Alas, as my fictional namesake said somewhere, time has a habit of turning all our lies into truths. It turns out Karl Marx was right after all. Who, I ask you, is more cartoonishly evil, more like the caricature capitalist of paranoid Communist fantasies, than Jeff Bezos? Mark Zuckerberg? Tim Cook? Jack Dorsey? Sundar Pichai?
We’re actually living, comrades, in the class-warfare world Marx preached in the 1840s. Everything Marx said about the factory owners of the First Industrial Revolution, that seemed so luridly absurd that even other Socialists criticized him for it, is true of the tech fascists of the Biden-Harris Revolution. Solzhenitsyn cites Russian writers from the late nineteenth century noting that Marxian socialism would end up as nothing more than dialectically-constructed feudalism, and lo, here we are. America in 2021 looks almost exactly like the USSR looked upon Lenin’s death …
… that was 1924, gang, and in case you’ve forgotten, what happened next was a vicious intra-Party civil war, in which Stalin crushed his enemies. AOC makes a pretty unlikely Trotsky, but it’s no less ludicrous than the thought of Nancy Pelosi as Koba … but that’s just the thing, isn’t it? We’ve been noting here for years that the modern Left is dedicated to being the Hollow Men in all things. They’re Revolutionaries without a Revolution — they go on and on (and on and on and on) about fighting the power and sticking it to the Man, even though they, themselves, have been the Man since at least 1974. They’re moralizers without morality — you’ll be scolded for not being as perverse as humanly possible. And, of course, their politics is a cult of personality without the personality — not even Orwell or Kafka could’ve come up with the Party installing an obvious dementia patient as its figurehead, not even if you’d dropped LSD in their tea.
As always — and yes, even in the depths of Stalin’s terror — the real rulers are the nomenklatura, the apparatchiki. Not even Koba the Dread can be everywhere. Being Hollow Men, our Postmodern Leftist masters have decided to dispense with the whole Kremlin thing. Who needs the NKVD, the gulag, the dreaded Lubyanka? The Junior Volunteer Thought Police “fact checking” everything on social media will do it for free, and much more efficiently, at which point their fellow travelers in the banking system will simply cut the badthinkers off. The only reason the gulag persisted after Khrushchev’s “secret speech” was that the Soviets, those fools, wanted to exploit their natural resources themselves, to build things themselves; labor camps were thus integral to the Soviet economy. Our masters don’t care about that, and their masters, the Chinese, certainly don’t. Much more efficient, and psychologically effective, to let the unperson simply starve in the middle of the town square, pour encourager les autres.
But hey, at least we’ll have some fun figuring out who the new Trotsky is. Again, my money’s on AOC — she’s so stupid that she’s bound to do something irrecoverably dumb sooner or later, after which she gets the digital icepick. That’ll be a hoot. Enjoy what parts of the spectacle you can, comrades – if you’re a student of human folly, you’re going to love the next few decades, because Marx was right about that too, the bastard — second time as farce.
Severian, “Marx Was Right After All (on ongoing series”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-01-12.
September 5, 2023
September 3, 2023
The War is Five Years Old – WW2 – Week 262 – September 2, 1944
World War Two
Published 2 Sep 2023Five years of war and no real end in sight, though the Allies sure seem to have the upper hand at the moment. Romania is coming under the Soviet thumb and Red Army troops are at Bulgaria’s borders, the Allies enter Belgium and also take ports in the south of France. A Slovak National Uprising begins against the Germans, and the Warsaw Uprising against them continues, but in China it is plans for defense being made against the advancing Japanese.
(more…)
August 27, 2023
The Liberation of Paris – WW2 – Week 261 – August 26, 1944
World War Two
Published 26 Aug 2023Paris is liberated by the Allies, a symbolic act that causes the world to rejoice. Something far more important to the course of the war, though, happens this week in Romania. The Allies continue to advance in the south of France and begin a new offensive in Italy, though the Pacific War has quietened down once again.
(more…)
6 Strange Facts About the Cold War
Decades
Published 27 Jul 2022Welcome to our history channel, run by those with a real passion for history & that’s about it. In today’s video, we will be exploring 6 odd Cold War facts.
(more…)
August 25, 2023
The German Democratic Republic, aka East Germany
Ed West visited East Berlin as a child and came away unimpressed with the grey, impoverished half of Berlin compared to “the gigantic toy shop that was West Berlin”. The East German state was controlled by the few survivors of the pre-WW2 Communist leaders who fled to the Soviet Union:
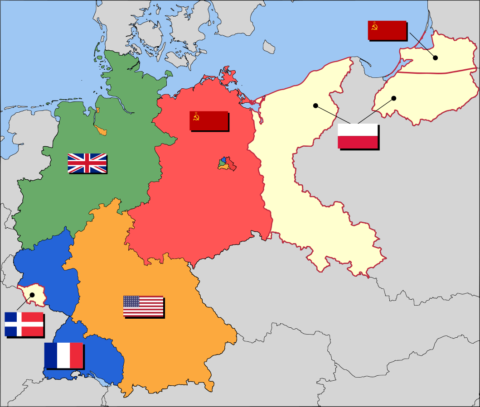
Occupation zone borders in Germany, 1947. The territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, under Polish and Soviet administration/annexation, are shown in cream as is the likewise detached Saar protectorate. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Image based on map data of the IEG-Maps project (Andreas Kunz, B. Johnen and Joachim Robert Moeschl: University of Mainz) – www.ieg-maps.uni-mainz.de, via Wikimedia Commons.
In my childish mind there was perhaps a sense that East Germany, the evil side, was in some way the spiritual successor both to Prussia and the Third Reich – authoritarian, militaristic and hostile. Even the film Top Secret, one of the many Zucker, Abrahams and Zucker comedies we used to enjoy as children, deliberately confused the two, the American rock star stuck in communist East Germany then getting caught up with the French resistance. The film showed a land of Olympic female shot put winners with six o’clock shadows, crappy little cars you had to wait a decade for, and a terrifying wall to keep the prisoners in – and compared to the gigantic toy shop that was West Berlin, I was not sold.
I suppose that’s how the country is largely remembered in the British imagination, a land of border fences and spying, The Lives of Others and Goodbye Lenin. When the British aren’t comparing everything to Nazi Germany, they occasionally stray out into other historic analogies by comparing things to East Germany, not surprising in a surveillance state such as ours (these rather dubious comparisons obviously intensified under lockdown).
This is no doubt grating to East Germans themselves, but perhaps more grating is the sense of disdain often felt in the western half of Germany; for East Germans, their country simply ceased to exist in 1990 as it was gobbled up by its larger, richer, more glamorous neighbour, and has been regarded as a failure ever since. For that reason, [Katja] Hoyer’s book [Beyond the Wall] is both enjoyable holiday reading and an important historical record for an ageing cohort of people who lived under the old system. To have one’s story told, in a sense, is to avoid annihilation.
Despite the similarities between the two totalitarian systems, East Germany almost defined itself as the anti-fascist state, and its origins lie in a group of communist exiles who fled from Hitler to seek safety in the Soviet Union. Inevitably, their story was almost comically bleak; 17 senior German Marxists in Russia ended up being executed by Stalin, suspected by the paranoid dictator of secretly working for Germany. Even some Jewish communists were accused of spying for the Nazis — which seems to a rational observer unlikely. As Hoyer writes, “More members of the KPD’s executive committee died at Stalin’s hands than at Hitler’s”.
Only two of the nine-strong German politburo survived life in Russia, one of these being Walter Ulbricht, the goatee-bearded veteran of the failed 1919 German revolution and communist party chairman in Berlin in the years before the Nazis came to power.
The war had brutalised the eastern part of Germany far more than the West. It suffered the revenge of the Red Army, including the then largest mass rape in history, and the forced expulsion of millions of Germans from further east (including Hoyer’s grandfather, who had walked from East Prussia). The country was utterly shattered.
From the start the Soviet section had huge disadvantages, not just in terms of raw materials or industry – western Germany has historically always been richer — but in having a patron in Russia. While the Americans boosted their allies through the Marshall Plan, the Soviets continued to plunder Germany; when they learned of uranium in Thuringia they simply turned up and took it, using locals as forced labour.
“In total, 60 per cent of ongoing East German production was taken out of the young state’s efforts to get on its feet between 1945 and 1953,” Hoyer writes: “Yet its people battled on. As early as 1950, the production levels of 1938 had been reached again despite the fact that the GDR had paid three times as much in reparations as its Western counterpart.”
After the war, so-called “Antifa Committees” formed across the Soviet zone, “made up of a wild mix of individuals, among them socialists, communists, liberals, Christians and other opponents of Nazism”. Inevitably, a broad and eclectic left front was taken over by communists who soon crushed all opposition.
And as with many regimes, state oppression grew worse over time. “By May 1953, 66,000 people languished in East German prisons, twice as many as the year before, and a huge figure compared to West Germany’s 40,000. The General Secretary’s revival of the ‘class struggle’, officially announced in the summer of 1952 as part of the state’s ‘building socialism’ programme, had escalated into a struggle against the population, including the working classes.” The party was also becoming dominated by an educated elite, as happened in pretty much all revolutionary regimes.
Protests began at the Stalinallee in Berlin on 16 June 1953, where builders marched towards the House of Ministries and “stood there in their work boots, the dirt and sweat of their labour still on their faces; many held their tools in their hands or slung over their shoulders. There could not have been a more fitting snapshot of what had become of Ulbricht’s dictatorship of the proletariat. The angry crowd chanted, ‘Das hat alles keinen Zweck, der Spitzbart muss weg!’ – ‘No point in reform until Goatee is gone!'”
The 1953 protests were crushed, the workers smeared as fascists, but three years later came Khrushchev’s famous denunciation of Stalin, which caused huge trauma to communists everywhere. “The shaken German delegation went back to their rooms to ponder the implications of what they had just learned.” By breakfast time, “Ulbricht had pulled himself together”, and decreed the new party line. Stalin, it was announced “cannot be counted as a classic of Marxism”.
Fortress Britain with Alice Roberts S01E03
Fortress Britain with Alice Roberts
Published 16 Apr 2023
August 20, 2023
Hitler Has a Bad Day – WW2 – Week 260 – August 19 – 1944
World War Two
Published 19 Aug 2023This week the Allies invade Southern France, and do so very successfully. They’re also successful in the north, closing the Falaise gap and trapping huge numbers of Germans. In the East, however, the Germans manage to stop the Soviet drive on Riga with a counter attack, and in Warsaw they continue to brutally put down the Warsaw Uprising.
(more…)
August 16, 2023
Hitler Youth Murder Canadian Soldiers – War Against Humanity 109
[NR: Between me scheduling this to post and it going live, there’s a strong possibility that YouTube will have retro-actively decided it must be restricted to viewing only on YouTube. My apologies if this is the case when you see this post.]
World War Two
Published 15 Aug 2023In Normandy, the Waffen SS butcher their military and civilian enemies while some Allied soldiers play fast and loose with the laws of the war. In China, hundreds of thousands flee their homes as friend, foe, and famine take their toll. Meanwhile, the spectre of deportation haunts Eastern Europe as Stalin reshapes his new empire.
(more…)
August 13, 2023
Panzer Revenge in Normandy – WW2 – Week 259 – August 12, 1944 (CENSORED)
World War Two
Published 12 Aug 2023The Germans launch a counter-attack to sabotage the Allied positions in France. In the Baltics the Soviet advances grind to a halt, but the Soviets are busy making plans to invade Romania in the south. Meanwhile in the center the Warsaw Uprising continues. Across the world the siege of Hengyang comes to its end with a Japanese victory, but the Battle for Guam ends with a Japanese loss.
[Promoted from the comments]: An increasingly persistent challenge for us at TimeGhost is that a growing number of our videos are being age restricted. While this was always the case with War Against Humanity, it’s started affecting this weekly series now too. This most recent video was restricted before it was even publicly published. As such we made the difficult decision to publish a censored version instead this week.
Why is it such a big issue? Well it doesn’t only limit the access to educational content for young people, but also to adult audiences. Age restricted videos have a barrier to viewing that ranges from territory to territory, with some countries requiring viewers not only to have a YouTube account, but to link it with their credit card. Even if an account belongs to a verified adult, it’s still less likely to be recommended an age restricted video.
Our core mission at TimeGhost is making the lessons of our past free and accessible to people around the world. While it’s challenging, especially with the new obstacles from YouTube, it’s still possible thanks to everyone in the TimeGhost Army who backs these videos. To all of you that signed up, or who watch regularly, thank you for joining us on this mission.
August 11, 2023
Toward a more perfect Homo Sovieticus
Ed West on the interplay between Soviet ideology and Soviet humour during the Cold War:

Krushchev, Brezhnev and other Soviet leaders review the Revolution parade in Red Square, 1962.
LIFE magazine photo by Stan Wayman.
Revolutions go through stages, becoming more violent and extreme, but also less anarchic and more authoritarian. Eventually the revolutionaries mellow, and grow dull. Once in power they become more conservative, almost by definition, and more wedded to a set of sacred beliefs, with the jails soon filling up with people daring to question them.
The Soviet system was based on the idea that humans could be perfected, and because of this they even rejected Mendelian genetics and promoted the scientific fraud Trofim Lysenko; he had hundreds of scientists sent to the Gulag for refusing to conform to scientific orthodoxy. Lysensko once wrote that: “In order to obtain a certain result, you must want to obtain precisely that result; if you want to obtain a certain result, you will obtain it … I need only such people as will obtain the results I need.”
Thanks in part to this scientific socialism, harvests repeatedly failed or disappointed, and in the 1950s they were still smaller than before the war, with livestock counts lower than in 1926.
“What will the harvest of 1964 be like?” the joke went: “Average – worse than 1963 but better than 1965”.
The Russians responded to their brutal and absurd system with a flourishing culture of humour, as Ben Lewis wrote in Hammer and Tickle, but after the death of Stalin the regime grew less oppressive. From 1961, the KGB were instructed not to arrest people for anti-communist activity but instead to have “conversations” with them, so their “wrong evaluations of Soviet society” could be corrected.
Instead, the communists encouraged “positive satire” – jokes that celebrated the Revolution, or that made fun of rustic stupidity. “An old peasant woman is visiting Moscow Zoo, when she sets eyes on a camel for the first time. ‘Oh my God,’ she says, ‘look what the Bolsheviks have done to that horse’.” The approved jokes blamed bad manufacturing on lazy workers, while the underground and popular ones blamed the economic system itself. This official satire was of course nothing of the sort, making fun of the old order and the foolish hicks who still didn’t embrace the Revolution and the future.
Communists likewise set up anti-western “satirical” magazines in Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia and Hungary, where the same form of pseudo-satire could mock the once powerful and say nothing about those now in control.
Indeed in 1956, the East German Central Committee declared that the construction of socialism could “never be a subject for comedy or ridicule” but “the most urgent task of satire in our time is to give Capitalism a defeat without precedent”. That meant exposing “backward thinking … holding on to old ideologies”.
[…]
Leonid Brezhnev had a stroke in 1974 and another in 1976, becoming an empty shell and inspiring the gag: “The government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics has announced with great regret that, following a long illness and without regaining consciousness, the General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party and the President of the highest Soviet, Comrade Leonid Brezhnev, has resumed his government duties.”
Brezhnev was an absurd figure, presiding over a system few still believed in. His jacket was filled with medals – he had 260 awards by the time of his death – and when told that people were joking he was having chest expansion surgery to make room for all the medals he’d awarded himself, he apparently replied: “If they are telling jokes about me, it means they love me.”
August 9, 2023
Russian 1895 Nagant Revolver
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 May 2013One of the mechanically interesting guns that is really widely available in the US for a great price (or was until very recently, it seems) is the Russian M1895 Nagant revolver. It was adopted by the Imperial Russian government in 1895 (replacing the Smith & Wesson No.3 as service revolver), and would serve all the way through World War II in the hands of the Red Army.
As with its other standard-issue arms, the Russian government intended to manufacture the M1895 revolvers domestically. However, when the Nagant was officially adopted the major Russian arsenals were already working at capacity to make the relatively new M1891 rifle, so the first 20,000 revolvers were made by Nagant in Liege, Belgium. In 1898 space had been freed up to start production at the Tula arsenal, where they would be made until 1945 (Ishevsk put the Nagant revolver into production as well during WWII).
The common version available in the US today is a 7-shot, double action revolver chambered for 7.62x38mm. That cartridge is a very long case with the bullet sunk down well below the case mouth. The cylinder of the Nagant cams forward upon firing, allowing the case mount to protrude into the barrel and seal the cylinder gap, thus increasing muzzle velocity slightly. This also allows the Nagant to be used effectively with a suppressor, unlike almost all other revolvers (in which gas leaking from the cylinder gap defeats the purpose of a suppressor).
The Nagant’s 7.62x38mm cartridge pushes a 108 grain jacketed flat-nose projectile at approximately 850 fps (I believe a lighter 85-grain load was also used by the military later, but I haven’t fired any of it), which puts it roughly between .32 ACP and .32-20 ballistics. Not a hand cannon by any stretch, but fairly typical for the era (the 8mm Nambu and 8mm French revolver cartridges were both pretty similar in performance to the 7.62mm Nagant).
As far as being a shooter, the Nagant is mediocre, but reliable. The grip and sights are acceptable (but not great), and the cylinder loads and unloads one round at a time. The low pressure round doesn’t stick in the cylinder, at least. The worst part for a recreational shooter is the trigger, which is very heavy in double action. Single action is also heavy, but very crisp. Recoil is mild, and not uncomfortable at all. The design was simple and effective, and really a good fit for the Red Army and WWII fighting conditions.
August 6, 2023
The Warsaw Uprising Begins! – WW2 – Week 258 – August 5, 1944
World War Two
Published 5 Aug 2023As the Red Army closes in on Warsaw, the Polish Home Army in the city rises up against the German forces. Up in the north the Red Army takes Kaunas. The Allies take Florence in Italy this week, well, half of it, and in France break out of Normandy and into Brittany. The Allies also finally take Myitkyina in Burma after many weeks of siege, and in the Marianas take Tinian and nearly finish taking Guam. And in Finland the President resigns, which could have serious implications for Finland remaining in the war.
(more…)
August 5, 2023
Tempting Armageddon: Soviet vs. NATO Nuclear Strategy
Real Time History
Published 4 Aug 2023Since the inception of the nuclear bomb, military strategists have tried to figure out how to use them best. During the Cold War, this led to two very different doctrines but on both sides of the Iron Curtain the military wasn’t sure if you could actually win Nuclear War.
(more…)
August 4, 2023
Tsar Vlad’s biography
Scott Alexander reviews The Man Without A Face: The Unlikely Rise of Vladimir Putin by Masha Gessen:
Vladimir Putin appeared on Earth fully-formed at the age of nine.
At least this is the opinion of Natalia Gevorkyan, his first authorized biographer. There were plenty of witnesses and records to every post-nine-year-old stage of Putin’s life. Before that, nothing. Gevorkyan thinks he might have been adopted. Putin’s official mother, Maria Putina, was 42 and sickly when he was born. In 1999, a Georgian peasant woman, Vera Putina, claimed to be his real mother, who had given him up for adoption when he was ten. Journalists dutifully investigated and found that a “Vladimir Putin” had been registered at her village’s school, and that a local teacher remembered him as a bright pupil who loved Russian folk tales. What happened to him? Unclear; Artyom Borovik, the investigative journalist pursuing the story, died in a plane crash just before he could publish. Another investigative journalist, Antonio Russo, took up the story, but “his body was found on the edge of a country road … bruised and showed signs of torture, with techniques related to special military services”.
Still, I’m inclined to doubt the adoption theory. Vladimir Putin’s official father, a WWII veteran and factory worker, was also named Vladimir Putin. The adoption story requires that a child named Vladimir Putin was coincidentally adopted by a man also named Vladimir Putin. Far easier to believe that an old Georgian woman had a son who died or was adopted out. Then, when a man with the same name became President of Russia, she assuaged her broken heart by pretending it was the same guy. Records of Putin’s early life are surprisingly sparse. But there are a few photos (admittedly fakeable), and people who aren’t face-blind tell me that Putin looks very much like his official mother.
As for the investigative journalist deaths, it would be more surprising for a Russian investigative journalist of the early 2000s not to die horribly. Both were researching other things about Putin besides his childhood. and had made themselves plenty of enemies. Russo was in Chechnya at the time, another known risk factor for horrible death. I wouldn’t over-update on this.
Still, I found the adoption controversy interesting as a metaphor for everything about Putin. Vladimir Putin really did seem to appear on Earth – or at least in the corridors of power in Russia – fully formed. At each step in his career, he was promoted for no particular reason, or because he seemed so devoid of personality that nobody could imagine him causing trouble. This culminated in his 2000 appointment as Yeltsin’s successor when “The world’s largest landmass, a land of oil, gas, and nuclear arms, had a new leader, and its business and political elites had no idea who he was.”
My source for this quote is The Man Without A Face: The Unlikely Rise Of Vladimir Putin by Masha Gessen, a rare surviving Russian investigative journalist. As always in Dictator Book Club, we’ll go through the story first, then discuss if there are any implications for other countries trying to avoid dictatorship.
July 30, 2023
Bradley Unleashes His Cobra – WW2 – Week 257 – July 29, 1944
World War Two
Published 29 Jul 2023Operation Cobra is the drop that finally opens the floodgates and the Allies make a breakthrough in Normandy; up in the Baltics the Soviets take Shaulyai, Dvinsk, and finally Narva, though their big prize this week is Lvov further south. This happens during the Poles’ Lvov Uprising, which ends badly for the Poles. Things also go badly for the Japanese on Guam, though, as their assault this week devastates their own troops.
(more…)




