Real Time History
Published 10 Oct 2023In 1965, US troops officially landed in Vietnam, but American involvement in the ongoing conflict between the Communist North and the anti-Communist South had started more than a decade earlier. So, why did the US-Vietnam War break out in the first place?
(more…)
October 14, 2023
Why Did the Vietnam War Break Out?
October 7, 2023
Rearming West Germany: The G1 FAL
Forgotten Weapons
Published 19 Jun 2023Today we are taking a look at a German G1 pattern FAL. The initial purchased of the G1 were actual made by the German Border Guard (the Bundesgrenschutz). In the aftermath of World War Two, the western Allies decided to perpetually disarm Germany, and German security was provided by French, British, and American forces. As the Iron Curtain fell across Europe, that attitude softened — West Germany was on the front lines of the Cold War, and could be a valuable ally against Communism in the East. Thus in 1951, the West German Bundesgrenzschutz (Border Guards) were formed and armed — basically with all WW2 Wehrmacht equipment. Looking to improve its small arms in 1955/56, the BGS tested a number of modern rifles and decided to adopt the FAL.
The BGS initially ordered 2,000 FAL rifles from FN, with wooden hand guards and a fixed flash hider (essentially a standard Belgian FAL) — these are known as the “A” pattern. A second BGS order for 4,800 more rifles followed, this time of the “B” pattern with a metal handguard and folding bipod. This was the first use of an integral bipod on the FAL, and would go on to be a popular option for other buyers.
In 1955, the German Army was reinstated as the Bundeswehr. Looking over the BGS rifle testing, the Bundeswehr also decided to adopt the FAL, and placed and order for 100,000 rifles — the “C” pattern. These include sights lowered 3mm by specific German request, as well as a set of swappable muzzle devices (flash hider and blank-firing adapter).
Ultimately, FN was unwilling to license FAL production to West Germany, and this drove the Germans to adopt the Spanish CETME as the G3 rifle, which it was able to license. The Bundeswehr G1 rifles were eventually transferred to the BGS and later sold to other allies as surplus.
Special thanks to Bear Arms in Scottsdale, AZ for providing access to this rifle for video!
(more…)
October 6, 2023
Farnborough Airshow – 1959 (in colour)
spottydog4477
Published 28 Dec 2009Farnborough Airshow – 1959 (in colour)
October 5, 2023
The Soviet Spies who Kickstarted the Nuclear Arms Race
World War Two
Published 4 Oct 2023Last episode we saw Klaus Fuchs steal details of the American atomic bomb for the Soviet Union. But he’s only one component of a much bigger conspiracy. Today, Astrid introduces you to the mysterious web of Soviet atomic spies. Their work changed our world forever.
(more…)
October 3, 2023
The William Tell Aerial Gunnery Competitions; The CF-101 Voodoo in action
Polyus
Published 23 Aug 2021William Tell: an aerial gunnery competition to assess NORAD’s interceptor squadrons. Canadian CF-101s entered 7 of these competitions and won 3 overall “Top Gun” awards as well as one “Top Unit” award. Pretty impressive results when considering how few squadrons Canada fielded as compared with the vast United States Air Force. Results confirmed that the CF-101s on quick reaction alert at bases across the country were indeed useful in their defense.
(more…)
October 2, 2023
Why France Lost Vietnam: The Battle of Dien Bien Phu
Real Time History
Published 29 Sept 2023After the French success in the Battle of Na San, the battle of Dien Bien Phu is supposed to defeat the Viet Minh once and for all. But instead the weeks-long siege becomes a symbol of the French defeat in Vietnam.
(more…)
September 30, 2023
The Man Who Stole the Atomic Bomb
World War Two
Published 29 Sep 2023In the New Mexico desert, a secret team of scientists is working flat out to develop atomic bombs. It’s the most important American military project in history. But one of those scientists lives a double life. Klaus Fuchs has decided to betray his country and share America’s most secret technology with the Soviet Union. But is he the only person who has turned traitor?
(more…)
September 22, 2023
MAS 49: A Universal Service Rifle
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 May 2019As the MAS 44 saw combat service with French Marines in Indochina, some of its shortcomings began to reveal themselves. The rifle was reliable and durable, but it lacked some capabilities, most importantly rifle grenade launching and an optics mounting. After a test series of MAS 44A rifles, a new pattern was adopted as the MAS 49 and put into production in 1951.
A total of about 80,000 MAS 49 rifles were made, and they incorporated a scope mounting dovetail in the left side of the receiver and a grenade launching muzzle device and sight. In addition, the bayonet was left out, as it was no longer seen as necessary. Not all rifles were used with scopes or for launching grenades, but with the universal capability it was simple to adapt any rifle to whatever specialized role was required. Ultimately the MAS 49 would be replaced again in only a few year, by the MAS 49-56 iterative improvement — but that’s a subject for a future video.
(more…)
September 21, 2023
A new paper on the cancellation of the Avro Arrow in 1959
The National Post republished a Canadian Press article about a new research paper by Alan Barnes in the Canadian Military History journal:
In the years after the Second World War, Canada developed its ability to prepare strategic intelligence assessments on defence and foreign policy, the paper notes. It would no longer have to rely entirely on assessments from the United States and Britain.
The analytic capability allowed Canada to fully participate in preparing the assessments on the Soviet threat to North America that would underpin joint Canada-U.S. planning for continental defence, Barnes notes.
“The CF-100 Canuck, a jet interceptor developed and manufactured in Canada, was just entering service, but there were already concerns that it might soon be outclassed by newer Soviet bombers operating at higher altitudes and faster speeds.”
In November 1952, the Royal Canadian Air Force called for an aircraft with a speed of Mach 2 and the ability to fly at 50,000 feet. “These demanding specifications contributed to the escalating costs and frequent delays in the CF-105 program.”
The Soviets would soon display a new long-range jet bomber, the Bison, at the 1954 May Day parade in Moscow. At an airshow the following year, a fly-past of 28 Bison seemed to indicate that the bomber had entered serial production, two years earlier than predicted, the paper says. In fact, only 18 prototype aircraft participated in the airshow, flying past several times to give the impression of larger numbers.
Even so, this display, along with the appearance of a new Soviet long-range turboprop bomber, the Tu-95 (dubbed the Bear), raised fears that the Soviet Union would soon outnumber the United States in intercontinental bombers, sparking a “Bomber Gap” controversy that figured prominently in American politics, the paper says.
[…]
A January 1958 assessment, “The Threat to North America, 1958-1967”, by Canada’s Joint Intelligence Committee, a co-ordinating body, ultimately had the greatest impact on decisions related to the Arrow, the paper says.
The assessment laid out clear judgments concerning the imminent transition from crewed bombers to ballistic missiles and described the limited size and capabilities of the Soviet bomber force, Barnes notes.
It observed that the Soviet ballistic missiles which were on the verge of being developed were likely to be markedly superior to the foreseeable defences, and concluded that missiles would progressively replace aircraft as the main threat to North America.
The assessment said this meant there would be little justification for the Soviet Union to increase the number of bombers, or to introduce new ones, after 1960.
“The (Joint Intelligence Committee)’s January 1958 assessment was correct in foreseeing Moscow’s shift from bombers to missiles over the subsequent decade,” Barnes writes.
He points out that following the Sputnik launch, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev came to see missiles as a panacea for a range of defence problems and as a cheaper alternative to conventional weapons. “With the Soviet bomber force now looking irrelevant and obsolete, it was relegated to a secondary position in Soviet military thinking.”
September 20, 2023
Wire Guided Tank Killer | Swingfire | Anti-Tank Chats
The Tank Museum
Published 2 Jun 2023In this video, Chris Copson looks at the Swingfire, a Cold War period anti-tank guided weapons system. This powerful and hard-hitting missile was mounted on vehicles including Striker, Ferret, and FV 432. With a range of up to 4km, it had the significant advantage that it would outrange tank guns and could be fired remotely by the controller, enabling the launch vehicle to remain in cover.
(more…)
September 18, 2023
BM59: The Italian M14
Forgotten Weapons
Published 25 Oct 2017After World War Two, both the Beretta and Breda companies in Italy began manufacturing M1 Garand rifles. When Italy decided that they wanted a more modern selective-fire, magazine-fed rifle, they chose to adapt the M1 Garand to that end rather than develop a brand new rifle. Two Beretta engineers, Vittorio Valle and Domenico Salza, began work in 1957 on what would become the BM-59. Prototypes were ready in 1959, trials were run in 1960, and by 1962 the new weapon was in Italian military hands.
The BM59 is basically an M1 Garand action and fire control system, but modernized. The caliber was changed to 7.62mm NATO, and the barrel shortened to 19.3 inches. A simple but effective selective fire system was added to the fire control mechanism, and the en bloc clips replaced with a 20-round box magazine (and stripper clip loading guide to match). A folding integral bipod was added to allow the rifle to be used for supporting fire on full auto, and a long muzzle device was added along with a gas cutoff and grenade launching sight to allow the use of NATO standard 22mm rifle grenades.
In this form, the BM59 was a relative quickly developed and quite successful and well-liked rifle. In addition to the Italian military, it was purchased by Argentina, Algeria, Nigeria, and Indonesia. A semiautomatic version was made for the US commercial market and designated the BM62, and a small number of fully automatic BM-59 rifles — like the one in this video — were imported into the US before the 1968 Gun Control Act cut off importation of foreign machine guns.
(more…)
September 16, 2023
France’s Vietnam War: Fighting Ho Chi Minh before the US
Real Time History
Published 15 Sept 2023After the Second World War multiple French colonies were pushing towards independence, among them Indochina. The Viet Minh movement under Ho Chi Minh was clashing with French aspirations to save their crumbling Empire.
(more…)
August 27, 2023
6 Strange Facts About the Cold War
Decades
Published 27 Jul 2022Welcome to our history channel, run by those with a real passion for history & that’s about it. In today’s video, we will be exploring 6 odd Cold War facts.
(more…)
August 25, 2023
The German Democratic Republic, aka East Germany
Ed West visited East Berlin as a child and came away unimpressed with the grey, impoverished half of Berlin compared to “the gigantic toy shop that was West Berlin”. The East German state was controlled by the few survivors of the pre-WW2 Communist leaders who fled to the Soviet Union:
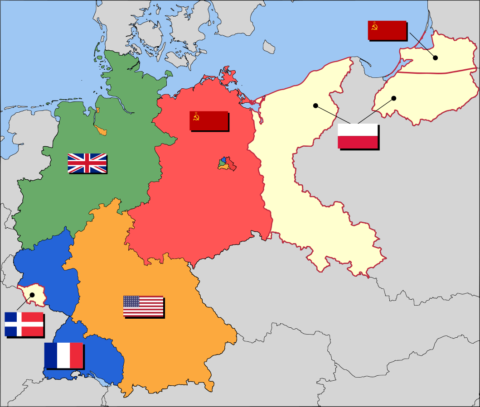
Occupation zone borders in Germany, 1947. The territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, under Polish and Soviet administration/annexation, are shown in cream as is the likewise detached Saar protectorate. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Image based on map data of the IEG-Maps project (Andreas Kunz, B. Johnen and Joachim Robert Moeschl: University of Mainz) – www.ieg-maps.uni-mainz.de, via Wikimedia Commons.
In my childish mind there was perhaps a sense that East Germany, the evil side, was in some way the spiritual successor both to Prussia and the Third Reich – authoritarian, militaristic and hostile. Even the film Top Secret, one of the many Zucker, Abrahams and Zucker comedies we used to enjoy as children, deliberately confused the two, the American rock star stuck in communist East Germany then getting caught up with the French resistance. The film showed a land of Olympic female shot put winners with six o’clock shadows, crappy little cars you had to wait a decade for, and a terrifying wall to keep the prisoners in – and compared to the gigantic toy shop that was West Berlin, I was not sold.
I suppose that’s how the country is largely remembered in the British imagination, a land of border fences and spying, The Lives of Others and Goodbye Lenin. When the British aren’t comparing everything to Nazi Germany, they occasionally stray out into other historic analogies by comparing things to East Germany, not surprising in a surveillance state such as ours (these rather dubious comparisons obviously intensified under lockdown).
This is no doubt grating to East Germans themselves, but perhaps more grating is the sense of disdain often felt in the western half of Germany; for East Germans, their country simply ceased to exist in 1990 as it was gobbled up by its larger, richer, more glamorous neighbour, and has been regarded as a failure ever since. For that reason, [Katja] Hoyer’s book [Beyond the Wall] is both enjoyable holiday reading and an important historical record for an ageing cohort of people who lived under the old system. To have one’s story told, in a sense, is to avoid annihilation.
Despite the similarities between the two totalitarian systems, East Germany almost defined itself as the anti-fascist state, and its origins lie in a group of communist exiles who fled from Hitler to seek safety in the Soviet Union. Inevitably, their story was almost comically bleak; 17 senior German Marxists in Russia ended up being executed by Stalin, suspected by the paranoid dictator of secretly working for Germany. Even some Jewish communists were accused of spying for the Nazis — which seems to a rational observer unlikely. As Hoyer writes, “More members of the KPD’s executive committee died at Stalin’s hands than at Hitler’s”.
Only two of the nine-strong German politburo survived life in Russia, one of these being Walter Ulbricht, the goatee-bearded veteran of the failed 1919 German revolution and communist party chairman in Berlin in the years before the Nazis came to power.
The war had brutalised the eastern part of Germany far more than the West. It suffered the revenge of the Red Army, including the then largest mass rape in history, and the forced expulsion of millions of Germans from further east (including Hoyer’s grandfather, who had walked from East Prussia). The country was utterly shattered.
From the start the Soviet section had huge disadvantages, not just in terms of raw materials or industry – western Germany has historically always been richer — but in having a patron in Russia. While the Americans boosted their allies through the Marshall Plan, the Soviets continued to plunder Germany; when they learned of uranium in Thuringia they simply turned up and took it, using locals as forced labour.
“In total, 60 per cent of ongoing East German production was taken out of the young state’s efforts to get on its feet between 1945 and 1953,” Hoyer writes: “Yet its people battled on. As early as 1950, the production levels of 1938 had been reached again despite the fact that the GDR had paid three times as much in reparations as its Western counterpart.”
After the war, so-called “Antifa Committees” formed across the Soviet zone, “made up of a wild mix of individuals, among them socialists, communists, liberals, Christians and other opponents of Nazism”. Inevitably, a broad and eclectic left front was taken over by communists who soon crushed all opposition.
And as with many regimes, state oppression grew worse over time. “By May 1953, 66,000 people languished in East German prisons, twice as many as the year before, and a huge figure compared to West Germany’s 40,000. The General Secretary’s revival of the ‘class struggle’, officially announced in the summer of 1952 as part of the state’s ‘building socialism’ programme, had escalated into a struggle against the population, including the working classes.” The party was also becoming dominated by an educated elite, as happened in pretty much all revolutionary regimes.
Protests began at the Stalinallee in Berlin on 16 June 1953, where builders marched towards the House of Ministries and “stood there in their work boots, the dirt and sweat of their labour still on their faces; many held their tools in their hands or slung over their shoulders. There could not have been a more fitting snapshot of what had become of Ulbricht’s dictatorship of the proletariat. The angry crowd chanted, ‘Das hat alles keinen Zweck, der Spitzbart muss weg!’ – ‘No point in reform until Goatee is gone!'”
The 1953 protests were crushed, the workers smeared as fascists, but three years later came Khrushchev’s famous denunciation of Stalin, which caused huge trauma to communists everywhere. “The shaken German delegation went back to their rooms to ponder the implications of what they had just learned.” By breakfast time, “Ulbricht had pulled himself together”, and decreed the new party line. Stalin, it was announced “cannot be counted as a classic of Marxism”.
Fortress Britain with Alice Roberts S01E03
Fortress Britain with Alice Roberts
Published 16 Apr 2023




