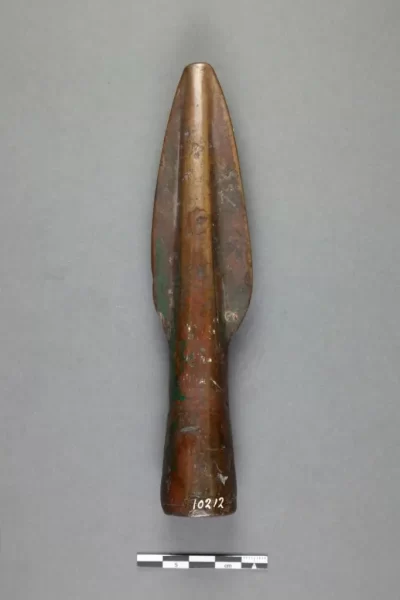
From the Museo Arqueológico Nacional in Madrid, a bronze spearhead (inv. 10212) from Italy, c. 1300-900 BC, identified as Villanovan or proto-Villanovan.
Why are so many early iron spearheads shaped this way? Well, the easy answer to the question is that it is because even earlier bronze spearheads were shaped this way. In every culture I’ve studied with the omni-spear, you can find bronze spearheads with the same basic shape – the strong mid-ridge, leaf-shaped blades and circular socket – proceeding them. There are differences; the bronze spearheads of this type tend to be shorter and as a result somewhat “stubbier” (that is, they’re just as wide, but not as long) compared to the later iron spearheads which borrow their shape. That seems like it is probably a concession to metallurgy and possibly production. On the production side, bronze artifacts were generally cast to shape and depending on the temperature of the cast and type of casting method, that can place upper-limits on the size of the final artifact. Certainly ancient bronze-smiths were capable of managing very large casts with high quality metals – the heaviest recovered naval ram (the Athlit ram, as far as I know) is absolutely massive at 465kg, cast in a single piece.
That said, I suspect the real issue that limits the size of bronze spearheads is the metal itself. Weapons generally tend to push their materials to the outer edges of what they are capable of, because of the demand to keep weight low: the smith is looking to hit the absolute minimum amount of metal which will handle the strains of impact. And the strains of impact here are considerable! Bronze under stress tends to undergo plastic deformation, which is to say that it bends and doesn’t bend back, it isn’t “springy”. As a result bronze weapons – swords, spearheads, arrow-heads, etc. – tend to be quite a bit shorter than later iron weapons, so that they can withstand the rigors of combat without permanently deforming in a way that would render them useless. But iron when put under mild stress deforms elastically, which is to say it is “springy” and when the force of stress is removed it bends back to its original shape (adding carbon to make a high-carbon “spring steel” can improve this quality), so even while iron isn’t any harder than bronze (though steel most certainly is), an iron weapon can take a bigger hit and not end up hopelessly bent. And that is even more true once you begin adding really any amount of carbon to make even very mild steels.
Consequently, you can push an iron sword to be longer for the same weight because you can count on it withstanding a hit, bending a bit to absorb the force and bending back when the force is removed, better than bronze. I suspect the same thing is happening as bronze spearhead designs shift to iron: smiths are realizing they can get a somewhat longer point, with a longer more deadly taper, without an unacceptable increase in weight.
But then why keep the shape? Because a lot of bronze age sword shapes drop or are extensively modified fairly quickly in the shift to iron in places where the omni-spearhead remains the standard shape, albeit somewhat larger than its bronze variant.
Well, the answer, to me, seems to be that its a pretty useful shape, at least in a particular combat environment.
The round socket, of course, is to fit the round haft of the spear. These sockets are, as noted, generally round, which suggests that these spears are almost entirely being used to thrust. You probably could cut with the edges of these blades, but if that was how you expected to use the spear, you’d want a different haft shape so that you could feel the alignment of the edges of the blades. Interestingly, octagonal or rhombic sockets are a minority type that appears in a lot of places (both Gaul and Spain, for instance), but they remain really rare, as opposed to, say, medieval polearms, where non-circular hafts become common over time so that the wielder can feel that edge-alignment.
Extending the socket to make the mid-ridge also makes a lot of sense, as it provides a nice, thick, stout element of the spear to resist the forces of impact, which is going to be a mix of compression and bending. In an ideal, perfect impact, it’d be all compression, but in the real world, your target isn’t standing still and your hit probably isn’t dead-on, so you want some part of the spearhead that can resist that impact and hold its shape, transmitting the force instead into the shaft. The mid-ridge, being nice and thick (and generally not hollow past the socket) accomplishes this neatly.
Meanwhile, those wide, thin blades ensure a wide wound that is going to slice through a lot of the target. You want that too, because the fellow striking with the weapon wants a wound which will disable their opponent as quickly as possible. After all, all of the time between the delivery of a wound and it becoming disabling is, definitionally, a period where you are in range of their counter-attack and they are not disabled and so able to give it. If you ever wondered why a lot of really narrow, quick effective piercing weapons like rapiers were less common on the battlefield, this is a big part of it: those penetrating wounds are really lethal but often not very quickly and in a battlefield (where you may not be able to quickly back off after having delivered a fatal wound) you want a wound that, fatal or not, is going to disable fast.
Wide slicing wounds do that for you, because they cut across blood vessels, muscles and tendons. The former leads to rapid blood-loss, which can be disabling (and of course, fatal, but again, you care about disabling; fatal or not is a problem to consider once you are out of danger), while the later can instantly render limbs useless. It doesn’t matter how much adrenaline or willpower an enemy has, if a blow has sliced the muscles they would use to move their limbs, they cannot physically move those limbs.
The shape of the blades also seems intentional. While we do see neatly “oval” shaped blades, the most common shapes are “teardrop” or “leaf” shapes, which are widest close to the base. That probably helps in preventing over-penetration, because you need to be able to pull the spear back after delivering a strike; you do not want it stuck in the target. Likewise, I think that’s why truly “arrow” shaped spearheads tend to be both early and relatively rare. Instead the base curves back into the socket rather than having barbs, to make it easier to get that spear back out of an opponent after you strike them.
At the same time, spears are by no means immune to weight considerations. Ideally a combatant wants the longest spear they can manage easily in a single hand. That in turn is going to place a hard limit on the weight of the spearhead; every gram in the spearhead shifts the center of balance forward, making the weapon harder to handle. Shifting that center of balance back means adding a gram to the spear butt. Spearheads are pretty much always heavier than spear butts (often several times over), but the basic interaction is there where adding mass to the tip of the spear imposes weight costs which limit length. The trade-off is actually quite clear in medieval spears, where winged and “hewing” spears with larger spear-tips do, in fact, tend to be shorter and may have often been intended for use in two hands.
And because the humans in these systems don’t differ all that much, everyone more or less hits the same set of tradeoffs at basically the same point and so ends up developing spears with very similar weight and length characteristics. This should, I hope, help to dispel any myths that this or that group of ancient agrarian people were super-strong supermen; Greek, Roman, Spanish, Gallic, and Persian spears are all of the same basic length and weight and modern enthusiasts, reenactors and experimental archaeologists can wield those spears just fine. The basic limits of an average warrior haven’t changed all that much.
What you are left with is a spear with a 2-2.5m haft (probably just under 1kg), with spear-tips ranging from 150-450g, mostly clustered in the center of that range around 200g, and spear-butts typically very light, less than 100g and very simple in design (with an exception here for the elaborate Greek saurotar). A simple, no-frills design that would have been very effective on foot or on horseback.1
But as a basic design, the typical omni-spear provides a very effective balance of capabilities: the longest infantry spear that is easy enough to handle with a tip that is suitably deadly against lightly armored or unarmored targets and typically a spear-butt which both encloses the base of the spear (preventing it from delaminating) and provides a point which can be used to both brace the weapon and as an emergency back-up weapon, without adding unacceptable amounts of weight. Note, of course, that I’ve said unarmored or lightly armored: the wide blade on that spearhead is going to cause a strike to have to move aside quite a bit of armor if your opponent is wearing some, greatly limiting the depth of a strike if you have to move the weapon through, say, thick textile armor or mail. But assuming you only expect to strike unarmored targets, or the unarmored portions of armored targets, the shape is very effective.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Mediterranean Iron Omni-Spear”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry,
- Though the Greek cavalry spear of the late-Classical and Hellenistic, the xyston – pronounced ksuston, not zystin – is differently structured than this.