Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 13 Sep 2022
September 14, 2022
Whisky – Scotland’s Water of Life
“Americans, particularly the kind of Very Serious people who make up our intelligentsia, are desperate for a good war”
Freddie deBoer thinks he’s sussed out the reason so many Americans are so very, very pro-Ukraine in the ongoing fighting between the Russian invaders and the Ukrainian defenders (beyond the normal desire to “root for the underdog”):
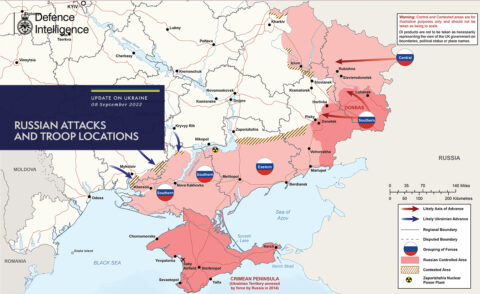
Approximate front-line positions just before the Ukrainian counter-attack east of Kharkiv in early September 2022.
It was not until I was an adult that I realized that the absurd fervor for Desert Storm was in fact about Vietnam. Fifteen years earlier, American helicopters had fled in humiliation from Saigon, and nothing had happened to take the sour taste out of the mouth of Americans since. There was plenty of power projection in that decade and a half, but no great good wars for the United States to win in grand and glorious fashion, unless you worked really hard to talk yourself into Grenada. America had been badly stung by losing a war to a vastly poorer and less technologically-advanced force. Americans had been nursing their wounds all those years. So when Saddam Hussein invaded Kuwait, and the “international community” rose to expel him, the country was ready. We were ready for another righteous combat of the Goodies vs. the Baddies. We were ready for the good guys to be the winners again.
This dynamic, I’m certain, is the source of American bloodlust over Ukraine.
We have now spent twenty years without good, noble wars against the Baddies ourselves. Afghanistan was a war effort undertaken in rage and terror, and was accordingly never intelligently conceptualized at the most basic level. The war aim of finding and capturing bin Laden and destroying Al Qaeda gave way to a war on the Taliban that ensured an endless occupation. The Potemkin government we installed was never popular with the people of the country, entailed comical levels of corruption, and showed no ability to train a loyal and effective Afghan army. After 20 years our country tired of spending hundreds of billions on that failure, we left, the government collapsed almost without resistance, and the Taliban are in power again. In Iraq, the basic arguments for the war (WMDs and a Hussein-al Qaeda connection) were swiftly revealed to be bullshit. Saddam’s army fell quickly and he was dispatched after a show trial, but a persistent insurgency inflicted thousands of American casualties. The chaos enabled the rise of ISIS and its various horrors. The new Iraqi government we’ve installed is impossibly corrupt and scores a 31/100 on Freedom House’s ratings of a country’s dedication to political rights and civil liberties. That’s what the United States has gotten for $8 trillion spent on warmaking since 9/11.
America loves a winner, and will not tolerate a loser. So I once heard. Americans, particularly the kind of Very Serious people who make up our intelligentsia, are desperate for a good war. A just war. A war where we win. They’re sick of wars that feel morally complicated, sick of wars that they have to feel queasy about, sick of wars that aren’t just Goodies and Baddies. They are very, very hungry for good war. I think Ukraine is the Desert Storm a lot of people have been waiting for: a war with (they insist) perfectly simplistic moral stakes, an impossibly noble (they assume) set of Goodies, a marauding and senseless (they demand) set of Baddies. All they’re waiting on is victory. And it’s for this reason, this view of war as one big cope, that the pro-Ukraine position is the single most rigidly enforced consensus in our country since 9/11. There is no other issue on which the majority has more vociferously demanded total consensus or more viciously attacked any who dissent or even ask questions. Because America needs a win. People need to believe in a Goodies and Baddies world again.
There are, of course, all manner of hard questions that we could ask, even if we were supportive of Ukraine in this war. That this is a conflict that has constantly inspired left-leaning people to literally say “well, yes, there’s Nazis, but …” might be seen as a matter of some concern. Perhaps, we might just say, isn’t that a little disturbing? But not in this discursive environment. Or we might consider that a total loss for Russia could be one of the most dangerous outcomes for the world even if you support Ukraine. What do you think happens, with a wounded and isolated Russia? Let’s say people get what they want and Putin is deposed. What do you think happens next? We finally get that shining city on a hill in Moscow that we were promised with the collapse of the Soviet Union? That we’ll get the world leader we expected Bagdhad to be in 2003, that a foreign country with foreign people and foreign concerns will suddenly become a docile member of the liberal-capitalist order? Maybe the best post-Putin outcome would be for a similar corrupt autocrat to take his place; at least then there might be stability. A far more likely and more frightening outcome is that leadership is splintered, you have in effect a set of rival warlords squabbling over the spoils, and the world’s largest nuclear arsenal is exposed in a terrifying way. Seems like something to worry about.
But, no. To a degree that genuinely shocks me, hard questions have been forbidden. Complications have been denied. Comparisons to previous conflicts have been forsaken. And this from Democrat and Republican, liberal and leftist, neocon and Never Trumper. It’s constant, everpresent, and relentless, the denial of any complication in the case of Ukraine and Russia. The glee and the gloating and the urge to ridicule anyone who takes even a single step outside of the consensus is remarkable, unlike anything I’ve ever really encountered before. And I find that I can’t even get people to have a conversation about that, a meta-conversation about why the debate on Ukraine is not a debate, about why there are many people who will consider any political position except one that troubles the moral question of Russia’s invasion, about why so many people who learned to speak with care and equivocation during Iraq now insist that there is no complication at hand with this issue at all. I can’t even get a conversation about the conversation going. People get too mad.
Marmite Dynamite Limited Edition — Tasting (Also Re-Tasting The Others, With A Spoon)
Atomic Shrimp
Published 20 Mar 2021More Marmite – I couldn’t get hold of a jar of this for the group tasting last week, but here it is now!
Here’s the previous video: https://youtu.be/MjrBTcnnK6c
QotD: The Wars of Religion and the (eventual) Peace of Westphalia
Thomas Hobbes blamed the English Civil War on “ghostly authority”. Where the Bible is unclear, the crowd of simple believers will follow the most charismatic preacher. This means that religious wars are both inevitable, and impossible to end. Hobbes was born in 1588 — right in the middle of the Period of the Wars of Religion — and lived another 30 years after the Peace of Westphalia, so he knew what he was talking about.
There’s simply no possible compromise with an opponent who thinks you’re in league with the Devil, if not the literal Antichrist. Nothing Charles I could have done would’ve satisfied the Puritans sufficient for him to remain their king, because even if he did everything they demanded — divorced his Catholic wife, basically turned the Church of England into the Presbyterian Kirk, gave up all but his personal feudal revenues — the very act of doing these things would’ve made his “kingship” meaningless. No English king can turn over one of the fundamental duties of state to Scottish churchwardens and still remain King of England.
This was the basic problem confronting all the combatants in the various Wars of Religion, from the Peasants’ War to the Thirty Years’ War. No matter what the guy with the crown does, he’s illegitimate. It took an entirely new theory of state power, developed over more than 100 years, to finally end the Wars of Religion. In case your Early Modern history is a little rusty, that was the Peace of Westphalia (1648), and it established the modern(-ish) sovereign nation-state. The king is the king because he’s the king; matters of religious conscience are not a sufficient casus belli between states, or for rebellion within states. Cuius regio, eius religio, as the Peace of Augsburg put it — the prince’s religion is the official state religion — and if you don’t like it, move. But since the Peace of Westphalia also made heads of state responsible for the actions of their nationals abroad, the prince had a vested interest in keeping private consciences private.
I wrote “a new theory of state power”, and it’s true, the philosophy behind the Peace of Westphalia was new, but that’s not what ended the violence. What did, quite simply, was exhaustion. The Thirty Years’ War was as devastating to “Germany” as World War I, and all combatants in all nations took tremendous losses. Sweden’s king died in combat, France got huge swathes of its territory devastated (after entering the war on the Protestant side), Spain’s power was permanently broken, and the Holy Roman Empire all but ceased to exist. In short, it was one of the most devastating conflicts in human history. They didn’t stop fighting because they finally wised up; they stopped fighting because they were physically incapable of continuing.
The problem, though, is that the idea of cuius regio, eius religio was never repudiated. European powers didn’t fight each other over different strands of Christianity anymore, but they replaced it with an even more virulent religion, nationalism.
Severian, <--–>”Arguing with God”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-01-20.



