Kings and Generals
Published 12 Aug 2018Napoleonic Wars are back! It is 1807, and we find the Emperor of the French Napoleon Bonaparte at the height of his power, as he controls most of Europe after the War of the Fourth Coalition and the treaties of Tilsit. Napoleon decided to strangle his remaining enemy the United Kingdom economically by enacting Europe-wide Colonial Blockade, yet as Portugal defied him, he invaded it and then Spain. This was the beginning of the Peninsular War. Soon Spain and Portugal were in open rebellion. The first phase of the war ended when the British forces under Wellington landed in Portugal and fought the French General Junot at Vimeiro.
This script was researched and written by Everett Rummage. Check out his brilliant Age of Napoleon podcast – http://bit.ly/2vC3cIE In our opinion, it is the best podcast on the Napoleonic era.
Support us on Patreon: http://www.patreon.com/KingsandGenerals or Paypal: http://paypal.me/kingsandgenerals
We are grateful to our patrons and sponsors, who made this video possible: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1jjh…
This video was narrated by Officially Devin (https://www.youtube.com/user/OfficiallyDevin)
Machinimas were made on NTW3 mod for Napoleon Total War by Malay Archer (https://www.youtube.com/user/Mathemed…)
✔ Merch store ► teespring.com/stores/kingsandgenerals
✔ Twitch ► https://www.twitch.tv/nurrrik_phoenix
✔ Twitter ► https://twitter.com/KingsGenerals
✔ Instagram ► http://www.instagram.com/Kings_GeneralsProduction Music courtesy of Epidemic Sound: http://www.epidemicsound.com
#Documentary #Kingsandgenerals #Napoleon
November 4, 2021
Napoleonic Wars: Battle of Vimeiro (1808) – Peninsular War
October 23, 2021
French Guerrilla War & German Retaliation during the Franco-Prussian War 1870
Real Time History
Published 21 Oct 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimeh…
The French increasing reliance on franc-tireurs, guerrilla style fighters, is causing brutal German retaliation and a spiral of violence in the fall phase of the Franco-Prussian War.
Special thanks goes out to Quentin Censier from Sur le Champ. Check out his Channel: https://www.youtube.com/surlechamp
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan
James Giliberto
Kurt Gillies
Albert B. Knapp MD
Tobias Wildenblanck
Richard L Benkin
Scott Deederly
John Belland
Adam Smith
Taylor Allen
Jim F Barlow
Rustem Sharipov» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französischen Krieges erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Keegan, John: Die Kultur des Krieges. Berlin 1995
Neitzel, Sönke/Hohrath, Daniel (Hrsg.): Kriegsgreuel. Die Entgrenzung der Gewalt in kriegerischen Konflikten vom Mittelalter bis ins 20. Jahrhundert. Paderborn, München 2008
Roth, François: La Guerre de 1870. Paris 1990
» SOURCES
Busch, Moritz: Graf Bismarck und seine Leute während des Krieges mit Frankreich. Bd. I. Berlin 1878Chuquet, Arthur: La Guerre 1870-71. Paris 1895
Engels, Friedrich: Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg. Sechzig Artikel aus der “Pall Mall Gazette”. Berlin (Ost) 1957
Fontane, Theodor: Kriegsgefangen. Erlebtes 1870. Briefe 1870/71. Berlin (Ost) 1984
Kriegsgeschichtliche Abteilung des Großen Generalstabs (Hrsg.): Der deutsch-französische Krieg 1870-71. II.1 Berlin 1878
Kürschner, Joseph (Hrsg.): Der große Krieg 1870–71 in Zeitberichten. Leipzig o. J. (1895)
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
Roux, Georges: La Guerre de 1870. Paris 1966
Sarrepont, Major H. de (i.e. Eugène Hennebert): Histoire de la défense de Paris en 1870-1871. Paris 1872
Zeitz, Karl: Kriegserinnerungen eines Feldzugsfreiwilligen aus den Jahren 1870 und 1871. Altenburg 1905
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
October 15, 2021
Nazis “Restore” Law and Order – WAH 044 – October 1942, Pt. 1
World War Two
Published 14 Oct 2021Resistance against occupation starts rising in the Autumn of 1942. It faces opposition not only from the occupiers, but also from collaborators killing their own countrymen.
(more…)
October 13, 2021
Josip Broz Tito — The “Maharaja of the Balkans”
In The Critic, Thomas Gallagher looks at the man and the myth of Yugoslavia’s communist leader, known to the world as “Tito”:
Decades after his death in 1980, Josip Broz Tito still casts a spell as a larger-than-life figure.
The legend portrays him as a famous military leader and anti-fascist guerrilla fighter who fought off the Nazis and defied Stalin. He then went on to be a champion of peace who stood up for various small nations snapping the coils of European overlordship. He was at home on imperial estates or, more often, on his secluded luxury home on the island of Brioni, with Old Masters adorning his walls and kings, emperors and fellow communist strongmen paying homage.
Despite clumsy language and hyperbole in places, as well as some avoidable errors, Tito’s Secret Empire seeks to debunk Tito’s legend and in several key respects it succeeds. The authors William Klinger and Dennis Kuljiš accord some honours to their subject.
He was a unique character well-equipped to surmount various obstacles during his 88-year life. For the British diplomat, Sir Fitzroy Maclean, he was “a fail-proof survivor”. In 1974 he was hailed by Germany’s Chancellor, Helmut Schmidt, as “the greatest of the winners of the Second World War”.
A benign image persisted, despite Tito being responsible for more acts of mass cruelty than any other European communist leader with the exception of the Soviets. He was admired as a wheeler-dealer in international affairs, from murky transactions to the most delicate undertakings in statecraft. This well-researched book deserves attention for those who wish to peer beyond the carefully cultivated image.
[…]
His 1954 state visit to then-royalist Greece, a regime which he had spent years trying to topple, was an unmistakable indication that he was placing himself at the head of a hybrid regime. Britain’s foreign secretary, Anthony Eden, had already visited him and urged the United States to prop up Tito financially. The favour was not returned. Evidence is provided that Tito played a major role in encouraging Egypt to nationalise the Suez Canal. He saw President Nasser as a kindred spirit, a populist unencumbered by ideology. Tito even more keenly sought to end French rule in Algeria, arming the rebels and offering diplomatic support.
In September 1961, he welcomed dozens of leaders from the promising new “non-aligned” bloc to a conference in Belgrade. Next year China invaded India and his soul-mate, Nehru, turned to the West for help. Thereafter, the non-aligned movement’s influence waned, as did Tito’s with it.
He increasingly became a pensioner of the Soviet Union. American ardour cooled as it became clear how reliant he was on Soviet arms and industrial licences which enabled this supposed ambassador of peace to export weapons to the Third World.
October 8, 2021
Rise of Guerrilla Warfare & Daring Balloon Escapes – The Franco-Prussian War Early October 1870
Real Time History
Published 7 Oct 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimehistory
In early October 1870, the German states are still confident the Franco-Prussian War is as good as over. But two events might cross their plans: One of the leaders of the new French Republic, Leon Gambetta, escapes the Siege of Paris in a hot-air balloon to coordinate the French Armies outside of Paris. And in Ablis, French guerrilla fighters, the so-called Franc-Tireurs, ambush a German patrol in their sleep — with swift German retribution.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Arand, Tobias: Gestorben für “Vaterland” und “Patrie” – Die toten Krieger aus dem Feldzug von 1870/71 auf dem “Alten Friedhof” in Ludwigsburg. Ludwigsburg 2012
Hahn, Joachim: Jüdisches Leben in Ludwigsburg. Geschichte, Quellen, Dokumentation. Karlsruhe 1998
Schneider, Fernand Thiébaut: “Der Krieg in französischer Sicht”, in: Entscheidung 1870. Der deutsch-französische Krieg, hrsg. v. Wolfgang von Groote und Ursula von Gersdorff. Stuttgart 1970. S. 165-203
» SOURCES
Engels, Friedrich: Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg. Sechzig Artikel aus der “Pall Mall Gazette”. Berlin (Ost) 1957Huber, Rudolf (Hrsg.): Dokumente zur deutschen Verfassungsgeschichte. Bd. 2. 1851-1900. Stuttgart 1964
Kürschner, Joseph (Hrsg.): Der große Krieg 1870-71 in Zeitzeugenberichten. Leipzig o.J. (1895)
N.N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Philippson, G.: “Jom Kippur 1870 vor Metz”, in: Wegweiser für die Jugendliteratur, Heft 4, 6 (1910). S. 26-27
Steenackers, François-Frédéric/Le Goff, F.: Histoire du gouvernement de la Défense nationale en province, 4 Septembre 1870 – 8 Février 1871. Bd. II. Paris 1884
Tissandier, Gaston: Souvenirs et récits d’un aérostier militaire de l’armée de la Loire. Paris 1891
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
September 28, 2021
Debunking the notion that Stalin was an innocent victim of Hitler
At Instapundit, Ed Driscoll links Jakub Grygiel’s review of a new look at World War 2 in Europe, Stalin’s War by Sean McMeekin, which includes a bit of debunking about the relationship between Hitler and Stalin from 1939 to 1941:

Translation of the Russian caption for this image:
People’s Commissar of Foreign Affairs of the USSR V.M. Molotov signs a friendship and border treaty between the USSR and Germany. Among those present: I.V. Stalin, translator of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs V.N. Pavlov, German diplomat G. Hilger (“truncated” version of the photograph of M. Kalashnikov distributed on the net)
Photograph attributed to Mikhail Mikhaylovich Kalashnikov (1906-1944) via Wikimedia Commons.
Stalin was always interested in a war, especially one that would pit the other powers against each other. The expansion of Soviet influence and control required the weakening of the other powers, in particular the Western ones that were opposed to the Communist virus. For Stalin, therefore, the growth of Nazi Germany was a great opportunity: a violent and expansionistic power in the middle of Europe that could take the first swing against the polities standing on his path. Unsurprisingly, the Soviet tyrant was deeply disappointed when France and Britain signed the Munich Agreement with Nazi Germany in 1938 postponing the great European war that he desired. The 1939 Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact coordinated the efforts of Hitler and Stalin, but it benefited the latter more, allowing him to conquer a large swath of Polish territory with minimal effort, eliminating one of the staunchest opponents to Russian westward expansion. A year later, by murdering almost 22,000 Polish officers in Soviet captivity, Stalin further weakened the Polish obstacle to his expansion. “Nations which had been ruled by powerful aristocracies,” Stalin told once to the Yugoslav Milovan Djilas, “like the Hungarians and the Poles, were strong nations” — and, fearing them, he sought to eliminate them. Then, while Germany invaded France, Stalin took over the three Baltic states in a further step westward.
Hitler’s decision to invade Russia in mid-1941 was a surprise to Stalin, but not because he was expecting a lasting peace on his western frontier. Rather, as McMeekin documents, Stalin had ordered very rapid and large military preparations, building airbases and placing forces near the border with the Third Reich in the first half of 1941. None of them were in a defensive posture, and presented a vulnerable high value target to Nazi attacks. When Hitler decided to attack the USSR in June 1941, these Soviet forces were easy pickings for the well-organized, trained, and war tested German army. McMeekin here expands and amends a bold thesis offered in 1990 by Viktor Suvorov, a pseudonym for a GRU agent who defected to the West in the late ’70s and became a historian, that argued that Stalin was actively planning an attack on Germany but was preempted by Hitler. While Suvorov was excessive in his claim that the Red Army was ready for an offensive campaign in 1941 (because, among other reasons, the officer corps was still in shambles after Stalin’s purges) and that Stalin had plans to conquer Europe, he argued that the USSR was never a status quo power satisfied in its borders. After all Soviet Russia had already attempted to march westward in 1920 and was stopped only by the Poles in a desperate battle near Warsaw (the “Miracle on the Vistula”). This westward vector and ambition of Moscow did not abate, and had to pause because of Hitler’s rise and the might of Nazi Germany. As McMeekin points out, the Soviet military posture in 1941 makes no sense if the goal was to defend Soviet-held lands, suggesting that Stalin was thinking of pouncing on Berlin, now the last remaining continental power in Europe. As the Soviet tyrant himself put it, the USSR no longer needed to be locked in a defensive posture, and was “a rapacious predator, coiled in tense anticipation, waiting for the chance to ambush its prey.”
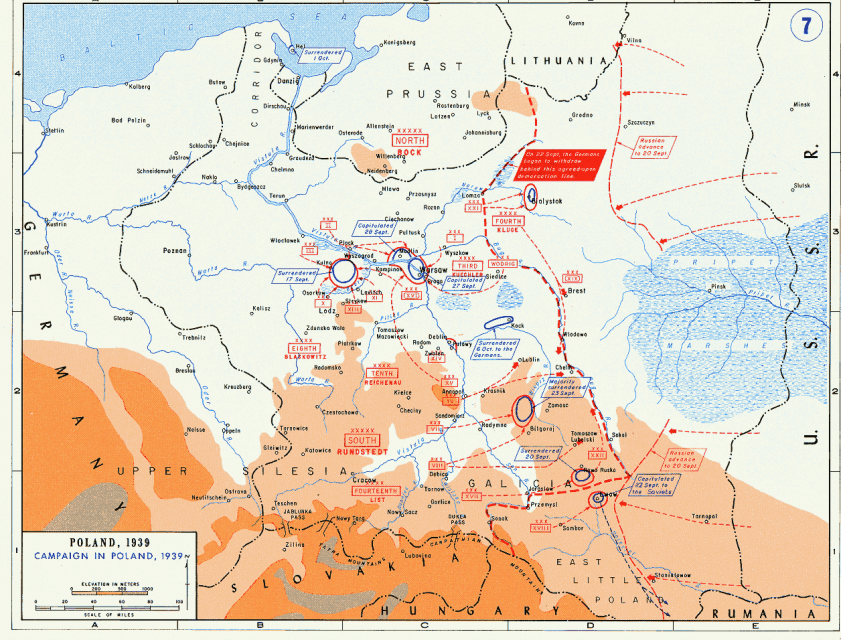
Military situation in Poland, 14 September 1939 (map does not show Slovak Army activity in southern Poland).
United States Military Academy, Department of History via Wikimedia Commons.Stalin, that is, was not an innocent victim of Hitler. Not only he was an active partner from 1938 until 1941, but also he had geopolitical aspirations that were more ambitious than those held by Hitler. And he pursued them methodically and ruthlessly, leaving a trail of death that dwarfed the one produced by the Nazis.
McMeekin then focuses on how the Western allies, Churchill but especially FDR, abetted Stalin’s ambitions. This part of the book is fascinating and depressing at the same time. In a nutshell, Stalin obtained from FDR more than he expected: territory, influence, and materiel. And he did not give anything in exchange for it because FDR and his advisors never asked him for it. For instance, FDR supported the Lend-Lease program, putting his friend Harry Hopkins in charge. Under this program of military aid, the United States supplied a massive amount of weapons, trucks, airplanes, tanks, foodstuff to the Soviet Union in the months of its greatest need, as German troops were driving deep into Russia while the vaunted Soviet armies were melting away. Without such aid, the USSR would have likely been unable to stop the German onslaught and certainly would have been incapable of mustering the resources necessary to push westward. Hence, in this moment there was a good strategic rationale for the American support of Stalin’s defensive efforts against Nazi Germany.
Prior to the launch of Operation Barbarossa, you’d have been hard-pressed to find a more anti-Soviet leader than Winston Churchill, but he immediately recognized that Stalin was more useful to the British as an ally than as a passive enemy. Earlier this year, McMeekin wrote that Stalin “could not have asked for a friendlier British government” than Churchill’s wartime coalition. As Connor Daniels wrote in response at The Churchill Project:

The “Big Three” meet at Tehran, 28 November-1 December, 1943.
Photo attributed to US Army photographer, via Wikimedia Commons.
Churchill’s support for Stalin during the Second World War followed from a simple calculus of the lesser of two evils. Britain could only take on one evil empire at a time, and, of the two, Churchill believed that Nazi Germany posed the greater threat to liberty. He famously remarked, “If Hitler invaded Hell I would make at least a favourable reference to the Devil in the House of Commons.” McMeekin attempts to sidestep this harsh reality, writing: “Whether or not the payoff was worth the price is a question well worth debating.” Churchill’s alliance with the Soviets stands or falls on this question: was Nazi Germany or the Soviet Union the greater danger in 1939?
With hindsight, one can easily marshal facts that portray Soviet communism as the greater evil. According to the best available estimates, the Stalin regime killed 20 millions of its own citizens. Nearly six million of those deaths occurred during the 1932–33 famine brought about by Stalin’s collectivization policies. While Nazi Germany also killed 17 million civilians, most of those deaths occurred after Hitler’s invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941. Thus, on the eve of the Second World War, one could argue — as Chamberlain and the appeasers did — that Nazi Germany served as a useful bulwark against a greater danger: the Soviet Union.
This analysis, however, misses a crucial point — one that Churchill recognized. Until 1939, the horrors of the Soviet regime had been primarily restricted to its own borders, while Nazi Germany had already made its expansionist ambition clear. In 1938, Germany annexed Austria. Later that year, Germany seized the Sudetenland. In 1939, the rest of Czechoslovakia passed under Hitler’s control. The Nazi doctrine of Lebensraum dictated even greater expansion. By contrast, Stalin’s doctrine of “socialism in one country” had kept the Soviet Union relatively peaceful until the Second World War began.
September 14, 2021
QotD: “In 1918 it was statistically safer for a British soldier to fight in the trenches of the Western Front than be a prisoner in Germany”
… the Kaiser’s armies behaved abysmally on the battlefields of the Great War fighting foreigners. As soon as the Germany Army crossed the border into Belgium, the atrocities began. If the sensational stories of German soldiers eating Belgian babies can be discounted as Allied propaganda, the painstaking research of Alan Kramer and John Horne, in German Atrocities, 1914: A History of Denial (2001), demonstrates beyond reasonable doubt that Germany engaged in a systematic programme of civilian executions with the purpose of striking terror into the heart of the Belgian population. On 23 August, 1914, in the city of Dinant, the German army burned down a thousand buildings and executed some 674 civilians. The oldest among them was in his 90s; the youngest was barely a month old.
On and on the German outrages went: the sinking of the Lusitania, the execution of Nurse Cavell. Of course, the Allies were not saints, but the fashionable fallacy of moral equivalence — that all sides in the Great War were as bad as each other — founders on the rocks of Germany’s treatment of prisoners of war, who became slave labourers.
This was the main substance of the British agenda at Leipzig. Almost 165,000 British soldiers were taken prisoner on the Western Front between 1914-18; by the end of 1916, almost 80% were forced into labour for the Second Reich. Prisoners were literally worked to death in salt mines. And conditions in many camps were inhuman: in Wittenberg, two water taps served 17,000 Allied PoWs. When typhus struck the camp, the German staff abandoned it and left the prisoners to die. Some 13,000 Brits perished in the Kaiser’s camps — the vast majority because of brutality, disease, malnutrition or exhaustion. But 500 British soldiers were summarily shot or beaten to death at the Kaiser’s pleasure during their detention.
Of all the German PoWs held in Britain during the Great War, 3% died; of the British PoWs held in Germany, more than 10% perished. In 1918 it was statistically safer for a British soldier to fight in the trenches of the Western Front than be a prisoner in Germany. That year, 5.8% of British PoWs in Germany died, compared to 4% of British soldiers on the battlefield.
John Lewis Stempel, “Germany’s First World War Guilt”, UnHerd, 2021-05-25.
September 4, 2021
Battle of Sedan – German Victory and Fall of the French Empire (Franco-Prussian War)
realtimehistory
Published 2 Sep 2021The Battle of Sedan was one of the pivotal moments in the 19th century. The French 2nd Empire’s defeat at Sedan (and the capture of Emperor Napoleon III) unleashed social tensions in Paris and a new French republic was proclaimed. And while the victory of the German Armies was resounding, the cost at places like Bazeilles was also high.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französischen Krieges erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Barry, Quintin: The Franco-Prussian War 1870-1871. Vol 1: the Campaign of Sedan. Solihull 2006
Bourguinat, Nicolas/Vogt, Gilles: La guerre franco-allemande de 1870. Une histoire globale. Paris 2020
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite de 1870-1871. Paris 2015
Howard, Michael: The Franco-Prussian War. London 1961
Herre, Franz: Eugénie. Kaiserin der Franzosen. Stuttgart, München 2000
Milza, Pierre: L’année terrible. Paris 2009
» SOURCES
Chuquet, Arthur. La Guerre 1870-71. Paris 1895Fontane, Theodor: Der Krieg gegen Frankreich. Bd. Berlin 1874
Kühnhauser, Florian: Kriegs-Erinnerungen eines Soldaten des königlich bayerischen Infanterie-Leib-Regiments. Patenkirchen 1898
N.N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870-71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Sheridan, Philip H.: Von Gravelotte nach Paris. Erinnerungen aus dem deutsch-französischen Kriege. Leipzig 1889
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
August 11, 2021
The Symphony That Defeated the Wehrmacht – WAH 040 – August 1942, Pt .1
World War Two
Pubished 10 Aug 2021The Big Action at the Warsaw Ghetto continues, while The Japanese carry out retaliations against the Chinese for aiding American airmen. Dmitri Shostakovich’s “Symphony no. 7” premieres in the besieged city of Leningrad.
(more…)
July 16, 2021
Forced Sterilization Experiments Begin at Auschwitz – WAH 038 – July 1942, Pt. 1
World War Two
Published 15 Jul 2021Operation Millennium is discontinued, while in Poland the Auschwitz Birkenau camp starts to systematically gas thousands of people a week. Some who aren’t murdered on arrival are subjected to horrific medical and sterilization experiments.
(more…)
July 14, 2021
Jewish Luftwaffe Officers, Allied POW’s, and Vichy Islands near Canada – WW2 – OOTF 023
World War Two
Published 13 Jul 2021How did Germans with Jewish heritage still serve in the Luftwaffe? And what happened to the Allied POW’s from the German invasions of France and Belgium? And what the hell happened with those tiny Vichy islands near Canada? We answer all of this in today’s Out of the Foxholes.
(more…)
July 2, 2021
Japan’s Institutionalization of Rape – WAH 037 – June 1942, Pt. 2
World War Two
Published 1 Jul 2021During the occupation of South-East Asia, Japan builds a large system of institutionalised rape to “keep their soldiers happy”. Meanwhile, Allied refugees from Burma find a safe haven in India, but for some, hardship continues.
(more…)
June 8, 2021
Midway pt.2 – A New War? – WW2 – 145c – June 7, 1942
World War Two
Published 7 Jun 2021We left off last time with several burning behemoths. Watch today to see the action that follows, not just on the high seas, but also in Alaska. We also turn to Washington DC and Tokyo and follow the reaction to the Battle of Midway there. The Japanese one may surprise you.
(more…)
June 6, 2021
Turning Point of History: D-Day Juno Beach
ch1201
Published 8 Nov 2014Examines Canada’s role on June 6th, 1944 and the advance through Normandy, France.
May 29, 2021
History Buffs: Midway Part Two
History Buffs
Published 28 May 2021As promised here is Part Two of my Midway review. Hope you guys enjoy it 🙂
You can join Nebula today and get Curiosity Stream at 26% off for a year! Click on the link below
http://curiositystream.com/historybuffs
Part Two of this review will be out next Friday on the 28th of May!● Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/HistoryBuffs_