The Canadian federal government is not eager to share the details of a new agreement they’ve signed with the Musqueam First Nation that apparently cedes most of the city of Vancouver to the band, casting the property rights of two million people into legal limbo:
The Liberal government is refusing to publicly release an agreement with the Musqueam Indian Band that recognizes Aboriginal title over a vast area of British Columbia, including Metro Vancouver and surrounding areas, potentially affecting nearly two million people.
Buried in a seemingly mundane fisheries announcement put out on February 20th, the acknowledgement could radically undermine property rights in one of Canada’s largest and most populated metropolitan regions.
On February 20, Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada issued a news release with little fanfare titled “Musqueam and Canada Sign Historic Agreements Recognizing Rights, Stewardship and Fisheries”.
The news release reads: Canada “recognizes that Musqueam has Aboriginal rights including title within their traditional territory and establishes a framework for incremental implementation of rights and nation-to-nation relations with Canada”.
That phrase “including title” refers to Aboriginal title. Under Canadian constitutional law, Aboriginal title is a contentious but increasingly recognized property interest, affirmed by recent court rulings, including the controversial Cowichan decision. Courts have recognized Aboriginal title as a prior and senior right to land that critics say threatens fee simple title or traditional private property ownership in Canada.
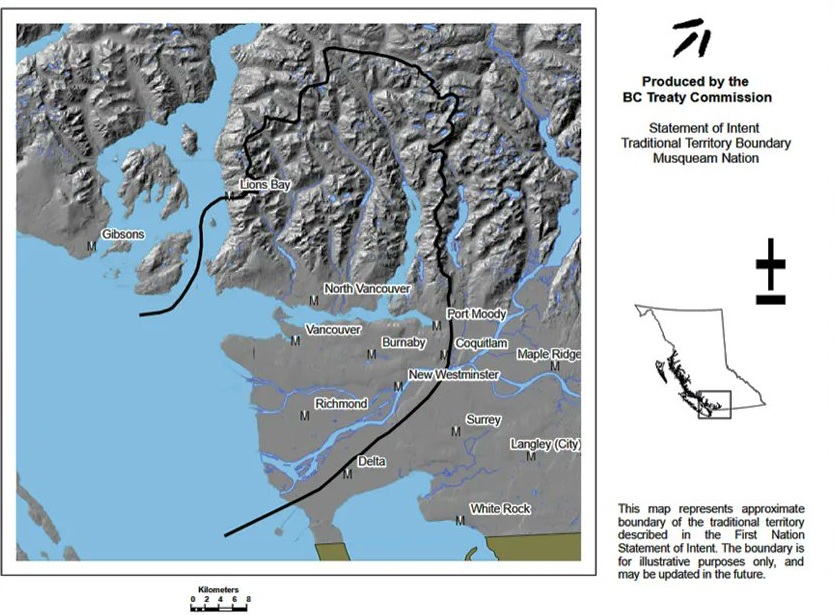
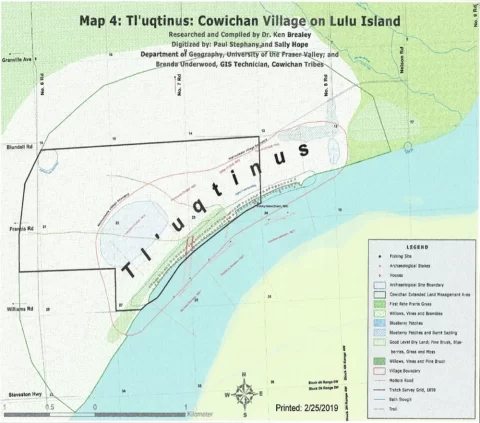
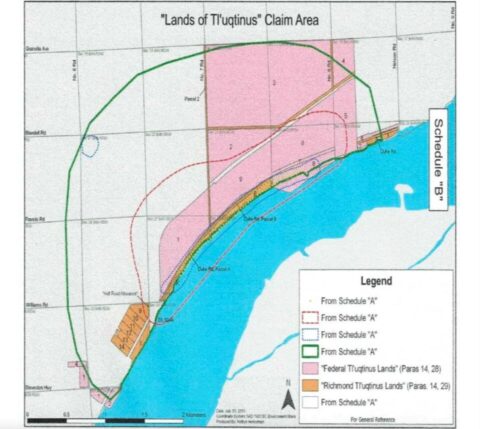
The Musqueam Indian Band’s traditional territory encompasses virtually all of Metro Vancouver, including Vancouver, West Vancouver, North Vancouver, Burnaby, Richmond, New Westminster, parts of Delta and Surrey and other regions.
Based on 2021 census and other data, that territory is home to an estimated 1.8 million British Columbians.
The federal government has now formally recognized in writing Musqueam Indian Band’s Aboriginal title over that territory, yet Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada refuses to make the agreement public.
The February 20 announcement specifically refers to the “šxʷq̓ʷal̕təl̕tən Rights Recognition Agreement”, described as recognizing Musqueam’s Aboriginal rights, “including title” and establishing a framework for implementation.
Musqueam Chief Wayne Sparrow emphasized the Aboriginal title component directly in the release:
Our Musqueam community celebrates these historic agreements as a step forward in our path to Reconciliation. In signing these agreements, the Government of Canada is acknowledging Musqueam’s Aboriginal title and rights to our traditional territory and recognizing our expertise in both marine management and fisheries management.
But when Juno News requested a copy of the agreement from Crown-Indigenous Relations, the department’s media relations spokesperson Eric Head confirmed receipt of the request and then cut communication altogether, even when pressed to ask if the agreement would be made public.