[David Cay] Johnston’s piece is titled America should be more like Disneyland but instead of thinking seriously about what this means he fumbles on the 20 yard line and concludes that what makes Disneyland different is… happy thoughts. If only we were more like W.D., he says, “we could make America into a happy place.”
No, what makes Disney invest in infrastructure is not happy thoughts. Johnston is in fact clear about this:
The Walt Disney Co. invests in infrastructure because it makes the company money.
The problem with America is that our public infrastructure has been turned over to a fickle political process that is not governed by a rational calculation of cost and benefit, market test and experimentation but by a pursuit of power, glory and advantage that only rarely coincides with the public interest.
America should be more like Disneyland and to do that we need to develop institutions that allow more infrastructure to built by the private sector. Most ambitiously we need more cities as hotels, more proprietary cities. As Rajagopolan and I wrote in our study of India (in Cities and Private Planning):
The lesson of Gurgaon, Walt Disney World, and Jamshedpur is that a system of proprietary, competitive cities can combine the initiative and drive of private development with the planning and foresight characteristic of the best urban planning. A proprietary city will build infrastructure to attract residents and revenues. A handful of proprietary cities built within a single region will create a competitive system of proprietary cities that build, compete, innovate, and experiment.
Alex Tabarrok “How to make America more like Disneyland”, Marginal Revolution, 2014-12-17.
March 25, 2016
QotD: The infrastructure problem in America
September 26, 2015
The LCBO backs away from auctioning rare wines in Ontario
Rick Van Sickle on the LCBO’s recent decision to hand over the rare wine auction market to a private auctioneer:
Quietly last week, Ontario’s booze monopoly finally threw in the towel over its glitzy rare and fine wine auctions and awarded the contract to an independent auction house — another case of letting private industry do a job that the LCBO couldn’t handle.
Canadian auction house Waddington’s will now conduct the auctions under a special licence through the LCBO.
The company added a new addition to their portfolio of fine art and luxury goods – Waddington’s Fine Wine and Spirits Auctions. “Ontario wine enthusiasts will now be able to better manage their cellars of fine wines and spirits with this connection to the enormous world wine market,” said Waddington’s President Duncan McLean.
The Toronto-based, Canadian-owned auction company was awarded the exclusive contract to provide fine wine and spirit auction services in Ontario under the authority of the LCBO, a first for an Ontario auction company. Waddington’s conducted the LCBO’s Vintages Fine Wine and Spirits auctions from 2009 until 2013.
The inaugural live fine wine auction will be conducted Dec. 12 at Waddington’s Toronto gallery, and an online fine wine auction will be offered Nov. 23-26. These auctions launch what will be a regular schedule of wine and spirits auctions and events for which Waddington’s is currently accepting consignments. All wines consigned are stored in a secure, temperature, light, and humidity-controlled wine vault.
August 27, 2015
Incentives matter … but in a perverse manner for public employees
On the Property and Environmental Research Center website, Warren Meyer explains why the US Forest Service is cutting ties with private organizations that have been running federally owned facilities for less than the Forest Service is able to do … despite the private company’s proven higher levels of service:
Private concessionaires pay all operations costs out of the entrance fees paid by the public — and without further taxpayer subsidies. In addition, the concessionaire pays the public agency a concession fee. The resulting savings to taxpayers can be quite compelling. In a recent PERC case study, I showed how a parks agency had to supplement every dollar in visitor fees with an equal amount of tax dollars to keep a park open. By privatizing the park’s operations, the need for tax revenues could be eliminated. And in fact, the park could be turned into a money maker for the agency.
While this may resonate with the public, it’s a hard sell to the agencies themselves. The National Park Service uses concessionaires to provide some visitor services, but it has not considered private operation of entire parks. Even the Forest Service — which does allow some private park management — often seems eager to go back to running the parks themselves.
[…]
No private company would behave like this. So why does the government? Over the years, I have observed three possible explanations:
1. Government employees have incentives that go beyond “public service.” For most agency managers, their pay and prestige and future job prospects are tied to the size of their agency’s headcount and budget. Privatization savings that look like a boon to taxpayers may look like a demotion to agency managers.
2. People who are skeptical of private enterprise and more confident in government-led solutions tend to self-select for government jobs. Even in the Forest Service, concessionaires frequently experience outright hostility from the agency’s rank and file. “It’s wrong to make a profit on public lands” is one common statement.
3. Government accounting is not set up to make these sorts of decisions well. Few agencies have reports that tell them whether an individual park’s revenues are covering its full operational costs. Costs can be spread over multiple budgets, making it seem as though public park operation is less expensive than it really is.
To overcome these obstacles, we’ve learned that progress generally has to start above the agency. Some sort of legislative push is necessary. And we try to find ways to pitch our solutions as a way for agencies to free up money to address other problems, such as fixing rotting infrastructure.
July 26, 2015
Colonize the moon … now 90% off!
In Popular Science, Sarah Fecht dangles the tantalizing prospect that we may be over-estimating the costs of colonizing the Moon by a huge margin:
Only 12 people have walked on the moon, and we haven’t been back since 1972. But a new NASA-commission study has found that we can now afford to set up a permanent base on the moon, by mining for lunar resources and partnering with private companies.
Returning humans to the moon could cost 90 percent less than expected, bringing estimated costs down from $100 billion to $10 billion. That’s something that NASA could afford on its current deep space human spaceflight budget.
“A factor of ten reduction in cost changes everything,” said Mark Hopkins, executive committee chair of the National Space Society, in a press release.
The study, released today, was conducted by the National Space Society and the Space Frontier Foundation — two non-profit organizations that advocate building human settlements beyond Earth — and it was reviewed by an independent team of former NASA executives, astronauts, and space policy experts.
To dramatically reduce costs, NASA would have to take advantage of private and international partnerships — perhaps one of which would be the European Space Agency, whose director recently announced that he wants to build a town on the moon. The new estimates also assume that Boeing and SpaceX, NASA’s commercial crew partners, will be involved and competing for contracts. SpaceX famously spent just $443 million developing its Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon crew capsule, where NASA would have spent $4 billion. The authors of the new report are hoping that 89 percent discount will extend beyond low Earth orbit as well.
Similar to SpaceX’s goals of creating a reusable rocket, the plan also relies on the development of reusable spacecraft and lunar landers to reduce costs.
Plus, mining fuel from the lunar surface could make going back to the moon economically viable. Data from the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) suggest that water ice may be plentiful on the moon, especially near the poles. That’s important because water can be broken down into hydrogen propellant for rockets (and, conveniently, oxygen for humans to breathe).
May 14, 2015
Solving the Amtrak problem requires thinking outside the box … really outside
At The Federalist, Sean Davis explains why throwing more taxpayer money at Amtrak isn’t going to do much good:
“Amtrak doesn’t get enough government money,” is the kind of thing someone says when that person doesn’t understand anything about Amtrak, or government, or money.
Created by Congress in 1970, Amtrak was meant to replace the private rail companies that, according to Amtrak, “had operated services at a net loss of millions of dollars for many years.” Net losses of millions of dollars, you say? According to its unaudited financial statements, Amtrak lost over a billion dollars in 2014, the last year for which annual revenue and expense data are available.
Amtrak lost nearly $1.3 billion in 2013. Since its creation, Amtrak has racked up over $31 billion in accumulated losses. And every penny of those losses has been covered by federal taxpayers.
Amtrak has a lot of problems. A lack of taxpayer generosity is not one of them, not even close. The key to fixing Amtrak, to making it function as a “for-profit corporation,” which is how the Federal Railroad Administration, Amtrak’s overseer, officially describes the passenger rail organization, is not increasing the volume of federal cash it sucks up every year. The solution is not to reform this and that to make the government-owned company work better or more efficiently. And selling off its assets to the highest bidder won’t fix Amtrak, either.
No, the key to fixing Amtrak is to just give it away. Hand over the entire enterprise to whichever rail company wants it. “But that’s crazy!” you might say. “Giving it away for free makes no cents!”
January 22, 2015
Rumours of privatization in Ontario’s liquor control monopoly?
In the latest issue of Michael Pinkus Wine Review, Michael talks about the hints and portents (dealing with the Ontario government requires a certain amount of Kremlinological observation skills) that a tiny measure of privatization may be coming:
There’s a rumour in the wind that a certain amount of privatization is coming to Ontario (wouldn’t that be nice), but I wouldn’t get my hopes up about it just yet – no time line has been given and I am sure that ‘more study’ is necessary … and of course, if track record is any indication, this government will find some way to either screw it up or make it such a complicated piece of legislation that it’ll take years to get through all the red tape behind it. I once heard Jerry Agar, of NewsTalk 1010 fame, say (and I’m paraphrasing here) ‘if you want something screwed up get government involved’; he’s a proponent of the private sector because they can do it more efficiently than government if only ‘the man’ would just get outta the way … I would have to agree with him here. So far the government has made a mess of our liquor system that even repressed, despotic and 3rd world countries have better access to alcohol then we do.
Sadly, I believe it might be too little too late for some of Ontario wineries who have suffered this long, but might not be around to see the light at the end of the tunnel (if and/or when it comes). Yes, this might be the end of the line for a number of our precious wineries and we only have ourselves to blame for their demise. They have been as vocal as any sector, crying for help, not necessarily a hand out (which the grape growers seem to get) as much as a hand up – basically they’ve been pleading with each government: “please give us access to (our own) market (at the very least) and we’ll show you what we can do”, all to no avail.
Why the pessimistic attitude? Let’s look at the facts. It takes some rather deep pockets to own a winery in Ontario, that or a good credit rating, because money is the number one thing required to open the doors. But making it is more of an uphill battles then in any other business I this province. Post-1993, when the majority of the wineries around today opened their doors, your cellar door is the only place you can sell your wine – sure you could tap into the LCBO and the restaurant market, but that’s it. And although recent federal regulations have been lifted regarding the selling and especially shipping of wine across the country, many provinces have yet to enact their own legislation governing the practice, hence leaving the entire topic, not to mention hundreds of wineries, in limbo, unable to tap the rest of the country as a market for fear of breaking the law. With so few avenues to sell home-grown wine the government has basically handcuffed the industry – let alone the number of asinine rules that govern the industry from within (more on that next time) – it has all been put in place it would seem, so that wineries are destined to fail; that they remain open is a testament to their resolve and passion.
August 20, 2014
New report calls for Ontario to break up the LCBO
In the Toronto Star, Richard Brennan reports on a new study by the C.D. Howe Institute calling for the province to join the modern era:
The “quasi-monopoly” LCBO and The Beer Store have hosed Ontario consumers long enough, a C.D. Howe Institute report says.
The right-wing think tank said the Ontario government should strip them both of their almost exclusive right to sell beer, wine and spirits, suggesting the report proves that opening up to alcohol sales to competition will mean lower prices.
“The lack of competition in Ontario’s system for alcoholic beverage retailing causes higher prices for consumers and foregone government revenue,” states the 30-page report, Uncorking a Strange Brew: The Need for More Competition in Ontario’s Alcoholic Beverage Retailing System, to be released publicly Wednesday.
The report includes tables comparing Ontario beer prices to other provinces with greater private sector involvement, particularly with Quebec, where a case of 24 domestic beers can be as much as $10 cheaper and even more for imported brands.
Since 1927, when the Liquor Control Act was passed, the Liquor Control Board of Ontario and the privately owned Brewers Warehousing Company Limited have had a stranglehold on alcohol sale in the province.
“The Beer Store’s quasi-monopoly of beer retailing is … an anachronism,” the report says, referring to the foreign-owned private retailer that is protected by provincial legislation.
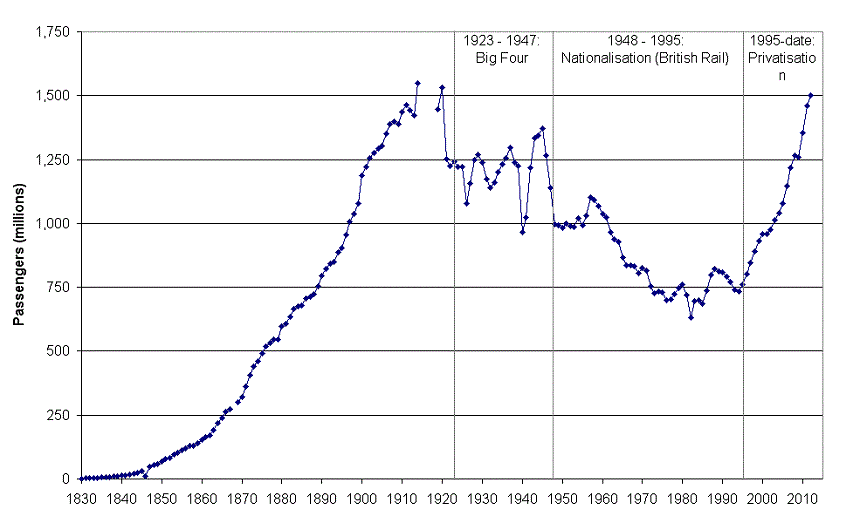
Britain’s railway system under private and public ownership
At the Adam Smith Institute blog, Ben Southwood asks the question “What would we consider a successful railway system?”
Under many measures, the railways have performed remarkably since privatisation. It is not surprising that the British public would nevertheless like to renationalise them, given how ignorant we know they are, but it’s at least slightly surprising that large sections of the intelligentsia seem to agree.
Last year I wrote a very short piece on the issue, pointing out the basic facts: the UK has had two eras of private railways, both extremely successful, and a long period of extremely unsuccessful state control. Franchising probably isn’t the ideal way of running the rail system privately, but it seems like even a relatively bad private system outperforms the state.
Short history: approximately free market in rail until 1913, built mainly with private capital. Government control/direction during the war. Government decides the railways aren’t making enough profit in 1923 and reorganises them into bigger regional monopolies. These aren’t very successful (in a very difficult macro environment) so it nationalises them — along with everything else — in the late 1940s.
By the 1960s the government runs railways into the ground to the point it essentially needs to destroy or mothball half the network. Government re-privatises the railways in 1995 — at this point passenger journeys have reached half the level they were at in 1913. Within 15 years they’ve made back the ground lost in the previous eighty.
May 29, 2014
The “Pairs Perfectly” campaign
Just as the Ontario election writ was dropped, the small wineries of Ontario started pushing the Pairs Perfectly campaign, to move the province toward a more mature wine retailing model (like British Columbia’s). While I’d prefer a full privatization model (like Alberta’s), at least the move to allowing some private wine stores would be an improvement. Despite the quick work to launch the campaign, Michael Pinkus says it’s already being forgotten on the hustings:
Ontario is deep into an election campaign and the best thing done so far is a little initiative from the Wine Council called “Pairs Perfectly”. They’ve backed it with radio and television promos and in truth they make a lot of sense. Ontario is one of the only provinces not to have some sort of private system in place, either along with their provincial monopoly (a la British Columbia) or fully privatized (a la Alberta). This initiative seemed to be already formed and waiting in the wings: no sooner had an election been called than the “Pairs Perfectly” slogan was in my inbox (with its twitter handle @PairsPerfectly, hashtag #PairsPerfectly and website PairsPerfectly.com), articles were written to explain the notion, social media seemed abuzz from wineries to writers to the average-Joe, all were tweeting, re-tweeting, blogging, tumbling, gramming, hooting, hollering, casting, accosting and I initially thought, “Wow, the buzz is really out there, this just might have legs, or at least more legs that that ‘My Wine Shop’ that seemed to go nowhere.”
But 6 weeks is a long time in the political realm, just ask Rob Ford, so much can happen over the course of 6 weeks that can turn the tide on a well-thought-out, well-organized plan of attack. Instead of the Ontario booze media jumping whole hog onto the initiative and writing piece after piece after piece about the benefits of privatization to keep the idea in our collective consciousness, a new issue has come along to polarize: the VQA, which I have repeatedly said is a sham of a system, most notably because of its tasting panel. Now there’s a new horse to ride, a newer and shinier issue to get all worked up about. The VQA is easy pickings because it is so wrong, crushes creativity and stymies’ our winemakers making them think “will this pass VQA”. Every winery has come into conflict with it at least once in its existence and it needs an overhaul (radical? Maybe not, but definitely a big tweak).
[…]
I believe this: Ontario is a mess and is destined to remain that way long after this election season has been put to bed. We already know the Liberals position on privatization of any sort (over their dead body); the NDP seem in lockstep with the Liberals train of thought because it would disrupt union jobs. And the Conservatives, before the campaign the only party willing to talk privatization, have somehow gone mute about the whole issue – as if someone told them not to rock the boat; which makes them the wild card. But if history shows us anything it’s doubtful it’ll get past committee if it ever does come up.
And don’t even get me started on the asinine things happening on the beer side of the ledger. The Beer Store’s cockamamie campaign against corner stores carrying the product that they have a duopoly to sell (with the LCBO), is as misguided and ill-conceived as any I can think of. Does beer not also get sold in corner stores in other provinces? Are all those owners corrupt-minor-sellers? It seems to have galvanized the public against them; especially when people find out they aren’t government controlled; which a vast majority of the province was under the false notion it was. This also took focus away from the larger issue of an open and freer market for all in the alcohol industry (craft brewers, craft winemakers, etc.)
March 25, 2014
BBC to be (effectively) privatized in proposed new legislation
British TV viewers are required to pay a regular license fee (which funds the BBC) or they can be prosecuted. The British government may be on the verge of changing this:
Budgets come and go, but something more far-reaching will take place in the House of Commons today; something that might change our political discourse significantly, benignly and permanently.
The Government has indicated that it will back a Bill, brought in by the backbench MP, Andrew Bridgen, to decriminalise non-payment of the Television Licence Fee. Instead of being dragged through the courts, defaulters will simply have their access to the BBC switched off — in the same way that Sky withdraws its services from those who don’t pay their subscriptions.
The practical case for the measure is unarguable. The BBC’s privileged legal position is silting up our criminal justice system. A ridiculous 180,000 people face prosecution every year over non-payment. Under the new regime, they will instead be in the position people who don’t cough up for their gas or electricity bills. A great deal of time and money will be saved.
But the real significance of the proposal is that it will, in practice, remove the BBC’s monopoly. If the penalty for non-payment of the licence fee is withdrawal of the service, rather than prosecution, then that fee ceases to be a tax and becomes a subscription. Refusal to pay is no longer a criminal act, but an exercise of consumer choice. The BBC will become, in practice, a pay-on-demand service like its rivals.
February 12, 2014
The Beer Store’s pre-emptive strike against a competitive market in Ontario
Yesterday I got a robo-call from someone representing The Beer Store (what used to be known as the Brewer’s Retail … for my American readers, think of your local DMV crossed with a Cold War-era Soviet department store). The call was to alert me to the possibility that the Ontario government might do something to destroy the worker’s paradise we live in today and allow the total anarchy of private sales of beer, wine, and liquor. I was invited to take part in some sort of “town hall” meeting where all the interested parties would be represented … if you consider only those who are afraid of this change being introduced as being all of the interested parties.
As we all know, the Ontario government isn’t comfortable with the idea of letting go of their own vast-profit-generating booze sales machine (the LCBO), and I doubt that the current Premier and her party are actually going to break the foreign-owned oligopoly that currently controls the sale of beer in the province. In spite of that, the Beer Store and their “stakeholders” are mounting a rather hysterical counter-offensive to preserve the current status quo. As Colby Cosh points out, their success or failure will probably hinge on keeping Ontarians innocent of how a non-monopolized market works in other jurisdictions … particularly in Alberta:
It is encouraging to see so much ridicule being flung at the Beer Store’s “study” defending its role in the Soviet-flavoured Ontario liquor retailing system. The effectiveness of the Beer Store’s white paper depends on its Ontario audience knowing no practical details of freer retail schemes, particularly Alberta’s: yet, by an amusing paradox, the ur-source for the report appears to be Alberta. No one was willing to attach his name to the report itself, but it comes with a foreword by the Parkland Institute’s Greg Flanagan, who deems it a “valuable contribution”—one that, on an unrelated note, makes heavy use of Flanagan’s own past polemics against liquor privatization. What a terrible shame nobody took credit for this excellent document!
What Colby is missing is that Ontario is a unique, precious snowflake of a province, whose residents are unable to handle this so-called “freedom of choice”. Our loving government is protecting our vulnerable, weak-willed selves from the evils of a callous, uncaring, exploitative sector of the economy that ruthlessly wants to sell us more of their intoxicating poisons at lower prices. This is why we must stand firm against “free markets” and rally our shrinking moral forces!
He even admits that the destruction of Alberta’s proud, noble, and much-loved liquor monopoly has brought untold misery and ruin to literally tens, possibly even hundreds, of Albertans:
The effect of liquor-retail privatization in Alberta was to put liquor stores in many small towns that did not have them before and on darn near every block in the big cities. Most, by design, are small stores with large markups. Before privatization you had a handful of stores in the entire province, all offering strongly regulated uniform prices. But you might have to travel a long way to get the advantage of these prices; you might have to leave work early to show up before closing, particularly if you intended to load up for a weekend or a party; and you might have to stand in a queue when you arrived. (Ah, memories.) And if you didn’t compute your needs accurately and you ran out of booze at the wrong moment, you were out of luck.
After privatization, there are stores everywhere, open all the time, on every day but Christmas; and you might be charged an extra buck on a 12-pack. Go on: ask 10 Albertans who are old enough to remember the old system if they would like to go back. I’ve actually performed this exercise, and I usually get ten “hell no”s. But if you make your sample a hundred, you will certainly find a person or two in one of two categories: (1) socialists nostalgic for the days when ALCB employees were duly organized, and could shut down all liquor sales in the province by striking; (2) geriatric grouches who really don’t enjoy alcohol and don’t like its ready availability and what’s with those goddamn kids these days with the reefer and the XBox and the hey hey hey.
See? He even admits that prices went up! Proof that market failure is smeared all over Alberta! And queues are a good thing: they allow you to meet your neighbours and have long, pleasant conversations about all kinds of things! Albertans have been wantonly deprived of this wonderful balm of human contact and interaction!
No, Ontarians are not ready — and may never be ready — for the additional burden of free choice and wider selections at lower prices. We must set our hearts and minds to work against this tradition-destroying innovation and keep our booze prices high and variety minimal!
September 26, 2013
Crony Capitalism and prison privatization
I’m generally in favour of moving economic activities out of the government sphere and into the competitive marketplace, but the privatization of prisons is a great example not of free enterprise but of crony capitalism run amok:
Private prisons are antithetical to a free people. Of all the functions a civilized society should relegate to the public sector, it’s abundantly clear incarceration should be at the very top of the list. Jailing individuals is a public cost that a society takes on in order to ensure there are consequences to breaking certain rules that have been deemed dangerous to the happiness and quality of life within a given population. However, the end goal of any civilized culture must be to try to keep these cost as low possible. This should be achieved by having as few people as possible incarcerated, which is most optimally achieved by reducing incidents of criminality within the population. Given incarceration is an undesirable (albeit necessary) part of any society, the idea is certainly not to incentivize increased incarceration by making it extremely profitable. This is a perverse incentive, and one that is strongly encouraged by the private prison industry to the detriment of society.
[…]
In the Public Interest describes itself as:
A comprehensive resource center on privatization and responsible contracting. It is committed to equipping citizens, public officials, advocacy groups, and researchers with the information, ideas, and other resources they need to ensure that public contracts with private entities are transparent, fair, well-managed, and effectively monitored, and that those contracts meet the long-term needs of communities.
Their report explains how private prison companies insist that states embed “occupancy guarantees” into their contracts with the public sector. They estimate that at least 65% of all private prison contracts have such guarantees, and in some states, like Arizona, the guarantee is a shockingly high 100%. This leads to overcrowding in many instances, and sometimes violent offenders are placed in prisons set up for nonviolent offenses just to fill the quotas. In the event that the beds can’t be filled, the taxpayer makes up the difference to the private prison company. They win no matter what. It’s just more crony capitalism. Below are some highlights from this excellent report.
Major Findings
- 65 percent of the private prison contracts ITPI received and analyzed included occupancy guarantees in the form of quotas or required payments for empty prison cells (a “low-crime tax”). These quotas and low-crime taxes put taxpayers on the hook for guaranteeing profits for private prison corporations.
- Occupancy guarantee clauses in private prison contracts range between 80% and 100%, with 90% as the most frequent occupancy guarantee requirement.
- Arizona, Louisiana, Oklahoma and Virginia are locked in contracts with the highest occupancy guarantee requirements, with all quotas requiring between 95% and 100% occupancy.
Update: On the topic of prison abuse, there’s an interesting post at Reason talking about the hidden-yet-pervasive practice of locking up children in solitary confinement “for their own protection”:
Solitary confinement was once a punishment reserved for the most-hardened, incorrigible criminals. Today, it is standard practice for tens of thousands of juveniles in prisons and jails across America. Far from being limited to the most violent offenders, solitary confinement is now used against perpetrators of minor crimes and children who are forced to await their trials in total isolation. Often, these stays are prolonged, lasting months or even years at a time.
Widely condemned as cruel and unusual punishment, long-term isolation for juveniles continues because it’s effectively hidden from the public. Research efforts by the American Civil Liberties Union and the Texas Criminal Justice Coalition have struggled to uncover even the most basic facts about how the United States punishes its most vulnerable inmates.
How can a practice be both widespread and hidden? State and federal governments have two effective ways to prevent the public from knowing how deep the problem goes.
The first has to do with the way prisons operate. Sealed off from most public scrutiny, and steeped in an insular culture of unaccountability, prisons are, by their very nature, excellent places to keep secrets. Even more concealed are the solitary-confinement cells, described by inmates as “prisons within prisons.” With loose record-keeping and different standards used by different states, it’s almost impossible to gather reliable nation-wide statistics.
The second method is to give the old, horrific punishment a new, unobjectionable name. Make the torture sound friendly, with fewer syllables and pleasant language. This way, even when abuse is discovered, it appears well-intentioned and humane.
So American prisons rarely punish children with prolonged solitary confinement. Instead, they administer seclusion and protective custody. Prison authorities don’t have to admit that “administrative segregation” is used to discipline children. Just the opposite, actually. It’s all being done “for their own protection.”
September 11, 2013
L.Neil Smith responds to Allison Benedikt’s “manifesto”
In the latest Libertarian Enterprise, L. Neil Smith calls for “Public schools delenda est” in response to Benedikt’s paean to the glories of government-run schools:
Which brings us to the subject of today’s diatribe, an article I was directed to (hat-tip to Tatiana Covington) on Slate.com, awkwardly entitled, “If You Send Your Kid to Private School, You Are a Bad Person — A Manifesto”. This unintelligent but very revealing piece, posted Thursday, August 29, 2013, was written by somebody called Allison Benedikt, who slings a keyboard like some breathless high school cheerleader, but is apparently a movie critic for the Chicago Tribune.
As Joe-Bob would say, check it out.
What this little death-dealer proposes — “demands” would be more accurate — is that all private schools be outlawed (whoops there go the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Tenth Amendments) and everybody forced to send their children to, and participate in the public school system. (Later in the essay she denies wanting to outlaw private schools, but, as we all know, consistency is the hobgoblin of small minds.)
This is, given the unignorable temper and tendency of our times, exactly like seeing the private structure of the Internet demolished, and then being compelled at bayonet-point (Why is it that liberals never seem to remember that the law, no matter how noble it may sound or high-minded its intentions, consists of nothing but brute force: guns, clubs, noxious sprays, and tasers?) to go back to the United States Postal System or the good old mercantilist Bell Telephone monopoly.
“Progressives”? I call them regressives.
What’s more, she issues this bizarre edict — which she labels a “manifesto” — not for the sake of your children, nor even for their children down the road. In words straight from an Ayn Rand villain’s mouth (what critic says real people don’t talk like this?), she says this: “Your children and grandchildren might get mediocre educations in the meantime, but it will be worth it, for the eventual common good.”
Yes, she openly admits that your progeny will probably suffer, educationally (and no doubt otherwise — look at the extracurricular activities she admits to), as a result of being forced back into the public system as it exists and operates today. she waxes positively lyrical over the egalitarian ecstasy of attending school with individuals more likely to knife somebody for a pair of shoes than she is.
She keeps congratulating herself on how well she turned out, even as she almost brags at how badly educated she is — and demonstrates it with her writing. Would she brag if she knew she’s an enabler of democide?
May 9, 2013
Let ’em strike!
We’re in the final week before the LCBO is threatening a strike. Michael Pinkus suggests we should let ’em walk:
For the third time in a decade the LCBO is holding Ontario hostage — and just like they did in 2005 and 2009 when the threat of a strike was on the table, they’ll be an 11th hour (more like on the 11th hour and 59 minute mark) resolution where the LCBO employees get everything they want because the province does not want to lose the revenue the LCBO brings into the province. Screw the teachers, they take money out of the system, but the LCBO brings it in, so they should get whatever they ask for, right? It’s the approach taken by every government who has “stared down” the LCBO, and lost. Not that I’m necessarily for the teachers, but if it’s a choice between educating our youth or feeding our appetite for liquor I know which side I fall on … and so would any right minded Ontarian — it’s the booze that wins out every time.
And just like in 2005 and 2009 the LCBO will make a ton of money in the days before the “strike”. It’ll be a feeding frenzy of mammoth proportions in the aisles, right up to the last hour. Shelves will be decimated as people stock up for what surely will be touted as long, drawn out labour strife … that’ll never come. And why do I say that? Because any right thinking Ontarian knows that if the LCBO goes on strike it means more than loss of revenue to the province, or an inability to get out of country booze … it means the end of the LCBO (and everyone involved knows that).
Take a peak around us privatization is today’s buzz-word and it’s all around us. In our own country, to the south, in Europe — at corner stores, in supermarkets and in specialty stores … heck even Pennsylvania is getting into the act of loosening their liquor laws (and nobody thought that day would come) — but not here in NO-FUN-Tario, a have not province … we sit under the rules and thumb of the Liquor Control Board. If they go on strike questions will be raised as to why we have a provincially run system, why we support unionized workers, or why we can’t be more liberal with our booze (plus you just know some idiot will want to declare it an essential service). So it does not behoove the LCBO to walk off the job and the government won’t allow it because they’ll be tough questions to answer. So don’t go betting the farm on a labour dispute and seeing picket sign toting employees at the local Board store — this one will end like all the others, with the LCBO threatening to walk out, a mass throng of buyers the day before, and the sun rising to a new dawn the next day with a new deal for LCBO employees … and all will be right in Ontario for another 4 years … when we’ll do it all again.
Update: A report in the Toronto Star claims that Ontario could earn a $1 billion windfall by allowing private liquor stores into the province:
“If the Ontario liquor industry mirrored ours in B.C., instead of $1.6 billion going to government, that number could be around $2.7 billion,” he states in his 15-page speech, which highlights the pluses for locally produced wines, beers and spirits.
With 635 stores and 219 convenience store locations in rural and northern Ontario, the LCBO last year reported net sales of $4.71 billion — up $218 million — and handed over to the Ontario treasury an all-time high of $1.63 billion, not including taxes.
“If Ontario allowed private liquor stores, consumers would have access to hundreds of new VQA wines, craft beers and spirits.”
His comments come at a time when the LCBO plans to spend $100 million on expansion, including express outlets in 10 large grocery stores and expanded VQA sales, and while Tory Leader Tim Hudak calls for the booze monopoly to be privatized and for beer and wine to be sold in corner stores.
“A bit of competition makes the world go round . . . I think now that we are (in) 2013 it’s time for some change,” Hudak told reporters at Queen’s Park.
B.C. has had a mix of private and public liquor stores “to create better choices for producers to sell and for consumers to buy,” Baillie said.
Ontario currently does allow a tiny number of private wine stores to operate, but under incredibly restrictive conditions. For one thing, they’re only allowed to be located in areas the LCBO has determined are “underserved”, they may only sell wine from a single winery or winery group, and the number of stores is limited to the licenses that were granted to certain wineries before 1993.
Oh, and the kicker to all those restriction? If you manage to put in a store in an “underserved” area and make a profit? The LCBO can then turn around and re-designate your area to invalidate your license or place one of their own stores in the area and take away the business you’ve built up. Catch-22.
April 16, 2013
The anti-libertarian legacy of Margaret Thatcher
Sean Gabb explains why Thatcher should not be considered in any way “libertarian”:
She started the transformation of this country into a politically correct police state. Her Government behaved with an almost gloating disregard for constitutional norms. She brought in money laundering laws that have now been extended to a general supervision over our financial dealings. She relaxed the conditions for searches and seizure by the police. She increased the numbers and powers of the police. She weakened trial by jury. She weakened the due process protections of the accused. She gave executive agencies the power to fine and punish without due process. She began the first steps towards total criminalisation of gun possession.
She did not cut government spending. Instead, she allowed the conversion of local government and the lower administration into a system of sinecures for the Enemy Class. She allowed political correctness to take hold in local government. When she did oppose this, it involved giving central government powers of supervision and control useful to a future politically correct government. She extended and tightened the laws constraining free speech about race and immigration.
Her encouragement of enterprise never amounted to more than a liking for big business corporatism. Genuine enterprise was progressively heaped with taxes and regulations that made it hard to do business. Big business, on the other hand, was showered with praise and legal indulgences. Indeed, her privatisation policies were less about introducing competition and choice into public services than in turning public monopolies into corporate monsters pampered by the State with subsidies and favourable regulations — corporate monsters that were expected in return to lavish financial rewards on the political class.