In The Critic, Jonathan Glancey sings the praises of the steam locomotive designs and liveries of the pre-nationalization Great Western Railway:
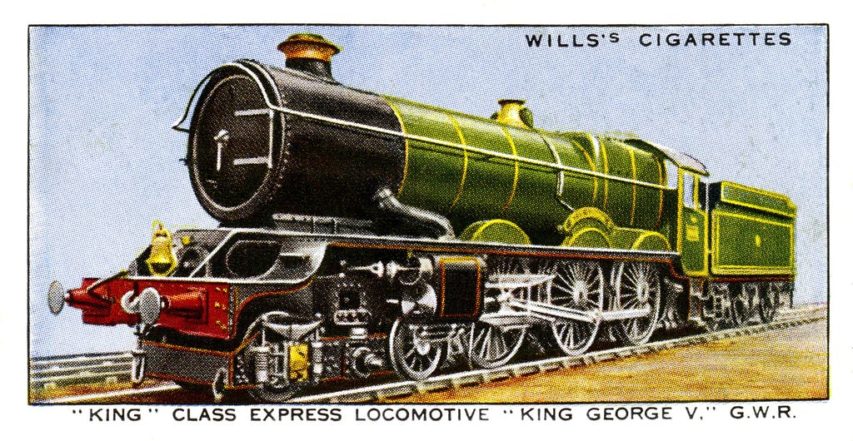
The greatest of all Great Western Railway locomotives were the King Class 4-6-0s. From 1927, and for more than 30 years, they headed principal express trains from Paddington to Bristol, Plymouth, South Wales and the West Midlands with power, precision and truly regal style.
In a livery of lined dark green with copper-capped chimneys, brass safety valve covers, and names emblazoned above their driving wheels, the Kings led long chocolate and cream-coloured trains through landscapes they enhanced in days of both private and public ownership. Together with their less powerful shed-mates — Castles, Halls, Granges and Manors — these puissant machines breathed “Great Western” with every beat of their crisp exhausts.
In the beginning, the Kings were to have been Cathedrals, an appropriate name for locomotives representing a concern that, incorporated in 1835 and engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, was revered by many employees, passengers and most enthusiasts as something more akin to a religion than a mere railway. Its engineering was progressive, and yet its corporate identity (what today’s marketing jargoneers would call its “brand”) retained a gloriously ecclesiastical and slightly old-fashioned air throughout the railway’s life.
Sir William Stanier, a Great Western engineer who moved from Swindon to the LMS at Crewe and then to the chairmanship of Power Jets in the Second World War, was asked by Cuthbert Hamilton Ellis, a writer on railways, “whether there was some nameless cabal at Swindon which ruled the styling of a Great Western locomotive” from the latest 1940s designs back through the Edwardian Saints and Stars to engines of the 1880s designed by William Dean. Stanier smiled and exclaimed: “Dean? Gooch! [the GWR’s first locomotive engineer]. It was traditional.”
The tradition lives on. In 2015, today’s Great Western Railway — an operation owned by the multi-national FirstGroup — adopted a handsome dark green livery, created by the design agency Pentagram, that reaches back to the Kings and, by association, all the way to Gooch and Brunel.
The new look was sung as if from the Great Western’s “Ancient and Modern” hymn book of design. In a privatised railway world of largely gimcrack style and branding, with all too many trains looking as if their design inspiration has been that of sports shoes or the packaging of sweets such as Refreshers, the Great Western re-introduced gravitas, continuity and regional sensibility to the way its trains looked.
This is something those in charge of the newly announced Great British Railways (GBR) should think about carefully as this new public body takes over the national railway infrastructure in 2023, its remit including corporate identity. While its name is, perhaps, rather too close to Little Britain’s Great British Air, the possibility of it exercising a civilising influence over the design of our trains is there. A national design standard and identity could yet be created that speak of the unity of the British railway network and its diversity in the same breath.