Along with this, you see a growing respect for numbers [in the 15th century]. Medieval statistics are Rachel Maddowesque — whatever they felt they needed to say to get the job done. “We were opposed by fifty thousand Saracens” could mean anything from “bad guys as far as the eye could see” to “we were slightly outnumbered” to “it just wasn’t our day, so we ran”. 15th century numbers aren’t what you’d call real factually accurate, but they’re getting there. 16th century numbers are usually in the ballpark, and you can usually cross-check them in various ways. There’s just a hell of a lot more paper in general, and that paper is a lot more scrupulous.
All of this, I suggest, is because people increasingly thought factual accuracy was important. And that only comes with the increasing sense of linear time. The chronicles of the first two or three Crusades, for instance, are filled with wild exaggerations and impossible claims … but they’re not lies. They just serve a different purpose. They’re called “histories”, but that’s a misleading translation (of the word historia, I’ll admit). What they really are is much closer to exempla — saints’ lives, that kind of thing. Their point isn’t “This and that actually happened”; it’s more like “Let us all praise God, for the wondrous things he allowed us to do!”
Gesta Francorum means “deeds of the French”, but in the sense of “The wonders done in God’s name,” not “a list of battles and their outcomes”.
Severian, “The Ghosts (II)”, Founding Questions, 2022-05-18.
March 3, 2026
QotD: The rise of archives-based history in the late Middle Ages
February 22, 2026
QotD: The shift from “motte-and-bailey” construction to stone castles
As we move to stone construction and especially full stone construction (which we’ll define as the point when at least one complete curtain wall – don’t worry, we’ll define that in a second – is in stone) in the 12th century, we’re beginning to contemplate a different kind of defense. The wooden motte and bailey, as we’ve seen, mostly served to resist both raids and “hasty” assaults, thus forcing less coordinated or numerous attackers to set in to starve the castle out or go home. But stone walls are a much larger investment in time and resources; they also require a fair bit more careful design in order to be structurally sound. For all of that expense, the builder wants quite a bit of a security, and in the design of stone castles it is hard not to notice increasing attention towards resisting a deliberate assault; stone castles of the 12th century and beyond are increasingly being designed to stand up to the best that the “small army” playbook can throw at them. Of course it is no accident that this is coming at the same time that medieval European population and wealth is beginning to increase more rapidly, leaving political authorities (read: the high nobility) with both the resources for impressive new castles (although generally the number of castles falls during this period – fewer, stronger castles) and at the same time with more resources to invest in the expertise of siegecraft (meaning that an attacker is more likely to have fancy tools like towers, catapults and better coordination to use them).
To talk about how these designs work, we need to clear some terminology. The (typically thin) wall that runs the circuit of the castle and encloses the bailey is called a “curtain wall“. In stone castles, there may be multiple curtain walls, arranged concentrically (a design that seems to emerge in the Near East and makes its way to Europe in the 13th century via the crusades); the outermost complete circuit (the primary wall, as it were) is called the enceinte. Increasingly, the keep in stone castles is moved into the bailey (that is, it sits at the center of the castle rather than off to one side), although of course stone versions of motte and bailey designs exist. In some castle design systems, with stone the keep itself drops away, since the stone walls and towers often provided themselves enough space to house the necessary peacetime functions; in Germany there often was no keep (that is, no core structure that contained the core of the fortified house), but there often was a bergfriede, a smaller but still tall “fighting tower” to serve the tactical role of the keep (an elevated, core position of last-resort in a defense-in-depth arrangement) without the peacetime role.
While the wooden palisade curtain walls of earlier motte and bailey castles often lacked many defensive features (though sometimes you’d have towers and gatehouses to provide fighting positions around the gates), stone castles tend to have lots of projecting towers which stick out from the curtain wall. The value of projecting towers is that soldiers up on those towers have clear lines of fire running down the walls, allowing them to target enemies at the base of the curtain wall (the term for this sort of fire is “enfilade” fire – when you are being hit in the side). Clearly what is being envisaged here is the ability to engage enemies doing things like undermining the base of walls or setting up ladders or other scaling devices.
The curtain walls themselves also become fighting positions. Whether on a tower or on the wall itself, the term for the fighting position at the top is a “battlement”. Battlements often have a jagged “tooth” pattern of gaps to provide firing positions; the term for the overall system is crenellation; the areas which have stone are merlons, while the gaps to fire through are crenals. The walkway behind both atop the wall is the chemin de ronde, allure or “wall-walk”. One problem with using the walls themselves as fighting positions is that it is very hard to engage enemies directly beneath the wall or along it without leaning out beyond the protection of the wall and exposing yourself to enemy fire. The older solution to this were wooden, shed-like projections from the wall called “hoarding”; these were temporary, built when a siege was expected. During the crusades, European armies encountered Near Eastern fortification design which instead used stone overhangs (with the merlons on the outside) with gaps through which one might fire (or just drop things) directly down at the base of the wall; these are called machicolations and were swiftly adopted to replace hoardings, since machicolations were safer from both literal fire (wood burns, stone does not) and catapult fire, and also permanent. All of this work on the walls and the towers is designed to allow a small number of defenders to exchange fire effectively with a large number of attackers, and in so doing to keep those attackers from being able to “set up shop” beneath the walls.
[I]t is worth noting something about the amount of fire being developed by these projecting towers: the goal is to prevent the enemy operating safely at the wall’s base, not to prohibit approaches to the wall. These defenses simply aren’t designed to support that much fire, which makes sense: castle garrisons were generally quite small, often dozens or a few hundred men. While Hollywood loves sieges where all of the walls of the castle are lined with soldiers multiple ranks deep, more often the problem for the defender was having enough soldiers just to watch the whole perimeter around the clock (recall the example at Antioch: Bohemond only needs one traitor to access Antioch because one of its defensive towers was regularly defended by only one guy at night). It is actually not hard to see that merely by looking at the battlements: notice in the images here so far often how spaced out the merlons of the crenellation are. The idea here isn’t maximizing fire for a given length of wall but protecting a relatively small number of combatants on the wall. As we’ll see, that is a significant design choice: castle design assumes the enemy will reach the walls and aims to prevent escalade once they are there; later in this series we’ll see defenses designed to prohibit effective approach itself.
As with the simpler motte and bailey, stone castles often employ a system of defense in depth to raise the cost of an attack. At minimum, generally, that system consists of a moat (either wet or dry), the main curtain walls (with their towers and gatehouses) and then a central keep. Larger castles, especially in the 13th century and beyond, adopting cues from castle design in the Levant (via the crusades) employed multiple concentric rings of walls. Generally these were set up so that the central ring was taller, either by dint of terrain (as with a castle set on a hill) or by building taller walls, than the outer ring. The idea here seems not to be stacking fire on approaching enemies, but ensuring that the inner ring could dominate the outer ring if the latter fell to attackers; defenders could fire down on attackers who would lack cover (since the merlons of the outer ring would face the other way). As an aside, the concern to be firing down is less about the energy imparted by a falling arrow (though this is more meaningful with javelins or thrown rocks) and more about a firing position that denies enemies cover by shooting down at them (think about attackers, for instance, crossing a dry moat – if your wall is the right height and the edges of the moat are carefully angled, you can set up a situation where the ditch never actually offers the attackers any usable cover, but you need to be high up to do it!).
Speaking of the moat, this is a common defensive element (essentially just a big ditch!) which often gets left out of pop culture depictions of castles and siege warfare, but it accomplishes so many things at such a low cost premium. Even assuming the moat is “dry”! For attackers on foot (say, with ladders) looking to approach the wall, the moat is an obstacle that slows them down without potentially providing any additional cover (it is also likely to disorder an attack). For sappers (attackers looking to tunnel under the walls and then collapse the tunnel to generate a breach), the depth of the ditch forces them to dig deeper, which in turn raises the demands in both labor and engineering to dig their tunnel. For any attack with siege engines (towers, rams, or covered protective housings made so that the wall can be approached safely), the moat is an obstruction that has to be filled in before those engines can move forward – a task which in turn broadcasts the intended route well in advance, giving the defenders a lot of time to prepare.
Well-built stone castles of this sort were stunningly resistant to assault, even with relatively small garrisons (dozens or a few hundred, not thousands). That said, building them was very expensive; maintaining them wasn’t cheap either. For both castles and fortified cities, one ubiquitous element in warfare of the period (and in the ancient period too, by the by) was the rush when war was in the offing to repair castle and town walls, dig out the moat and to clear buildings that during peace had been built int he firing lines of the castle or city walls.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part III: Castling”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-12-10.
May 30, 2025
QotD: “Have fun storming the castle!”
… the expected threat is going to shape the calculation of what margin of security is acceptable, which brings us back to our besieger’s playbook. You may recall when we looked at the Assyrian siege toolkit, that many of the most effective techniques assumed a large, well-coordinated army which could dispose of a lot of labor (from the soldiers) on many different projects at once while also having enough troops ready to fight to keep the enemy bottled up and enough logistic support to keep the army in the field for however long all of that took. In short, this is a playbook that strong, well-organized states (with strong, well-organized armies) are going to excel at. But, as we’ve just noted, the castle emerges in the context of fragmentation which produces a lot of little polities (it would be premature to call them states) with generally quite limited administrative and military capacity; the “big army” siege playbook which demands a lot of coordination, labor and expertise is, for the most part, out of reach.
Clifford Rogers has already laid out a pretty lay-person accessible account of the medieval siege playbook (in Soldiers’ Lives Through History: The Middle Ages (2007), 111-143; the book is pricey, so consider your local library), so I won’t re-invent the wheel here but merely note some general features. Rogers distinguishes between hasty assaults using mostly ladders launched as soon as possible as a gamble with a small number of troops to try to avoid a long siege, and deliberate assaults made after considerable preparation, often using towers, sapping, moveable shelters designed to resist arrow fire and possibly even catapults. We’ve already discussed hasty assaults here, so let’s focus on deliberate assaults.
While sapping (tunneling under and collapsing fortifications) remained in use, apart from filling in ditches, the mole-and-ramp style assaults of the ancient world are far less common, precisely because most armies (due to the aforementioned fragmentation combined with the increasing importance in warfare of a fairly small mounted elite) lacked both the organizational capacity and the raw numbers to do them. The nature of these armies as retinues of retinues also made coordination between army elements difficult. The Siege of Antioch (1097-8) [during] the First Crusade is instructive; though the siege lasted nine months, the crusaders struggled to even effectively blockade the city until a shipment of siege materials (lumber, mostly) arrived in March of 1098 (five months after the beginning of the siege). Meanwhile, coordinating so that part of the army guarded the exits of the city (to prevent raids by the garrison) while the other part of the army foraged supplies had proved mostly too difficult, leading to bitter supply shortages among the crusaders. Even with materials delivered to them, the crusaders used them to build a pair of fortified towers blocking exits from the city, rather than the sort of elaborate sapping and ramps; the city was taken not by assault but by treachery – a very common outcome to a siege! – when Bohemond of Taranto bribed a guard within the city to let the crusaders sneak a small force in. All of this despite the fact that the crusader army was uncommonly large by medieval European standards, numbering perhaps 45,000.
Crucially, in both hasty and deliberate assaults, the emphasis for the small army toolkit tends to be on escalade (going over the walls) using ladders or moveable wooden towers, rather than the complex systems of earthworks favored by the “big army” siege system or breaching – a task which medieval (or ancient!) artillery was generally not capable of. The latter, of course, is a much more certain method of assault – give a Roman army a few months and almost any fortress could be taken with near certainty – but it was a much more demanding method in terms of the required labor and coordination. Thwarting escalade is mostly a question of the height of defenses (because a taller wall requires a taller ladder, tower or ramp) and good fields of fire for the defenders (particularly the ability to fire at attackers directly up against the wall, since that’s where the ladders are likely to be).
The other major threat to castle walls (apart from the ever-present threat of sapping) was catapults, but I want to deal with those next time for reasons that I suspect will make sense then. For now it is worth simply noting that catapults, even the mighty trebuchets of the 14th century were generally used to degrade defenses (smashing towers, destroying crenellation, damaging gatehouses) rather than to produce breaches. They could in some cases do that, but only with tremendous effort and a lot of time (and sometimes not even then). Consequently, for most castles the greatest threat remained escalade, followed by treachery or starvation, followed by sapping, followed by artillery.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part III: Castling”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-12-10.
June 28, 2024
Ruling Medieval France
In Quillette, Charlotte Allen reviews House of Lilies: The Dynasty That Made Medieval France by Justine Firnhaber-Baker, a period of history I know mainly from the English point of view:
I’m a PhD medievalist, but the history of medieval French royalty was never my specialty, and my ignorance was vast.
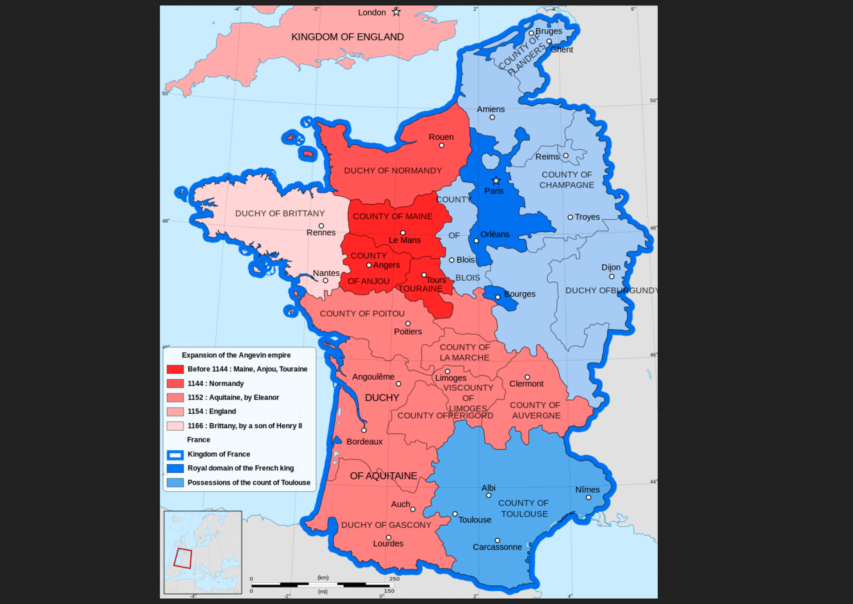
I’d assumed, for example, that the French kings of the Middle Ages were mostly fainéants whose writ scarcely ran past the Île-de-France region (encompassing the city of Paris and its environs). The English monarchy across the Channel had been centralised since the days of Alfred the Great (849–899); but the French kings seemed to rule in a more symbolic capacity, being perpetually at the mercy of the powerful dukes and counts of autonomous French regions such as Normandy, Burgundy, Aquitaine, Anjou, Blois, Toulouse, and Languedoc. These regional rulers were technically royal vassals. But, in actuality, they saw themselves as absolute rulers in their own right, and so had no compunction against turning on the crown when they thought it would further their interests.
My impressions had been formed by accounts of the 17-year-old Joan of Arc’s having to personally drag the Dauphin (the future King Charles VII) to Reims for his coronation in 1429, and by Shakespeare’s historical plays, which portrayed the French as fops incapable of defending their territory against the robust and brotherly English during the Hundred Years’ War. Indeed, the whole point of that war (from the English perspective) was that, by dynastic right, large portions of France’s fractured political landscape actually belonged to England.
The one medieval French royal (by marriage) I did know something about, Eleanor of Aquitaine (c. 1122–1204), dumped her French husband, King Louis VII (1120–1180) after he bungled the Second Crusade, a costly and embarrassing adventure on which Eleanor had accompanied him on horseback. (“Never take your wife on a Crusade”, a medievalist friend of mine once sensibly quipped). To top off his disastrous final loss of his Crusader army in 1148 during an ill-considered attack on Damascus — which, although Muslim-ruled, was in fact an ally of Latin-Christian Jerusalem — Louis and Eleanor had failed to produce a son. No sooner was the ink dry on their divorce in 1152 (technically an annulment, since the two were Catholics), than she married Henry Plantagenet, son and heir of the duke of Anjou, who two years later became King Henry II of England. Henry quickly procreated five sons (among fourteen surviving children) with his new bride. Thus began the dynasty that would rule England for more than three centuries.
As everyone who has seen The Lion in Winter knows, Henry II’s relationship with Eleanor was far from tranquil, but two of their sons succeeded him to the English throne: Richard the Lionheart and King John (of Magna Carta fame or infamy, depending on your perspective). Henry was, besides king of England, duke of Normandy and count of Anjou, through his great-grandfather, William the Conqueror, and his mother, Matilda, who’d married Henry’s Anjevin father, Geoffrey, after her first husband, the Holy Roman Emperor Henry V, died in 1125.
Eleanor’s grounds for annulling her marriage to Louis had been that he was her fourth cousin, which violated the Catholic Church’s (selectively applied) consanguinity restrictions. But Henry was even closer kin, being her third cousin. The humiliated and (understandably) rankled Louis demanded that Henry, as his feudal vassal, explain why he’d failed to ask permission to marry (let alone marry his boss’s ex). Henry declined to reply, the feudal equivalent of declaring oneself in rebellion. Louis retaliated by invading Normandy — unsuccessfully — and trying to hold onto Eleanor’s Aquitaine on the claim that he’d become its duke by marriage (Henry II was meanwhile making the same claim) before giving up and remarrying himself in 1154.
A colour-coded political map of France during the twelfth century, indicating the early expansion of the Angevin Empire — i.e., the territorial possessions of the House of Plantagenet — from the time of Geoffrey V of Anjou (1113–1151). The Plantagenets would rule in England, and parts of France, till the demise of Richard III of England (1452–1485).
I’d assumed that French kings wouldn’t hold much in the way of real royal power until the time of King Louis XIV (1638–1715), who declared (perhaps apocryphally), L’État, c’est moi, and forced French regional nobles to reside in his over-the-top palace at Versailles (where they’d dissipate their incomes via elaborate court ceremonies instead of making trouble from their provincial power bases).
But the scales have now been knocked from my eyes, thanks to Justine Firnhaber-Baker, a professor of French medieval history at the University of St Andrews. The subtitle of her new book, House of Lilies: The Dynasty That Made Medieval France, refers to the Capetian dynasty founded by Hugh Capet (c. 940–996), who took his royal title in 987 A.D. Every French monarch, from Hugh’s reign to the French Revolution and beyond, had Capetian blood running through his veins — including the aforementioned Louis VII, who was a direct descendant of Hugh, and the bookish, dithering King Louis XVI, who was not, but who nevertheless went to the guillotine in 1793 under the derisive sobriquet “Citizen Louis Capet”.
January 13, 2024
History RE-Summarized: The Byzantine Empire
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 29 Sept 2023The Byzantines (Blue’s Version) – a project that took an almost unfathomable amount of work and a catastrophic 120+ individual maps. I couldn’t be happier.
SOURCES & Further Reading:
“Byzantium” I, II, and III by John Julius Norwich, The Byzantine Republic: People and Power in New Rome by Anthony Kaldellis, The Alexiad by Anna Komnene, Osman’s Dream: The History of the Ottoman Empire by Caroline Finkel, Sicily: An Island at the Crossroads of History by John Julius Norwich, A History of Venice by John Julius Norwich. I also have a degree in classical civilization.Additionally, the most august of thanks to our the members of our discord community who kindly assisted me with so much fantastic supplemental information for the scripting and revision process: Jonny, Catia, and Chehrazad. Thank you for reading my nonsense, providing more details to add to my nonsense, and making this the best nonsense it can be.
(more…)
January 24, 2023
The Byzantine Empire: Part 9 – The Last Centuries
seangabb
Published 30 Dec 2022In this, the ninth in the series, Sean Gabb gives an overview of the last years of Byzantium, from the Crusader sack in 1204 to the Turkish capture in 1453.
Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or the Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
(more…)
November 5, 2022
The Byzantine Empire: Part 8 – The Breakdown, 1025-1204
seangabb
Published 20 May 2022In this, the eighth video in the series, Sean Gabb explains how, having acquired the wrong sort of ruling class, the Byzantine Empire passed in just under half a century from the hegemonic power of the Near East to a declining hulk, fought over by Turks and Crusaders.
Subjects covered include:
The damage caused by a landed nobility
The deadweight cost of uncontrolled bureaucracy
The first rise of an insatiable and all-conquering West
The failure of the Andronicus Reaction
The sack of Constantinople in 1204Between 330 AD and 1453, Constantinople (modern Istanbul) was the capital of the Roman Empire, otherwise known as the Later Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Mediaeval Roman Empire, or The Byzantine Empire. For most of this time, it was the largest and richest city in Christendom. The territories of which it was the central capital enjoyed better protections of life, liberty and property, and a higher standard of living, than any other Christian territory, and usually compared favourably with the neighbouring and rival Islamic empires.
The purpose of this course is to give an overview of Byzantine history, from the refoundation of the City by Constantine the Great to its final capture by the Turks.
Here is a series of lectures given by Sean Gabb in late 2021, in which he discusses and tries to explain the history of Byzantium. For reasons of politeness and data protection, all student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
September 29, 2022
The History of Cyprus Explained in 10 minutes
Epimetheus
Published 24 May 2022The history of Cyprus explained from ancient times to modern.
(more…)
September 19, 2022
City Minutes: Crusader States
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 13 May 2022Crusading is one thing, but holding your new kingdoms is a much trickier business. See how the many Christian states of “Outremer” rolled with the punches to evolve in form and function over multiple centuries.
(more…)
September 12, 2022
The Lord of the Rings and Ancient Rome (with Bret Devereaux)
toldinstone
Published 10 Sep 2022In this episode, Dr. Bret Devereaux (the blogger behind “A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry”) discusses the relationships between fantasy and ancient history – and why historical accuracy matters, even in fiction.
(more…)
June 3, 2022
The Crusades: Part 10 – The End of the Crusader Kingdoms
seangabb
Published 27 Mar 2021The Crusades are the defining event of the Middle Ages. They brought the very different civilisations of Western Europe, Byzantium and Islam into an extended period of both conflict and peaceful co-existence. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this long encounter with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
May 31, 2022
The Crusades: Part 9 – The Other Crusades
seangabb
Published 18 Mar 2021The Crusades are the defining event of the Middle Ages. They brought the very different civilisations of Western Europe, Byzantium and Islam into an extended period of both conflict and peaceful co-existence. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this long encounter with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
May 27, 2022
The Crusades: Part 8 – The Rise of Venice
seangabb
Published 12 Mar 2021The Crusades are the defining event of the Middle Ages. They brought the very different civilisations of Western Europe, Byzantium and Islam into an extended period of both conflict and peaceful co-existence. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this long encounter with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
May 20, 2022
The Crusades: Part 7 – The Third Crusade
seangabb
Published 5 Mar 2021The Crusades are the defining event of the Middle Ages. They brought the very different civilisations of Western Europe, Byzantium and Islam into an extended period of both conflict and peaceful co-existence. Between January and March 2021, Sean Gabb explored this long encounter with his students. Here is one of his lectures. All student contributions have been removed.
(more…)
May 19, 2022
Feeding a Templar Knight
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 25 Jan 2022Support the Channel with Patreon ► https://www.patreon.com/tastinghistory
Merch ► crowdmade.com/collections/tastinghistory
Instagram ► https://www.instagram.com/tastinghist…
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/TastingHistory1
Tiktok ► TastingHistory
Reddit ► r/TastingHistory
Discord ► https://discord.gg/d7nbEpy
Amazon Wish List ► https://amzn.to/3i0mwGtSend mail to:
Tasting History
PO Box 766
Burbank, CA 91503Recipe
Boar Tenderloin
Equal parts wine and water for boiling
1 thick slice of bread without crust
1 ¼ cups white wine
¼ cup red wine
1 teaspoon ginger
2 teaspoon cinnamon
½ teaspoon nutmeg
Pinch of saffron threads
2 tablespoons brown sugar
Pinch of salt
1 tablespoon red wine vinegar (optional)1. Heat olive oil in a pot then sear the boar on all sides. Remove it from the pot and boil equal parts wine and water, then add the boar back in and boil, covered, for 10-15 minutes or until fully cooked. Then let it rest.
2. To make the sauce, mix the spices and white wine. Separately, soak the bread in water for a few hours, then pour in the red wine. Strain the bread/wine into a saucepan, then press the bread through the strainer. Add the spiced wine mixture and bring to a simmer. Let simmer for 15 minutes, or until half reduced, then add the sugar and salt, and if you with, a tablespoon of red wine vinegar. Simmer until thickened.
3. Slice the boar and pour the sauce over it. Serve with roasted chestnuts.LINKS TO SOURCES**
Le Viandier de Taillevent: https://amzn.to/3FWD7FS
Le Ménagier de Paris: https://amzn.to/3fKgyt0
The Primitive Rule of the Templars by Bernard de Clairvaux: https://amzn.to/3ItxiRY
The Templars by Dan Jones: https://amzn.to/3qOIlin**Some of the links and other products that appear on this video are from companies which Tasting History will earn an affiliate commission or referral bonus. Each purchase made from these links will help to support this channel with no additional cost to you. The content in this video is accurate as of the posting date. Some of the offers mentioned may no longer be available.
Subtitles: Jose Mendoza | IG @worldagainstjose
Music: Crusade – Video Classica by Kevin MacLeod is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/…
Source: http://incompetech.com/music/royalty-…
Artist: http://incompetech.com/#tastinghistory #knightstemplar
From the comments:
Tasting History with Max Miller
3 days ago
Templar should be pronounced TEM-pler, but sometimes I say tem-PLAR when I read it. Don’t do what I do