“An Army marches on its stomach.” — Napoleon
As we take our own little march down memory lane, let me state up front that I can’t stomach applesauce, just can’t. I liked it as a kid but now it has less appeal than the prospect of being duct taped to a chair, face down, in prison. Yeah, I hate it.
This may seem unreasonable, but anyone who was in at the time, at least in the Army or Marines, and some portion thereof that actually went to the field a lot, will probably remember the Great Applesauce Blight of 1977 and 1978, which was the reason I can’t stand the crap.
The “Great Applesauce Blight?” you ask. Oh, yeah.
The story I got, after some years and some digging, goes like this: It seems that sometime in the late 1960s or early 1970s, a fruit company – the Monterey Fruit Company, so it was said – was going out of business. So the Monterey Fruit Company, if that’s who it really was, called the Department of Defense and said, “Boys, have we got a deal for you. Hundreds upon hundreds of tons of Grade A applesauce, and you can have it. All of it. Cheap.”
McNamara and his Whiz Kids – neither of them ever sufficiently to be damned, of course – were gone, but their spirits remained. Department of Defense, ever conscious of the value of a well-squeezed penny, bought that inventory of applesauce, and began to put it into the old style, canned, MCI; Meal, Combat, Individual, which is to say, “C-rations”.
C Rations of the day were entirely canned and composed of a main meal, for one meal, plus either a cake (or very rarely, canned bread) or fruit of some kind, usually a small tin of peanut butter or cheese of some kind of jam or jelly, and one or another type of B Unit, which would have some variant of crackers plus either candy or cocoa. Sometimes, as with the B-2 unit, the cheese was in those.
Now, perusing a case of 1978 C-rats, which would have been newer than those of the Great Applesauce Blight, but still broadly similar, one notes that there were twelve menus, twelve different main meals, and 12 different kinds of dessert, a sundry pack, plus variable candies, spreads, etc. Of that latter twelve, eight were fruit and four were cake of some kind. I seem to recall that, possibly for reasons of economy, the amount of fruit during the Great Applesauce Blight had gone up to usually ten cans out of twelve, some extra cheese or peanut butter seemed to be included with some, and the cakes went down to two, one of which was going to be Chocolate Nut Roll, essentially inedible, from the Nashville Bread Company and the other would be the even more thoroughly disgusting fruit cake. I don’t recall who made that, and that lack of memory may have been an automatic defense against a future charge of capital murder. None of the cakes except pound cake could be relied on to be edible, and pound cake was always rare.
Now picture this, you’re a soldier in the Panama Canal Zone, training – training hard – to fight for the Canal, living in the jungle maybe twenty-five or more days and nights a month, eating C-rats to the tune of sixty or seventy a month, and virtually every meal contains applesauce or something more innately disgusting. “No, none of that nice fruit cocktail or those ever so delectable pear slices for you, young man; Department of Defense, to save a few bucks, has determined that applesauce is good enough, three meals a day, for weeks on end.”
*****
Now we were already kind of thin, because no military feeding system can ever completely keep up with the caloric requirements for a soldier either continuously fighting or realistically training to fight. Normally, this isn’t a problem because he can pack it on in the mess hall. These were unusual circumstances, though, with an unusually high chance of fighting – or riot control, which is worse – over the Canal. So we’re pretty much living out there, in pretty much trackless jungle, with nothing like enough helicopters for regular hot rations from the mess. Besides that, the old 193rd Infantry Brigade, in the Panama Canal Zone, was unusual in that it made a very serious effort to train even the cooks to fight, which takes time, too. C’s are pretty much it.
Even so, thin and hungry or not, after a month or two we could not eat the applesauce. That was probably seven or eight hundred calories a days that just got tossed.
We began going from thin to frigging emaciated.
*****
When I think upon the Great Applesauce Blight, though, I do not think about hardship or hunger. No, I think – as we old farts are wont to – about happier aspects of it.
Now this is no shit:
There we were, the heavy mortar platoon of 4th Battalion, 10th Infantry, stuck on top of a non-descript hill somewhere southwest of Gamboa, Canal Zone.
PFC McBrayer had a birthday out there in the jungle. I think it was his nineteenth birthday. None of us had been able to do any shopping, so we were all just stuck for getting him a birthday present. “I’m not giving up my pet scorpion,” said Big Al, who in fact, had a pet scorpion for the mega-ant versus scorpion gladiatorial combats we used to stage. “I’d offer to give him some of my crotch rot,” said Art, “but I think he already has some of his own.” “Howler monkey?” “Who’s going to catch it? And those suckers are mean, too.” “How about a sloth? They’re easy to catch.” “If the Lord God didn’t see fit to give B’rer Sloth an asshole, I don’t see why we should add to his troubles by catching him and wrapping him as a present.” Finally someone, I don’t think it was me, might have been Sergeant Sais, said, “Gentlemen, there can be only one proper gift under the circumstances,” and then he held up a – you guessed it – can of applesauce.
So we stuck nineteen or twenty Canal Zone Matches in a Nashville Bread Company Chocolate Butt Roll, invited McBrayer over, torched off the matches, sang Happy Birthday, then presented him his can of applesauce.
He was touched; you could see that. As he dashed tears from his eyes while making his, “Gee, you guys are just all so special … you shouldn’t have,” speech, you could see the emotion radiating from his face. And then, all choked up, he turned to go and tossed that can off applesauce off the hill with a casual contempt I have never seen before or since. It was the sheer, distilled essence of everything we all felt about applesauce.
Tom Kratman, The social media site formerly known as Twitter, 2025-09-05.
December 7, 2025
QotD: The Great Applesauce Blight of 1977/78
December 3, 2024
Evolution of Airborne Armour
The Tank Museum
Published Jul 19, 2024Lightly armed airborne troops are at a huge disadvantage when faced with regular troops with heavy weapons and armour. In World War II this led to huge losses for paratroops on Crete and at Arnhem. Since then, many attempts have been made to level the playing field, to give airborne soldiers a fighting chance.
From the Hamilcar gliders of World War II to the C17 Globemaster, we look at how to make a tank fly.
00:00 | Intro
00:47 | The Origins of Airbourne Operations
02:34 | Gliders
07:20 | A Tank Light Enough to Fly?
09:02 | Success & Failure
14:24 | Post-War Solutions
17:41 | Better Aircraft – Better Tanks?
20:15 | Strategic Deployment
21:39 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé. This video features imagery courtesy of http://www.hamilcar.co.uk/
#tankmuseum
February 1, 2023
Surviving on Leather
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 31 Jan 2023
(more…)
October 15, 2021
Alphonso Davies is “CONCACAF’s best player — which is to say, the continent’s best player”
I had been a follower of the Canadian national soccer teams back when I was coaching my son and his friends in U-4 through U-16 house league soccer, but while the women’s team is among the world’s best, the men’s team has always lagged a long way behind. In Thursday’s NP Platformed newsletter, Colby Cosh shows that there’s a very big spark of hope in the person of Alphonso Davies of Edmonton:

Alphonso Davies playing for FC Bayern Munich, 28 April, 2019.
Photo by Granada via Wikimedia Commons.
Reaching the [2022 FIFA World Cup] tournament involves finishing in the top four in an eight-country “octagonal” round-robin tournament that include the best sides from our continental soccer federation, CONCACAF. Last night, Canada faced a critical home match in Toronto against a traditional close rival, Panama, who stood just ahead of us in the octagonal table after a shock 1-0 home win against the United States.
This game wasn’t a very big deal even in dedicated sports media, but if you were paying close attention, you knew this was a crucial match for our World Cup hopes, which have quietly begun to build in the last year or two. Panama has a strong side, strong enough to have qualified for the 2018 World Cup finals ahead of us. But some awesome young Canadian talent is coming into full flower, and our country now possesses, by common consensus, CONCACAF’s best player — which is to say, the continent’s best player.
If anyone doubted the credentials of 20-year-old Edmontonian Alphonso Davies before last night, they have been silenced, if not entombed. Canada fell behind one-nil to Panama early in the match, then equalized shortly before half-time. Panama was lucky, at that point, to stand even, and their players knew it.
That’s when Davies, who had already filled a highlight reel with unstoppable dribbles in the first 45 minutes, put Canada ahead with the most astonishing goal ever scored by any man wearing the national colours. [Twitter link] Let us emphasize: you don’t need to be a soccer fan to appreciate this one. Phonzie’s pursuit and robbery of Panama’s Harold Cummings, who had a 35- or 45-metre head start to a harmless ball on the touchline, resembles nothing so much as the targeting and evisceration of an antelope by a cheetah. Davies then humiliated a second defender and wrong-footed Panama keeper Luis Mejia, who certainly would have made a better effort if his soul hadn’t already departed his body.
The match ended 4-1 in Canada’s favour, with Panama visibly discouraged at the failure of brutal rugby tactics facilitated by a typically inept CONCACAF referee. Davies plays his professional football at Euro-giant club Bayern Munich, and his galactico ability is no secret across the pond. Over here, he has already won (half of) a Lou Marsh Trophy as Canadian sportsman of the year. But one doubts, talking to people who don’t follow soccer, that he has the appropriate degree of fame in Canada yet. He is probably not as famous as Penny Oleksiak, or Bianca Andreescu, or whomever’s the seventh defenceman on the Montreal Canadians depth chart.
Two years ago, the possibility that Davies might one day help drag Canada to a World Cup final or two was a foggy hypothetical for the future. Last night he took a giant step, or several hundred of them, toward doing exactly that. Canada still has to follow through in the remaining half of the octagonal, but the outlook is now good. (Many Canadian national sides might have wilted against Panama after falling behind and being presented with rapacious unpenalized violence, but our manager John Herdman has achieved a deserved new level of respect in the past year, too.)
October 11, 2021
The Darien Venture: The Colony that Bankrupted Scotland
Geographics
Published 14 Nov 2019If a Nation’s wealth and power were to be measured in stubbornness, resilience, and inventiveness, rather than GDP, Scotland would be a top-5 superpower. The people that brought to you televisions, refrigerators, penicillin, and gin & tonic have gone through many a rough patch throughout their history. Very often, hard times were related to their rocky relationship with their Southern neighbours, the English.
Credits:
Host – Simon Whistler
Author – Arnaldo Teodorani
Producer – Jennifer Da Silva
Executive Producer – Shell HarrisBusiness inquiries to admin@toptenz.net
April 6, 2017
American “isolationism” between the wars
Reason‘s Jesse Walker linked to this article by Andrew Bacevich which helps to debunk the routine description of US foreign policy between the first and second world wars as “isolationism”:
… McCain is worried about the direction of world events, with Russian provocations offering but one concern among many. Patterson shares McCain’s apprehensions, compounded by what he sees as a revival of “the isolationism in Europe and America that precipitated World War II.”
Now as an explanation for the origins of the war of 1939-1945, American “isolationism” is as familiar as the sweet-and-sour pork featured at your local Chinese takeout joint. Its authenticity is equally dubious. Yet Patterson’s assertion has this virtue: It captures in less than a sentence a prime obstacle to instituting a realistic, fact-based approach to foreign policy.
In truth, isolationism is to history what fake news is to journalism. The oft-repeated claim that in the 1920s and 1930s the United States raised the drawbridges, stuck its head in the sand, and turned its back on the world is not only misleading, but also unhelpful. Citing a penchant for isolationism as a defect afflicting the American character is like suggesting that members of Congress suffer from a lack of self-esteem. The charge just doesn’t square with the facts, no matter how often repeated.
Here, by way of illustrating some of those relevant facts, is a partial list of places beyond the boundaries of North America, where the United States stationed military forces during the interval between the two world wars: China, the Philippines, Guam, Hawaii, Panama, Cuba, and Puerto Rico. That’s not counting the U.S. Marine occupations of Nicaragua, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic during a portion of this period. Choose whatever term you like to describe the U.S military posture during this era — incoherent comes to mind — but isolationism doesn’t fill the bill.
As for Patterson’s suggestion that the behavior of the United States “precipitated” World War II, the claim is simply laughable. World War I precipitated World War II, or more specifically the European malaise resulting from the bloodletting of 1914-1918, compounded by the Bolshevik Revolution and the spread of fascism, and further exacerbated by profoundly shortsighted policies pursued by Great Britain and France. Throw into the mix the Great Depression, Japanese imperial ambitions, and the diabolical plotting of Adolf Hitler and his henchmen, and you have the makings of a catastrophe. Some few observers foresaw that catastrophe, but preventing it lay well beyond the ability of the United States, even if U.S. leaders had been clairvoyant.
January 20, 2015
A tight squeeze indeed
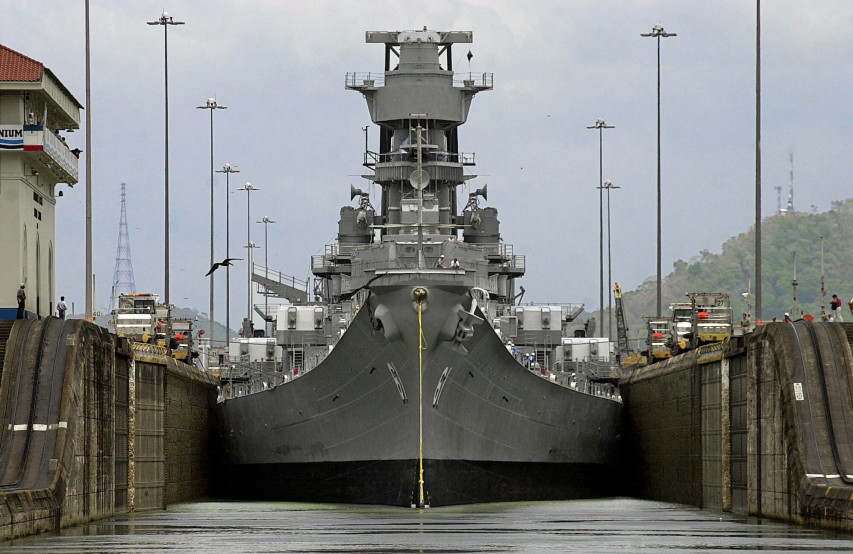

The USS Iowa crosses the Panama Canal at Miraflores Lock near Panama City, Panama Wednesday, March 28, 2001. At 108.2 feet wide, the Iowa-class battleships are the largest vessels ever to scrape their way through the 110-foot-wide locks of the canal. They were designed so that they could just fit through the waterway. (AP Photo/Tomas Munita)
H/T to Tyler Rogoway, who has a few other photos of Iowa-class battleships moving through the Panama canal.
October 30, 2014
“Free Trade” deals usually have little to do with actual free trade
It’s not exactly a revelation that what politicians call “free trade” agreements are usually tightly constrained, regulated, and micro-managed trade: almost the exact inverse of what a genuine free trade deal would look like. This is primarily because politicians and diplomats have hijacked the original term to describe modern mercantilism. In The Diplomat, Ji Xianbai looks at how so-called free trade negotiations are little more than diplomatic beat-downs of the weaker parties by the stronger:
The classic mercantilism, the one associated with the idea that the precious metals obtained through a favorable balance of foreign trade were essential to a powerful nation, may be historically obsolete. The core of the mercantilist view, namely that self-interested states maximize economic development by optimizing political control to strengthen national power, is very much alive and well. Indeed, the vitality of mercantilism as a state of mind may have infiltrated every corner of the international political economy. If one considers the essence of mercantilism through Robert Gilpin’s definition – the attempt of governments to manipulate economic arrangements in order to maximize their own interests – multiple examples immediately come to mind: Japan’s “economic totalitarianism” system in which the entire society was united in deterring foreign competition in the postwar period, China’s ascendance since 1980s through an export-led development mode underpinned by a deliberately undervalued currency, and Germany’s unprecedented trade surplus accrued from the stringent austerity imposed on its economy to sustain competitiveness in the aftermath of the euro crisis.
Compared to those national triumphs of classic mercantilism, there is a less visible showroom, but one in which mercantilism presents itself over and over again in the form of legal mercantilism. This would be free trade agreements (FTAs), negotiations of which are usually kept in the dark. In bilateral FTA negotiations, legal mercantilist governments endeavor to impose their own (or desirable) trade rules and economic policies on other sovereign countries, usually with the aid of a combination of economic immensity, political hegemony, and asymmetric trade dependence, to create a sort of “international best practice,” favorable trade rules, and legal gains that can be leveraged and multilateralized at a regional and/or global level. The “competitive liberalization” strategy aptly pursued by the U.S. since 2002 is one such legal mercantilist policy, which aims to create another “gold standard” in international trade standard setting to project U.S.-friendly economic policies all over the world. In short, the U.S. expects the trade policies of other nations to follow those of the U.S., in the same way that their currencies used to peg to the U.S. dollar.
The U.S.–Peru FTA (PTPA) marks the very first success of Washington’s attempts to subordinate other countries’ sovereignty to its own national interest by squeezing non-trade-related provisions into a bilateral trade liberalization agreement and overriding foreign national laws. To provide a level playing field for American companies, the PTPA lays out detailed measures that Peru is obliged to take to govern its forest sector. The Forest Annex of the PTPA requires Peru to set up an independent forestry oversight body and even enact new Forestry and Wildlife Laws to legalize key provisions of PTPA. The U.S.–Colombia FTA (CTPA)’s labor provisions represent an “even more blatant assault on another country’s sovereignty.” Meanwhile, Colombia was forced to agree to establish a dedicated labor ministry; endorse legislations outlawing interference in the exercise of labor rights; double the size of its labor inspectorate; and set up a phone hotline and an internet-based system to deal with labor complaints. Examples of similar provisions abound: Don’t forget that the U.S.-Panama FTA has “helped” revamp Panama’s tax policy on behalf of Panamanians.
February 19, 2013
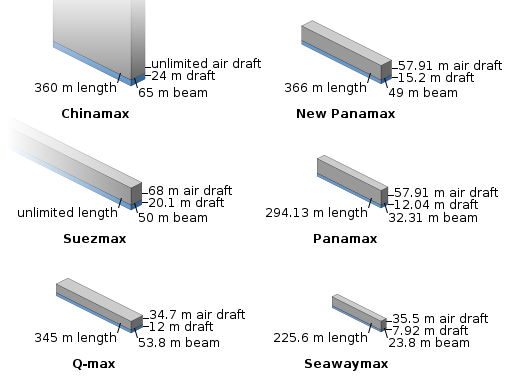
Container ships embiggen again
BBC News looks at the soon-to-be-launched Triple-E container ships:
What is blue, a quarter of a mile long, and taller than London’s Olympic stadium?
The answer — this year’s new class of container ship, the Triple E. When it goes into service this June, it will be the largest vessel ploughing the sea.
Each will contain as much steel as eight Eiffel Towers and have a capacity equivalent to 18,000 20-foot containers (TEU).
If those containers were placed in Times Square in New York, they would rise above billboards, streetlights and some buildings.
Or, to put it another way, they would fill more than 30 trains, each a mile long and stacked two containers high. Inside those containers, you could fit 36,000 cars or 863 million tins of baked beans.
The Triple E will not be the largest ship ever built. That accolade goes to an “ultra-large crude carrier” (ULCC) built in the 1970s, but all supertankers more than 400m (440 yards) long were scrapped years ago, some after less than a decade of service. Only a couple of shorter ULCCs are still in use. But giant container ships are still being built in large numbers — and they are still growing.
It’s 25 years since the biggest became too wide for the Panama Canal. These first “post-Panamax” ships, carrying 4,300 TEU, had roughly quarter of the capacity of the current record holder — the 16,020 TEU Marco Polo, launched in November by CMA CGM.
In the shipping industry there is already talk of a class of ship that would run aground in the Suez canal, but would just pass through another bottleneck of international trade — the Strait of Malacca, between Malaysia and Indonesia. The “Malaccamax” would carry 30,000 containers.
November 3, 2012
Remembering the ill-starred Darien expedition
History Today notes that the Darien Colony was founded by Scottish would-be colonists in what is now Panama on November 3, 1698:
On July 12th, 1698 five ships carrying 1,200 eager colonists left the Port of Leith in Scotland to a rapturous send-off. Most of the ill-fated emigrants did not know where they were going and did not find out until the sealed orders were opened at Madeira, but they were brimming with enthusiasm anyway.
A voyage of three months took them across the Atlantic to a harbour on the mangrove-studded Caribbean coast of Panama. On November 3rd, they took formal possession of their new territory, confidently naming it Caledonia and laying the foundations of the settlement of New Edinburgh. But it all went horribly wrong. Hundreds died of fever and dysentery before the colony was abandoned.
[. . .]
Scotland blamed the whole fiasco on the English. Paterson himself was bankrupt, but still believed in his scheme and tried vainly to revive it. Meanwhile, the Darien disaster seems to have persuaded hard-headed Scotsmen that their country could not prosper by itself, but needed access to England’s empire, and it helped to pave the way for the Act of Union between the two countries in 1707. Under the Act the investors in the Darien scheme were quietly compensated for their losses at taxpayers’ expense.