CDR Salamander on how the EU’s movers and shakers (i.e., mostly not democratically elected leaders) seem to have decided that their one true enemy is the United States:
If you are an American who lived on the European Continent, specifically Western Europe, you’re very familiar with an exceptionally sharp strain of anti-Americanism that resides in a significant percentage of their ruling elite – an adult version of the middle school mean girls. Though present in all nations to one degree to another, it is especially acute in Germany and France for slightly different reasons but are all working towards the same goal; degrade American influence in Europe.
The best way for this political and corporate anti-Americanism to find a lever of power is through the the trans-national and anti-democratic modern iteration of the European Union – made even more problematic with the departure of Great Britain who once played a balancing role between the Continental powers as she has for centuries.
Why primarily France and Germany? To start with, this is part of the sibling rivalry between the children of Charlemagne for primacy in Europe that has churned Europe over the last thousand years. The Anglo-Saxons on both sides of the Atlantic kept getting in the way of their return to the struggle.
Their armies under various blood-soaked leaders moved across Iberia to Moscow and back for centuries in order to be THE driver of power in influence on the continent. The European Union, once the “trade association” nose was in the tent, is now seen – fairly – as a mechanism to centralize power so The Smartest People in the Room™ no longer have pesky minor powers and – Buddha forgive – voters getting in their way. Without checks, power only seeks more power for itself. The morphing of the EU is just the latest example.
Not unlike their American counterparts who would like the USA to extract itself from foreign entanglements (NB: as I have written through the years, I am sympathetic/supportive of these efforts), many of the strongest proponents of the EU just want the USA to go home.
The Europeans, while benefiting from the WWII/Cold War leftover presence of the USA, want it to end and the influence that comes with it. If any opportunity to push back against the USA appears, they have their talking points ready to dirty up the reputation and standing of the USA. If that can be done while blaming Eurocrat failures on the USA as well, even better.
You know the Americans, citizens of that mongrel nation whose gene pool is full of religious zealots, failed revolutionaries, slaves, economic refugees, grasping second sons, criminals, and their descendants – spoiled with a continent overflowing with food, water, minerals, forests and open land they don’t even appreciate.
Loud. Fat. Pushy. Americans.
The usual snarled insults cobbled together by smug people who get much of their opinions of the USA by reading The Washington Post or The New York Times. “I know America, I read your newspapers.” That is right after, “I’ve been to America. I spent a week in DC/NYC/Boston/Chicago. I studied a semester at Brown.”
[…]
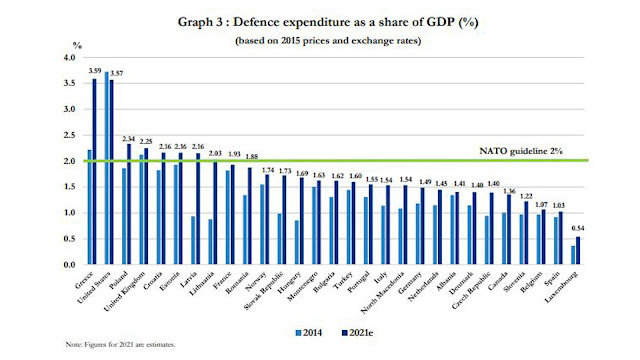
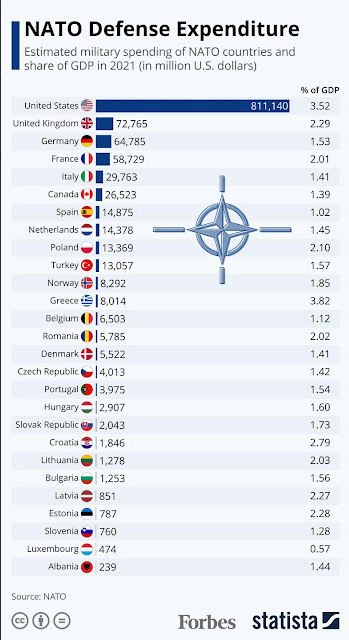
The smaller European nations don’t trust France and Germany all that much, for good historical reasons. Most of the Europeans in the “new territories” in the east like the USA. They see the Americans as a more reliable guarantee of safety from hostile powers in the East, having a few centuries of experience of the Western European Frankish tribes carving them up for fun and profit – irrespective of local desires. Collectively these nations are not that large in GDP or population – not much more than Italy (for now), but that’s OK. They have the correct geography.
If we shape this relationship correctly, we don’t have to permanently garrison this part of Europe. Poland is already establishing a new paradigm of proper levels of security investment. Once NATO’s eastern front calms down a bit, we can rotate through forces for exercises and training. Perhaps even create some combined training and logistics bases ready to scale up in case of trouble in Mordor. A template we should have put in place in Western Europe decades ago.
Reward positive behavior and let the French and Germans continue their millennium-length struggle – peaceful this time – in the west; keep them frothing in Brussels and Strasbourg while the forward-looking nations try to set up the next thousand years of Western progress in a positive direction.
Perhaps.