World War Two
Published 27 Feb 2024Hitler hopes that the V-2 rocket will turn the tide of the war. It’s cutting edge technology and impossible to intercept. Right now, the first long-range ballistic missile is raining death on London and Antwerp. But is it too little, too late? Find out the backstory to this powerful weapon.
(more…)
February 28, 2024
V-2: Hitler’s Wunderwaffe
February 26, 2024
FN Model 30: The First Belgian BAR
Forgotten Weapons
Published Nov 22, 2023FN played a role in the production of Polish wz.28 BARs, and in the process obtained a copy of the technical package for the weapon, and converted it to metric measurements. Under the supervision of Dieudonne Saive, this was used as the basis for FN’s own BAR production, called the Modelé 30. Production was done with a license from Colt, who owned the rights to Browning’s patents on the BAR.
The Model 30 was basically a Colt R75 (Model 1925), but incorporated a few improvements. Most significantly, the male and female parts of the gas system were swapped, which prevented carbon from building up and eventually jamming the gas piston. In addition, the bolt removal latch was improved from the US pattern, and the Polish wz.28-style rear sight was used. Lastly, a rate-reduction mechanism on the fire control group gave the gun “slow” and “fast” settings, of roughly 350rpm and 600rpm instead of the traditional semi and full auto settings.
Production began in 7.65mm, and the Belgian Army adopted the weapon, taking deliveries from 1930 until occupation in 1940. The Model 30 was also made in 8mm Mauser, and exported to China and Ethiopia. The design was fairly quickly supplanted in 1932 by the FN Modelé D, which added a quick-change barrel mechanism to the design, and this pattern sold more widely.
(more…)
February 25, 2024
QotD: From the M1903 Springfield to the M1 Garand
The M1 Garand is correctly considered the best battle rifle of World War II. It was the only semi-automatic rifle — meaning that it fired each time the operator pulled the trigger — to be the standard issue infantry rifle of any army during the war. Other forces were equipped with bolt-action rifles — the British Lee Enfield, Soviet Mosin Nagant, Japanese Type 99, German K98k, etc. — that required the operator to manually pull back a bolt to eject the [expended cartridge], and then push it forward again to insert a fresh cartridge into the chamber. The most obvious advantage was an increased rate of fire: a semiautomatic rifleman with an M1 had an official aimed rate of fire of 24 shots per minute.1 Compare this to the 15 aimed shots that British soldiers were expected to pop off with a bolt-action Lee Enfield in a “mad minute” drill. And the Lee Enfield was one of the fastest bolt-action rifles ever produced! In a pinch, a GI could blast out a clip in a few seconds, approximating a burst from an automatic weapon.2 Furthermore, with semi-automatic fire, the shooter could stay focused on his target, whereas working the bolt generally forced the shooter off target, requiring time to reacquire a proper sight picture.
Lt. General George Patton famously called the M1 Garand “the greatest battle implement ever devised“, a quote often repeated reverently in the context of World War II nostalgia. The US Government after the war gave away millions of M1 Garands, making it a popular civilian rifle for hunting and competitive shooting.
But nostalgia aside, it is also possible to view, from the high perch of hindsight, the M1 Garand as a missed opportunity. The most advanced battle rifle of World War II ultimately looked back too much to the past rather than pointing the way to the future. During its development, senior military officials applied the perceived lessons of the Spanish American War to a rifle designed to solve the problems of the Great War. This intervention prevented the M1 Garand from becoming something closer to a modern assault rifle, with an intermediate power cartridge and higher magazine capacity. The army was in no hurry to ditch the rifle that had won World War II, meaning that the United States did not field its first true assault rifle until two decades after the concept had been invented by the Germans in 1943 and soon successfully adapted by the Soviets in 1947. The first American assault rifle, the M16, would not debut until 1965.
First a necessary caveat: rifles were not the decisive weapon in World War II. For the most part the small arms deployed by the United States had been designed to fight World War I: the Browning Automatic Rifle (1918), the M1919 Browning Medium Machine Gun (as the date implies, first fielded in 1919) and the M2 Browning heavy machine gun, designed in 1918 and so good it is still used over a century later. In contrast, German machine guns were somewhat more recent in design: the MG 34 (as the name implies, first fielded 1934) and the MG 42. During the war, the Germans invented the first true assault rifle, the StG 44.
The secret sauce of the US Army by 1944-45 had little to do with firearms at all: it was a combination of ready mobility through motorization combined with deadly artillery and close air support, enabled by an unmatched communication system that allowed forward observers to direct and adjust fires to lethal effect. The American way of war was rooted in fleets of trucks and jeeps, networks of radios and heaps of shells. Having a nice semi-automatic rifle was ancillary to a conflict like World War II. But the M1 Garand is a useful window into the vagaries of military procurement and technological innovation, which require developers to at once predict the operational environment of the future and analyze the lessons of the past.
Throughout the 1920s, officers at the Infantry School in Fort Benning experimented with new tactics that they hoped would again allow for mobile infantry combat and avoid the trench stalemate of World War I. The basic solution was some form of “fire and maneuver”, in which one section of a unit (say a squad or platoon) would lay down a sufficient base of small arms fire to suppress the enemy so as to facilitate the other section’s advance. By alternating suppression and assault the element might leapfrog its way forward, even against entrenched enemy machine guns.
For such a tactic to work, infantry platoons needed a lot of firepower. Some might come from light machine guns, like the Browning Automatic Rifle, which was issued to individual infantry squads. But it was generally realized that individual infantrymen needed to be capable of a far higher rate of fire than could be provided by the standard issue rifle, the bolt-action M1903 Springfield, fed from a five round magazine. To this end, the US government set about developing a semi-automatic rifle.
The charge was taken up by John C. Garand, a Canadian-born, self taught firearms designer who worked for the Springfield Armory in Massachusetts. Garand’s solution to make the rifle self-loading was to insert a piston beneath the barrel. When the gunpowder exploded in the cartridge, the gas produced in the explosion propelled the bullet out the barrel. But some gas was bled off into a cylinder below the barrel (which gives the M1 its peculiar appearance of seeming to have two barrels); the pressure of the gas in the cylinder drove a piston.3 This piston attached to an operating rod which pushed the bolt of the rifle back, ejecting the spent casing, and allowing a spring in the internal magazine to insert another cartridge into the chamber before a separate spring pushed the operating rod forward and closed the bolt for the next shot, all in a fraction of a second.
Garand had initially worked on a rifle chambering the standard .30-06 cartridge used by the M1903 Springfield rifle (the .30 indicates that the bullet had a diameter of .30 inches, while the 06 indicates that the cartridge had been adopted in 1906; the round is often pronounced “thirty-ought-six”. But when a rival designer named John Pedersen, also affiliated with Springfield Armory, developed a semi-automatic design that chambered a lighter .276 (7mm) round, Garand retooled his project for the lighter round as well, producing a prototype known as the T3, with subsequent refinements labeled the T3E1 and T3E2. The smaller round meant that the internal magazine of the T3E1/2 could accept clips of 10 bullets, doubling the magazine capacity of the M1903 Springfield.
Army officials were very interested in the new round, but wanted proof that a lighter bullet would be sufficiently lethal in combat. A series of grisly ballistic tests were therefore ordered, pitting the .276 round against the traditional .30-06. In 1928, anesthetized pigs were shot through with both rounds. To the surprise and consternation of traditionalists, the .276 did far more damage in the so-called “Pig Board”. This is not paradoxical: the lighter round was more likely to “tumble”, precisely because it was lighter and so more likely to have its trajectory disrupted by bone and tissue; the tumble meant that more of the kinetic energy was expended inside the target, causing far more damage. The .30-06, meanwhile, as a more powerful round, was more likely to punch clean through, retaining its kinetic energy to keep moving forward after passing through the target. Eventually, tests of this sort would be used to sell the army on the lethality of the 5.56mm round used by the M16/M4, which has an even greater tumble, and causes even more grievous injuries. Out of concern that the fat bodies of pigs did not accurately replicate the human teenagers that the new round was designed to kill, a new test was inflicted upon goats, seen as more appropriately lean and therefore better analogs. The result was the same in favor of the .276 (a lighter .256 performed even better). With two rounds of tests vindicating the .276, the Army demanded that its new rifle chamber the .30-06. The final decision was made by Douglas MacArthur himself.
The .30-06 round itself had been the product of a painful lesson learned during the Spanish American War. Here, American troops, armed with Krag M1892 rifles, had found themselves badly out-ranged by Spanish troops armed with Mausers; the famous charge up San Juan Hill occurred after US troops had advanced for some distance under a hail of unanswered rifle fire. Given the importance of sharp shooting to the American military mythos, getting handily outranged and outshot by Spanish forces was a painful embarrassment. The first order of business had been to adopt the Mauser design: the M1903 Springfield was essentially a modified Mauser, as the US government had licensed a number of Mauser’s patents. By upgrading the M1903 to take the heavy .30-06 round, the Army ensured that soldiers could engage targets over a kilometer away. Beyond the deeply ingrained “lessons learned” from the Spanish American War, the mythos of the deadly American sharpshooter was strongly entrenched. Even as disruptors at Benning developed new infantry tactics that stressed volume of fire over accuracy, the phantoms of buck skinned frontiersmen sniping at British redcoats from a thousand paces still occupied the headspace of military leaders; they wanted a rifle with long distance accuracy. The sights on the M1 Garand adjust out to 1200 yards.
But MacArthur’s reasoning seems to have been primarily motivated by administrative and logistical concerns, as he cited the generic difficulties of fielding a lighter round. Some of these challenges may have been related to production and distribution of a sufficient stockpile of new caliber ammunition. There may have also been a concern with the new round complicating the logistics of line companies. The army also used .30-06 for the BAR and Browning medium machine gun, and having all of these shoot the same round in theory simplified the supply of line companies, and allowed for cross-leveling between weapons systems. Similar concerns have the US Army maintaining a policy of only having 5.56mm weapons at the squad level (thus the M4 and M249 Squad Automatic Weapon both shoot 5.56, and the SAW can shoot from M4 magazines).4 Still, MacArthur’s concerns seem unfounded in hindsight. The United States was about to produce billions of bullets during World War II. American troops were about to be so lavishly supplied that distributing two types of bullets would have been readily feasible given the soon to be proven quality of American logistics.5
With MacArthur’s edict, Garand retooled his rifle back to the .30-06 caliber, and his design was finally accepted in 1936. But the larger and more powerful round required a design change: the internal magazine now took clips of eight bullets instead of ten. Two rounds may not sound like much, but every bullet can be precious in a firefight, and this represented a 20% reduction in magazine capacity. Spread over a company sized element, the reduced clip capacity represented over two-thousand fewer rounds that a company commander could expect to fire and maneuver with. Indeed, the M1’s volume of fire proved generally insufficient to suppress the enemy on its own during the war, evidenced by the habit of equipping rifle squads with two Browning Automatic Rifles, instead of one. Marine divisions by the end of the war often deployed three BARs per squad.6
Michael Taylor, “Michael Taylor on The Development of the M1 Garand and its Implications”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-09-08.
1. TM 9-1005-222-12.
2. Thus George Wilson, a platoon leader and later company commander in the Fourth Infantry Division, describing a platoon scout stumbling upon the enemy: “The second scout emptied the eight round clip in his M-1 so fast it seemed like a machine gun … the rest of us moved very cautiously and found three dead enemy soldiers in the road.” (G. Wilson. If You Survive. Ivy, 1987).
3. John Garand’s initial design, and early production M1s, had a gas trap inserted over the muzzle to catch the gas after the bullet had exited; when this proved prone to fouling, a design modification drilled a small hole in the barrel just before the muzzle to allow the gas to bleed into the cylinder, most M1 Garands had this “gas port” system.
4. In 2023, US Army infantry will begin transition to the M7 carbine and M250 Squad Automatic weapon, which will both use a 6.8mm bullet, out of concerns that the 5.56 NATO is insufficient to penetrate body armor.
5. Editor’s Note: I agree with Michael here in principle: US logistics could have managed this. But I would also note that part of the reason American logistics were so good is that they applied MacArthur’s reasoning to everything, reusing vehicle chassis, limiting the number of different ammunition calibers and demanding interchangeable parts across the whole range of military equipment. Take one of those decisions away and the whole still functions. Take all of them away and one ends up with the mess that was German production and logistics.
6. Editor’s Note: BAR goes BARRRRRRRRRRR.
February 23, 2024
The Royal Navy ballistic missile submarine commander’s “Letter of Last Resort”
Britain’s Royal Navy always has a nuclear submarine — currently one of the Vanguard-class — at sea with a unique mission … stay undetected to ensure the survival of Britain’s nuclear deterrent in the form of the boat’s live nuclear weapons. Ned Donovan reposted an article on the mission orders each sub commander has locked in a safe for the duration of the mission:

HMS Victorious, a Vanguard-class ballistic missile submarine in the Clyde estuary on transit to base at Faslane on 8 December, 2003.
Photo: LA(phot) Mez Merrill/MOD via Wikimedia Commons
Somewhere out in the North Atlantic, every hour of the day, every day of the year, a lone submarine glides through the ocean with no real destination. Since 1969, one of the four boats of the UK’s Continuous At-Sea Submarine Deterrent has always been on patrol. Its location is known to only a handful, even many of her crew will have no idea where they are.
While many Royal Navy captains hold responsibility for their crew, Trident submarine commanders also bear a far more macabre role: the duty to play Britain’s final political and diplomatic hand possible. Within the bowels of each boat lays two safes, an outer and an inner, and within that inner safe sits the letter of last resort.
One of the first tasks of the Cabinet Secretary on the appointment by the Queen of a new prime minister, is to have the new leader write that very letter.
After the elation of an election victory, the civil servant informs the politician that this letter will lay out the action the prime minister wishes to take, should the government and chain of command be totally destroyed by nuclear attack. Tony Blair, according to his cabinet secretary, was said to have gone “quite white” on being told of his options.
Options do allow a great deal of latitude, with varying degrees of widespread destruction of human life:
- Retaliate with nuclear weapons without prejudice.
- Do not retaliate at all.
- Allow the commander to act within his own discretion.
- Place the boat under the control of an allied navy, specifically the Royal Australian Navy or US Navy.
Given some time alone, the prime minister is requested to decide and write it in a letter addressed to the commanders of each of the Vanguard-class submarines in the navy. The message is then sealed in an envelope and sent to be placed into the boats’ safes. So far, none of these missives have been opened, and the letters are burned at the end of each premier’s term.
The only prime minister to comment openly on their orders was Lord Callaghan in an interview with historian Peter Hennessy:
If it were to become necessary or vital, it would have meant the deterrent had failed, because the value of the nuclear weapon is frankly only as a deterrent. But if we had got to that point, where it was, I felt, necessary to do it, then I would have done it. I’ve had terrible doubts, of course, about this. I say to you, if I had lived after having pressed that button, I could never ever have forgiven myself.
To get to the stage where the letters can be opened is a long and purposefully difficult journey. First, the prime minister must have perished or become incapacitated in some way. Then, his proposed alternate decision makers would had to have met the same fate. It is only after that point that the submarine commanders go anywhere near their safes.
Updated to fix broken link.
The Gun Science Says Can’t Work – Madsen LMG Mechanics
Forgotten Weapons
Published 21 Nov 2023The Madsen LMG is generally considered an extremely complex and confusing system — but is it really? Today we are taking one apart to see just how it actually works. Because in fact, it’s a very unusual system, but not really any more complicated than any other easy self-loading action.
(more…)
February 22, 2024
Allied War Crimes, Latin American Troops, and Top-Secret Proximity Fuzes – WW2 – OOTF 033
World War Two
Published 21 Feb 2024Did the Western Allies commit war crimes? What did Latin American troops do during the war? And, how did the top-secret proximity fuze change the face of warfare? Find out in this episode of Out of the Foxholes.
(more…)
February 21, 2024
Can you make a tank disappear? The Evolution of Tank Camouflage
The Tank Museum
Published Nov 17, 2023It’s not easy to hide a tank. But over the years, military commanders have developed ways to disguise, cover and conceal the presence of their tanks from the enemy. This video is about the “art of deception” – and how, since World War One, through World War Two and into the present day, the science of tank camouflage has evolved to meet the conditions and threats of the contemporary battlefield.
00:00 | Intro
01:38 | WWI
06:26 | WW2
13:42 | Post War
19:40 | Conclusion
(more…)
February 20, 2024
Belt-fed Madsen LMG: When the Weird Get Weirder
Forgotten Weapons
Published Nov 15, 2023First produced in 1902, the Madsen was one of the first practical light machine guns, and it remained in production for nearly 5 decades. The Madsen system is a rather unusual recoil-operated mechanism with a tilting bolt and a remarkably short receiver. The most unusual variation on the system was the belt-fed, high rate-of-fire pattern developed for aircraft use. This program was initiated by the Danish Air Force in the mid 1920s, and several different patterns were built by the time World War Two erupted.
The model here was actually a pattern that was under production for Hungary when German forces occupied Denmark. Taking over the factory, they continued the production and the guns went to the Luftwaffe for airfield defensive use.
In order to use disintegrating links instead of box magazines, some very odd modifications had to be made to the Madsen. One set of feed packs are actually built into the belt box itself, and the gun cannot function without the box attached. The only feasible path for empty link ejection is directly upwards, and so a horseshoe-shaped link chute was attached to the top cover, guiding links up over the gun and dropping them out the right side of the receiver. Very weird!
While several thousand of these were made under German occupation, very few survive today and they are extremely rare on the US registry.
(more…)
February 17, 2024
Breda 37: Italy’s Forgotten Heavy Machine Gun
Forgotten Weapons
Published Nov 11, 2023The Breda Model 37 was Italy’s standard heavy machine gun (which meant a rifle-caliber gun fired only from a tripod) during World War Two. It was chambered for the 8x59mm cartridge, as Italy used a two-cartridge system at the time, with 6.5mm for rifles and the heavier 8mm for machine guns to exploit their longer effective range. Production began in 1937 and continued until the end of the war, with a batch being made for German use after the Italian armistice in 1943. Pre-war it was also sold to Portugal as the m/938. It remained in Italian use after the war as well, eventually replaced by the MG42/59.
The Breda 37 is a durable, reliable, and overall very good design. It uses 20-round feed strips, with the quite unusual feature of placing fired cases back into the strips rather than ejecting them out of the gun. It is a relatively unknown gun today, but this is not because of any inferiority on its part.
(more…)
February 15, 2024
Artillery! A WW2 Special
World War Two
Published 14 Feb 2024The modern artillery of the Great War was responsible for the vast majority of military deaths in that conflict, but how has artillery developed from that war to this one? Today we take a look at some of the artillery of WW2.
(more…)
February 14, 2024
Soviet World War Two Swords? The M1927 Shashka
Cossack forces have long been a key cavalry element of the Russian military, and this did not change during the Soviet era. The Cossacks had their own rather distinctive style of sword, the shashka, and the Red Army maintained the tradition of issuing them to Cossack cavalry troopers. In 1927, a new pattern was adopted, and it was produced and issued from 1928 until 1946. The shashka has a slightly curved, single-edged blade and no handguard. The model 1927 military type was initially made with a rather decorative pommel, but this was simplified to just a plain 5-pointed star as German advances into Russia really stressed Soviet industrial production. However, production and issue of the shashka continued uninterrupted throughout the war.
Originally there were separate trooper and officer versions of the model 1927, with the trooper version including the ability to stow the trooper’s Mosin-Nagant rifle bayonet on the side of the shaskha scabbard. As cavalry, the Cossacks were not expected to carry their rifles with bayonets fixed, and this served in lieu of a bayonet sheath. By 1944 this feature was omitted, as the M91/30 was replaced by the M38 and M44 carbines and submachine guns, which did not use bayonets.
The decorations returned to the M1927 shashka in 1945, with a series made for the Victory Day parade celebrating the defeat of Germany. Today’s example is one of these, and in beautiful condition.
February 11, 2024
Inkunzi PAW aka Neopup – 20mm Direct-Fire Grenade Launcher
Forgotten Weapons
Published Jun 22, 2018The Inkunzi PAW (Personal Assault Weapon) is a 20mm shoulder fired semiautomatic grenade launcher designed by Tony Neophytou (and previously known as the Neopup). It is a creative and very interesting weapon system, both from a mechanical perspective and also from a question of practical application.
The PAW has a 6-round detachable rotary magazine, and an effective range of 1000m for area targets and 600m for point targets. Its purpose is to give the individual soldier an explosive area-effect weapon that fires like a rifle. To this end, the ammunition has been developed to give a muzzle velocity of 1000fps (310m/s), giving it a far flatter trajectory and shorter flight time than a 40mm grenade, either low pressure or high. It allows rapid repeat shots, rapid reloading, and easy target transition. The high muzzle velocity (for a grenade launcher) makes range estimation and engagement of moving targets much simpler than with the rainbow-like trajectory of 40mm systems. For specialized modern applications like guarding against one or more vehicle suicide bombs, fast-moving pirate skiffs, it seems extremely compelling. That utility extends to typical targets as well, like light armored vehicles, buildings, gun emplacements, and even something as simply as a patch of brush with an enemy hiding within somewhere. Typical small arms fire requires a substantial expenditure of ammunition for targets like those, while an explosive 20mm projectile can neutralize them in one or two rounds, without the need for a direct hit. The lethal radius of a 20mm HEI shell is between 6 and 18 feet (2m – 6m) depending on who you ask. That’s a significant margin of error.
Mechanically, the PAW is a simple system to disassemble, and it uses a quite clever inertial locking system which is clean and reliable. The unique layout with the grip on the right side is done to accommodate the hydraulic recoil system, which allows the action to slide back into the stock assembly on each shot. This absorbs much of the recoil and spreads its effect out on the shooter, making it not unpleasant to shoot. An easy stowage feature allows the gun to be locked in its compressed configuration, shortening it for transit and also offering a way for the gun to be carried with a round chambered and ready to use, but with the trigger safely disconnected to prevent accidental firing for troops in armored vehicles or helicopters.
Compared to the American XM-25, the PAW strips away the overcomplications of laser designation and complex projectile fusing, which are arguably not really necessary anyway. It offers a simple and effective system, with tremendous firepower as well as suppression capability (nothing says go away quite like rapid fire explosives). It does this with a larger magazine and more compact and lighter weight design, no less.
It is rare to find a truly unique and innovative firearm these days, but that is exactly what Tony Neophytou has done here. The design is elegant in its simplicity, and well refined. It truly offers a unique set of capabilities — while it has been purchased in limited numbers by several smaller militaries, I hope to see it given serious consideration by some first-tier forces, as I think it has tremendous potential.
(more…)
February 9, 2024
You can’t pro-actively synergize action-oriented metrics in the heat of battle
No, I’m not sure if that headline makes any sense, as I was never particularly receptive to the latest buzzwords of any given management fad that went through from the 70s onwards. They all seemed to share a few characteristics along with a bespoke sheaf of buzzwords, PowerPoint slides galore, and lots of spendy courses you had to send all your employees to endure. Is there anything more dispiriting to staff morale than a VP or director who’s just returned from a week-long training seminar in an exotic location on this year’s latest “revolutionary” “transformational” management fad?
It’s bad when companies that make widgets or smartphone apps or personal hygiene products fall for these scams, but it’s terrifying to discover that your military isn’t immune … and in fact revel in it:
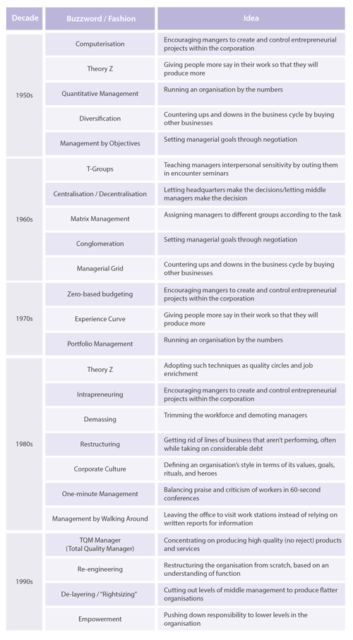
Image from “Fads and Fashions in Management”, The European Business Review, 2015-07-20.
https://www.europeanbusinessreview.com/fads-and-fashions-in-management/
We spent these last few decades since the fall of the Soviet Union weaving a comfortable web of CONOPS and implemented “efficiencies” constructed of consultant-speak, weekend-MBA jargon, and green eyeshade easy-buttons bluffed from the podium by The Smartest People in the Room™ to an audience on balance populated by people who already had the short list of jobs they wanted once they shrugged off their uniform in a PCS cycle or two.
Agree, endorse, parrot, prepare …. profit!
War is New™!, Revolutionary™!, Transformational™!. Hard power is Offset™! If we change a bunch of simple words in to multi-syllabic cute acronyms … then the future will be ours, our budgets will be manageable, and our board seats will be secured! Efficiency to eleventy!
Facing the People’s Republic of China on the other side of the International Date Line … how efficient do you feel? How effective?
Something very predictable happened in our quarter century roadtrip on the way to Tomorrowland; we realized instead we wound up on Mr. Toad’s Wild Ride instead.
I would like the record to show here in 2QFY24 that this exact problem was discussed in detail back when I was a JO in the mid-1990. This is not shocking to anyone who is wearing the uniform of a GOFO. They lived the same history I did.
We knew we were living a lie that we could sustain a big fight at sea. An entire generation of Flag Officers led this lie in the open and ordered everyone else to smile through it. Ignore your professional instincts, and trust The Smartest People in the Room™.
Once again, Megan Eckstein brings it home;
If U.S. military planners’ worst-case scenario arose in the Pacific — having to defend Taiwan from a Chinese invasion — American military forces would target Chinese amphibious ships.
Without them, according to Mark Cancian, who ran a 2022 wargame for the Center for Strategic and International Studies that examined this exact scenario, China couldn’t invade the neighboring island.
…
U.S. submarines would “rapidly fire everything they have” at the multitude of targets, Cancian said, “using up torpedoes at a much, much higher rate than the U.S. has expected to do in the past.”
Navy jets, too, would join in — but they’d run out of Long Range Anti-Ship Missiles within days, …
It’s this nightmare scenario that’s driving the Navy to increase its stockpile of key munitions: the LRASM, the MK 48 heavyweight torpedo, the Standard Missile weapons and the Maritime Strike Tomahawk, among others.
Over a decade after the Pacific Pivot, a couple of years after the US Navy became the world’s second largest navy after being the worlds largest for living memory of 99% of Americans, and two years after the Russo-Ukrainian War reminded everyone that, yeah … 3-days wars usually aren’t.
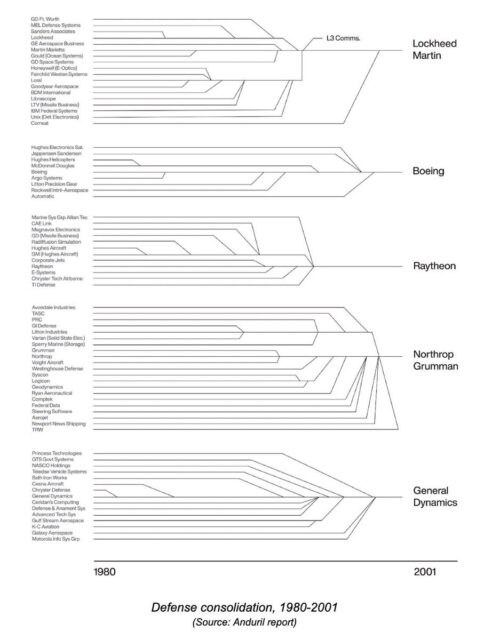
And the defence industries of the 1980s and 90s have all swallowed up smaller competitors — again following “normal” business practices of the time, seeking economies of scale and manufacturing efficiencies and closing down less-profitable assembly lines or entire lines of business.
Let’s go back to SECDEF Perry’s 1990s “Last Supper”, you know, the one that was all about the efficiencies of consolidation of the defense industry.
Three decades later, what is the solution to the strategic risk we find ourselves in due to our inability to arm ourselves?
… “the bottleneck is rocket motors” because so few companies are qualified to build them for the United States, Okano explained. To help, the Navy issued a handful of other transaction agreement contracts to small companies who will learn to build the Mk 72 booster and the Mk 104 dual-thrust rocket motor so prime contractors have more qualified vendors to work with, she added.
LOLOLOL … what “small companies?” That ecosystem is “old think”. If we need to go back to that structure, that will take decades not just to build, but decades of a viable demand signal.
Looks like we have started that as “small companies” perhaps repurpose part of their company to a military division. If we can just stop them from being gobbled up by the primes, it might be nice to return to a more robust, competitive ecosystem. Soviet-like consolidation and McNamaraesque efficiencies got us here, perhaps time to try something old as new again.
Nothing is less efficient to go to war with than a military designed for an efficient peace.
February 8, 2024
Beretta 1915: The first of the Beretta pistols
Forgotten Weapons
Published Jun 22, 2016The Italian military went into WWI having already adopted a semiautomatic sidearm — the Model 1910 Glisenti (and its somewhat simplified Brixia cousin). However, the 1910 Glisenti was a very complex design, and much too expensive to be practical for the needs of the global cataclysm that was the Great War. In response to a need for something cheaper, Tulio Marengoni of the Beretta company designed the Model 1915, a simple blowback handgun chambered for the 9mm Glisenti cartridge.
Only 15,300 of the Model 1915 pistol were made, because even they proved to be a bit more than the military really needed. One of their most interesting mechanical features is a pair of manual safeties — one on the back of the frame to lock the hammer and one on the left side to block the trigger. This proved a bit redundant, and the gun overall was rather large and heavy. In 1917 a scaled-down version in .32 ACP (7.65mm) was introduced which would be produced in much larger numbers. The 1915/17 would also omit the rather unnecessary hammer safety.
It is important to note that while the 9mm Glisenti cartridge is dimensionally interchangeable with 9×19 Parabellum, pistols designed for the Glisenti cartridge should never be used with standard 9×19 ammunition, as it is nearly 50% more powerful than the Glisenti specs, and doing so will quickly cause damage (and potentially catastrophic failure).
February 6, 2024
5 HEAVY Tanks | Tank Chats
The Tank Museum
Published Nov 10, 2023Enjoy this compilation of classic Tank Chats presented by David Fletcher. We’ve put together David’s chats on TOG 2, FV4005, Conqueror, Conway and the 40 Ton Centurion – representing some of the heaviest tanks in our collection.
(more…)