In The Line, Jaclyn Victor discusses Canada’s longstanding military freeloading habits and how Chinese interest in the Arctic are only the latest concerns pushing the government to start taking national sovereignty seriously:
![]()
Arctic Offshore Patrol Ship HMCS Harry DeWolf shortly after launch in 2018. The ship was commissioned into the Royal Canadian Navy in June, 2021.
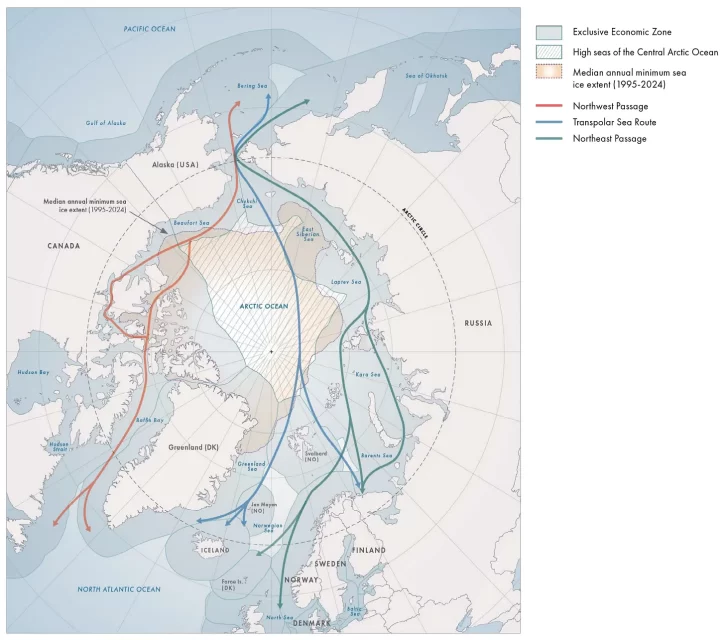
If the West has learned anything about China in recent years, it’s that its leaders will stop at nothing to advance their interests, and will often do so in unpredictable ways. For Canada, the most obvious lesson here was the brazen hostage diplomacy that saw “the two Michaels”, Kovrig and Spavor, imprisoned for nearly three years in retaliation for Canada’s detention of Huawei executive Meng Wanzhou. But there’s another area in which China is flexing its muscles that is much closer to home: the Arctic.
Despite being nearly 1,500 kms from the Arctic Circle, China claims to be a “near-Arctic” state. This alone might not be concerning if it weren’t also for China’s efforts to increase its Arctic presence while simultaneously undermining that of legitimate Arctic states. Although Canada staunchly claims to have sovereignty over the Northwest Passage, China hasn’t accepted this, yet has (concerningly) demonstrated an increased interest in the Arctic. Canada’s periodic military exercises and lack of assertion in the North are clearly not effective in dissuading Chinese interest in the region. As the world recognizes the importance of the Arctic we must do more if we want to maintain our influence.
From claims that Trudeau has personal ties to the Chinese Communist Party to the general belief that he has no backbone in Chinese foreign policy matters, it is clear that many Canadians are less than confident in our prime minister’s ability to defend Canadian interests when up against Xi Jinping. Perhaps the most relevant example of this is the release of the Two Michaels after nearly three years in Chinese captivity — a momentous occasion that filled many Canadians with a renewed hope — but only happened thanks to support from President Biden. And what about China’s alleged election interference, which was aimed at supporting the Trudeau Liberals at the expense of the more hawkish Erin O’Toole? Simply put, China wouldn’t want Trudeau in power if they thought he’d put a damper on their interests.
Our allies, unfortunately, also recognize that our inaction is no match for China’s “coercive diplomacy” and military preparedness. Canada could have contributed to, and hugely benefited from, the recently signed AUKUS pact. The agreement was largely intended to provide Australia with nuclear submarines to fend off Chinese aggression, but it also committed the partners to collaborate on AI and other technologies. Canada seems to have been deliberately excluded. We’re skilled in many of the information-sharing focus areas specified in the agreement, and we clearly need increased submarine capabilities in order to help maintain the Arctic sovereignty we claim to have. On top of this, many of our closest allies have outright denied Canadian claims to the NWP, leaving us with limited defence partnerships as they relate to the Arctic.
In the meantime, China has been establishing itself in the Arctic in an effort to get a foothold. In 2018, China’s Arctic Policy was published — the first of its kind for an Asian state. The policy, which discusses Chinese interest in Arctic resource extraction, brings light to Chinese efforts to develop industry in the region. China currently controls about 90 per cent of the global trade of rare minerals, and they want to maintain this dominance. As Arctic ice melts and additional resources become accessible, one can bet that China will want a piece of the pie. China already has a robust starting point for strategic investments, with US $19 billion invested in Canadian Arctic mining projects. Until the NWP (or “golden waterway” as it’s been called) becomes ice-free in the summers, China will likely continue seeking additional investment opportunities to increase its hold and resulting influence. Once the strait inevitably becomes easy to transit, China will already have a legitimate reason to do so.