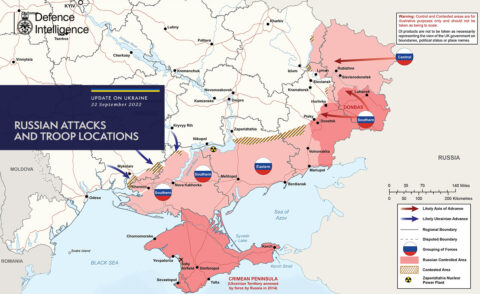
In Strategika, Edward Luttwak considers what lessons can be drawn from wars of the past to help inform the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine:
Every war must end, but no war need end quickly — neither world war makes it to the top ten in longevity. The nearest parallel to the Ukraine war – the Dutch War of Independence (1568–1648), fought between a smaller but more advanced nation, and the world-spanning Spanish Empire, the superpower of the age – persisted for eighty years because the Spanish kept losing, but there was so much ruination in that declining power.
In our own days, expeditionary wars fought against enemies far away who could hardly fire back, lasted for many years as the different war-ending theories promoted by fashionable generals were tried seriatim to no avail, till the day when evacuation was preferred even if utterly ignominious.
The eighteenth-century wars fought by rival European monarchs who could all converse in French with each other, were enviously admired in the bloody twentieth century, because they allowed much commerce and even tourism to persist — utterly unimaginable even in Napoleon’s wars, let alone the two world wars — and because they ended not in the utter exhaustion of the collapsing empires of 1918, nor in the infernal destructions of 1945, but instead by diplomatic arrangements politely negotiated in-between card games and balls. The 1763 Treaty of Paris that ended the Seven Years’ war and French America, inadvertently opening the way for the American republic, was not drafted by the victorious British Prime Minister Lord Bute, but by his very good friend the French foreign minister Étienne-François de Stainville, duc de Choiseul, who solved the three-way puzzle left by the French defeat by paying off Spain with Louisiana, Britain with money-losing Canada, and regaining the profitable sugar islands for France, which still has them.
And instead of the winners charging the losers with incurable bellicosity as Versailles did with Germany, or stringing them up individually as war criminals, as in the ending of twentieth-century wars, eighteenth-century winners were more likely to console the losers just short of “better-luck next time” — and in a century in which there was war every single year without exception from 1700 to 1800, if one war ended another necessarily started or at least persisted, allowing a “next time” soon enough.
By contrast, the ensuing nineteenth-century wars held no lessons at all for the twentieth century, which was equally bereft of a Napoleonic superman at the start and ample tropical lands easily conquered later on, while the Crimea expedition in the middle was mostly a counter-example of how not to wage war, and the Franco-Prussian war was just as sterile: all it proved was that there really was only one Helmuth von Moltke who could win wars by parsimonious force, unlike his homonymous nephew who lost a five-year war in its first five weeks; and that there really was only one Otto von Bismarck, who crowned his incomplete 1871 unification of German lands by refusing to complete it by unifying all Germans as the Italians were unified, lest the world combine to make a bigger Germany smaller.
Clearly only the eighteenth-century precedents apply to the Ukraine War. Neither Putin nor Zelensky speaks French but neither needs it to converse in their Russian mother-tongue, and if they do not actually talk (Putin demurely said that he could not possibly be expected to negotiate with Kiev’s drug addicts and Neo Nazis), their officials certainly can, and do so often.
When it comes to the persistence of commerce in war — the habit that Napoleon wanted to break with his Blocus Continental against British exports — every day Russian gas flows to the homes and factories of Ukraine on its way into Western Europe, with Ukraine transferring money to Russia every day, even as it attacks its faithful customer. And, Ukrainian wheat is now shipped past Russian navy vessels to reach the hungry Middle East, after a negotiation unthinkable in twentieth-century wars, or in Napoleon’s either.
In Russia, sanctions have certainly diminished easy access to imported luxuries in local franchised shops, but they still arrive via Turkey at a slight premium … or discount depending on the previous Moscow markup. All over Russia the sanctions have been felt in all sorts of ways because the country was actually more internationalized than anyone realized, including Putin no doubt (arriving in Tomsk at 0600 one winter morning at a temperature of minus infinity, the one place to eat was McDonalds).
But unlike China, which must choose between fighting and eating protein — some 90% of its chicken, pork, and beef is raised on imported cereals plus some 150 million metric tons of soya per annum from U.S. and Canadian Pacific ports, or the Atlantic ports of Brazil and Argentina that would be an ocean too far for China-bound vessel – Russia produces all its own staple foods and can therefore fight and eat indefinitely, and neither does it import any energy as China must.
In other words, just as Russian propaganda has claimed from day one, the sanctions cannot stop the war materially, even if they played a large role in the flight of tens of thousands of elite Russians, once again diminishing the human capital of the largest European nation, as the Bolsheviks and Civil War did a century ago, and the opening of borders did again a generation ago.
It is a problem that the sanctions, which end the war by stopping Russia, might cause defections from the Western camp if the winter happens to be unusually cold, a subject on which Angela Merkel – so enthusiastically applauded for closing nuclear power stations and preferring Russian piped gas over American and Qatari liquified gas – has remained strangely silent.