these stories is trust.
Everybody is trying to kill it — criminals, technocrats, politicians, you name it. Not long ago, Disney was the only company selling a Fantasyland, but now that’s the ambition of every tech empire.
The trust crisis could hardly be more intense.
But it’s hidden from view because there’s so much information out there. We are living in a culture of abundance, especially in the digital world. So it’s hard to believe than anything in the information economy is scarce.
Whatever you want, you can get — and usually for free. You can have free news, free music, free videos, free everything. But you get what you pay for, as the saying goes. And it was never truer than right now — when all this free stuff is starting to collapse in a fog of fakery and phoniness.
Tell me what source you trust, and I’ll tell you why you’re a fool. As B.B. King once said: “Nobody loves me but my mother — and she could be jivin’ too.”
Years ago, technology made things more trustworthy. You could believe something because it was validated by photos, videos, recordings, databases and other trusted sources of information.
Seeing was believing — but not anymore. Until very recently, if you doubted something, you could look it up in an encyclopedia or other book. But even these get changed retroactively nowadays.
For example, people who consult Wikipedia to understand the economy might be surprised to learn that the platform’s write-up on “recession” kept changing in recent months — as political operatives and spinmeisters fought over the very meaning of the word. It got so bad that the site was forced to block edits on the entry.
There’s an ominous recurring theme here: The very technologies we use to determine what’s trustworthy are the ones most under attack.
Trust used to be a given in most western countries … it was a key part of what made us all WEIRD. Mass immigration from non-WEIRD countries dented it, but conscious perversion of trust relationships by government, media, public health, and education authorities has caused far more — and longer lasting — damage to our culture. Trust used to be given freely, but now must be earned. And that’s difficult for organizations that have proven repeatedly that they can’t be trusted.