Ideological revolutions follow a predictable pattern. At some point, you see what the Bolsheviks called “the Revolt of the Left SR’s.” “SR” stands for “socialist revolutionaries”, so their “left” was, of course, radical by all but Bolshevik standards. Nonetheless, they actually meant it when they said they were for “soviet power”, the “soviets” in this case being “assemblies made up of actual workers, not limpwristed eggheads like Lenin whose fathers were minor nobility”.
As Solzhenitsyn explained it, in the early days of the Bolshevik revolution, these SRs were part of a coalition government with the Bolsheviks. As such, they had to be given a certain amount of jobs in the ministries, including the justice ministry. They actually believed that stuff about The Workers, so they weren’t ready to send people to Siberia for twenty, thirty, forty years like Lenin demanded. They broke with Lenin (over other issues as well, obviously), the Bolsheviks crushed them, and once the Bolsheviks had power over all the ministries, there’s your gulag archipelago. Same as it ever was.
The Nazis had their “Left SR’s”, too. These were the Strasserites, led by brothers Otto and Gregor, the guys who put the “Socialist” in “National Socialism”. The Night of the Long Knives was a purge against both “left” and “right” — though Röhm and his butt boys get all the press, one of the Strasser brothers got his, too. That’s German efficiency for you!
And then there was the original Terror, in France, and even before that we had ours, too — the Whiskey Rebellion and Shays’ Rebellion aren’t usually taught as ideological (they’re usually not taught at all, of course), but they were. We’ve had two revolutions (before this week), in fact, and in both cases you had those pesky “we really believe this shit!” types causing all kinds of problems for the revolutionary government — see, for example, those state governors who made Jeff’s life hell in Richmond, objecting to the nationalization of their state militias on the grounds that the Confederacy is actually, you know, a confederacy, and that drafts and war production boards and taxes in kind and all the rest are exactly the kind of tyranny you’d expect from Abe’s gang in Washington …
Severian, “Speaking of Purges…”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-01-08.
June 13, 2023
QotD: The purge of the Socialist Revolutionaries
June 10, 2023
QotD: The word “objectively”
For years past I have been an industrious collector of pamphlets, and a fairly steady reader of political literature of all kinds. […] When I look through my collection of pamphlets — Conservative, Communist, Catholic, Trotskyist, Pacifist, Anarchist or what-have-you — it seems to me that almost all of them have the same mental atmosphere, though the points of emphasis vary. Nobody is searching for the truth, everybody is putting forward a “case” with complete disregard for fairness or accuracy, and the most plainly obvious facts can be ignored by those who don’t want to see them. The same propaganda tricks are to be found almost everywhere. It would take many pages of this paper merely to classify them, but here I draw attention to one very widespread controversial habit — disregard of an opponent’s motives. The key-word here is “objectively”.
We are told that it is only people’s objective actions that matter, and their subjective feelings are of no importance. Thus pacifists, by obstructing the war effort, are “objectively” aiding the Nazis; and therefore the fact that they may be personally hostile to Fascism is irrelevant. I have been guilty of saying this myself more than once. The same argument is applied to Trotskyism. Trotskyists are often credited, at any rate by Communists, with being active and conscious agents of Hitler; but when you point out the many and obvious reasons why this is unlikely to be true, the “objectively” line of talk is brought forward again. To criticize the Soviet Union helps Hitler: therefore “Trotskyism is Fascism”. And when this has been established, the accusation of conscious treachery is usually repeated.
This is not only dishonest; it also carries a severe penalty with it. If you disregard people’s motives, it becomes much harder to foresee their actions. For there are occasions when even the most misguided person can see the results of what he is doing. Here is a crude but quite possible illustration. A pacifist is working in some job which gives him access to important military information, and is approached by a German secret agent. In those circumstances his subjective feelings do make a difference. If he is subjectively pro-Nazi he will sell his country, and if he isn’t, he won’t. And situations essentially similar though less dramatic are constantly arising.
In my opinion a few pacifists are inwardly pro-Nazi, and extremist left-wing parties will inevitably contain Fascist spies. The important thing is to discover which individuals are honest and which are not, and the usual blanket accusation merely makes this more difficult. The atmosphere of hatred in which controversy is conducted blinds people to considerations of this kind. To admit that an opponent might be both honest and intelligent is felt to be intolerable. It is more immediately satisfying to shout that he is a fool or a scoundrel, or both, than to find out what he is really like. It is this habit of mind, among other things, that has made political prediction in our time so remarkably unsuccessful.
George Orwell, “As I Please”, Tribune, 1944-12-08.
June 2, 2023
February 24, 2023
QotD: Relearning lessons as old as warfare
DURING THE FIRST MONTHS of American intervention in Korea, reports from the front burst upon an America and world stunned beyond belief. Day after day, the forces of the admitted first power of the earth reeled backward under the blows of the army of a nation of nine million largely illiterate peasants, the product of the kind of culture advanced nations once overawed with gunboats. Then, after fleeting victory, Americans fell back once more before an army of equally illiterate, lightly armed Chinese.
The people of Asia had changed, true. The day of the gunboat and a few Marines would never return. But that was not the whole story. The people of the West had changed, too. They forgot that the West had dominated not only by arms, but by superior force of will.
During the summer of 1950, and later, Asians would watch. Some, friends of the West, would even smile. And none of them would ever forget.
News reports in 1950 talked of vast numbers, overwhelming hordes of fanatic North Koreans, hundreds of monstrous tanks, against which the thin United States forces could not stand. In these reports there was truth, but not the whole truth.
The American units were outnumbered. They were outgunned. They were given an impossible task at the outset.
But they were also outfought.
In July, 1950, one news commentator rather plaintively remarked that warfare had not changed so much, after all. For some reason, ground troops still seemed to be necessary, in spite of the atom bomb. And oddly and unfortunately, to this gentleman, man still seemed to be an important ingredient in battle. Troops were getting killed, in pain and fury and dust and filth. What had happened to the widely heralded pushbutton warfare where skilled, immaculate technicians who had never suffered the misery and ignominy of basic training blew each other to kingdom come like gentlemen?
In this unconsciously plaintive cry lies buried a great deal of the truth why the United States was almost defeated.
Nothing had happened to pushbutton warfare; its emergence was at hand. Horrible weapons that could destroy every city on earth were at hand — at too many hands. But pushbutton warfare meant Armageddon, and Armageddon, hopefully, will never be an end of national policy.
Americans in 1950 rediscovered something that since Hiroshima they had forgotten: you may fly over a land forever; you may bomb it, atomize it, pulverize it and wipe it clean of life — but if you desire to defend it, protect it, and keep it for civilization, you must do this on the ground, the way the Roman legions did, by putting your young men into the mud.
T.R. Fehrenbach, This Kind of War: A Study in Unpreparedness, 1963
January 17, 2023
“Karl Marx was one hollow and rotten tree, inside and out, from beginning to end”
To mark the passing of Paul Johnson, the Foundation for Economic Education reposted an appreciation of Johnson’s Intellectuals by Lawrence W. Reed praising his essay on Karl Marx:
None of Johnson’s subjects can match Karl Marx for sheer loathsomeness and shameless fakery. He was a virulent racist and anti-Semite with a vicious temper (“Jewish n****r” was one of his favorite epithets). On a good day, he enjoyed threatening those who disagreed with him by blurting, “I will annihilate you!” His personal hygiene was, well, suffice it to say he had none. He was heartlessly cruel to his family and anyone who crossed him. This is the same man who postured as a thinker whose ideas would save humanity.
We learn in Intellectuals that the chef who cooked up communism professed to be “scientific”. In reality, Johnson argues, “there was nothing scientific about him; indeed, in all that matters he was anti-scientific”. His most famous lines — including “religion is the opiate of the masses” and workers “have nothing to lose but their chains” — were flagrantly ripped off from other authors. He “never set foot in a mill, factory, mine or other industrial workplace in the whole of his life”, steadfastly abjured invitations to do so, and denounced fellow revolutionaries who did. He never let a fact or a glimmer of reality stem the flow of poison from his pen. He had no money because he refused to work for it, then cursed those who had it and didn’t share it with him. His own mother said she wished her son “would accumulate some capital instead of just writing about it”.
And that’s for starters. Read Johnson’s chapter on Marx, and you’ll begin to understand the connection between the evil within the man and the evil his gibberish wrought. The Black Book of Communism estimates the death toll from attempts to put the rantings of this detestable lunatic into practice at minimally 100 million.
“What emerges from a reading of Capital is Marx’s fundamental failure to understand capitalism”, writes Johnson.
He failed precisely because he was unscientific: he would not investigate the facts himself, or use objectively the facts investigated by others. From start to finish, not just Capital but all his work reflects a disregard for truth which at times amounts to contempt. That is the primary reason why Marxism, as a system, cannot produce the results claimed for it; and to call it “scientific” is preposterous.
Many people who don’t know better, and an awful lot of those in “intellectual” circles who should, still think Karl Marx was some sort of prescient genius motivated by compassion for workers. Some even disgrace themselves with T-shirts bearing his unkempt image. They really ought to thank Paul Johnson for doing the thinking they themselves never made time for.
Actually, we were warned about people like Marx 2,000 years before Johnson. Matthew 7:16 wisely counsels:
Beware of false prophets. They come to you in sheep’s clothing, but inwardly they are ravenous wolves. By their fruit you will know them. Are grapes gathered from thornbushes, or figs from thistles? Likewise, every good tree bears good fruit, but a bad tree bears bad fruit.
Karl Marx was one hollow and rotten tree, inside and out, from beginning to end.
December 6, 2022
The coming of the Korean War
In Quillette, Niranjan Shankar outlines the world situation that led to the outbreak of the Korean War in 1950:
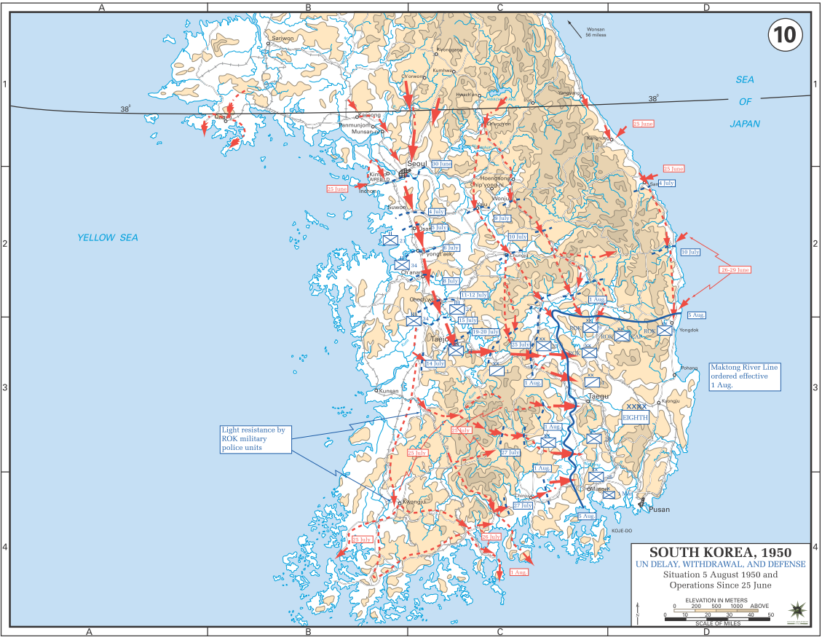
Initial phase of the Korean War, 25 June through 5 August, 1950.
Map from the West Point Military Atlas — https://www.westpoint.edu/academics/academic-departments/history/korean-war
The Korean War was among the deadliest of the Cold War’s battlegrounds. Yet despite yielding millions of civilian deaths, over 40,000 US casualties, and destruction that left scars which persist on the peninsula today, the conflict has never received the attention (aside from being featured in the sitcom M*A*S*H) devoted to World War II, Vietnam, and other 20th-century clashes.
But like other neglected Cold War front-lines, the “Forgotten War” has fallen victim to several politicized and one-sided “anti-imperialist” narratives that focus almost exclusively on the atrocities of the United States and its allies. The most recent example of this tendency was a Jacobin column by James Greig, who omits the brutal conduct of North Korean and Chinese forces, misrepresents the underlying cause of the war, justifies North Korea’s belligerence as an “anti-colonial” enterprise, and even praises the regime’s “revolutionary” initiatives. Greig’s article was preceded by several others, which also framed the war as an instance of US imperialism and North Korea’s anti-Americanism as a rational response to Washington’s prosecution of the war. Left-wing foreign-policy thinker Daniel Bessner also alluded to the Korean War as one of many “American-led fiascos” in his essay for Harper’s magazine earlier this summer. Even (somewhat) more balanced assessments of the war, such as those by Owen Miller, tend to overemphasize American and South Korean transgressions, and don’t do justice to the long-term consequences of Washington’s decision to send troops to the peninsula in the summer of 1950. By giving short shrift to — or simply failing to mention — the communist powers’ leading role in instigating the conflict, and the violence and suffering they unleashed throughout it, these depictions of the Korean tragedy distort its legacy and do a disservice to the millions who suffered, and continue to suffer, under the North Korean regime.
Determining “who started” a military confrontation, especially an “internal” conflict that became entangled in great-power politics, can be a herculean task. Nevertheless, post-revisionist scholarship (such as John Lewis Gaddis’s The Cold War: A New History) that draws upon Soviet archives declassified in 1991 has made it clear that the communist leaders, principally Joseph Stalin and North Korean leader Kim Il-Sung, were primarily to blame for the outbreak of the war.
After Korea, a Japanese imperial holding, was jointly occupied by the United States and the Soviet Union in 1945, Washington and Moscow agreed to divide the peninsula at the 38th parallel. In the North, the Soviets worked with the Korean communist and former Red Army officer Kim Il-Sung to form a provisional “People’s Committee”, while the Americans turned to the well-known Korean nationalist and independence activist Syngman Rhee to establish a military government in the South. Neither the US nor the USSR intended the division to be permanent, and until 1947, both experimented with proposals for a united Korean government under an international trusteeship. But Kim and Rhee’s mutual rejection of any plan that didn’t leave the entire peninsula under their control hindered these efforts. When Rhee declared the Republic of Korea (ROK) in 1948, and Kim declared the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK) later that year, the division was cemented. Each nation threatened to invade the other and began preparing to do so.
What initially prevented a full-scale attack by either side was Washington’s and Moscow’s refusal to provide their respective partners with support for the military reunification of the peninsula. Both superpowers had withdrawn their troops by 1949 to avoid being dragged into an unnecessary war, and the Americans deliberately withheld weapons from the ROK that could be used to launch an invasion.
However, Stalin began to have other ideas. Emboldened by Mao Zedong’s victory in the Chinese Civil War and frustrated by strategic setbacks in Europe, the Soviet premier saw an opportunity to open a “second-front” for communist expansion in East Asia with Beijing’s help. Convinced that Washington was unlikely to respond, Stalin gave Kim Il-Sung his long-sought “green-light” to reunify the Korean peninsula under communist rule in April 1950, provided that Mao agreed to support the operation. After Mao convinced his advisers (despite some initial difficulty) of the need to back their Korean counterparts, Red Army military advisers began working extensively with the Korean People’s Army (KPA) to prepare for an attack on the South. When Kim’s forces invaded on June 25th, 1950, the US and the international community were caught completely off-guard.
Commentators like Greig, who contest the communists’ culpability in starting the war, often rely on the work of revisionist historian Bruce Cumings, who highlights the perpetual state of conflict between the two Korean states before 1950. It is certainly true that there were several border skirmishes over the 38th parallel after the Soviet and American occupation governments were established in 1945. But this in no way absolves Kim and his foreign patrons for their role in unleashing an all-out assault on the South. Firstly, despite Rhee’s threats and aggressive posturing, the North clearly had the upper hand militarily, and was much better positioned than the South to launch an invasion. Whereas Washington stripped Rhee’s forces of much of their offensive capabilities, Moscow was more than happy to arm its Korean partners with heavy tanks, artillery, and aircraft. Many KPA soldiers also had prior military experience from fighting alongside the Chinese communists during the Chinese Civil War.
Moreover, as scholar William Stueck eloquently maintains, the “civil” aspect of the Korean War fails to obviate the conflict’s underlying international dimensions. Of course, Rhee’s and Kim’s stubborn desire to see the country fully “liberated” thwarted numerous efforts to establish a unified Korean government, and played a role in prolonging the war after it started. It is unlikely that Stalin would have agreed to support Pyongyang’s campaign to reunify Korea had it not been for Kim’s persistent requests and repeated assurances that the war would be won quickly. Nevertheless, the extensive economic and military assistance provided to the North Koreans by the Soviets and Chinese (the latter of which later entered the war directly), the subsequent expansion of Sino-Soviet cooperation, the Stalinist nature of the regime in Pyongyang, Kim’s role in both the CCP and the Red Army, and the close relationship between the Chinese and Korean communists all strongly suggest that without the blessing of his ideological inspirators and military supporters, Kim could not have embarked on his crusade to “liberate” the South.
Likewise, Rhee’s education in the US and desire to emulate the American capitalist model in Korea were important international components of the conflict. More to the point, all the participants saw the war as a confrontation between communism and its opponents worldwide, which led to the intensification of the Cold War in other theaters as well. The broader, global context of the buildup to the war, along with the UN’s authorization for military action, legitimized America’s intervention as a struggle against international communist expansionism, rather than an unwelcome intrusion into a civil dispute among Koreans.
QotD: Mao Zedong’s theory of “Protracted War”
The foundation for most modern thinking about this topic begins with Mao Zedong’s theorizing about what he called “protracted people’s war” in a work entitled – conveniently enough – On Protracted War (1938), though while the Chinese Communist Party would tend to subsequently represent the ideas there are a singular work of Mao’s genius, in practice he was hardly the sole thinker involved. The reason we start with Mao is that his subsequent success in China (though complicated by other factors) contributed to subsequent movements fighting “wars of national liberation” consciously modeled their efforts off of this theoretical foundation.
The situation for the Chinese Communists in 1938 was a difficult one. The Chinese Red Army has set up a base of power in the early 1930s in Jiangxi province in South-Eastern China, but in 1934 had been forced by Kuomintang Nationalist forces under Chiang Kai-shek to retreat, eventually rebasing over 5,000 miles away (they’re not able to straight-line the march) in Shaanxi in China’s mountainous north in what became known as The Long March. Consequently, no one could be under any illusions of the relative power of the Chiang’s nationalist forces and the Chinese Red Army. And then, to make things worse, in 1937, Japan had invaded China (the Second Sino-Japanese War, which was a major part of WWII), beating back the Nationalist armies which had already shown themselves to be stronger than the Communists. So now Mao has to beat two armies, both of which have shown themselves to be much stronger than he is (though in the immediate term, Mao and Chiang formed a “United Front” against Japan, though tensions remained high and both sides expected to resume hostilities the moment the Japanese threat was gone). Moreover, Mao’s side lacks not only the tools of war, but the industrial capacity to build the tools of war – and the previous century of Chinese history had shown in stark terms how difficult a situation a non-industrial force faced in squaring off against industrial firepower.
That’s the context for the theory.
What Mao observed was that a “war of quick decision” would be one that the Red Army would simply lose. Because he was weaker, there was no way to win fast, so trying to fight a “fast” war would just mean losing. Consequently, a slow war – a protracted war – was necessary. But that imposes problems – in a “war of quick decision” the route to victory was fairly clear: destroy enemy armed forces and seize territory to deny them the resources to raise new forces. Classic Clausewitzian (drink!) stuff. But of course the Red Army couldn’t do that in 1938 (they’d just lose), so they needed to plan another potential route to victory to coordinate their actions. That is, they need a strategic framework – remember that strategy is the level of military analysis where we think about what our end goals should be and what methods we can employ to actually reach those goals (so that we are not just blindly lashing out but in fact making concrete progress towards a desired end-state).
Mao understands this route as consisting of three distinct phases, which he imagines will happen in order as a progression and also consisting of three types of warfare, all of which happen in different degrees and for different purposes in each phase. We can deal with the types of warfare first:
- Positional Warfare is traditional conventional warfare, attempting to take and hold territory. This is going to be done generally by the regular forces of the Red Army.
- Mobile Warfare consists of fast-moving attacks, “hit-and-run”, performed by the regular forces of the Red Army, typically on the flanks of advancing enemy forces.
- Guerrilla Warfare consists of operations of sabotage, assassination and raids on poorly defended targets, performed by irregular forces (that is, not the Red Army), organized in the area of enemy “control”.
The first phase of this strategy is the enemy strategic offensive (or the “strategic defensive” from the perspective of Mao). Because the enemy is stronger and pursuing a conventional victory through territorial control, they will attack, advancing through territory. In this first phase, trying to match the enemy in positional warfare is foolish – again, you just lose. Instead, the Red Army trades space for time, falling back to buy time for the enemy offensive to weaken rather than meeting it at its strongest, a concept you may recall from our discussions of defense in depth. The focus in this phase is on mobile warfare, striking at the enemy’s flanks but falling back before their main advances. Positional warfare is only used in defense of the mountain bases (where terrain is favorable) and only after the difficulties of long advances (and stretched logistics) have weakened the attacker. Mobile warfare is supplemented by guerrilla operations in rear areas in this phase, but falling back is also a key opportunity to leave behind organizers for guerrillas in the occupied zones that, in theory at least, support the retreating Red Army (we’ll come back to this).
Eventually, due to friction (drink!) any attack is going to run out of steam and bog down; the mobile warfare of the first phase is meant to accelerate this, of course. That creates a second phase, “strategic stalemate” where the enemy, having taken a lot of territory, is trying to secure their control of it and build new forces for new offensives, but is also stretched thin trying to hold and control all of that newly seized territory. Guerrilla attacks in this phase take much greater importance, preventing the enemy from securing their rear areas and gradually weakening them, while at the same time sustaining support by testifying to the continued existence of the Red Army. Crucially, even as the enemy gets weaker, one of the things Mao imagines for this phase is that guerrilla operations create opportunities to steal military materiel from the enemy so that the factories of the industrialized foe serve to supply the Red Army – safely secure in its mountain bases – so that it becomes stronger. At the same time (we’ll come back to this), in this phase capable recruits are also be filtered out of the occupied areas to join the Red Army, growing its strength.
Finally in the third stage, the counter-offensive, when the process of weakening the enemy through guerrilla attacks and strengthening the Red Army through stolen supplies, new recruits and international support (Mao imagines the last element to be crucial and in the event it very much was), the Red Army can shift to positional warfare again, pushing forward to recapture lost territory in conventional campaigns.
Through all of this, Mao stresses the importance of the political struggle as well. For the guerrillas to succeed, they must “live among the people as fish in the sea”. That is, the population – and in the China of this era that meant generally the rural population – becomes the covering terrain that allows the guerrillas to operate in enemy controlled areas. In order for that to work, popular support – or at least popular acquiescence (a village that doesn’t report you because it supports you works the same way as a village that doesn’t report you because it hates Chiang or a village that doesn’t report you because it knows that it will face violence reprisals if it does; the key is that you aren’t reported) – is required. As a result both retreating Red Army forces in Phase I need to prepare lost areas politically as they retreat and then once they are gone the guerrilla forces need to engage in political action. Because Mao is working with a technological base in which regular people have relatively little access to radio or television, a lot of the agitation here is imagined to be pretty face-to-face, or based on print technology (leaflets, etc), so the guerrillas need to be in the communities in order to do the political work.
Guerrilla actions in the second phase also serve a crucial political purpose: they testify to the continued existence and effectiveness of the Red Army. After all, it is very important, during the period when the main body of Communist forces are essentially avoiding direct contact with the enemy that they not give the impression that they are defeated or have given up in order to sustain will and give everyone the hope of eventual victory. Everyone there of course also includes the main body of the army holed up in its mountain bases – they too need to know that the cause is still active and that there is a route to eventual victory.
Fundamentally, the goal here is to make the war about mobilizing people rather than about mobilizing industry, thus transforming a war focused on firepower (which you lose) into a war about will – in the Clausewitzian (drink! – folks, I hope you all brought more than one drink for this …) sense – which can be won, albeit only slowly, as the slow trickle of casualties and defeats in Phase II steadily degrades enemy will, leading to their weakness and eventual collapse in Phase III.
I should note that Mao is very open that this protracted way of war would be likely to inflict a lot of damage on the country and a lot of suffering on the people. Casualties, especially among the guerrillas, are likely to be high and the guerrillas own activities would be likely to produce repressive policies from the occupiers (not that either Chiang’s Nationalists of the Imperial Japanese Army – or Mao’s Communists – needed much inducement to engage in brutal repression). Mao acknowledges those costs but is largely unconcerned by them, as indeed he would later as the ruler of a unified China be unconcerned about his man-made famine and repression killing millions. But it is important to note that this is a strategic framework which is forced to accept, by virtue of accepting a long war, that there will be a lot of collateral damage.
Now there is a historical irony here: in the event, Mao’s Red Army ended up not doing a whole lot of this. The great majority of the fighting against Japan in China was positional warfare by Chiang’s Nationalists; Mao’s Red Army achieved very little (except preparing the ground for their eventual resumption of war against Chiang) and in the event, Japan was defeated not in China but by the United States. Japanese forces in China, even at the end of the war, were still in a relatively strong position compared to Chinese forces (Nationalist or Communist) despite the substantial degradation of the Japanese war economy under the pressure of American bombing and submarine warfare. But the war with Japan left Chiang’s Nationalists fatally weakened and demoralized, so when Mao and Chiang resumed hostilities, the former with Soviet support, Mao was able to shift almost immediately to Phase III, skipping much of the theory and still win.
Nevertheless, Mao’s apparent tremendous success gave his theory of protracted war incredible cachet, leading it to be adapted with modifications (and variations in success) to all sorts of similar wars, particularly but not exclusively by communist-aligned groups.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How the Weak Can Win – A Primer on Protracted War”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-03-03.
November 29, 2022
Near Peer: Russia
Army University Press
Published 25 Nov 2022AUP’s Near Peer film series continues with a timely discussion of Russia and its military. Subject matter experts discuss Russian history, current affairs, and military doctrine. Putin’s declarations, advances in military technology, and Russia’s remembrance of the Great Patriotic War are also addressed. “Near Peer: Russia” is the second film in a four-part series exploring America’s global competitors.
November 28, 2022
Near Peer: China (Understanding the Chinese Military)
Army University Press
Published 29 Jul 2022This film examines the Chinese military. Subject matter experts discuss Chinese history, current affairs, and military doctrine. Topics range from Mao, to the PLA, to current advances in military technologies. “Near Peer: China” is the first film in a four-part series exploring America’s global competitors.
(more…)
November 27, 2022
Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn and One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich
In Quillette, Robin Ashenden discusses the life experiences of Aleksandr Slozhenitsyn that informed the novel that made him famous:
The book was published less than 10 years after the death of Joseph Stalin, the dictator who had frozen his country in fear for nearly three decades and subjected his people to widespread deportation, imprisonment, and death. His successor Nikita Khrushchev — a man who, by his own admission, came to the job “elbow deep in blood” — had set out on a redemptive mission to liberalise the country. The Gulags had been opened and a swathe of prisoners freed; Khrushchev had denounced his predecessor publicly as a tyrant and a criminal and, at the 22nd Party Congress in October 1961, a full programme of de-Stalinisation had been announced. As for the Arts, previously neutered by the Kremlin’s policy of “Socialist Realism” — in which the values of Communism had to be resoundingly affirmed — they too were changing. Now, a new openness and a new realism was called for by Khrushchev’s supporters: books must tell the truth, even the uncomfortable truth about Communist reality … up to a point. That this point advanced or retreated as Khrushchev’s power ebbed and flowed was something no writer or publisher could afford to miss.
Solzhenitsyn’s book told the story of a single day in the 10-year prison-camp sentence of a Gulag inmate (or zek) named Ivan Denisovich Shukhov. Following decades of silence about Stalin’s prison-camp system and the innocent citizens languishing within it, the book’s appearance seemed to make the ground shake and fissure beneath people’s feet. “My face was smothered in tears,” one woman wrote to the author after she read it. “I didn’t wipe them away or feel ashamed because all this, packed into a small number of pages … was mine, intimately mine, mine for every day of the fifteen years I spent in the camps.” Another compared his book to an “atomic bomb”. For such a slender volume — about 180 pages — the seismic wave it created was a freak event.
As was the story of its publication. By the time it came out, there was virtually no trauma its author — a 44-year-old married maths teacher working in the provincial city of Ryazan — had not survived. After a youth spent in Rostov during the High Terror of Stalin’s 1930s, Solzhenitsyn had gone on to serve eagerly in the Red Army at the East Prussian front, before disaster struck in 1945. Arrested for some ill-considered words about Stalin in a letter to a friend, he was handed an eight-year Gulag sentence. In 1953, he was sent into Central Asian exile, only to be diagnosed with cancer and given three weeks to live. After a miraculous recovery, he vowed to dedicate this “second life” to a higher purpose. His writing, honed in the camps, now took on the ruthless character of a holy mission. In this, he was fortified by the Russian Orthodox faith he’d rediscovered during his sentence, and which had replaced his once-beloved, now abandoned Marxism.
Solzhenitsyn had, since his youth, wanted to make his mark as a Russian writer. In the Gulag, he’d written cantos of poetry in his head, memorized with the help of matchsticks and rosary beads to hide it from the authorities. During his Uzbekistan exile, he’d follow a full day’s work with hours of secret nocturnal writing about the darker realities of Soviet life, burying his tightly rolled manuscripts in a champagne bottle in the garden. Later, reunited with the wife he’d married before the war, he warned her to expect no more than an hour of his company a day — “I must not swerve from my purpose.” No friendships — especially close ones — were allowed to develop with his fellow Ryazan teachers, lest they take up valuable writing time, discover his perilous obsession, or blow his cover. Subterfuge became second nature: “The pig that keeps its head down grubs up the tastiest root.” Yet throughout it all, he was sceptical that his work would ever be available to the general public: “Publication in my lifetime I must put out of my mind.”
After the 22nd Party Congress, however, Solzhenitsyn recognised that the circumstances were at last propitious, if all too fleeting. “I read and reread those speeches,” he wrote later, “and the walls of my secret world swayed like curtains in the theatre … had it arrived, then, the long-awaited moment of terrible joy, the moment when my head must break water?” It seemed that it had. He got out one of his eccentric-looking manuscripts — double-sided, typed without margins, and showing all the signs of its concealment — and sent it to the literary journal of his choice. That publication was the widely read, epoch-making Novy Mir (“New World”), a magazine whose progressive staff hoped to drag society away from Stalinism. They had kept up a steady backwards-forwards dance with the Khrushchev regime throughout the 1950s, invigorated by the thought that each new issue might be their last.
November 12, 2022
QotD: The short careers of secret police chiefs
The first thing you learn on even the most cursory look at any secret police is: they aren’t. Secret, that is. Otherwise they wouldn’t be effective. Oh, they’d probably be a lot better at gathering certain kinds of intel, but intelligence gathering is really only their secondary function. Their primary function, of course, is intimidation. That’s why every Hans and Franz on the street in Nazi Germany could tell you exactly where the nearest Gestapo office was.
(The Romanian Securitate had public intimidation down to an art form. They’d follow random guys around using big, obvious details, the better to prove to the proletariat that everyone was suspect. It is to them, not Mafia dons or aspiring rappers, that we owe the now-standard Eurotrash track suit look).
Secret police goons suffer from two serious structural problems, though, that not even the guys in Stove’s book [The Unsleeping Eye] really ever solved. The first is the obvious one, that guys who know where the bodies are buried are always at risk of using that knowledge. Napoleon’s guy Joseph Fourche, and FDR’s main man J. Edgar, lived out their natural lives (as did Elizabeth’s spymaster Sir Francis Walsingham), but of them, only Fourche lived in anything approaching what we would call an ideologized society, and that was small beer.
The rest of those guys died in harness, because of course they did. Adolf Hitler was an especially stupid dictator, and Heinrich Himmler an especially servile little freak, but I have no doubt that if the Reich had gone on much longer [Himmler] would’ve shanked [Hitler]. If Heydrich hadn’t gotten perforated in Prague, he no doubt would’ve gone after [Himmler] even sooner. Lenin and especially Stalin burned through secret police chiefs on the regular, because they pretty much had to.
I don’t know about the goons in the Chinese etc. secret police, but I’d be shocked to find anyone with more than a few years’ tenure, because purges are simply a way of life in totally ideologized societies. For every Khrushchev who manages to hang on – n.b. he was a Red Army commissar during the war, i.e. a not-so-secret police goon — there are fifty guys who live fast and die hard, because that’s just how totalitarians rule.
The stoyaknik, of course, is well served to consider the current scene as if he were watching the Politburo of an exceptionally deluded Commie regime, one made up almost entirely of ruthless yet clueless retards … who still believe, for the most part, in Communism.
That was always the problem for Kremlinologists in evaluating the USSR — whatever the Boss of the moment decided would, of course, immediately be retconned into the Scriptures by the Academicians, but what did the Big Guy himself think about it? That constrained his choices. Stalin and Khrushchev were true Communists, there’s no question about that, but they came up in the school of the hardest possible knocks — if they needed to do something directly contrary to Leninism in order to hang on to power, then Comrade Ilych can suck it.
For anything short of mortal, though, they’d more often than not behave as stereotypical Commies, so the first thing any Kremlinologist had to do was determine the seriousness of the situation from the Politburo’s perspective. Not an easy task, as you might imagine, and what made it worse was: as the USSR gained stability and Communism matured, the old school hardasses all died off and were replaced by True Believers. Mikhail Gorbachev, for instance, didn’t start making his mark until after Stalin’s death, and he wasn’t a real up-and-comer until after Khrushchev — that is, he started rising through the ranks only after the hard boys were gone.
Thus, while Khrushchev was a true Commie, he still had some hard reality to constrain him. Gorby didn’t. He really believed all that Marxist-Leninist horseshit about democracy and etc.; he was far more doctrinaire than the earlier generation could possibly be. Thus Kremlinologists were forever baffled when he did stupid things that made no sense from the Realpolitik perspective, but were perfectly in keeping with the Scriptures. They thought Perestroika was some big 4D chess feint, for instance, instead of just a soft boy doing something noodle-headed.
Severian, “Book Review: The Unsleeping Eye by R.J. Stove”, Founding Questions, 2022-08-09.
November 7, 2022
Inside the Gulag System – WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 4 Nov 2022Even as the Allied powers condemn the German crimes against humanity, their recent victories are in part thanks to the massive system of forced labour built by Joseph Stalin’s Soviet Union. Over one million prisoners work in the Gulag to power the Soviet war economy.
(more…)
October 29, 2022
Witches, beware! It’s the Malleus Maleficarum!
It’s the season for ghosts, goblins, and — of course — witches, so Scott Alexander decided to review that famous book for witch-hunters, the Malleus Maleficarum:
Did you know you can just buy the Malleus Maleficarum? You can go into a bookstore and say “I would like the legendary manual of witch-hunters everywhere, the one that’s a plot device in dozens of tired fantasy novels”. They will sell it to you and you can read it.
I recommend the Montague Summers translation. Not because it’s good (it isn’t), but because it’s by an slightly crazy 1920s deacon every bit as paranoid as his subject matter. He argues in his Translator’s Introduction that witches are real, and that a return to the wisdom of the Malleus is our only hope of standing against them:
Although it may not be generally recognized, upon a close investigation it seems plain that the witches were a vast political movement, an organized society which was anti-social and anarchical, a world-wide plot against civilization. Naturally, although the Masters were often individuals of high rank and deep learning, that rank and file of the society, that is to say, those who for the most part fell into the hands of justice, were recruited from the least educated classes, the ignorant and the poor. As one might suppose, many of the branches or covens in remoter districts knew nothing and perhaps could have understood nothing of the enormous system. Nevertheless, as small cogs in a very small [sic] wheel, it might be, they were carrying on the work and actively helping to spread the infection.
And is this “world-wide plot against civilization” in the room with us right now? In the most 1920s argument ever, Summers concludes that this conspiracy against civilization has survived to the modern day and rebranded as Bolshevism.
Paging Arthur Miller…You can just buy the Malleus Maleficarum. So, why haven’t you? Might the witches’ spiritual successors be desperate to delegitimize the only thing they’re truly afraid of — the vibrant, time-tested witch hunting expertise of the Catholic Church? Summers writes:
It is safe to say that the book is to-day scarcely known save by name. It has become a legend. Writer after writer, who had never turned the pages, felt himself at liberty to heap ridicule and abuse upon this venerable volume … He did not know very clearly what he meant, and the humbug trusted that nobody would stop to inquire. For the most part his confidence was respected; his word was taken.
We must approach this great work — admirable in spite of its trifling blemishes — with open minds and grave intent; if we duly consider the world of confusion, of Bolshevism, of anarchy and licentiousness all around to-day, it should be an easy task for us to picture the difficulties, the hideous dangers with which Henry Kramer and James Sprenger were called to combat and to cope … As for myself, I do not hesitate to record my judgement … the Malleus Maleficarum is one of the most pregnant and most interesting books I know in the library of its kind.
Big if true.
I myself read the Malleus in search of a different type of wisdom. We think of witch hunts as a byword for irrationality, joking about strategies like “if she floats, she’s a witch; if she drowns, we’ll exonerate the corpse”. But this sort of snide superiority to the past has led us wrong before. We used to make fun of phlogiston, of “dormitive potencies”, of geocentric theory. All these are indeed false, but more sober historians have explained why each made sense at the time, replacing our caricatures of absurd irrationality with a picture of smart people genuinely trying their best in epistemically treacherous situations. Were the witch-hunters as bad as everyone says? Or are they in line for a similar exoneration?
The Malleus is traditionally attributed to 15th century theologians/witch-hunters Henry Kramer and James Sprenger, but most modern scholars think Kramer wrote it alone, then added the more famous Sprenger as a co-author for a sales boost. The book has three parts. Part 1 is basically Summa Theologica, except all the questions are about witches. Part 2 is basically the DSM 5, except every condition is witchcraft. Part 3 is a manual for judges presiding over witch trials. We’ll go over each, then return to this question: why did a whole civilization spend three centuries killing thousands of people over a threat that didn’t exist?
September 26, 2022
QotD: “Comrades of proven worth”
This would be funny if it wasn’t quite such a jarring reminder of how the Soviets used to manage matters. The revolutionary vanguard were not held to the same standards as everyone else because, you know, they were the revolutionary vanguard, leaders of the people. They thus got all the nice apartments in central Moscow as they had to be close to the Ministries where they directed the peasants. They didn’t have to share the apartment because they needed to rest after their labours. And surely those working for the workers should be well rewarded?
So too they didn’t have to line up for the scraps of whatever rotting junk the ration stores had. The KGB, for example, had its own commissary just around the back of Lubyanka – I know, I’ve shopped in it. And higher ranks simply never needed to go shopping at all, the nomenklatura had the government delivery service. Ocado for commies but only really important commies.
This all came under the rubric of comrades of proven worth…
Tim Worstall, “Emma Thompson Is A Comrade Of Proven Worth To Extinction Rebellion”, Continental Telegraph, 2019-04-19.
September 21, 2022
QotD: Why postwar western economic and humanitarian “interventions” almost always failed
… it is a general truism that the majority of persons who run for office in North America and various European countries do so because they sincerely want to help and improve their communities/countries. However, in all of Africa and most of Asia, persons who seek public office do so for one purpose, and one purpose only: to steal everything that they can get away with. So when some ignorant, naïve, American shows up with buckets full of money, oblivious of the culture and the longstanding, entrenched, corruption, and with an announced intention to make the local community more like an American community, they are welcomed with open arms while suppressing their snickering. This also explains something where Americans exhibit willful blindness: other cultures don’t play fair. Honesty is seen as the trait of fools. Fools are to be taken advantage of. Especially in trade and diplomacy. Just look at China.
Prior to the Cold War, America’s interference in other countries’ internal affairs was practically nonexistent outside of the Caribbean where America’s preoccupation was with the stability in the region. What went on in Egypt, Thailand, Argentina, or Greece was none of our business, nor did we frankly care. However, having just survived the cataclysm of WWII, and the realization that Communism was a danger bent on world domination, and that each country that became Communist made that possibility much more likely changed that laissez faire attitude 180 degrees. Whereas NATO was formed for the purpose of deterring a military attack on Western Europe by the Soviet Union (the generals mentally fighting the last war as is always the case, not realizing that the war now was ideological and propagandistic rather than military), diplomats began to question how to best combat Communist insurgencies in the Third World. The arrived (wrong) conclusion was that the reason a country became Communist was because the dirt-poor people were so desperate that they became Marxists in order to improve their lives, so if the West helped poor countries economically Communists could not gain a foothold. As such, they ignored the fact that most Communist movements are organized and headed not by poor people, but by a cadre of power-hungry middle-class intellectuals.
As has been mentioned, the first approach was with foreign aid. The second was with military intervention, in Korea, Vietnam, Santo Domingo, Grenada, and Lebanon. Although such interventions were mostly successful, they carried a heavy price as American blood was spilled in foreign countries. America’s supposed allies hardly helped at all, including the citizens of the countries (Korea and Vietnam) that themselves were in danger of being conquered by Communist forces.
Armando Simón, “Schlimmbesserung“, New English Review, 2022-06-16.