Terra Incognita
Published 5 Dec 2017100 years ago, the Canadian port city of Halifax was struck by one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history. How did it happen?
(more…)
December 6, 2023
Halifax Explosion: Minute by Minute
November 11, 2023
The Mississauga Train Derailment (1979)
The Raven’s Eye
Published 8 Nov 2022It was called “The Mississauga Miracle” — a train derailment involving 26 cars of toxic and flammable materials, just a few miles from a major Canadian city center. Faced with the prospect of a cloud of killer phosgene gas being released, authorities had no choice but to order the mass evacuation of an entire city …
(more…)
QotD: Diary entry, 11 November, 1979
I hope you’ll forgive my self-insert here, but watching the video on the Mississauga train derailment prompted me to dig up a bit of personal history related to this thankfully non-tragic event in Canadian history. This is what I wrote about the events of that week not at the time (I was far too busy living it to record anything) but a couple of months after the fact. Samuel Pepys I wasn’t. I note in passing that my memories today don’t exactly match what I wrote in early 1980, which does bring home to me the fallibility of “eyewitness” reports after the fact.

On the night of November 10, 1979, a 106-car Canadian Pacific freight train derailed at Mavis Road, north of Dundas Street. As a result of the subsequent explosion, when one of the tank cars carrying propane exploded, and because other tank cars were carrying chlorine, the decision was made to evacuate nearby residents in one of the largest peace time evacuations in history. This photo shows flames from the wreckage, with hoses pouring water on it.
Photo from the Mississauga Library System website, Identifier M466. Full gallery here.
In November of ’79, on the 11th actually, a chemical train derailed just northwest of [our apartment near Dundas and Hurontario Streets]. It spilled 16 tank cars full of propane and one full of chlorine all over the Mavis Road crossing.
I was driving back to Hamilton on Saturday night to drop off [my girlfriend]. Rockney was inexplicably along with us that night. Around midnight, I noticed the road all around us light up as though dawn had come early. Also noticed a pronounced mushroom-type cloud and lots of incident light at its base. Right there, my mind kicked into Hyperdrive and I analyzed the data, assumed the worst, and nearly swung off the highway to protect us behind an embankment. [The others] saw that it wasn’t an H- or A-type of explosion, and so we didn’t worry too much. Flames [on the eastern horizon] were easily visible from Hamilton.
I went back [to Mississauga], dropped Rockney off [and] noticed a police car blocking the intersection of Dundas and Hurontario with its lights going. Talked to Mum, who was still up, and went to bed at 3:00am.
We were woken up at 10:00am by police evacuating the building. I called Rockney and we all trooped over to his place. I stayed for 1/2 an hour, and decided to go back to the house, change into [my army reserve] uniform, and go up to Brampton for our Remembrance Day parade. On the way, I was stopped by the police and directed to go to Square One, where an evacuation centre had been set up. As I arrived there, the last bus-load of evacuees left headed for Streetsville Secondary School. I arrived there in time [to be given responsibility for security] with 15 assorted army and navy cadets [who were in uniform for their respective Remembrance Day services] who had no officer handy. We cleared the halls [at the direction of police and school authorities] and tried to maintain calm among the evacuated throng.
By 8 that evening, my force had shrunk to seven cadets led by Petty Officer Linda P. An officer cadet of the Air Reserve and five air cadets with him refused to assist me or the police. [I was angry at the time, but he was probably worried about the legal side of providing “aid to the civil power” while in uniform without permission from his chain of command. I was a junior NCO, so that thought never crossed my mind until much later.]
By this time, I had attached Chris P. [a friend of Rockney’s who was evacuated to Streetsville] and several other husky teenagers to my “security force” and we were able to keep things fairly quiet.
As people [started to realize] that they would be there all night, most of them settled down very nicely. [My team of cadets] issued blankets we’d received on a truck from CFB Downsview and shared out the available gym mats [as makeshift mattresses].
A local McDonalds sent in a “breakfast” of cold Big Macs [I’m sure they were hot going out the door, but they took a long time to get to us] — [the non-cadet members of] my security force got more than their fair share, but that was expected. Most of the media had disappeared by this time so we soon got involved in minor disputes with some irate citizens.
Sometime during Monday afternoon a Master Corporal from CFB Downsview called me to arrange a coffee run down to the [emergency crews working to contain] the fire. Nothing came of it in the end [I have no idea why they thought I’d be a useful participant, as I had no transportation other than my own car … maybe I was the only member of the military in the immediate vicinity].
Tried calling Rockney’s place [to see how my family were doing] but got no answer, same at Bill & Clive’s apartment [several miles further east of Rockney’s]. No idea where my parents have gone. [After being evacuated a second time, they’d ended up at the International Centre with the family cat and stayed there until later in the week, as I found out later. My sister hadn’t been at home so she was evacuated elsewhere with her boyfriend’s family. I have no idea where she spent the week.]
Monday night wasn’t too bad, except for [media reports] that there were 3 escaped cons in the area so i couldn’t send girls out alone on security sweeps [outside the school building]. Me, Chris P., Jordan L., and John D. were the only [ones available to do exterior security] now, getting VERY tired. Got an hour’s sleep.
On Tuesday a bunch of students from Humber College showed up. They were all taking the Law Enforcement course and wanted to help me with security. [The] only problem was that the course was 9/10ths female [so] I couldn’t use them [for exterior patrols, which is where we needed help the most].
Also showing up [later on Tuesday] was a local CB radio group who tried to take over from me and my team. It took two hours [of argument] before they gave up and went off to try to take over some other evacuation centre. [Around this time,] vandalism started on the back side of the school and in the portable classrooms. No one was caught at it, unfortunately. [I didn’t note it here, but I strongly suspected that one or more of my volunteers had done some of the damage out of boredom, but I had no proof.]
The biggest problem, however, was racial. A large group of black teenagers had taken over one of the Home Economics classrooms and had 2 competing ghetto blasters to make mucho noise. 2 fights had to be broken up in there and we had to call the police in to cope with the second fight.
[Tuesday] night was uneventful for a change. Wednesday wasn’t, as rumours of being able to go home kept hitting the people in the evacuation centre and nearly overwhelming the security teams at the doors. One asshole, a guy about 20-25 years old, kept buttonholing me and other members of my team and demanding shampoo, of all things. Eventually, someone got him some and he “went to the showers”. [In hindsight, he probably had just come down from whatever drugs he’d been on for the previous few days.]
On Wednesday night, the evacuation centre in Streetsville was shut down and everyone was moved to other facilities on Mississauga Transit buses. Most were taken to the Royal York Hotel in downtown Toronto, but my remaining team members were sent to a Holiday Inn in Scarborough. [I was in rough shape by then and someone got me to hospital to get checked out. I was there for about 10 hours before they discharged me with advice to “get plenty of rest”.]
Thursday we spent in the hotel, charging everything to CP Rail. They must have hit the roof when the bill arrived — especially the bar bill! We threw an “exhaustion party” in our room on Thursday night and on Friday we were finally allowed to go home (most of us, anyway).
When I went back to school the following week, I was given the third degree by the vice principal because the Red Cross didn’t have me listed as an evacuee. I had to get the hospital records to show that I had actually taken part before I was allowed back into class. [A similar thing happened the next unit parade night, as I’d been on TV several times in my uniform during the event and my commanding officer was quite upset about it, thinking I’d been pretending to act in some sort of official capacity, which I hadn’t been.]
August 11, 2023
Queer Eye for the Tudor ?guy?
At First Things, Carl R. Trueman looks into a recent post from the Mary Rose Museum (where the remains of King Henry VIII’s favourite warship now resides), considering Tudor artifacts recovered from the wreck from a Queer perspective:

“Mary Rose Museum & HMS Victory” by Silly Little Man is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0 .
The anti-Western left has been exposed for its sexual imperialism over the last few months. Evidence is all around. American Muslims have led protests against the imposition of LGBTQ policies and curricula in schools, leaving American progressives uncomfortably caught between two pillars of their favored rhetoric of political thought-crime: transphobia and Islamophobia. The Washington Post opined that anti-LGBTQ moves in the Middle East were “echoing” those of the American culture wars—as if Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan had been listed by the Human Rights Campaign as favored vacation destinations until their ruling elites started reading the website of Moms for Liberty.
It is, of course, the nature of imperialism that everything, everywhere, is always to be measured by the imperialists’ standards. And that is also what makes them so impervious to spotting their own imperialism. “Queering the Mary Rose‘s Collection”, an article on the website of the Mary Rose Museum in Portsmouth, England, is a recent example of this. The Mary Rose was a Tudor warship that sank in 1545 and was raised from the seabed in 1982 in a groundbreaking act of marine archaeology. The museum is dedicated to displaying artifacts retrieved from the wreck, some of which are now been analyzed “through a Queer lens”.
The specific examples are an octagonal mirror, nit combs, a gold ring, and Paternosters. Apparently, looking into a mirror can stir strong emotions for both straight and queer people, and for the latter it can generate, for example, feelings of gender dysphoria or euphoria, depending on whether the reflection matches their gender identity. Combs would have been used by the sailors to remove the eggs of hair lice. Today they are reminders of how hairstyles can be the result of imposed gender stereotypes, but also make possible the subverting of these through hairdos that break with social expectations. Rings are a reminder of marriage and, of course, that the Church of England founded by Henry VIII, king during the Mary Rose‘s working life, still does not allow gay marriage. Finally, the Paternosters remind us that the crew were “practicing” Christians and that, once again, Henry VIII, via his initiation of the English Reformation, facilitated the civil criminalization of homosexual acts.
Two things are striking about the article, in addition to its lack of any intellectual merit. First, the absence of any historical awareness is striking. For example, the category of “practicing Christian” is essentially meaningless when applied to the early sixteenth century. Everybody, bar a few underground Jews, Anabaptists, and radicals, was part of the Catholic Church by baptism. The question of how the crew might have understood themselves, whether in terms of mirrors, rings, combs, or Paternosters, is never asked. To be fair, a short blog post cannot ask all the relevant questions, but this does not even nod in the direction of suggesting that the differences between yesterday and today might be remotely interesting or instructive.
David Thompson also has some thoughts on the Mary Rose artifact interpretations:
It’s quality stuff. Just like being there, in the mists of history. And not at all inept, or jarring, or comically incongruous.
As we have seen, many objects can be viewed through a Queer lens and can indirectly tell LGBTQ+ stories.
And thanks to peering through this “Queer lens”, readers will doubtless find that their understanding of Tudor history has been enriched no end.
We’re told – indeed, assured – by Hannah McCann, of the museum’s collections and curatorial staff,
From the Tate Britain and the Wellcome Collection, to the Rijks Museum in Amsterdam and the Whitney Museum of American Art in New York City, museums are reinterpreting and Queering their objects.
A comfort, I know.
Exactly why such “queering” is underway – what its relevance might be – is not, however, made clear. An explanation for this bolting-on of irrelevant, flimsy tat – in the name of “queer theory” – was not, it seems, deemed necessary. Nor is it entirely obvious how such “queering” of museum contents benefits those who wish to know more about Henry VIII’s favourite warship.
June 14, 2023
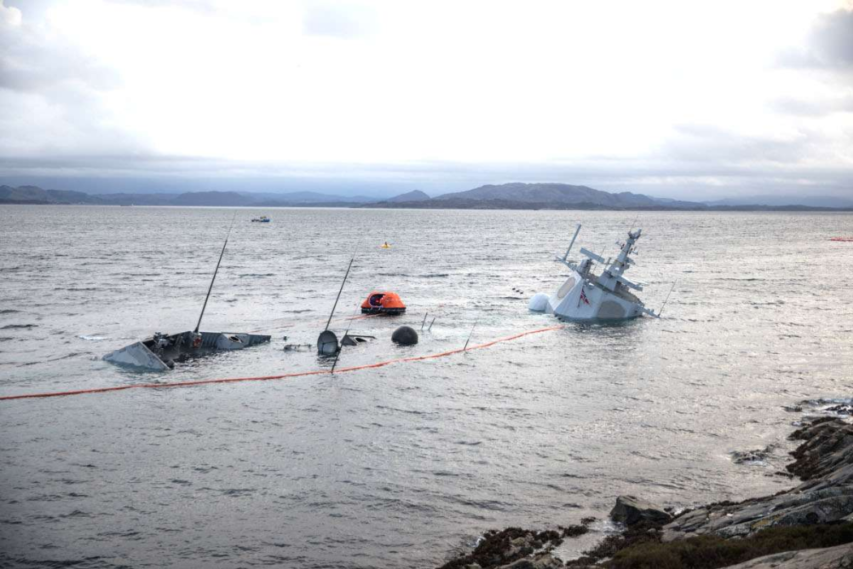
The sinking of Norwegian frigate HNoMS Helge Ingstad in 2018
CDR Salamander must follow Norwegian court cases more closely than I do … which is “not at all” in my case. Oddly, I was just thinking about the loss of HNoMS Helge Ingstad last week, and here’s follow-up information from the appeals process:

HNoMS Helge Ingstad, a Fridtjof Nansen-class frigate commissioned in 2009.
Photo detail via Wikimedia Commons.
The court case against the officer of the watch (vaktleder) and its appeals has brought the issue back to the front in Norway.
In yesterday’s Forsvarets Forums article (remember to translate it), retired Norwegian naval officer with multiple command tours, Hans Petter Midttun, outlines a must read wire brushing of the entire “optimal manning” concept.
You will see that his view of what it caused to the Norwegian Navy’s nightmare is a direct parallel of that happened to the US Navy in that horrible month of 2017; too much to do with too little people with too thin training.
Let’s dive in;
The Ministry of Defense (FD), the Defense Staff (FST) and the Norwegian Navy (SST) have, in my opinion, knowingly or unknowingly breached the prerequisites for proper operation of the frigates.
My claim is rooted in 23 years of frigate competence. I have held most of the operational positions in the frigate force. This includes the positions as ship commander at KNM Narvik and KNM Roald Amundsen, as well as a period at the Navy’s competence center and two periods as staff officer for the “shipowner”.
That is the extended way of saying, “I know you because I am you“. He’s raising his voice here because it is personal and he wants to go on the record that there are causes to this mishap much deeper than just the one officer on trial.
In light of the extensive changes that lay before the Armed Forces in 2004, we considered it crucial to describe the assumptions on which the staffing concept was based. It was not a new concept. It just hadn’t been described before. It had been developed as a consequence of continuous efficiency measures in the 90s.
One of our main messages was:
The Lean Manning Concept was not chosen because it was operationally smart. It was chosen because it enabled the Navy to man and sail (at the time) a balanced structure. It was an absolute minimum crew that could only work if all the prerequisites were met.
The last part — here on the Front Porch we describe that as “exquisite“. Everything — and everyone — has to work just right to make the formula work.
It doesn’t work that way outside the briefing room. Never does.
During a five-year period, the crew sailed one year less than what Nato considered necessary to maintain the operational level (for a frigate with a larger crew). But in addition, the crews never reached more than a maximum of 80 percent of their expected combat power. This meant that each year the training activity started at a lower level than the previous year.
You design minimum manning — and you get 80% of the minimum. It might work for awhile in peace — but it unquestionably won’t work in combat. Exactly the stew that contributed to the McCain & Fitzgerald collisions. Senior leaders try to convince everyone that 9-to-11 month deployments are a “new normal” and humans can do 100-hr work weeks for weeks to months on end with no downside. Just sadistic malpractice.
March 24, 2023
From “railway spine” to “shell shock” to PTSD
At Founding Questions, Severian discusses how our understanding of what we now label “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder” evolved from how doctors visualized bodily ailments over a century ago:
I mentioned “shell shock” yesterday, so let’s start there. Medicine in 1914 was still devoted to the “Paris School,” which assumed nothing but organic etiology for all syndromes. Sort of a reverse Descartes — as Descartes (implicitly) “solved” the mind-body problem by disregarding the body, so the “Paris School” of medicine solved it by disregarding the mind. So when soldiers started coming back from the front with these bizarre illnesses, naturally doctors began searching for an organic cause. (That’s hardly unique to the Paris School, of course; I’m giving you the context to be fair to the 1914 medical establishment, whose resistance to psychological explanations otherwise seems so mulish to us).
They’d noticed something similar in the late 19th century, with industrial accidents and especially train crashes. When a train crashed, the people in the first few cars were killed outright, those in the next few wounded, but the ones in the back were often physically fine. But within a few hours to weeks, they started exhibiting all kinds of odd symptoms. Hopefully you’ve never been in a train crash, but if you’ve ever been in a fender-bender you’ve no doubt experienced a minor league version of this.I hit a deer on the highway once. Fortunately I was at highway speed, and hit it more or less dead on (it jumped out as if it were committing suicide), so it got thrown away from the car instead of coming through the windshield. The car’s front end was wrecked, naturally, but I was totally fine. I don’t think the seatbelt lock even engaged, much less the airbag, since I didn’t even have time to hit the brakes.
The next few hours to days were interesting, physiologically. It felt like my body was playing catch up. I had an “oh shit, I’m gonna crash!!!” reaction about 45 minutes after I’d pulled off to the side of the road, duct-taped the bumper back on as best I could, and continued to my destination. All the stuff I would have felt had I seen the deer coming came flooding in. Had I not already been where I was going, I would’ve needed to pull over, because that out of the blue adrenaline hit had my hands shaking, and my vision fuzzed out briefly.
The next morning I was sore. I had all kinds of weird aches, as if I’d just played a game of basketball or something. I assume part of it actually was the impact — it didn’t feel like much in the moment, but if it’s enough to crumple your car’s front end (and it was trashed), it’s enough to give you a pretty good jolt. That would explain soreness in the arms, elbows, and shoulders — a stiff-armed, white-knuckle grip on the steering wheel, followed by a big boom. But I was also just kinda sore all over, plus this generalized malaise. I felt not-quite-right for the next few days. Nothing big, no one symptom I can really put my finger on, but definitely off somehow — a little twitchy, a little jumpy, and really tired.
Having done my WWI reading, I knew what it was, and that’s when I really understood the doctors’ thought processes. I really did take some physical damage, because I really did receive a pretty good full-body whack. It just wasn’t obvious to the naked eye. And since everyone has experienced odd physical symptoms from being rattled around, or even sleeping on a couch or sprung mattress, it makes sense — the impact obviously jiggled my spine, which probably accounts for a great many of the physical symptoms. Hence, “railway spine”. And from there, “shell shock” — nothing rattles your back like standing in a trench or crouching in a dugout as thousands of pounds of high explosive go off around you. It must be like going through my car crash all day, every day.
Skip forward a few decades, and we now have a much better physiological understanding of what we now call (and I will henceforth call) Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). There’s a hypothesis that I personally believe, that “shell shock” is also a whole bunch of micro-concussions as well as “classic” PTSD, but let’s leave that aside for now. The modern understanding of PTSD is largely about chemistry. Cortisol and other stress chemicals really fuck you up. They have systemic physical and mental effects. If those chemicals don’t get a chance to flush out of your system — if you’re in a trench for weeks on end, let’s say — the effects are cumulative, indeed exponential.
Returning to my car crash: I was “off” for a few days because my body got a huge jolt of stress chemicals. That odd not-quite-right thing I felt was those chemicals flushing through. Had I gone to a shrink at that moment, he probably would’ve diagnosed me with PTSD. But I didn’t have PTSD. I had a perfectly normal physiological reaction to a big shot of stress chemicals. If I’d gotten into car crash after car crash, though, day in and day out, that would’ve been PTSD. I’d be having nightmares about that deer every night, instead of just the once. And all that would have cumulative, indeed exponential, effects.
He then goes on to cover similar physical reactions to stimuli in modern life, so I do recommend you RTWT.
March 22, 2023
First Class Breakfast on the RMS Titanic
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 21 Mar 2023
(more…)
February 25, 2023
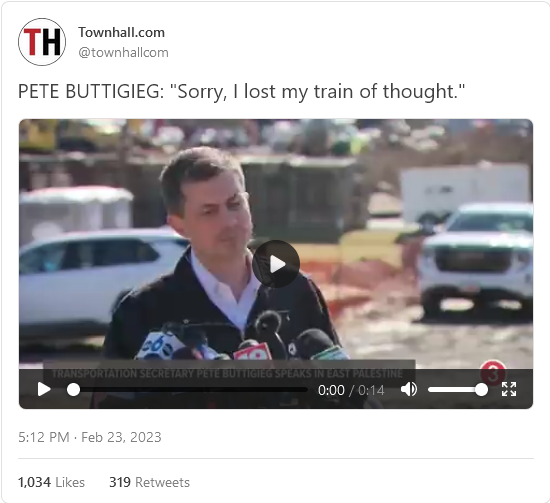
Buttigieg isn’t covering himself in glory over his belated East Palestine train derailment response
Jim Treacher is clearly trying to at least pretend some sympathy for Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, but it’s a tough assignment:
Pete Buttigieg is the type of guy who walks into a job interview and says his biggest weakness is his perfectionism. As a kid he always had an apple for the teacher, and if she forgot to assign homework that day, he was the first with his hand up. He’s a repulsive little hall monitor, so all the other repulsive little hall monitors think he’s simply divine.
Mayor Pete and his fan club are having a really bad time right now, because for once he’s expected to actually do something. Producing results simply isn’t his specialty. After spending three weeks hoping the East Palestine, Ohio rail disaster would stop bothering him if he just ignored it, he finally showed up there yesterday.
And I’m starting to understand his reluctance:
What a visual, huh? He looks like a little kid playing Bob the Builder. It’s not quite Dukakis in the tank, but it’s close.
And then it got worse: He started talking.
He’s just so gosh-darn dedicated to his job, you see. His only mistake was listening to you people. He followed the norm. This is your fault!
And then he blurted out this instant classic:
Now, which of those words should you try to avoid when you’re talking about a disastrous train derailment? I’m starting to suspect this guy isn’t the unparalleled megagenius the libs keep telling us he is.
[…]
Team Pete is more concerned about reporters asking about East Palestine than about the disaster itself. The rest of us are just an abstraction to them. If they accidentally manage to help some of us, that’s fine. If not, that’s also fine. Either way, we cannot be allowed to stand in the way of their political aspirations.
Mayor Pete really did think this gig would be a cinch, didn’t he? Like, he could just do all the reading the night before the final and ace it. He’s positively resentful at being expected to do what we’re paying him to do. He thinks he’s too good for this job, which is why he’s very bad at this job.
Will Buttigieg’s tenure as transportation secretary ruin his presidential prospects? After all, that’s what this is all about for him. Maybe, maybe not. It’s not as if politics is about solving problems. All you have to do is claim you solved the problems, and your team will cheer for you no matter what.
December 7, 2022
Pearl Harbor: Before and After December 7th
Geographics
Published 20 Sep 2022
(more…)
December 5, 2022
The Halifax Explosion
[For more on the events leading up to the explosion, you can read my page on the event here.]
OTD Canadian Military History
Published 3 Dec 2022Halifax, Nova Scotia was rocked by a massive explosion on the morning of 6 December 1917 after the French cargo ship SS Mont-Blanc collided with the Norwegian vessel SS Imo in the harbour. Nearly 2000 people were killed and 9000 were injured. More than 25,000 were left without adequate shelter.
This video includes a photo of the Halifax explosion itself and footage from its aftermath as I explain details of the explosion and the relief efforts.
(more…)
November 8, 2022
Look at Life — Underwater Menace (1969)
PauliosVids
Published 20 Nov 2018Dealing with the hazardous legacy of World War II.
July 26, 2022
Flying Failures – Christmas Bullet (The Worst Plane Ever Built)
Ruairidh MacVeigh
Published 25 Dec 2020Merry Christmas everyone! 😀
To coincide with this most special of holidays, in this episode of Flying Failures we will be examining the dubious history of the Christmas Bullet, a divisive little plane that could either be seen as the brainchild of a man whose ambition outweighed his abilities, or perhaps one of the greatest cons in aviation history, a con that left two planes destroyed, two test pilots dead, and the US taxpayer several million dollars out of pocket.
(more…)
July 14, 2022
The plight of 1st Canadian Infantry Division during the opening stages of Operation Husky, July 1943
First Canadian Infantry Division had an exciting start to Operation Husky — for certain values of “exciting” — as told in Mark Zuehlke’s Operation Husky: The Canadian Invasion of Sicily, July 10-August 7, 1943:
Every day [during the convoy to Sicily], Major General Guy Simonds and Lieutenant Colonel George Kitching performed the same macabre ritual. Kitching would take a hat filled with equal-sized chits of paper on which the names of every ship bearing Canadian personnel and equipment was written and hold it out to the divional commander. Simonds drew three chits and those three ships were declared lost, victims of torpedoes from a German U-boat — the scenario at times being that about one thousand men aboard the fast convoy had drowned and burned in oil-drenched seas, or hundreds of trucks, tanks, guns, radios, and other equipment in the slow convoy had plummeted to the bottom of the Mediterranean. All lost, gone. Kitching and his staff would then sit down and coldly “examine the effect the loss of these three ships would have on our projected plans.”
On July 3, Simonds pulled from the hat chits for three ships travelling in the Slow Assault Convoy — City of Venice, St. Essylt, and Devis. The coincidence was chilling, for it was aboard these vessels that equal portions of the divisional headquarters equipment — including all the trucks, Jeeps, radio sets, and a panoply of other gear that kept a division functioning — had been distributed. Were one or even, God forbid, two of these ships sunk, the headquarters could function almost as normal. But lose the three and the division was crippled.
Kitching considered the “chance of all three ships being sunk as a million to one”. Deciding there was no point in studying the implications of such a wildly remote possibility, he asked Simonds to draw another three names from the hat, which the general did.
As you’ve probably already figured out, the one-in-a-million situation turned up on schedule. City of Venice took a torpedo during a submarine alert, with Royal Navy escort ships dropping depth charges on a suspected U-boat position. The convoy instructions were for damaged ships to be left behind and for the undamaged ships to carry on, as the danger was greater if the whole convoy slowed or stopped to aid the stricken ship(s). City of Venice could not be saved, and ten crew members and ten Canadian soldiers were killed, but the other 462 men on board were transferred to a rescue ship. A few hours later, two more ships from the convoy were lost: St. Essylt, and Devis.
While the loss of lives aboard the three torpedoed slow convoy ships was relatively small, the amount and nature of equipment and stores sent to the bottom of the Mediterranean was serious. A total of 562 vehicles were lost, leaving 1st Canadian Infantry Division facing a major transportation shortage. Also lost were fourteen 25-pounders [gun-howitzers], eight 17-pounders [heavy anti-tank guns, equivalent to German 88mm guns], and ten 6-pounder anti-tank guns that would significantly reduce the division’s artillery support. “In addition to the above,” the divisional historical officer, Captain Gus Sesia, noted in his diary, “we lost great quantities of engineers’ stores and much valuable signals equipment.” The biggest immediate blow was the loss of all divisional headquaters vehicles and equipment, including many precious wireless sets — precisely the nightmare scenario forecast and rejected by Kitching as infeasible when Simonds had drawn these ships by lot a few days earlier.
Equally serious was the loss in equipment and lives suffered by the Royal Canadian Army Medical Coprs personnel attached to the division. Due to a loading error, instead of No. 9 Field Ambulance’s vehicles being distributed among several ships, fifteen out of eighteen were on Devis. Accompanying the vehicles was a medical officer and nineteen other ranks and medical orderlies. Four of the other ranks were among the fifty-two Canadian troops killed and another four suffered injuries. The other field ambulance, field dressing station, and field surgery units assigned to the division were largely unaffected. No. 5 Field Ambulance’s vehicles had been distributed correctly so only two of them and a ton of medical supplies went down with St. Essylt. City of Venice had just one medical officer, Captain K.E. Perfect, aboard and he escaped uninjured. But Perfect was overseeing safe passage of nine tons of stretchers and blankets, which all went to the bottom.
[…]
A fully accounting of the losses would not be completed for days. Even on July 7, reports were still coming in that City of Venice remained under tow and bound for Algiers. Finally, at 1900 hours on that day, its sinking was confirmed. The report also stated that most of the surviving Canadian troops had been loaded on a Landing Craft, Infantry in Algiers and were en route for Malta. From there, they would eventually rejoin the division.
Compounding the loss of so many vehicles was the fact that the division had left Britain with a smaller than mandated number due to lack of shipping capacity. Once the seriousness of the situation was appreciated, Lieutenant Colonel D.G.J. Farquharson, the division’s assistant director of ordnance services, and his staff “tried to make [the losses] good … by emergency measures, improvising and obtaining what could be obtained buckshee from the Middle East.” They soon had commitments for some vehicles, but these would not be available until after the initial landings. The fact that every vehicle to be found locally was a Dodge posed “a considerable ordnance problem, because what spare parts we had were based on Ford and Chevrolet makes.” Improvisation would be the order of the day.
April 27, 2022
Why It Sucked To Be on a Merchant Ship in World War Two – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 26 Apr 2022Serving on board a merchant ship during the Second World War was a hazardous endeavor. Stalked by submarines, attacked by surface raiders, and hunted by bombers, the convoys and individual cargo ships faced constant danger on their routes across the seas. And that is in addition to the job’s typical hazards. But what was life like for a regular sailor on board these ships? And what motivates a man to sign up for such a dangerous job?
(more…)
April 23, 2022
Historic “innovation prizes” (somewhat) debunked
In the most recent Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes does a bit of heavy lifting to debunk some accreted nonsense about the origins and success of early innovation prizes:

Admiral of the Fleet Sir Cloudsley Shovell (1650-1707).
Portrait by unknown artist from the National Maritime Museum collection via Wikimedia Commons.
Yesterday I had a piece in Works in Progress magazine, on the best ways to design modern innovation prizes — and why many of them fail.
I examined the famous “Longitude Prize” of 1714, and in the process busted some major myths about it. Almost every element of the popular story is wrong — something that experts on the topic like Richard Dunn and Rebekah Higgitt have been going on about for years. The popular story’s hero, John Harrison, often portrayed as an inventor shunned by a haughty scientific establishment, actually received massive amounts of funding from the committee for awarding the prize. The story’s villain, the Astronomer Royal Neville Maskelyne, was no villain at all. And there’s very little evidence that the prize actually incentivised people to innovate. The Board of Longitude, for that matter, ended up more like a grant-giving agency — a kind of navigation-themed DARPA — than just a committee of prize judges.
You can read the full piece here.
So what is the rest of this week’s newsletter about? Well, I’d like to take the chance to bust even more myths about innovation prizes!
Let’s start with a fairly small one, to do with longitude, that I’d missed. Take the narrative about the 1707 naval disaster off the Isles of Scilly, which led to the demise of the wonderfully-named admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell. The disaster is usually cited as having been the direct cause of the institution of the 1714 reward, and, of course, gives most Youtubers, bloggers, and TV presenters discussing longitude the opportunity to say the name “Sir Cloudesley Shovell”. Who wouldn’t?
I had already been sceptical of the disaster’s relevance to Parliament’s creation of the longitude reward, because of the seven-year delay. I had then noticed, when researching for the piece, that the disaster was hardly mentioned at all by those lobbying for the reward, by those consulted on it, or by the MPs who voted on it. It seemed to be irrelevant as a cause, so I repurposed that part of the popular story to simply use as a general example of a naval disaster caused by not knowing one’s position at sea.
But even my downgrading of its relevance, it turns out, may have been over-generous. Yesterday, after I published my piece, Richard Dunn pointed out to me that not only was the 1707 disaster irrelevant as a cause of the 1714 reward, but that the disaster itself may not have had very much to do with a specific failure to find longitude. It certainly wasn’t singled out as a cause at the time.
As for the actual causes, they were probably compass error, inconsistent charts, and even uncertainty over the fleet’s latitude, not just its longitude. And to the extent that not knowing the fleet’s longitude appears to have been a major part of the problem, it was also related to failures to accurately calculate longitude on land — something that could already be done using existing techniques. The navigational text-books, for example, disagreed on the position of Cape Spartel, in Morocco, from which the fleet departed and took its bearings. As the maritime historian William E. May put it, when he looked into the detail of the fleet’s route and navigational measurements, “the errors in longitudes in the accepted text-books must have introduced a danger just as great as any errors in reckoning the longitude.”