Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 24 Jan 2020Tantalus! The number one dude known for his eternal punishment in Hades, perhaps second only to Sisyphus
Our content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS: https://www.redbubble.com/people/OSPY…
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/hhAZA2z
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
January 25, 2020
Miscellaneous Myths: Tantalus
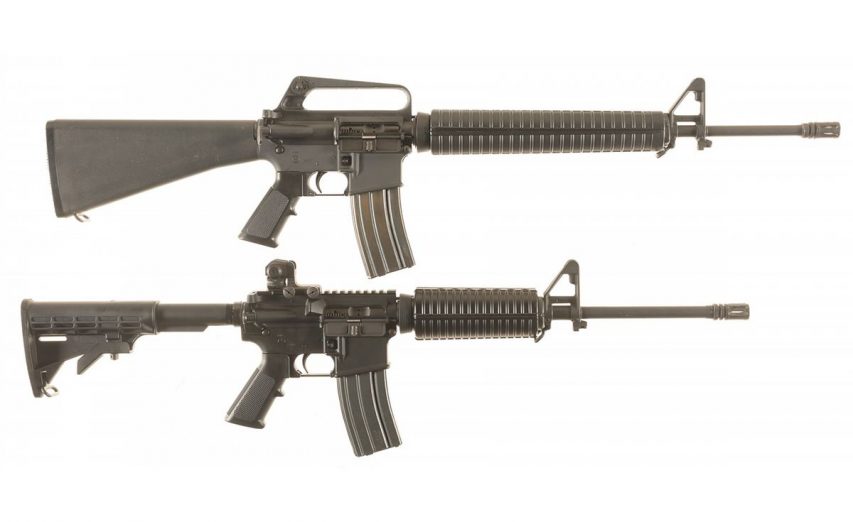
Petition against the Trudeau government’s proposed “military-style assault rifle” ban goes over 100,000 signatures
There may be little point in protesting, as the Trudeau government has a track record of ignoring what Canadians want to do what it intends regardless, but you can still sign the petition here (if you do sign, remember to click the confirmation link in the email you’ll receive after signing the petition). In the Post Millennial, Sam McGriskin reports that the petition has enough confirmed signatures to be the second-largest in Canadian history:
E-petitions can be open for 30, 60, 90 or 120 days for signature based on what the petitioner prefers. The petitions get a government response within 45 days of their opening. Public Safety Minister Bill Blair is overseeing the “buyback program” which Blair estimates could cost anywhere from $400 to $600 million.
Blair’s office did not respond to request for comment from The Post Millennial. His office was asked what the minister’s response is to over 100,000 Canadians calling on the government to drop what many experts see as a completely ineffectual action to curb gun violence. Blair was also asked about fellow Liberal MP Marcus Powlowsk’s letter addressed to him that opposed the gun ban (Powlowsk has since retracted the letter) and Winnipeg Police constable calling the ban “nonsense”.
“When we seize handguns, the handguns are always almost 100% in the possession of people who have no legal right to possess them. They’re almost always stolen or illegally obtained,” said Const. Rob Carver. “I simply don’t see how as a 27-year-old veteran, how adding another layer of law will make any difference, anywhere in this country.”
In Powlowski’s letter to Blair he wrote, “Over the course of the past three months, I have heard a wide variety of views on this proposed ban. I believe it is my role to ensure that these views are brought to your attention for consideration.”
“Given that there is currently no legal definition for a ‘military-style assault rifle’ in Canada, some community members I have spoken with are skeptical that a ban based on this term would make sense as a coherent firearm policy,” the letter continued.
In a CBC interview in the summer of 2018, Blair said that most of the gun crime is committed by illegal handguns smuggled in from the U.S. and he was skeptical of a gun ban being effective in combating gun crime. His position changed drastically once he was appointed by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau as the public safety minister.
The Liberal voters in downtown Toronto and other major cities want the government to “do something” about gun crimes, but nothing the government can do is going to make much of a difference for people who are already violating multiple laws, so all they can do is make things worse for those who are already obeying the laws as they stand. In the real world, this makes no sense, but in the fantasy world of electoral politics, the government needs to be seen to be “doing something” … and this, stupid as it may be, counts as “something”.
Swedish K: The Carl Gustav m/45B and the Port Said
Forgotten Weapons
Published 24 Jan 2020http://www.patreon.com/ForgottenWeapons
https://www.floatplane.com/channel/Fo…
Cool Forgotten Weapons merch! http://shop.bbtv.com/collections/forg…
During the 1930s, Sweden acquired an assortment of different submachine guns, including Bergmanns, Thompsons, and Suomis. As World War Two progressed, they decided that they really needed to standardize on a single caliber and model of gun, and requested designs from both the Carl Gustav factory and Husqvarna. The Carl Gustav design won out, and was adopted as the m/45.
It was a very simple open-bolt, tube-receiver, fixed-firing-pin design chambered for 9x19mm Parabellum ammunition. The original guns were built around Finnish Suomi magazines, both 71-round drums and 50-round “coffin” mags. After the war these were replace by a new 36-round traditional box magazine, and magazine well adapters were fitted to the guns which precluded the use of the larger mags. The new magazines were much more convenient to carry, less expensive, and more reliable.
The name “Swedish K” comes form the full designation: Kulsprutepistol m/45. The guns were used by American special operations forces in Vietnam until the Swedish government stopped export sales to the US, at which point the Navy commissioned Smith & Wesson to produce the Model 76 submachine gun (essentially a copy of the m/45). The design was also licensed by Egypt, which also licensed the AG-42 Ljungman rifle at the same time. The Egyptian copy was called the Port Said, and shows the features fo the original Swedish m/45 pattern, where the guns in Swedish service were mostly updated to the m/45B pattern.
Photo of m/45C with bayonet from: http://www.gotavapen.se/index_eng2g.htm
Check them out for a ton of information on Swedish small arms!
Contact:
Forgotten Weapons
6281 N. Oracle #36270
Tucson, AZ 85740
Refuting the pessimism of Malthus
In the latest edition of Anton Howes’ Age of Invention newsletter, he looks at the predictions of that old gloomy Gus, Thomas Malthus:
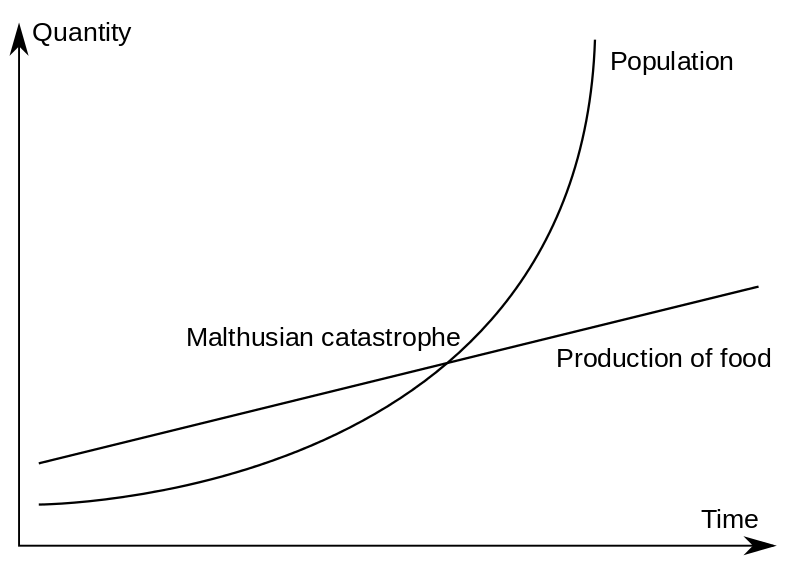
The Malthusian trap. For Malthus, as population increases exponentially and food production only linearly, a point where food supply is inadequate will inevitably be reached.
Graph by Kravietz via Wikimedia Commons.
For economies before the Industrial Revolution, population growth was an important and ever-present brake on prosperity — an observation most famously articulated by the Reverend Thomas Malthus. Writing at the end of the eighteenth century, he warned against the promises of improvement. Whereas the optimists looked at the acceleration of innovation around them and claimed infinite horizons for increasing living standards, Malthus pessimistically argued that population would always catch up. Although a new agricultural technology might briefly increase the amount of available food, the inexorability of population growth meant that it would soon be eaten up by extra mouths to feed. The population would end up larger than it was before the new technology, but with that population eventually no richer than it had been to begin with. Economic historians call this the Malthusian regime, or the Malthusian Trap.
Fortunately, Malthus’s pessimism would prove unfounded. Economy after economy has managed to escape the trap. British output had already been outpacing its population for two centuries by the time he was writing — England’s agricultural output alone had increased 171% while its population had grown 113% (not even taking into account the fact that it also increasingly relied on imported food, paid for by its other industries). And in the decades and centuries that followed, England’s output continued to shoot ahead, widening the lead. Output per capita rose and rose, to the extent that Malthus’s worries about overpopulation are now usually applied to resources other than food.
But while Malthus is famous for the theory, he wasn’t its inventor. Well before Malthus, the people who actually lived in the trap seem to have recognised its effects. Concerns about overpopulation may have led to the Garland or Flower Wars of the Aztec Empire and its neighbours: after a series of famines in the 1450s, the local states reportedly began to engage in ritual battles, with the losers captured and sacrificed to the gods. Still earlier, in ancient Greece, the young men of a settlement might be formally conscripted to go forth and colonise other islands and coastlines. They were typically banned from returning home for several years, and in at least one case slingers were posted on the shore to kill any of the colonists who tried to make a break for home. In a whole host of pre-industrial societies, “surplus” infants were often simply exposed to the elements.
By the sixteenth century, with the rise of print culture, Malthusian rationales were being clearly articulated. Here’s Richard Hakluyt writing in 1584, over two hundred years before Malthus:
Through our long peace and seldom sickness (two singular blessings of Almighty God) we are grown more populous than ever heretofore; so that now there are of every art and science so many, that they can hardly live one by another, nay rather they are ready to eat up one another.
It’s a direct statement of the Malthusian regime in action, expressed by one of England’s most influential Elizabethan intellectuals, and written specifically for the attention of the queen. Hakluyt thanked god for the recent and unusual lack of mass death, but now worried about overpopulation leading to low wages and unemployment. And he went on to list many other effects. Hakluyt argued that the misery would lead to unrest, thievery, begging, and “other lewdness”. The prisons filled up, where the poor either “pitifully pine away, or else at length are miserably hanged.”
Cursus honorum – Praetors
Historia Civilis
Published 19 Feb 2015Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/HistoriaCivilis
Website: https://www.historiacivilis.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/HistoriaCivilisMusic is “Sea” by Jahzzar (http://betterwithmusic.com)
QotD: The post-oil-crisis evolution of modern cars
Man I remember back in 1982, we all thought we’d be driving nothing but 3-cylinder diesels by the turn of the millennium. If you went back and told some gearhead in my high school class that in 2017 Dodge would be selling a “street legal” 10-second Hemi Challenger, he’d think you were talking about the 0-60 time of a 4-cyl car.
The computer changed everything. Not only in engine tuning and performance, but in design and modeling.
I had an example of a classic late Dark Ages car, an ’84 Trans Am with the LG4 305c.i. Rochester Quadrabog motor. A hunnert and fifty horsepower and nearly every engine function powered by enough dry-rotting vacuum tubing to reach to the moon and back…
Only a few years later and exotic computer-designed and controlled long-runner port fuel injection systems were common on domestic performance cars and HP numbers were on the right side of 200 for the first time in a decade.
It was coming out of an awful time. Like a friend wrote: When he went into seminary you could buy a Mustang with a nearly 400bhp engine option. When he left seminary, the Mustang was a Pinto.
Being a car enthusiast in America in the latter half of the 70s/first half of the ’80s was like being a dirt farmer in Fifth Century Britain, marveling at the weed-grown roads and disused aqueducts left by a race of giants and building your pig shed with stones looted from a burned library.
Tamara Keel, “Cars of the future from the past…”, View From The Porch, 2017-12-26.









