The Tank Museum
Published Aug 9, 2024The US built M47 probably isn’t the most interesting tank in history – but it was a vital part of NATO’s Cold War tank force.
Rushed into production at the outbreak of the Korean War, it never saw active service with the US military and was quickly superseded by the M48.
But large numbers were supplied to US Allies around the world – with Germany, Belgium, Italy, Portugal, Jordan, Pakistan and Austria being among the most significant users.
Probably the most famous M47 crewman of all, Arnold Schwarzenegger, served on the tank during his National Service.
00:00 | Intro
01:05 | M46 Sees Service in Korea
02:56 | Development Problems – And a Stop Gap
10:57 | Short Lived US service
12:47 | But An Export Success
15:24 | M47 plugs the gap for the US Army – goes on to serve abroad
15:46 | The Tank Museum’s M47 Restoration Project
(more…)
December 10, 2024
M47 – The Most Boring Tank Ever? | Tank Chat #178
October 21, 2024
Romanian Model 1879 Martini-Henry Rifles & Carbines
Forgotten Weapons
Published Jul 5, 2024Following its experience in the Russo-Turkish War, the Romanian Army was quite impressed by the Martini-Henry rifle in Turkish service. Unlike so many Western observers who were taken by the Winchester repeating rifles that actually didn’t make much battlefield impact, the Romanians recognized the all-around quality of the Martini. So after the war when looking to equip their own newly independent army, they went to Britain for Martinis. They were not able to get rifles made in Britain, but did purchase a license to make the rifle in .45 Gatling, which they took to a factory in Witten, in the German state of Wurtemburg. This factory was newly opened, run in part by Friedrich von Martini himself — so what better place to get Martini rifles?
An initial contract for 60,000 rifles and 8,000 carbines was accepted by the factory and delivered fairly quickly. When the Romanians came back for more guns the factory had gone bankrupt, however. Subsequent orders were instead made from OEWG Steyr in Austria. In total, Romania acquired about 145,000 Martini long rifles and between 12,000 and 18,000 carbines. They were replaced by the Model 1893 Mannlicher in the 1890s, and thus were never used as a front-line rifle in any major combat. They served in World War One in a secondary role only.
Thanks to the King Ferdinand I Military Museum for giving me access to these examples and to A.N.C.A. for coordinating the visit! If you are in Bucharest, make sure to stop in and visit the museum:
https://www.muzeulmilitar.ro/en/
(more…)
July 28, 2024
Allies Issue Potsdam Declaration – WW2 – Week 309 – July 27, 1945
World War Two
Published 27 Jul 2024China, Britain, and the US issue a Declaration demanding Japan’s unconditional surrender, and promising complete destruction if this does not happen and happen soon. The plan is to for the Americans to use their atomic bombs on Japan if she does not comply, but by the end of the week the Japanese have not replied. They still have hopes for the Soviets to mediate some sort sort of peace. What they don’t have is a navy, as its final destruction comes this week.
00:00 Intro
00:50 Recap
01:32 The Potsdam Conference
04:41 Japanese Hopes
05:56 The Potsdam Declaration
10:53 The Initial Reaction
14:48 The End Of The Japanese Navy
15:05 The War On Land
19:10 Summary
19:30 Conclusion
(more…)
June 4, 2024
Snipers in World War 1
The Great War
Published Feb 9, 2024In fall 1914, the British and French armies on the First World War’s Western Front were wrestling with a problem: unseen German riflemen were picking off any man who showed himself above the trench. Something had to be done about it – and the result was the birth of the modern sniper.
(more…)
May 6, 2024
Germans and Americans fighting side by side! – WW2 – Week 297B – May 5, 1945
World War Two
Published 5 May 2024I don’t want to give too much away about this extra regular episode here in the description, but it’s true- German and American soldiers fought side by side in the waning days of the European part of WW2, and not just once! And the second time is an all-time great tale of adventure.
(more…)
April 16, 2024
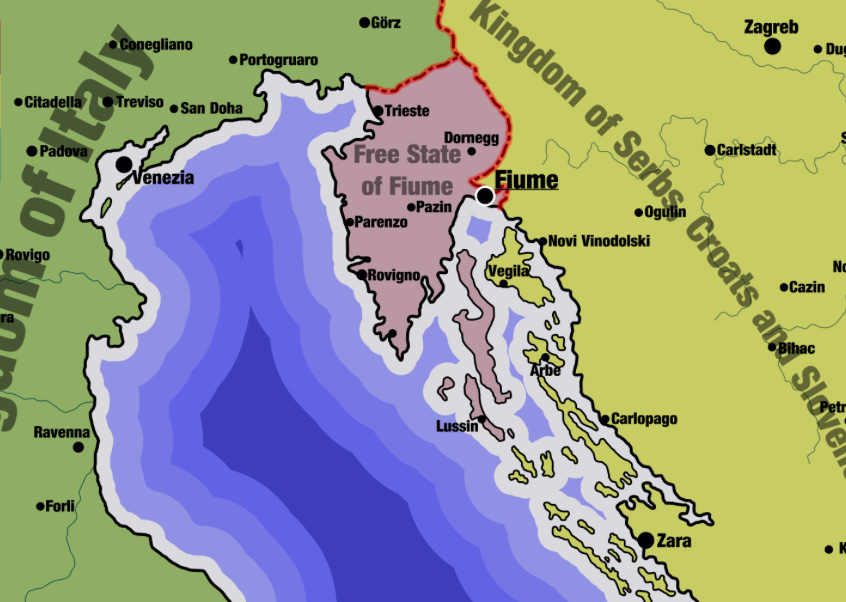
Gabriele D’Annunzio’s Impresa – the 1919 occupation of Fiume
Ned Donovan on the turbulent history of the Adriatic port of Fiume (today the Croatian city of Rijeka) after the end of the First World War:
Fiume was a port on the Adriatic coast with several thousand residents, almost half of whom were ethnic Italians that had been under Austro-Hungarian rule for several hundred years after it once having been a Venetian trade port. By some quirk, Fiume was missed in the Treaty of London, probably because it had never been envisioned by the Allies that the Austro-Hungarian Empire would ever truly disintegrate and the rump of it that would remain required a sea port in some form. The city’s other residents were ethnically Serbian and Croatian, who knew the city as Rijeka (as you will find it named on a map today). All of this complexity meant that the fate of Fiume became a major topic of controversy during the Versailles Peace Conference. President Woodrow Wilson had become so unsure of what to do that he proposed the place become a free city and the headquarters of the nascent League of Nations, under the jurisdiction of no country.
By September 1919 there was still no conclusion as to the fate of Fiume. Events had overtaken the place and through the Treaty of St Germain, the Austro-Hungarian Empire had been dissolved after the abdication of the final Habsburg Emperor Charles I. Once again, Fiume had not been mentioned in the treaty and the country it had been set aside for no longer existed. The city’s fate was still at play.
Enter Gabriele D’Annunzio, an aristocrat from Abruzzo on the eastern coast of Italy. Born in 1863, he was a handsome and intelligent child and was nurtured by his family to be exceptional, with a predictable side effect of immense selfishness. As a teenager, he had begun to dabble in poetry and it was praised by authors unaware of his age. At university he began to be associated with Italian irredentism, a philosophy that yearned for all ethnic Italians to live in one country – by retaking places under foreign rule like Corsica, Malta, Dalmatia and even Nice.
[…]
The Italian government’s lack of interest [in Fiume] was unacceptable to D’Annunzio and he made clear he would take action to prevent it becoming part of Yugoslavia by default. With his fame and pedigree he was able to quickly assemble a small private force of ex-soldiers, who he quickly took to calling his “legionaries”. In September 1919 after the Treaty of St Germain was signed, his small legion of a few hundred marched from near Venice to Fiume in what they called the Impresa – the Enterprise. By the time he had reached Fiume, the “army” numbered in the thousands, the vanguard crying “Fiume or Death” with D’Annunzio at its head in a red Fiat.
The only thing that stood in his way was the garrison of the Entente, soldiers who had been given orders to prevent D’Annunzio’s invasion by any means necessary. But amongst the garrison’s leaders were many [Italian officers] sympathetic to D’Annunzio’s vision, some even artists themselves and before long most of the defenders had deserted to join the poet’s army. On the 12th September 1919, Gabriele D’Annunzio proclaimed that he had annexed Fiume to the Kingdom of Italy as the “Regency of Carnaro” – of which he was the Regent. The Italian government was thoroughly unimpressed and refused to recognise their newest purported land, demanding the plotters give up. Instead, D’Annunzio took matters into his own hands and set up a government and designed a flag (to the right).
The citizens of what had been a relatively unimportant port quickly found themselves in the midst of one of the 20th Century’s strangest experiments. D’Annunzio instituted a constitution that combined cutting-edge philosophical ideas of the time with a curious government structure that saw the country divided into nine corporations to represent key planks of industry like seafarers, lawyers, civil servants, and farmers. There was a 10th corporation that existed only symbolically and represented who D’Annunzio called the “Supermen” and was reserved largely for him and his fellow poets.
These corporations selected members for a state council, which was joined by “The Council of the Best” and made up of local councillors elected under universal suffrage. Together these institutions were instructed to carry out a radical agenda that sought an ideal society of industry and creativity. From all over the world, famous intellectuals and oddities migrated to Fiume. One of D’Annunzio’s closest advisers was the Italian pilot Guido Keller, who was named the new country’s first “Secretary of Action” – the first action he took was to institute nationwide yoga classes which he sometimes led in the nude and encouraged all to join. When not teaching yoga, Keller would often sleep in a tree in Fiume with his semi-tame pet eagle and at least one romantic partner.
If citizens weren’t interested in yoga, they could take up karate taught by the Japanese poet Harukichi Shimoi, who had translated Dante’s works into Japanese. Shimoi, who quickly became known to the government of Fiume as “Comrade Samurai” was a keen believer in Fiume’s vision and saw it as the closest the modern world had come to putting into practice the old Japanese art of Bushido.
The whole thing would have felt like a fever dream to an outsider. If a tourist was to visit the city, they would have found foreign spies from across the world checking into hotels and rubbing shoulders with members of the Irish republican movement while others did copious amounts of cocaine, another national pastime in Fiume. The most fashionable residents of Fiume carried little gold containers of the powder, and D’Annunzio himself was said to have a voracious habit for it. Sex was everywhere one turned and the city had seen a huge inward migration of prostitutes and pimps within days of D’Annunzio’s arrival. Almost every day was a festival, and it was an odd evening if the harbour of Fiume did not see dozens of fireworks burst above it, watched on by D’Annunzio’s uniformed paramilitaries.
D’Annunzio himself lived in a palace overlooking the city, Osbert Sitwell describes walking up a steep hill to a Renaissance-style square palazzo which inside was filled with plaster flowerpots the poet had installed and planted with palms and cacti. D’Annunzio would cloister himself in his rooms for 18 hours a day and without food. Immaculate guards hid amongst the shrubs to ensure he would not be disturbed. In D’Annunzio’s study, facing the sea, he sat with statutes of saints and with French windows onto the state balcony. When he wanted to interact with his people he would wait for a crowd to form over some issue, walk to the balcony and then ask what they wanted.
April 14, 2024
Soviets Take Vienna and Königsberg – WW2 – Week 294 – April 13, 1945
World War Two
Published 13 Apr 2024The prizes of Vienna and Königsberg fall to the Soviets as they continue what seems an inexorable advance. In the West the Allies advance to the Elbe River, but there they are stopped by command. The big news in their national papers this week is the death of American President Franklin Roosevelt, which provokes rejoicing in Hitler’s bunker. The Allied fighting dash for Rangoon continues in Burma, as does the American advance on Okinawa, although Japanese resistance is stiffening and they are beginning counterattacks.
Chapters
00:32 Recap
01:05 Operation Grapeshot
01:57 Roosevelt Dies
06:01 Soviet Attack Plans for Berlin
12:45 Stalin’s Suspicions
14:31 The fall of Königsberg
17:02 The fall of Vienna
18:38 Japanese Resistance on Okinawa
20:34 The War in China
21:09 Burma and the Philippines
22:38 Summary
22:57 Conclusion
25:05 Memorial
(more…)
April 13, 2024
The Legend of the Wiener Schnitzel
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published Jan 9, 2024Variations of wienerschnitzel throughout history and its legendary origin stories, and a recipe for a 19th century version.
Fried breaded veal cutlets served with the traditional lemon wedges and parsley
City/Region: Vienna
Time Period: 1824Breaded and fried meat has been around for a very long time in many places, but it wasn’t until 1893 that we get the first mention of the word wienerschnitzel. Then in the early 20th century, the Austrian culinary scene decided to champion this term to refer to a veal cutlet that is made into a schnitzel, and restaurants in Vienna began specializing in schnitzel.
This recipe predates the term wienerschnitzel, and unlike modern versions it isn’t dredged in flour first. This makes it so that the breading doesn’t puff away from the meat, but the flavor is rich and delicious, just like I remember from my trip to Vienna. If you don’t like veal or don’t want to use it, you can use pork or chicken. It won’t technically be wienerschnitzel, but nobody’s going to judge you. You can also use another fat instead of the clarified butter, but butter gives the best flavor.
(more…)
April 8, 2024
The Battle of Okinawa Begins – WW2 – Week 293 – April 6, 1945
World War Two
Published Apr 6, 2024It’s the next step toward invading Japan’s Home Islands — invading Okinawa, and it begins April 1st. Advances are easy by land, but at sea the kamikaze menace is in full swing. In Burma, plans are made to liberate Rangoon; in the west hundreds of thousands of Germans are surrounded in the Ruhr; and in the east, the Soviets begin assaults on Königsberg and Vienna.
(more…)
February 28, 2024
Why Germany Lost the First World War
The Great War
Published Nov 10, 2023Germany’s defeat in the First World War has been blamed on all kinds of factors or has even been denied outright as part of the “stab in the back” myth. But why did Germany actually lose?
(more…)
February 25, 2024
Battleships – Ruling the Waves Across the 7 Seas – Sabaton History 124 [Official]
Sabaton History
Published Nov 16, 2023They were as much symbols of national pride as they were mighty weapons of war, but they were indeed MIGHTY. Dreadnoughts, battleships, super battleships — Sabaton has covered them in songs more than once, and today we dive into the battleship craze of the early 20th century: the Age of the Battleship!
(more…)
February 10, 2024
Napoleon’s Revenge: Wagram 1809
Epic History TV
Published Jun 21, 2019Six weeks after his bloody repulse at the Battle of Aspern-Essling, Napoleon led his reinforced army back across the Danube. The resulting clash with Archduke Charles’s Austrian army was the biggest and bloodiest battle yet seen in European history, and despite heavy French losses, resulted in a decisive strategic victory for the French Emperor.
(more…)
January 19, 2024
Vienna’s Iconic Chocolate Cake
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 17 Oct 2023
(more…)
November 23, 2023
QotD: The Austrian and Chicago schools of economics
[Bureaucracies will always expand far beyond the “problem” they were instituted to address] was, anyway, the view of that “Austrian school economist”, Ludwig von Mises, proponent like the rest in that school of “classical liberalism”. His hatred of bureaucracy was a wonderful, animated thing. In his great book, Human Action, and many others, he could become almost boring on the topic. What distinguishes the Austrian school from, say, the famous Chicago school of Milton Friedman and his ilk, was its European origin. (They were, however, consciously allied.) The “Austrians” go back, to Catholic antecedents, and their interests are not reducible to “pure economics” (scare quotes because there is no such thing). Over time it extended to broad social questions, and through a constant interest in the history of ideas. These were multilingual and multicultural, in the manner of the old Habsburg empire; where our American classical liberalism has been almost unilingually English, provincially distrustful of foreign thinkers, and buzzing with statistics. (You’ll need a degree in math.)
War propelled the “Austrian” thinkers westward, and the fall of the Berlin wall propelled the “Chicago” school east. The terms no longer have geographical significance.
What all classical liberals have in common is the passionate vindication and defence of human freedom. That is what makes them, unlike progressives, readable in subsequent generations. Their subject matter cannot become dated. The “Austrians” are also necessary to understand modern history, positively as well as negatively, in the evolution of, for instance, the Christian Democratic movement that conceived a peaceful post-war Europe, in defiance of secularizing bureaucratic trends and mass-man “ideals”. Alas, this was overall defeated by the Eurocratic trend-setters, determined to build a magnificent autocratic monument to themselves.
I have the most enchanting memory of opening the box that contained an American reprint of Human Action (big thick book), which I had ordered at the age of fifteen. I no longer own a copy, but gather it still stands as a monument to the resistance — a study of “praxeology”, or purposeful human choices, stretching so wide that even religion and morality could be touched. (Conventional economics has no time for either.) A half-century later, I can even remember the construction of an earnest reading list, that was soon abandoned when I went on the road.
One may see the great division in Western thought and politics, which the Austrian-school Friedrich Hayek traced back to Bacon and Descartes, and can be traced farther to the Nominalists of the later Middle Ages. Humans live in freedom and make choices, to be restrained only by the plainest moral codes. Or, by the alternative thesis, we are components of a machine, which the man with Power can monkey with, by implanting stimuli here and there.
We are creatures of God, or — we are replaceable parts in a bureaucracy.
David Warren, “Austrian schoolboy”, Essays in Idleness, 2019-09-17.
October 5, 2023
The Great War: Its End and Effects, Lecture by Prof Margaret MacMillan
McDonald Centre
Published 25 Jan 201922 January 2019, “How far did the Versailles Treaty make Peace?”, Professor Margaret MacMillan, Warden of St Antony’s College, Oxford. The lecture was sponsored by Christ Church Cathedral and the McDonald Centre for Theology, Ethics, and Public Life, Oxford.