Forgotten Weapons
Published 11 Nov 2022One would think that the Shpagin PPSh-41 was as simple as a submachine gun could get, but that wasn’t the case in World War Two USSR. Barely had the PPSh gotten into real production than the Army was looking for something even simpler. An answer came from young designer Aleksey Sudaev with a completely-stamped gun that used about half the raw material and a third the machine time to produce as the PPSh. After winning the competitive trials, Factory 828 in Moscow was chosen as the lead production facility. They produced a series of drawings and preproduction guns in the summer of 1942.
Sudaev took those drawings into besieged Leningrad with orders to et up production in three factories within the city. The main one was Factory 209, and after fixing a few minor design flaws, the gun went into production in the spring of 1943. Sudaev PPS-42 SMGs pretty much went out the doors of the factory and right into combat trying to break the siege of the city. In total, about 46,000 would be produced before that siege was finally broken.
Meanwhile, Factory 828 in Moscow put a higher priority on policing the design than on immediate production. They implemented a substantial number of improvements, although the lack of communication into Leningrad prevented them from being used in the production going on there. Instead, the improvements culminated in the PPS-43 design, of which more than a million were made by the end of the war.
(more…)
March 21, 2023
Born in the Heart of Besieged Leningrad: the PPS-42
March 19, 2023
Inside An M4 Sherman Tank With Historian James Holland
History Hit
Published 21 Nov 2022‘Inside An M4 Sherman Tank With Historian James Holland’
In this video, military historian James Holland gets inside the most iconic tank of the Second World War — the ubiquitous US M4 Sherman Tank.
With over 50,000 having produced between 1942 and 1945, the Sherman was the most widely used medium tank by the United States and Western Allies in World War II.
Easily produced, maintained and equipped with a 75mm gun as well as a single hatch-mounted .50 caliber machine gun (plus two lighter .30 cals positioned in the turret and forward hull), the Sherman proved extremely effective against soft targets. It still lacked the range and firepower of the German Panther and Tiger tanks, but its speed, manoeuvrability and fast rate of fire made it ideal wartime workhorse.
More recently, the M4 Sherman has risen to stardom with the release of Hollywood blockbuster Fury (2014), starring Brad Pitt and Shia LaBeouf.
(more…)
March 18, 2023
The US Adopts A Maxim: The Colt Model 1904
Forgotten Weapons
Published 9 Nov 2022The US Army spent nearly 16 years languidly testing the Maxim gun, but was never willing to actually make a decision until a final trial in 1903 finally settled the matter. The Maxim was deemed the best available machine gun and a contract was signed with Vickers, Sons, & Maxim to purchase 50 (later increased to 90). Eventually a total of 287 were procured; 90 from VSM and a further 197 made by Colt in the US. The first British guns were chambered for .30-03, with the Colts all made for the later .30-06 (and the VSM guns updated to that standard).
The Model 1904 was the heaviest Maxim gun ever made, weighing in at 62 pounds for the gun and another 80 for its tripod. Despite excellent reliability and durability, it was so heavy and unwieldy that it was pretty universally hated by American soldiers. The final order for 1904 Maxims was placed in 1908 and just the following year the M1909 Benet Mercie light Hotchkiss pattern was was adopted. By the time World War One arrived, half the Maxims had already been relegated to long-term storage. They were pulled out of the warehouses for training troops prior to their deployment to Europe, but they never saw any more significant military use.
(more…)
March 14, 2023
German Troop Trials “Push-Button” Gewehr 41(W)
Forgotten Weapons
Published 8 Nov 2022When the German army wanted a new semiauto service rifle in 1941, it received submissions from two companies; Walther and Mauser. Walther’s design didn’t strictly meet the criteria set forth, but it was clearly the better rifle and would eventually win the competition. This involved conducting troop trials, and Walther got an initial contract for 5,000 rifles for those trials. That first batch of rifles differed in several ways from the version that was ultimately put into mass production. Most substantially, the first version of the G41(W) had a push-button bolt release on the left side of the stock. After loading two stripper clips, one would push the button to close the bolt. Of course, one could also simply pull the bolt handle back slightly and release to do the same thing — and so the bolt release button was removed to simplify production. In addition, the bolt guide rail on the receiver would be lengthened on production, optics mounting rails were added (although never really used), and the serrations on the spring guide rod were dropped.
(more…)
March 11, 2023
Why Japan Surrendered in WW2: Stalin or the Bomb?
Real Time History
Published 10 Mar 2023
It’s common wisdom that the nuclear bombs dropped over Hiroshima and Nagasaki caused the Japanese surrender at the end of the 2nd World War. However, there has been a fierce historical debate if this narrative omits the role of the Soviet invasion of Manchuria in August 1945 — or if this invasion was actually the main cause for the surrender.
(more…)
M240 Bravo: America Replaces the M60
Forgotten Weapons
Published 7 Nov 2022In 1977, the US military adopted the FN MAG as the M240 in vehicular configuration to replace the less-than-successful M73/M219 machine guns. The USMC would get an early start adapting the 240 to ground configuration (the M240G), but it wasn’t until 1995 that the Army formally replaced the M60 with the MAG in M240B layout. The M240B has a number of differences from the standard MAG:
– Single-position gas regulator, giving about 600 RPM
– Picatinny rail on the top cover for mounting optics
– Front heat shield over the barrel to prevent heat mirage
– Top cover can be closed with the bolt either forward or backThe M240B has since been adopted by the Marines as well, and served extensively in Iraq and Afghanistan. It is a quite heavy gun (24+ pounds) but very well liked by its users for being exceptionally rugged, dependable, and accurate. The one we have today is in pristine condition, and one of just 11 transferrable examples registered in the US.
(more…)
March 10, 2023
Tank Chats #168 | Vixen & Fox | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 18 Nov 2022Join David Fletcher as he takes a look at the Vixen and Fox armoured cars.
(more…)
March 8, 2023
First to the Fight: The Marines’ Reising M50 SMG
Forgotten Weapons
Published 4 Nov 2022Eugene Reising developed a .45 ACP submachine gun in the late 1930s that was basically the opposite of the Thompson — it was light and handy, fired from a closed bolt with a delayed blowback action, and was inexpensive to produce. Reising contracted with Harrington & Richardson to produce the gun, and when it entered the market in early 1940 it found immediate interest from the USMC. Looking initially to equip the Marine Paratroop Regiment (Paramarines), the Corps wanted a gun that was light and compact. The Reising M55 with its folding stock was certainly those things and since the Thompson was essentially unavailable anyway (all production was going to the Army and foreign contracts), the Corps adopted the Reising with initial purchases of both the M50 and M55 in January and February of 1942.
What we are looking at today is an early production M50. It is blued with 29 barrel fins and the early style of sights, stock screw, trigger guard, magazine release, stock (the lacquer coating and sling swivels having been added by a previous owner), and firing pin. Later production guns would be improved and strengthened in various ways, but the Reising would never quite meet the needs of frontline combat troops, much to the displeasure of the Marines who first used them in the Pacific theater. Lacking interchangeable parts and susceptible to fouling and malfunctions, the Reisings were quickly replaced by other arms — some Johnson M1941 rifles, some M1 and M1A1 carbines, and various other guns. Rotated back to duties like ship boarding parties, guards, and military police, the Reising served very well. They were indeed handy and accurate guns, just not built for the extreme rigors of Pacific beach assaults and jungle foxholes.
(more…)
March 7, 2023
How Would a Nuclear EMP Affect the Power Grid?
Practical Engineering
Published 8 Nov 2022How a nuclear blast in the upper atmosphere could disable the power grid.
(more…)
March 4, 2023
Thompson SMG Cases: Police, FBI, and Secret Service
Forgotten Weapons
Published 3 Nov 2022The Auto Ordnance company made a couple of different types of cases for the Thompson SMG, and today we are going to look at two of the most common and one exceptionally cool type. The two most typically found are the Police and FBI cases. Both of these hold the gun along with the detached stock, one drum, and four box magazines. The Police type has the drum and box mags separated for balance and was lined with purple velvet; the FBI case was generally blue velvet and had all the magazines on the left (making it balance poorly).
The other case we have today is one fabricated by the Secret Service for one of its protective details. This is a flat-lying wooden case, which holds the gun, stock, and four box magazines — no drums for the Service.
(more…)
March 2, 2023
Anti-Tank Chats #6 | The Panzerfaust | The Tank Museum
The Tank Museum
Published 4 Nov 2022Historian Stuart Wheeler is back with another anti-tank chat. In this episode, he is looking at the development and use of the legendary panzerfaust.
(more…)
March 1, 2023
Mauser WW1 Flyer’s Rifle: the Flieger Selbstlader Karabiner 1916
Forgotten Weapons
Published 1 Nov 2022Paul Mauser dedicated much of his life to the development of a practical semiauto military rifle, and did manage to have a design that was used in combat by Germany in World War One. It began with the model 06/08, a short-recoil, flap-locked design made in both rifle and pistol form. The short recoil idea was disliked by the military for a shoulder rifle, and so Mauser redesigned it to be inertially locked with a fixed barrel. This was sold in small numbers as a sporting rifle, and tested by the military a few years before the war. Once war began, Mauser once again submitted the design for use in an infantry configuration, but the system was too delicate for infantry combat. A second pattern was made for use by fliers, and this was accepted and used in service for that brief period between the introduction of military aviation and the adoption of aerial machine guns.
Designated the FSK-16 (FliegerSelbstladeKarabiner 1916), it was used primarily by balloon and Zeppelin crews. With a large magazine and self-loading action, it was much better for use in aircraft than the typical bolt action infantry rifles — and there was no mud to get into the action while airborne.
(more…)
February 26, 2023
Ortgies Automatic Pistols: Not as Boring as You Think!
Forgotten Weapons
Published 16 Jun 2016The Ortgies is a pistol whose interesting aspects are often overlooked on the assumption that it is just another identical .32 ACP blowback pistol. Well, it is that — but it is also more.
Mechanically, the Ortgies has a rather unusual grip safety mechanism that is quite different from what we expect to see today. It is also interesting in that the .32 and .380 versions differ only in the easily-interchanged barrel — even the magazines are marked for both calibers.
However, the most interesting part of the Ortgies story (in my opinion) is its production. In less than 5 full years (1919-1923), close to a half million of these guns were made, primarily by an industrial subsidiary of the German government. The guns were in large part a work program, creating export goods which could bring desperately needed hard currency into Germany to counteract the economic devastation of the Versailles treaty.
Have a look at the video and you may come away with a newfound appreciation for the humble Ortgies, like I did!
(more…)
February 25, 2023
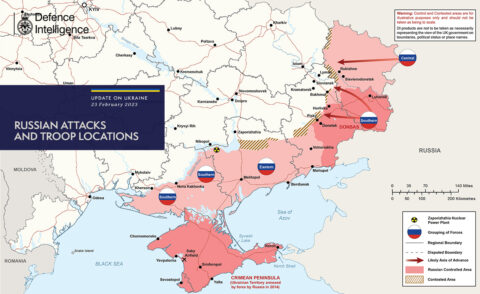
One year into Vladimir Putin’s “Three-Day War”
Tsar Vlad launched his short, victorious war a full year ago, expecting to have the troops home by spring if not sooner. It hasn’t worked out to his timetable at all. Ukraine still stands, although it’s taken one hell of a battering in the process and drawn in more and more vocal support in the west, which has belatedly been followed by actual military supplies and equipment to replace those expended holding back the Russian forces. CDR Salamander follows up his predictions from last year on how things looked to him at that moment in time:
On the day the war started I made 7-points. Let’s review them and see how I did back on 24 FEB 22.
1. The remaining delusions about the post-Cold War security arrangements in Europe should be firmly buried. History is back and she has her Festivus pole front and center. She has some issues with us, and we’re going to hear about it.
This continues to get firmer and displayed in stark relief. All the “offsets” and “transformations” and “war is new” snake oil sold the last few decades really should not be allowed to have any public space besides to say, “I was wrong.” Rest assured, that won’t stop them — but the issues we raised over the almost 18-yrs of this blog and 14-yrs of the Midrats Podcast remain true. From the shallow magazines to the fact you never have enough large caliber guns to no war is short … we — and a lot of other people tut-tut’d for years — were correct.
2. NATO has a German problem. While all the “right people” will not shut up about how wonderful former Chancellor Angela Merkle was, people need to be very clear eyed about what a complete disaster she and the German political class have been over the last two decades. They have starved what should be continental European NATO’s most potent military into irrelevance. Her disastrous feel-good, ethno-masochistic immigration policy weakened European cohesion and fed the worst parts of European political subcultures. Yes, she made a lot of well meaning Germans feel good about themselves, but it was a sugar-high that rotted the teeth and poisoned the national metabolism. While willing to defend Europe to the last Pole and Germany to the last American, she decided to preen in her neo-pagan EuroGreen superiority onomastic politics by ditching clean nuclear power and through the complete corruption of her elite, shacked herself to Russian energy oligarchs and thus the Kremlin. Germany needs to fix herself, and NATO needs to work around her and punish her until she starts to behave like a constructive 21st Century security partner.
Germany has made great progress, but is being dragged kicking and screaming in to the 21st Century.
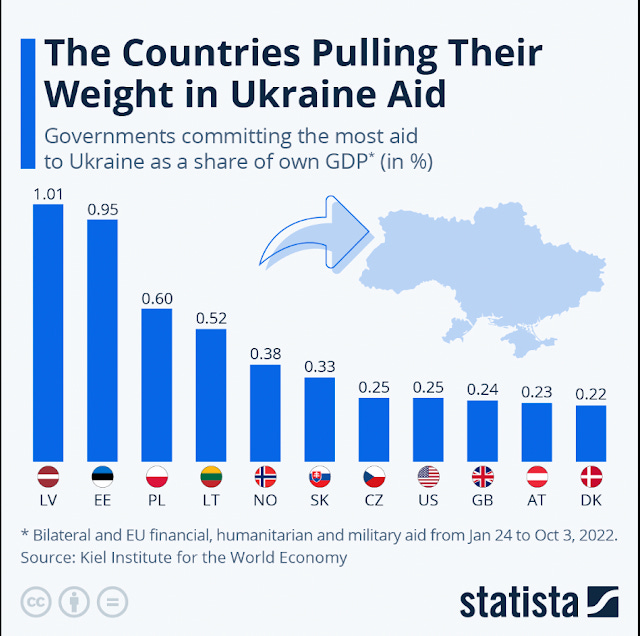
3. As our friend Jerry Hendrix pointed out yesterday, the moral leaders in NATO right now are the Baltic Republics and I would add Visegrad nations. You can throw Romania in there too. France will go hot and cold as she fights her desire to do the right thing for European security while at the same time nurse her 1,000 year old drive to be the premier leader of Western Europe. Serious but weaker nations will lean on a reluctant USA and limited United Kingdom … simply because — to be frank — much of the rest of the alliance is not that capable.
I think this graph tells that story well;
The front-line nations are putting their money where their existential threat is.
4. In line with #1 above, it is time for Finland at least, and probably Sweden, to join NATO. They both have a long and bloody history with the Russians and should see clearly what time it is.
Another check.
5. Ukraine waited too long to rearm. Weakened and distracted by a corrupt elite, the good parts of her nation could not get ready fast enough. After the first Russo-Ukraine war of 2014 she should have modeled the armed neutrality of Switzerland with a civilian populace trained and armed to the teeth. As we’ve discussed here before with the former Soviet republics and Warsaw Pact nations, every village needs a few ATGM militia teams trained to slow any advance through their patch of land. If Ukraine can, in whole or part, survive without vassalhood, perhaps they could get there. They can only get there if they build a nation people are willing to fight and die for.
Everyone is rediscovering the utility of a good military-industrial complex that can quickly grow to scale. Amazing what the green-eye-shade accounts forced those who actually are supposed to study war to believe.
A few days ago, Dominic Sandbrook explained that the Ukraine-Russia conflict “is not complicated”:
A year ago, as Vladimir Putin launched his so-called “special military operation” to seize the Ukrainian capital, kill Volodymyr Zelenskyy and wipe much of the latter’s country from the map of Europe, who’d have imagined that the third week of February 2023 would begin with Joe Biden strolling around the streets of Kyiv in sunglasses? For that matter, who would have predicted that Mr Zelenskyy, only recently returned from his own trip to London, would be at his side — still the president of a free country, and still very much alive?
Sometimes it’s nice to be wrong. Like many, probably most Western observers, I held out little hope for Ukraine once the drums of war began to beat in earnest. A couple of days after Mr Putin’s brutal invasion began, I wrote a bullish essay looking back at Ukraine’s history of suffering and resilience. But even as I was agonising over my prose, the bleak news continued to pour in. “Now, while I have been writing, Russian tanks are rolling into the suburbs,” I wrote at one stage. Did I think they would be driven back? I didn’t. “Kyiv will rise again,” I wrote at the end. Stirring words, or so I hoped. But the person I was really trying to persuade was myself, and I didn’t succeed.
In truth, I underestimated the Ukrainian people’s resilience, their courage, their love of country. And I was wrong, too, about the Western alliance. After more than a decade of drift and inaction, from the shameful failure to respond to the seizure of Crimea to the near-criminal indifference to the suffering in Syria, I doubted whether any major Western leader would make more than a token protest about the first full-scale European invasion since the Forties. I never expected to see Finland and Sweden jump off the fence and apply for Nato membership. Nor did I imagine that Joe Biden would be so unswerving in his commitment, or so generous with US military aid. Above all, I never anticipated that Kyiv would hold out, that Kharkiv would stand or that Kherson would be retaken. As I say, it’s nice to be wrong.
It’s often said that the war in Ukraine feels like a throwback, returning us to an age when nationalistic strongmen nursed atavistic dreams of conquest, sending thousands of men to die so that they might scratch new frontiers into the soil of Europe. For all the drones and social media gimmicks, the fighting certainly feels old-fashioned: reading David Patrikarakos’s harrowing dispatch from the front line in Bakhmut, it’s impossible not to think of Passchendaele or Verdun. But for a child of the Seventies, perhaps the most old-fashioned thing of all is the spectacle of a genuinely clear-cut conflict, an unambiguous clash of right and wrong, that feels closer in spirit to the struggle against Hitler’s Germany than to most of the wars in my lifetime.
Andrew Sullivan is convinced that the war is just, but worries whether it is prudent — and he calls it not Ukraine’s but “the West’s defensive war against Russia”:
It is right and just to defend a sovereign country from attack by a much larger neighbor; to fight back against an occupying force committing war crimes on a massive scale; to oppose the logic of dictatorships and defend the foundations of democracy; to uphold a post-Cold War international order which forbids the redrawing of borders by force; to unite democratic countries in Europe against a resurgence of imperial Russia; to defang and defeat a poisonous chauvinism that despises modern freedoms for women and gay people.
It is indeed right and just. But is it prudent?
That’s the question I’m still grappling with, in a week which saw the conflict deepen and the two sides entrench their positions further. President Biden’s trip to Kyiv and his speech in Poland have heightened the stakes, turning this into a more obvious proxy war between the United States and Russia … edging gingerly but relentlessly toward something more direct.
He’s all in now: declaring that Ukraine “must triumph” and that Russia cannot win a war that the Russian leader deems existential. NATO armaments are pouring into Ukraine at an accelerating rate. The training of Ukrainian troops is happening across the Continent. Germany is sending tanks. Pressure is building on Britain to send fighter jets.
The US is ratcheting up arms production as fast as it can, while seriously depleting our own Stinger surface-to-air missiles, 155mm howitzers and ammunition, and Javelin anti-tank missile systems. These are good times for arms producers:
The Army is planning a 500% increase in artillery shell production, from 15,000 a month to 70,000, according to Army acquisition chief Doug Bush … and intends to double the production of Javelin anti-tank missiles, make roughly 33% more Guided Multiple Launch Rocket Systems surface-to-surface medium-range missiles a year, and produce each month a minimum of 60 Stinger anti-aircraft missiles — which were “almost not in production at all”, according to Bush.
When Ukraine’s effective military is made up almost entirely of NATO equipment, and trained by NATO forces, there surely comes a point at which claiming NATO is not actually at war with Russia gets fuzzy.
February 23, 2023
Type 99 Arisaka Sniper Rifles
Forgotten Weapons
Published 29 Nov 2016The Japanese Army made significant use of snipers (or in today’s terminology, designated marksmen) as part of its infantry combined arms doctrine, and produced about 22,000 Type 97 sniper rifles for use in WWII and the Sino-Japanese War. In 1941, shortly after the adoption of the new 7.7mm rifle cartridge, it was decided that a sniper rifle variant of the Type 99 should be made in addition to the Type 97 (which was basically a scoped Type 38).
Testing through 1941 determined that there was almost no practical difference in accuracy between scoped examples of the Type 99 long and short rifles, and so the short rifle was chosen to be the basis for the Type 99 sniper (the Type 99 long rifles would drop from production altogether pretty quickly anyway). About 1,000 of the scoped 99s were manufactured by the Kokura Arsenal using the same 2.5x scope as on the Type 97 sniper, while the Nagoya Arsenal instead used a 4x scope, offering more magnification at the expense of a narrower field of view. Nagoya would produce approximately 10,000 of these rifles, with 4x scopes except for a period between serial numbers 5,000 and 7,000 with 2.5x scopes (most likely the remainder stored at Kokura when that plant ceased production). The rifles made into snipers were given no special selection criteria; simply taken at random from normal production. The utility of the weapon in Japanese practice came not from it being mechanically more accurate than any other issue rifle, but rather from the optical sight allowing better exploitation of that standard rifle’s inherent accuracy.
(more…)