These strategic (and operational) considerations dictate some of the tactical realities of most sieges. The attacker’s army is generally going to be larger and stronger, typically a lot larger and stronger, because if the two sides were anywhere near parity with each other the defender would risk a battle rather than submit to a siege. Thus the main problem the attacker faces is access: if the attacker can get into the settlement, that will typically be sufficient to ensure victory.
The problem standing between that attacking army and access was, of course, walls (though as we will see, walls rarely stand alone as part of a defensive system). Even very early Neolithic settlements often show concerns for defense and signs of fortification. The oldest set of city walls belong to one of the oldest excavated cities (which should tell us how short the interval between the development of large population centers and the need to fortify those population centers was), Jericho in the West Bank. The site was inhabited beginning around 10,000 BC and the initial phase of construction on what appears to be a city wall reinforced with a defensive tower was c. 8000 BC. It is striking just how substantial the fortifications are, given how early they were constructed: initially the wall was a 3.6m stone perimeter wall, supported by a 8.5m tall tower, all in stone. That setup was eventually reinforced with a defensive ditch dug 2.7m deep and 8.2m wide cutting through the bedrock (that is a ditch even Roel Konijnendijk could be proud of!), by which point the main wall was enhanced to be some 1.5-2m thick and anywhere from 3.7-5.2m high. That is a serious wall and unlikely the first defensive system protecting the site; chances are there were older fortifications, perhaps in perishable materials, which do not survive. Simply put, no one starts by building a 4m by 2m stone wall reinforced by a massive stone tower and a huge ditch through the bedrock; clearly city walls [were] something people had already been thinking about for some time.
I want to stress just how deep into the past a site like Jericho is. At 8000 BC, Jericho’s wall and tower pre-date the earliest writing anywhere (the Kish tablet, c. 3200 BC) by c. 4,800 years. The tower of Jericho was more ancient to the Great Pyramid of Giza (c. 2600 BC), than the Great Pyramid is to us. In short, the problem of walled cities – and taking walled cities – was a very old problem, one which predated writing by thousands of years. By the time the arrival of writing allows us to see even a little more clearly, Egypt, Mesopotamia and the Levant are already filled with walled cities, often with stunningly impressive stone or brick walls. Gilgamesh (r. 2900-2700 BC) brags about the walls of Uruk in the Epic of Gilgamesh (composed c. 2100) as enclosing more than three square miles and being made of superior baked bricks (rather than inferior mudbrick); there is evidence to suggest, by the by, that the historical Gilgamesh (or Bilgames) did build Uruk’s walls and that they would have lived up to the poem’s billing. Meanwhile, in Egypt, we have artwork like the Towns Palette, which appears to commemorate the successful sieges of a number of walled towns
So a would-be agrarian conqueror in Egypt, Mesopotamia or the Levant, from well before the Bronze Age would have already had to contest with the problem of how to seize fortified towns. Of course depictions like these make it difficult to reconstruct siege tactics (the animals on the Towns Palette likely represent armies, rather than a strategy of “use a giant bird as a siege weapon”), so we’re going to jump ahead to the (Neo)Assyrian Empire (911-609 BC; note that we are jumping ahead thousands of years).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Fortification, Part I: The Besieger’s Playbook”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-10-29.
February 10, 2026
QotD: The (historical) walls of Jericho
February 1, 2026
The Agora of Athens | A Historical Tour
Scenic Routes to the Past
Published 3 Oct 2025The Agora was the political and economic heart of ancient Athens. This tour explores its long history and evocative ruins.
Chapters
0:00 Introduction
0:47 Bouleuterion
1:44 Tholos
2:22 Monument of the Eponymous Heroes
2:56 Temple of Hephaestus
5:28 The Hellenistic Agora
6:16 Stoa of Attalos
6:57 Augustus and the Agora
8:06 Odeon of Agrippa
9:26 Herulian Wall
10:56 Overview
January 10, 2026
A Short Tour of Roman London
Scenic Routes to the Past
Published 19 Sept 2025The ruins of Londinium – London’s Roman predecessor – are not spectacular. But they are extremely interesting …
0:00 Introduction
0:40 City walls
1:47 St. Magnus the Martyr
2:26 Monument to the Great Fire
3:12 Leadenhall Market
4:10 London Mithraeum
6:19 Bank of England
7:08 Guildhall Amphitheater
8:14 The Gherkin
October 18, 2025
QotD: Civilizational survival after the Bronze Age Collapse
If post-Collapse Egypt is Britain, then perhaps post-Collapse Phoenicia is America: a relative backwater, dwarfed by the Great Powers of its day, that suddenly leaps to global prominence when the opportunity arises … but in doing so, changes in some very fundamental ways. Which raises a question about Cline’s subtitle, “The Survival of Civilizations”: what does it actually mean for a civilization to survive?
Sometimes the answer is obvious. The Assyrians and Babylonians clearly survived the Collapse: if you compare their architecture, inscriptions, artwork, settlement patterns, and political structures from the Late Bronze Age to the Iron Age, they are recognizably the same people doing the same things and talking about them in the same way. The Egyptians, too, are plainly the same civilization throughout their (very long!) history, even if they were notably weaker and less organized after the Collapse. The Hittites, just as obviously, did not survive (at least not outside their tiny rump states in northern Syria). But the Greeks and the Phoenicians are both murkier cases, albeit in very different ways.
On the one hand, Mycenaean civilization — the palace economy and administration, the population centers, the monumental architecture, the writing — indisputably vanished. The Greeks painstakingly rebuilt civilization over several hundred years, but they did it from scratch: there is no political continuity from the Mycenaean kingdoms to the states of the archaic or classical worlds. And yet as far as we can tell, there was substantial cultural continuity preserved in language and myth. Admittedly, “as far as we can tell” is doing a lot of work here: Linear B was only ever used for administrative record-keeping, so we can’t compare the Mycenaeans’ literary and political output to their successors the way we can in Assyria or Egypt. We can’t be sure that the character, the vibe, the flavor of the people remained. But the historical and archaeological records of the later Greeks contain enough similarities with the descendants of the Mycenaeans’ Indo-European brethren that the answer seems to be yes.
By contrast, civilization never collapsed in central Canaan. No one ever stopped having kings, writing, building in stone, or making art. The Bronze Age population centers were continuously occupied right up to … well, now. And yet their way of life shifted dramatically, to the point that we call them by a new name and consider them a different people. Cline thinks this is a success story: borrowing an analytical framework from a 2012 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report, he praises their “transformation”,1 which “include[d] actions that change the fundamental attributes of a system in response to actual or expected impacts”. (The Assyrians, by contrast, merely “adapted”, while the Egyptians barely “coped”.) But does there come a point when the change is so great, so fundamental, you’re no longer the same civilization? Can the Ship of Theseus really be said to have “survived”?
In the final section of his book, titled “Mycenaeans or Phoenicians”, Cline asks how we’ll react to the societal collapse we all sort of know is coming sooner or later. Our world just is too complicated, too interconnected, to survive a really massive shock (or, as in the Late Bronze Age, a “perfect storm” of smaller ones). Even the relatively mild disruptions of the past few years have revealed fragilities and vulnerabilities that we’ve done nothing to shore up since. Of course, he has an answer: Transform! Innovate! Flourish amidst chaos! Become a new iteration of yourself, like the bog-standard Canaanite cities that reinvented themselves as an Iron Age mercantile superpower and turned the Mediterranean into a “Phoenician lake”. But at what price?
Or, to think of it another way, what would you prefer for your society five hundred years from now?
Behind Door Number One: governmental collapse, abandonment of the population centers, dramatic reduction in societal complexity, and then a long, slow rebuilding where your time and your people are remembered only as myth — but when civilization is restored, it’ll be by people whose the desires, values, attitudes, and beliefs, their most basic ways of understanding the world, are still recognizably yours. They may have no idea you ever lived, but the stories that move your heart will move theirs too.
And behind Door Number Two: expansion, prosperity, and a new starring role on the world stage — but a culture so thoroughly reoriented towards that new position that what matters to you today has been forgotten. Do they remember you? Maybe, sort of, but they don’t care. They have abandoned your gods and your altars. Those few of your institutions that seem intact have in fact been hollowed out to house their new ethos. A handful of others may remain, vestigial and vaguely embarrassing. But boy howdy, line goes up.
Obviously, given our druthers, we’d all be the Assyrians: seize your opportunities, become great, but don’t lose your soul in the doing. But if it comes down to it — if, when the IPCC’s warning that “concatenated global impacts of extreme events continues to grow as the world’s economy becomes more interconnected” bears out, the Assyrian track isn’t an option — then I’d take the Greek way.
I don’t care whether, on the far side of our own Collapse, there’s still a thing we call “Congress” that makes things we call “laws”. Rome, after all, was theoretically ruled by the Senate for five hundred years of autocracy as all the meaning was leached from the retained forms of Republican governance. (Look, I’m sorry, you can call him your princeps and endow him with the powers of the consul, the tribune, the censor, and the pontifex maximus, but your emperor is still a king and the cursus honorum has no meaning when the army hands out the crown.) I don’t even really care if we still read Shakespeare or The Great Gatsby, although it would be more of a shame to lose those than the Constitution. But I do care that we value both order and liberty, however we structure our state to safeguard them. I care that we’re the sort of people who’d get Shakespeare and Fitzgerald if we had them around. Maybe we should start thinking about it before our Collapse, too.
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
- “Transformation” is always a term worth taking with a pinch of salt because so often it’s a euphemism for “total civilizational collapse”. In the chapter on the Hittites, for example, Cline quotes one archaeologist to the effect that “[a] deep transformation took place in the former core of the empire around the capital Hattusa, resulting in a drastic decrease in political complexity, a shift to a subsistence household economy and a lack of evidence for any public institutions”. Relatedly, one of my children recently transformed a nice vase into a pile of broken glass.
In this case, though, Cline really does mean transformation.
October 14, 2025
October 8, 2025
History of Britain IX: New Arrivals in the British Dark Age: Angles, Saxons, and Jutes
Thersites the Historian
Published 31 Mar 2025In this episode, we look at the invasion and overrun of most of southern Britain by newcomers from the European mainland, who set the stage for the transformation of that region into the Kingdom of England. We also explore the thorny issue of what a dark age is and why the label fits in the case of Britain.
September 23, 2025
QotD: “Bye, Phoenicia”
And now, as I promised, I’ll return to the Phoenicians, who are among Cline’s “winners” of the post-Collapse world. When things fell apart, their city-states — Sidon, Tyre, Byblos and all the rest — were just another motley collection of Canaanite settlements along the coast of what is now Lebanon. Two hundred years later, they were the centers of an enormous commercial and information network that spread across the entire Mediterranean world (and perhaps beyond). This makes them more than just resilient, Cline argues: they were actually antifragile, thriving in the chaos that followed the destruction of many of their powerful neighbors. (Can you even imagine how happy this chapter makes Nassim Taleb? Of course he blurbed the book.)
The long-distance trade of the Bronze Age had been dominated by large state actors. The ships were probably built and crewed by men from the Levantine coast, but the cargo was purchased and shipped by local representatives of the Great (and lesser) Powers of the age: luxury goods were an integral part of high-level diplomacy, so most trade was a virtual monopoly centrally directed from the palaces. When these polities were weakened (or in some dramatic cases like Ugarit completely destroyed) in the Collapse, they left behind a vacuum that independent Phoenician traders, operating without centralized control and serving only profit rather than the demands of empire, rapidly filled.
By the tenth century BC, the Phoenicians were importing silver from Spain, copper from Cyprus and Sardinia, and cinnamon from southeast Asia. They exported timber (the much-vaunted “Cedars of Lebanon”)1 and the valuable purple dye extracted from the murex sea snail, as well as a wide variety of finished luxury and quotidian goods they produced at home from raw materials obtained abroad. They founded colonies throughout the Mediterranean. And perhaps most importantly for the future of “the West”, they introduced the alphabet,2 which enabled the return of literacy to Greece and its far wider adoption than had ever been possible with Linear B.3
By the time the ascendant Neo-Assyrians began to encroach on their territory, the Phoenician city-states were so rich and economically well-connected that they were more valuable as semi-autonomous tributaries and middlemen than as conquered subjects. In fact, it was the Assyrian demands for metal (especially silver) that drove Phoenician colonization in the western Mediterranean: they founded Cadiz (Phoenician Gadir) to access the rich silver mines in the Spanish interior, as well as dozens of other smaller entrepôts along the sailing routes to and from the Levantine coast. Eventually they removed so much silver from Spanish mountains that its value in Assyria collapsed, inflated away by oversupply, just like Peruvian silver would destabilize the Spanish economy two thousand years later — but with the roles flipped. I enjoy these echoes.
It’s worth pointing out here that Phoenicians never called themselves Phoenicians: it’s a Greek word, deriving from a Mycenaean era (e.g., pre-Collapse) term for purple dye. In fact, they didn’t even have a term that clearly limned what the Greeks meant by “Phoenician” (essentially, “Levantine traders with really good ships who speak a related set of Semitic languages”). Instead, they sometimes referred to themselves more narrowly by reference to their native cities (Sidonian, Tyrian, Byblian, etc.) and other times more broadly as “Canaanite”, because of the cultural heritage they shared with the other survivors of Bronze Age Canaan. But even if they never employed it themselves, “Phoenician” is a terribly useful word, because these particular city-states had a lot in common with one another but diverged sharply from their Canaanite kin to both north and south.
Bronze Age Canaan had been relatively culturally homogenous, though the cities in the north came into the Hittites’ sphere of influence and those in the south the Egyptians’. After the Collapse, though, the city-states of northern Canaan (modern Syria), like their Neo-Hittite neighbors, seem to have continued more or less as they had been. Those in southern Canaan were not so lucky: weakened by the invading Sea Peoples and the withdrawal of Egyptian hegemony, the southern Canaanites were displaced by (or assimilated to) the new Semitic kingdoms in the region, including Israel, Judah, Edom, and Ammon. And the central Canaanites became the Phoenicians: master sailors and traders, they had seized their opportunity and so thoroughly transformed themselves that we join the Greeks in identifying them by a new name.
Most of the larger cities of the central Levant are buried beneath their modern equivalents, and Lebanon has not been a particularly salubrious place to excavate for the last few decades, so it’s hard to say a great deal about Phoenician continuity with their Bronze Age ancestors. There was obviously some, certainly genealogically but also linguistically and in terms of material culture. However, we also know that their lifestyles changed dramatically as their economic reach expanded and their cities became centers not only of exchange but of manufacturing. We know their commercial firms were organized around extended families, and that they began to settle foreign lands both as colonists in their own new cities and elsewhere as resident merchants with their own dedicated enclaves. And we know that as their city-states grew more powerful, they increasingly directed worship away from the traditional Canaanite pantheon, led by El, and towards the tutelary deity of each individual city. (The story that King Hiram of Tyre actually tore down the temples of El and Baal to make room for a magnificent new temple of his patron, Melqart,4 is probably an exaggeration, but points to the scale of the break with the past.)5
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
- For a very funny story about an Iron Age Egyptian attempt to buy some, which I simply could not fit into this review, see the “Story of Wenamun“. Bonus points for imagining how it would have played out under the New Kingdom.
- Okay, the Phoenician “alphabet” is actually an abjad — it contains no symbols for vowels — but the Greeks quickly added those.
- It is much, much easier to learn to write with an alphabet than with a logosyllabic system like Linear B or cuneiform.
- Melqart is also the patron of the Tyrian colony of Carthage, and his name contributes one element to that of Hamilcar Barca. The –bal in Hannibal, Hasdrubal, etc., is of course from Baal.
- Cline doesn’t give a ton of detail on Phoenician culture; in this section I am also drawing heavily on the opening chapter of Richard Miles’s Carthage Must Be Destroyed: The Rise and Fall of an Ancient Civilization, which sentiment I fully endorse even though I haven’t finished the book yet.
September 10, 2025
QotD: “The [western Roman Empire] did not drift hopelessly towards its inevitable fate. It went down kicking, gouging and screaming”
The fall of the Roman Empire in the West (please, right now, just mentally add the phrase “in the west” next to every “the fall of Rome” and similar phrase here and elsewhere) is complicated. I don’t mean it is complicated in its causes or effects (though it is that too), I mean it is complicated in its raw events: the who, what, where and when of it. Most students are taught a fairly simple version of this because most of what they need to actually learn is the cause and the effects and so the actual “fall” part is a sort of black box where Huns, Vandals, Goths, plague, climate and economic decline go in and political fragmentation, more economic decline and the European Middle Ages come out. The fall itself ends up feeling like an event rather than a process because it is compressed down to a single point, the black box where all of the causes become all of the effects. That is, frankly, a defensible way to teach the topic at a survey level (where it might get at most a lecture or two either at the end of a Roman History survey or the beginning of a Medieval History survey) and it is honestly more or less how I teach it.
But if you want to actually try to say something intelligent about the whole thing, you need to grapple with what actually happened, rather than the classroom black-box model designed for teaching efficiency rather than detail. We are … not going to do that today … though I will have some bibliography here for those who want to. The key thing here is that the “Fall of Rome” (in the West) is not an event, but a century long process from 376 to 476. Roman power (in the West) contracts for a lot of that, but it expands in periods as well, particularly under the leadership of Aetius (433-454) and Majorian (457-461); there are points where it would have really looked like the Romans might actually be able to recover. Even in 476 it was not obvious to anyone that Roman rule had actually ended; Odoacer, who had just deposed what was to be the last Roman emperor in the west promptly offered the crown to Zeno, the Roman emperor in the East (there is argument about his sincerity but James O’Donnell argues – very well, though I disagree on some key points – that this represented a real opportunity for Rome to rise from defeat in a new form yet again).
Glancing even further back historically, this wasn’t even the first time the Roman Empire had been on the brink of collapse. Beginning in 238, the Roman Empire had suffered a long series of crippling civil wars and succession crises collectively known as the Crisis of the Third Century (238-284). At one point, the empire was de facto split into three, with one emperor in Britain and Gaul, another in Italy, and the client kingdom of Palmyra essentially running the Eastern half of the empire under their queen Zenobia. Empires do not usually survive those kinds of catastrophes, but the Roman Empire survived the Crisis, recovered all of its territory (save Dacia) and even enjoyed a period of relative peace afterwards, before trouble started up again.
The reason that empires do not generally survive those kinds of catastrophes is that generally when empires weaken, they find that they contain all sorts of people who have been waiting, sometimes patiently, sometimes less so, for any opportunity to break away. The rather sudden collapse of the (Neo-)Assyrian Empire (911-609 BC) is a good case study. After having conquered much of the Near East, the Assyrians fell into a series of succession wars beginning in 627; their Mesopotamian subjects smelled blood and revolted in 625. That was almost under control by 620 when the Medes and Persians, external vassals of the Assyrians, smelled blood too and invaded, allying with the rebelling Babylonians in 616. Assyria was effectively gone by 612 with the loss and destruction of Ninevah; they had gone from the largest empire in the world at that time or at any point prior to non-existent in 15 years. While the Assyrian collapse is remarkable for its speed and finality, the overall process is much the same in most cases; once imperial power begins to wane, revolt suddenly looks more possible and so the downward slope of collapse can be very steep indeed (one might equally use the case study of decolonization after WWII as an example: each newly independent country increased the pressure on all of the rest).
Yet there is no great rush to the doors for Rome. Instead, as Guy Halsall puts it in Barbarian Migrations and the Roman West (2007), “The West did not drift hopelessly towards its inevitable fate. It went down kicking, gouging and screaming”. Among the kicked and gouged of course were Attila and his Huns. Fought to a draw at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, his empire disintegrated after his death two years later under pressure from both Germanic tribes and the Eastern Roman Empire (and the standard tendency for Steppe empires to fragment); of his three sons, Ellac was killed by revolting Germanic peoples who had been subject to the Huns, Dengizich by the (Eastern) Romans (we’re told his head was put on display in Constantinople) and the last, Ernak just disappears in our narrative after the death of Dengizich. The Romans, it turns out, did eventually get down to business to defeat the Huns. But the Romans doing all of that kicking, gouging and screaming were not the handful of old families from the early days of the Repulic; most of those hard-fighting Romans were people who in 14 AD would have been provincials. And indeed, the Roman Empire would survive, in the East, where Rome wasn’t, making for a Roman Empire that by 476 consisted effectively entirely of “provincial” Romans.
Instead what we see are essentially three sets of actions by provincial elites who in any other empire would have been leading the charge for the exits. There were the kickers, gougers and screamers, as Halsall notes. There were also, as Ralph Mathisen, Roman Aristocrats in Barbarian Gaul (1993) has noted, elites who – seeing the writing on the wall – made no effort to hasten the collapse of the empire but instead retreated into their estates, their books and their letters; these fellows often end up married into and advising the new “barbarian” kings who set up in the old Roman provinces (which in turn contributes quite a bit to the preservation and continued influence of Roman law and culture in the various fragmented successor states of the early Middle Ages). Finally, there were elites so confident that the empire would survive – because it always had! – that they mostly focused on improving their position within the empire, even at the cost of weakening it, not because they wanted out, but because “out” was inconceivable to them; both Halsall and also James O’Donnell, The Ruin of the Roman Empire (2009) document many of these. If I may continue my analogy, when the exit door was yawning wide open, almost no one walked through; some tried to put out the burning building they were in, others were content to be at the center of the ruins. But no one actually left.
During the Crisis of the Third Century, that set of responses had been crucial for the empire’s survival and for brief moments in the 400s, it looked like they might even have saved it again. For all of the things that brought the Roman Empire down, it is striking that “internal revolts” of long-ruled peoples weren’t one of them. And that speaks to the power of Rome’s effective (if, again, largely unintentional) management of diversity. The Roman willingness to incorporate conquered peoples into the core citizen body and into “Roman-ness” meant that even by 238 to the extent that the residents of the Empire could even imagine its collapse, they saw that potentiality as a disaster, rather than as a liberation. That gave the empire tremendous resiliency in the face of disaster, such that it took a century of unremitting bad luck to bring it down and even then, it only managed to take down half of it.
(As an aside, those provincial Romans were correct in the judgement that the collapse of the empire would mean disaster. The running argument about the fall of the Roman Empire is generally between the “decline and fall” perspective, which presents the collapse of the Roman Empire as a Bad Thing and the “change and continuity” perspective, which both stresses continuity after the collapse but also tends to try minimize the negative impacts of it, even to the point of suggesting that the average Roman peasant might have been better off in the absence of heavy Roman taxes. That latter view is particularly common among many medievalists, who are understandably quite tired of the unfairly poor reputation their period gets. This is an argument that for some time lived in the airy space of narrative and perspective where both sides could put an argument out. Unfortunately for some of the change-and-continuity arguments about living standards, archaeology has a tendency to give us data that is somewhat less malleable. That archaeological data shows, with a high degree of consistency, that while there is certainly some continuity between the Late Antique and the early Middle Ages the fall of Rome (in the West) killed lots of people (precipitous declines in population in societies without reliable birth control; probably this is mostly food scarcity, not direct warfare) and that living standards also declined to a degree that the results are archaeologically visible. As Brian Ward-Perkins notes in The Fall of Rome and the End of Civilization (2005), the collapse causes cows to shrink, speaking to sudden scarcity of winter fodder (which in turn likely speaks to a general reduction in available nutrition). Some areas were worse hit than others; Robin Flemming, Britain After Rome (2010) notes, for instance, that in post-Roman Britain, pot-making technology was lost (because ceramic production had been focused in cities which had been largely depopulated out of existence). The fall of Rome might have been good for some people, but the evidence is, I think, at this point inescapable that it was quite bad for most people. Especially, one assumes, all of the people who got depopulated.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans, Part V: Saving and Losing and Empire”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-07-30.
August 7, 2025
QotD: The lost-then-found-again Hittite civilization
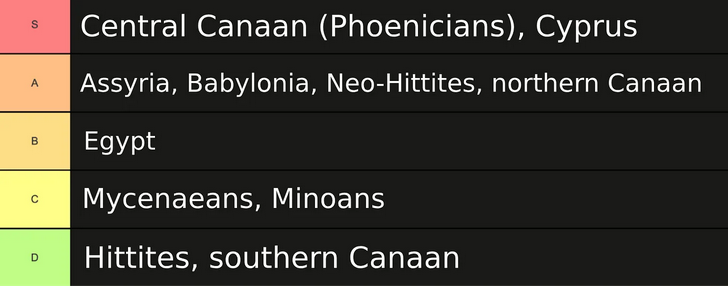
… Mycenaean Greece was as much an outlier as sub-Roman Britain: the civilizational collapse in the Aegean was unusually prolonged and severe compared to the fates of many of the other peoples of the Late Bronze Age. Here I have helpfully reformatted Cline’s chart of how resilient the various societies proved:
Let’s take a brief tour through the various fates of these societies. I’ll come back to the Phoenicians at the end, because their example raises interesting questions when considered in contrast with the Mycenaeans. For the moment, though, let’s begin like civilization itself: in Mesopotamia.
Before the Late Bronze Age Collapse, the Assyrian and Babylonian empires had numbered among the Great Powers of the age: linked by marriage, politics, war, and trade to the other mighty kings, they spent much of their time conducting high-level diplomacy and warfare. As far as we can tell, they did well in the initial collapse: there’s a brief hiatus in Assyrian royal inscriptions running from about 1208 to 1132 BC, but records resume again with the reign of Aššur-reša-iši I and his repeated battles with his neighbor to the south, the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar I (no relation). But although the kings of the late twelfth century continued much as their Bronze Age predecessors had — waging war, building palaces, going hunting, accepting tribute, collecting taxes, and ordering it all recorded in stone and clay — the world had changed around them. No longer were there huge royal gifts sent to and from fellow great kings, “My Majesty’s brother”1 overseas; now their diplomatic world consisted of tiny petty kings of nearby cities who could be looted or extorted at will.
Mesopotamia didn’t escape unscathed forever: beginning around 1080 BC, texts begin to record severe droughts, invading Aramaeans, and total crop failures. There was a major drought in 1060 BC, and then both the Assyrian and Babylonian records record further drought every ten years like clockwork — sometimes accompanied by plague, sometimes by “troubles and disorder” — until the end of the eleventh century BC. Most of the tenth century was equally dire, with chronicles recording grain shortages, invasions, and a cessation of regular offerings to the gods.
But unlike the Mycenaeans, and in spite of real suffering (ancient Babylonia is estimated to have lost up to 75% of its population in the three hundred years after the Collapse), both Mesopotamian empires were able to hang on to civilization. There were still kings, there were still scribes, and there were still boundary stones on which to record things like “distress and famine under King Kaššu-nadin-ahhe”. And when conditions finally improved, Assyria and Babylonia were both able to bounce back. When at last the Assyrian recovery began under Aššur-dan II (934-912 BC), for example, he (or more realistically, his scribe) was able to write: “I brought back the exhausted people of Assyria who had abandoned their cities and houses in the face of want, hunger, and famine, and had gone up to other lands. I settled them in cities and homes which were suitable and they dwelt in peace”. Clearly, Assyria still retained enough statehood to effect the sort of mass population transfer that had long been a feature of Mesopotamian polities.2
Over the next few centuries, the Neo-Assyrian Empire would come to dominate the Near East, regularly warring with (and eventually conquering) Babylon and collecting tribute from smaller states all over the region. At its peak, it was the largest empire history had ever known, covering a geographic extent unsurpassed until the Achaemenids. The Babylonians had to wait a little longer for their moment in the sun, but near the end of the seventh century they overthrew their Assyrian overlords and ushered in the Neo-Babylonian Empire. (Less than a century later, Cyrus showed up.)
So how did Babylon and Assyria hold on to civilization — statehood, literacy, monumental architecture, and so forth — when the Greeks lost it and had to rebuild almost from scratch? Unfortunately, Cline doesn’t really answer this. He offers extensive descriptions of all the historical and archaeological evidence for the diverse fates of various Late Bronze Age societies, but only at the very end of the book does he briefly run through the theories (and even then it’s pretty lackluster). He does have a suggestion about the timing — the ninth century Assyrian resurgence lines up almost perfectly with the abnormally wet conditions during the Assyrian megapluvial — but why was it the Assyrians who found themselves particularly well-positioned to take advantage of the shift in the climate? Why not, say, the Hittites?
Sometime around 1225 BC, the Hittite king Tudhaliya IV wrote to his brother-in-law and vassal, Shaushgamuwa of Amurru, that only the rulers of Egypt, Babylonia, and Assyria were “Kings who are my equals in rank”.3 A mere thirty years later, though, his capital city of Hattusa would lie abandoned and destroyed. Modern excavators describe ruins reduced to “ash, charred wood, mudbricks and slag formed when mud-bricks melted from the intense heat of the conflagration”.
And with that, the Hittites essentially vanished from history.
They were so thoroughly forgotten, in fact, that when nineteenth-century archaeologists discovered the ruins of their civilization in Anatolia, they had no idea who these people were. (Eventually they identified the new sites with the Hittites of the Bible, who lived hundreds of years later and hundreds of miles to the south, out of sheer ¯\_(ツ)_/¯.)4
What happened to the Hittites? Well, Cline suggests the usual mélange of drought, famine, and interruption of international trade routes, as well as a potential usurpation attempt from Tudhaliya’s cousin Kurunta, but the actual answer is that we’re not sure. Given the timing, they may have been the first of the Late Bronze Age dominos to fall; given the lack of major rivers in central Anatolia, they may have been uniquely susceptible to drought. Hattusa may have been abandoned before the fire — its palaces and temples show little sign of looting, suggesting they [may] already have been emptied out — but many other sites in the Hittites’ central Anatolian heartland were destroyed around the same time, and some of those have bodies in the destruction layer. But whatever the order of events, Hittite civilization collapsed as thoroughly and dramatically as the Mycenaeans’ had done, and with a similar pattern of depopulation and squatters in the ruins. Unlike the Mycenaeans, though, the Hittites would never be followed by successors who inherited their culture; the next civilization of Anatolia was the Phrygians, who probably arrived from Europe in the vacuum following the Hittites’ fall.
There was one exception: in the Late Bronze Age, cadet branches of the Hittite royal family had ruled a few small satellite statelets in what is now northern Syria, and many of these “Neo-Hittite” polities managed to survive the Collapse. A tiny, far-flung corner of a much greater civilization, they nevertheless outlasted the destruction of their metropole and maintained Hittite-style architecture and hieroglyphic inscriptions well into the Iron Age.5 (They would be swallowed up by the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the late eighth century BC.) And though the Neo-Hittite kings ruled over tiny rump states, we’re now able to translate inscriptions in which they referred themselves by the same titles the Bronze Age Hittite “Great Kings” had employed. The records of their larger neighbors, which had a much greater historical impact, seem to have followed suit: the Neo-Hittites in Syria probably actually were the Hittites of the Bible! Chalk up another one for nineteenth century archaeology.
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
1. I really think we should bring back monarchs referring to themselves as “my Majesty”. So much cooler than the royal “we”. Or combine them: “our Majesty”!
2. The Babylonian Captivity, much later in the Iron Age, was far from historically unique.
3. The list actually reads, “the King of Egypt, the King of Babylonia, the King of Assyria,
and the King of Ahhiyawa” — the strikethrough appears in the original clay tablet! A generation earlier, under Tudhaliya’s father Hattusili III, the Hittite texts had consistently referred to the king of Ahhiyawa as a “great King” and a “brother”, but apparently the geostrategic position of the Mycenaean ruler had degraded substantially.4. We now know that the Hittites spoke an Indo-European language and referred to themselves “Neshites”, but the name has stuck.
5. I went looking for a good historical analogy for the Neo-Hittite kingdoms and discovered, to my delight, the Kingdom of Soissons, which preserved Romanitas for a few decades after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The Neo-Hittites lasted a lot longer.
July 6, 2025
QotD: After the Bronze Age Collapse
The collapse itself has a certain drama — the tumbled ruins of monumental architecture, the skeletons and arrowheads amidst the rubble, the panicked requests for aid preserved in the archives of a society that lasted a few decades longer — but any sufficiently thorough collapse will leave few archaeological or historical traces of its aftermath. Civilization is in some sense defined as “stuff that leaves records”: monumental architecture, literacy, large-scale trade, specialist craft production, and so on. It’s much harder for us to know what was going on during an era when people are building with wood (instead of stone), or making pots at home out of lousy local clay (instead of in centralized and semi-industrial production centers), or relying on the oral tradition (instead of carving dynastic propaganda into the living cliff-face in friezes a thousand feet high). When we call these periods “Dark Ages”, we mean you can’t see anything when you look in.
But what surprised me most about After 1177 B.C. is how short this era was. In some places, anyway.
We have a vague picture of what happens after a civilizational collapse, but it’s been disproportionately influenced by two particularly dramatic examples: sub-Roman Britain and the Greek Dark Ages. This was perfectly sensible coming from the Anglo historians and archaeologists who have dominated the public conception of the field — after all, the only thing more interesting than the history of your own island is that of the classical world you’ve been studying since you got your first Latin grammar at age six — but it turns out that neither of these are the general rule. Foggy, faraway Britain, so reliant on imported goods and troops, was far more seriously impacted by the withdrawal of Rome than was most of the Empire and saw a longer and more significant reduction in cultural complexity, standards of living, average stature, and of course population. (Imagine what would happen to a Mars colony if the connections to the home planet stopped working.)
Greece after the fall of the Mycenaeans suffered an even more striking decline. As Austrian archaeologist Sigrid Deger-Jalkotzy summarizes:
The impressive palatial structures were not rebuilt, and very little of the representational arts and crafts of the palaces seems to have survived. The complex forms of political, social, and economic organization fell into oblivion. Palaces, kings, and royal families became matter for Greek myths. The art of writing was lost for centuries. In short, Greek civilization was reduced to the level of a prehistoric society.
The Greeks of the classical era had little conception that the Mycenaeans had even existed, let alone that they were their own ancestors: they retained a vague mythological tradition of past kings, but they attributed the few surviving Mycenaean structures to the work of cyclopes. In fact, the disconnect between the civilization of the Late Bronze Age and the later classical world was so great that until Michael Ventris deciphered Linear B, it was an open question whether the people responsible for the Lion Gate and the Treasury of Atreus were even Greeks at all. (The answer, in case you’re wondering, is yes: Linear B turns out to be a syllabic script for the most ancient attested form of Greek. It features a number of uniquely Greek words and deity names even in the limited surviving corpus. More recently, ancient DNA has confirmed the linguistic evidence: the classical Greeks were the descendants of the Mycenaeans.)1
But the more you look at the archaeological record, the more you can pick out signs of cultural continuity. Agricultural practices don’t seem to have changed much, nor did Mycenaean pottery styles, and the names and attributes of the gods preserved in Linear B are close if not identical to their forms as codified in Homer and Hesiod. Even the cyclopean architecture continued to provide shelter: the Mycenaean palace at Pylos was almost completely destroyed in the Collapse, but the few rooms that survived intact show signs of having been inhabited by squatters over the next century or two.
Homer too is chock full of details that turn out to be distant memories of the Mycenaean world, somehow preserved in the oral tradition until writing was reintroduced to Greece.2 For instance, he describes a kind of boar’s tusk helmet that, by his time, no one had worn for centuries, but which archaeologists have since regularly discovered in Mycenaean shaft graves throughout the Aegean. But my favorite example, which is of course linguistic, is the word for “king”: Homer describes Menelaus, Agamemnon, Odysseus and others with the word anax, which is recognizably the Linear B word 𐀷𐀙𐀏, wa-na-ka, used in the Bronze Age to describe the supreme rulers of the Mycenaean palatial societies. (The w sound was lost with the tragic death of the digamma.) By the classical era, however, anax had fallen out of use in preference for basileus (Linear B 𐀣𐀯𐀩𐀄, qa-si-re-u), which in the Mycenaean period had referred to a much lower-level chieftain.
This all paints an evocative picture of a post-apocalyptic world. You can imagine it transplanted to an American context, with the scattered survivors of some great cataclysm huddled around fires built in the corners of a crumbling Lincoln Memorial. You can picture them passing on stories of the great men of the past with their tall tube-shaped hats and the shiny black stones they carried in their pockets. And by the time this remnant rebuilt, they might well have forgotten the word “President” except as an archaism; after centuries of as a small-scale society, “Mayor” might become so deeply engrained as the highest title that two thousand years later they would still use it to refer to their emperor.
Jane Psmith, “REVIEW: After 1177 B.C., by Eric H. Cline”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2024-07-08.
1. It’s slightly more complicated than that, because of course it is; see here for more detail from Razib Khan.
2. A reasonable ballpark guess is that the poems traditionally attributed to Homer were composed in something like their current forms around 750 BC and written down for the first time shortly before 525 BC, although like the dating of Beowulf there’s a great deal of argument.
May 24, 2025
History of Britain, II: Stonehenge; The Druids, Vates, and Celtic Religion
Thersites the Historian
Published 15 Jan 2025In this episode, I briefly examine the presence of prehistorical megaliths on the British Isles and talk about the religion of the Celts, which was ascendant at the time that Britain entered entered the historical record.
May 16, 2025
A Very Basic Introduction To Ancient Carthage
MoAn Inc.
Published 1 Jan 2025Images Used
Hamilcar Barca and The Oath of Hannibal – Benjamin West (1738–1820) – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient…
Ancient Carthage. (2024, December 27). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient…
Numerius Fabius Pictor (antiquarian). (2023, October 11). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Numeriu…)
Aristotle. (2024, December 27). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aristotle
Herodotus. (2024, December 30). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herodotus
Cassius Dio. (2024, November 28). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cassius…
Plutarch. (2024, December 23). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plutarch
Polybius. (2024, December 31). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polybius
Livy. (2024, November 23). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Livy
File:Death Dido Cayot Louvre MR1780.jpg. In Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
Colosseum. (2024, December 21). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colosseum
Carthage Ports Puniques, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
File:Bardo National Museum tanit-edit.jpg. In Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
File:Bardo Baal Thinissut.jpg. In Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
File:Ginnasium Solunto.jpg. In Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…
File:Carthage 323 BC.png. In Wikipedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi…A Bit About MoAn Inc. –
Trust me, the ancient world isn’t as boring as you may think. In this series, I’ll be walking you through a VERY basic idea of what happened during Rome’s famous Punic Wars.Donate Here: https://www.ko-fi.com/moaninc
Free Marble Image Photo by Henry & Co.thanks to https://unsplash.com/wallpapers/desig…
#AncientRome #AncientHistory #PunicWars
April 13, 2025
History Hit Expert BLEW My MIND On Ancient Roman History
Metatron
Published 14 Dec 2024Link to the original video
• Historian Answers Google’s Most Popul…
Pompaia, on the River Sarnus — a river which both takes the cargoes inland and sends them out to sea — is the port-town of Nola, Nuceria, and Acherrae.
Strabone, Geografia, IV, 81 – Factors in the Establishment of Pompeii. Let’s begin by well what we know. How did it all start? Like many cities of the classical world, Pompeii also has its founding myth: according to Servius, the city was supposedly founded by none other than the demigod Hercules, and its name would have originated from “a Pompa Herculis”, meaning “from the triumph of Hercules”. However, the most recent archaeological discoveries confirm a foundation dating back to around the 8th century BC by the Oscan people, an Italic tribe, corroborating what Strabo reported in his Geography. The Oscans were part of the large linguistic family of Umbro-Sabellian or Osco-Umbrian peoples, distinct from the Latins, who probably arrived in Italy in the 12th century BC. While some Hellenists have proposed that the etymology of Pompeii should be sought in the Greek Πεμπo (Pempo), meaning “to send”, due to the thriving commercial activity, the original linguistic root is likely this Oscan word “pumpè“, from which comes the archaic name Pumpàiia. The Oscan “pumpè“, analogous to the Greek “penta” and Latin “quinque“, means “five”, and most likely refers to a proto-urban reality formed by the progressive fusion of five distinct residential centers, five small Oscan villages that were scattered on the southern slopes of mount Vesuvius, next to the course of the Sarno river.
2. Natural resources: Volcanic areas often provide access to valuable resources like obsidian, sulfur, and various minerals used in ancient crafts and trade.
3. Lack of geological understanding: Ancient people didn’t fully understand the mechanisms of volcanic eruptions or their potential for catastrophic destruction. The last major eruption of Vesuvius before 79 AD was likely prehistoric, so there was no living memory of its danger.
4. Infrequent eruptions: Many volcanoes, including Vesuvius, can remain dormant for long periods. This can create a false sense of security among nearby populations.
5. Strategic location: Pompeii was located in a prime spot for trade, with access to the sea and inland routes. The benefits of this location may have outweighed perceived risks.
6. Religious and cultural significance: Volcanoes were often seen as sacred in ancient cultures, associated with deities or supernatural forces. This could make living near them culturally desirable.
7. Limited mobility: Ancient societies were less mobile than modern ones. Once established, it was difficult to relocate entire cities, even if dangers became apparent.
8. Economic investments: As cities grew and prospered, the economic and social costs of abandoning them became increasingly high.
9. Adaptation and mitigation: Over time, societies living near volcanoes often developed strategies to cope with minor volcanic activity, like earthquakes or ash falls.
10. Lack of alternatives: In some regions, volcanic areas might have been among the best available locations for settlement, despite the risks.
It’s worth noting that while the destruction of Pompeii was catastrophic, the city had thrived for centuries before the eruption of 79 AD. From the perspective of the ancient inhabitants, the benefits of their location likely seemed to outweigh the potential for a disaster that might never occur in their lifetimes. This balance of risk and reward in choosing settlement locations is not unique to ancient times. Even today, many major cities are located in areas prone to natural disasters, demonstrating that humans often prioritize immediate benefits over long-term, uncertain risks
#pompeii #ancientrome #documentary
April 6, 2025
The Last Pagan Temple in Egypt
Scenic Routes to the Past
Published 6 Dec 2024The Temple of Isis at Philae, on Egypt’s southern edge, survived until the reign of Justinian, long after every other temple had been shut down.
February 2, 2025
Hierapolis: a city encased in stone
Scenic Routes to the Past
Published 18 Oct 2024Hierapolis — modern Pamukkale, Turkey — was built over hot springs. During the Middle Ages, these encased much of the city in gleaming travertine.
See my upcoming trips to Turkey and other historical destinations: https://trovatrip.com/host/profiles/g…