The Critical Drinker
Published 6 Feb 2026Since its the 25th anniversary of the trilogy, I figured I’d reminisce about my favourite ever scene from all three movies. And explain why I’m objectively right about it.
February 9, 2026
Why This Is The Greatest Lord Of The Rings Scene Ever
January 29, 2026
QotD: Nitpicking the Roman army in Gladiator (2000)
We pick up in an improbably mud-soaked clearing with a title card informing us that we’re in “Germania”, which is correct in a very broad sense that this is the Second Marcomannic War and the enemies here are the Marcomanni and Quadi, who are Germani (Germanic-language speakers), but the army here isn’t operating out of the Roman provinces of Germania (superior and inferior) which are on the Rhine, but rather on the Danube, from the provinces of Noricum and Pannonia (Superior). But in the sense that we’re in Germania magna, the greater zone of Germanic cultural influence, sure, fine.
In the process of Maximus riding up, the failure of negotiations and Maximus riding to join his cavalry, we get something of an overview of the Roman army and its position and both are wrong. Let’s start with the soldiers: we see a very clear distinction between two kinds of soldiers, the mail-clad auxilia, all archers, and the legionaries wearing the lorica segmentata and there appear to be about the same number of both groups. And here is where we first see the clear influence of the Column of Trajan (and to an unfortunately lesser degree, the far more appropriate Column of Marcus Aurelius) on the depiction, because this use of armor to distinctly signal the Roman citizen legionaries and non-citizen auxilia is straight from the Column of Trajan, completed probably around 113 and commemorating Trajan’s two Dacian Wars (101-102, 105-106).
What this sequence gets correct is that the Roman army was divided into those two groups, they were roughly equal in number (by this period, the auxilia probably modestly outnumber the legions in total manpower)1 and Trajan’s Column does use that visual signifier to distinguish them. This component is the crux of the verisimilitude that leads people to trust the rest of this sequence.
The problems start almost immediately from there. Roman auxilia were far more varied than what we see here in terms of equipment and tactics and only very few of them were archers. So let’s break down Roman auxiliary contingents. With all due caveats about the limits of our evidence, infantry auxilia outnumber cavalry by about 2:1 in attested auxilia units (auxilia were grouped into cavalry alae and infantry cohortes, generally of 480 men (sometimes around 800), but unlike for legionary citizen-infantry, these cohorts were not grouped into larger legions).2 So we ought to expect about a third of our auxilia to be cavalry, which is important because the cavalry detachments of Roman legions were very small (and mostly for scouting and messenger duties). Auxilia cavalry ranged in equipment and could include horse archers and even ultra-heavy cataphract cavalry, but most were mailed shock cavalry, equipped quite a lot like how Gallic or Germanic warrior-aristocrats or Roman legionary cavalry would be.
Of the remainder, the most common kind of infantry auxilia by far seem to have been heavy infantry, fighting in fairly heavy armor. These fellows get depicted in Roman artwork generally in mail armor, with flat oval shields (as opposed to the curved, rectangular imperial-period Roman scutum), spears and swords. These fellows, totally absent in this sequence are all over the Column of Trajan, with their flat oval shields being frequently seen (although one must distinguish them from Dacians who carry the same shield; the auxilia stick out for their mail and helmets). A bit less than 10% of auxilia units are attested as cohortes sagittariorum (“cohort of archers”). We also know the Romans used slingers within the auxilia, but as far as we can tell, not in specialized units; they may have been brigaded in with other auxilia cohorts. In either case, they appear in fairly small numbers. Finally, we also see on things like the Column of Trajan Roman allied or auxiliary units that are substantially lighter infantry: on the Column of Trajan, these are local troops shown wielding large clubs and stripped to the waist, presumably representing troops local to the Danube region, fighting in local (unarmored, with heavy two-handed weapons) style.
So whereas the army we see is a nearly even split between legionary heavy infantry and auxilia archers (with a small amount of legionary cavalry waiting for Maximus to show up to lead them), in practice a typical Roman field army would have far fewer archers, indeed around ten times fewer: not almost 50% of the force, but in fact probably a bit less than 5% of the force (since they’re less than 10% of the auxilia who would make up around half of a Roman field army). Meanwhile we’re simply missing the – by far – two most common sorts of auxilia cohorts, those of heavy infantry or heavy cavalry. This mangling of the structure of a Roman army is going to have implications when we get to Maximus’ overall plan for the battle as well.
Meanwhile, the legionary infantry are also much too uniform, literally. This is easily the most pardonable error, because what has happened here is that director Ridley Scott has copied the Column of Trajan but far too uncritically. After all, the Column of Trajan is not a photograph and thus has space for the artists producing it to take liberties, particularly in the name of imperial ideology and propaganda. In this case, showing large numbers of identically equipped soldiers, often moving in unified formation, serves the same rhetorical purpose in antiquity as it does today, suggesting an impressive, inhumanly uniformed and disciplined source. Moreover, the segmented Roman body armor, which we call the lorica segmentata (we don’t know what the Romans called it), was very distinctive to the legions, as it was the one armor that it seems like the auxilia probably (the evidence here can be tricky) didn’t share. And keeping the legions distinct from the auxilia also matters, as the legionary soldiers are higher status citizens who thus get “higher billing” in the imagery, as it were, than the auxilia. So showing all of the legions equipped neatly with this armor makes them seem distinct, impressive and uniform.
In short, it served Trajan’s image (and thus the artists aim) to suggest that all of his legions wore this armor.
Archaeology tells us quite clearly it was not so. Indeed, the lorica segmentata, so iconic because of its use in this way on the Column of Trajan, was probably the least common of the three major types of Roman legionary body armor in this period. The most common armor of the Roman legions was almost certainly still – as it had been in the Late Republic – mail, exactly the same as we see the auxilia wearing. We find fragments of Roman mail in legionary sites in all corners of the Empire and it remained common everywhere. To head off a standard question: no, it does not seem that the Romans ever got the idea to layer other defenses over mail, so when it was worn, it was the “primary” armor (worn over a padded textile defense called a subarmalis, but not under any other armor).3 We also see mail represented in Roman artwork, including on very high status soldiers, like senior centurions.
The next most common armor was probably scale armor, which we find very frequently in the East (that is, on the frontier with the Parthians/Sassanids) and often enough (if less frequently) in the West (that is, the Rhine/Danube frontier). We also know that some auxilia units wore this armor too and we see quite a bit of scale armor – wholly absent in this sequence – on the Column of – wait for it – Marcus Aurelius (completed c. 193). That’s the column that commemorates this war. Contemporary with this fictional battle. But it is less famous and somewhat less well-preserved than 70-years-earlier Column of Trajan, which they pretty evidently used quite a bit more of.
The lorica segmentata shows up the least often and – to my knowledge – effectively exclusively in the west on the Rhine/Danube frontier, where it is still probably not the most common (although it may have been more common than scale on that frontier). So what we ought to see in this army are legionaries who are marked out by their large scuta (the big Roman shield, by this period distinctly rectangular and also (as in the republic) curved), but in a range of mail, scale and lorica segmentata (with mail and segmentata being the most common, because we are on the Danube frontier, but scale hardly rare), along with auxilia divided into specialist cohorts (480 man units) each with different sets of armor and weapons: a few missile cohorts (archers, slingers), a lot more heavy infantry cohorts with spears and long shields, some lighter troops, and so on. The auxilia ought to be wearing basically every armor under the sun except for the lorica segmentata (which to my knowledge we’ve only ever found in sites associated with the legions).
Finally, these units are backed up by a whole load of catapults. We see two kinds, dual-arm arrow-throwing machines (which most folks would casually call ballistae) and single-armed pot-throwing machines (which most folks would casually call catapults), all of them in stationary mounts. Now on the one hand, “the Romans use lots of torsion-based catapults as artillery” is a true statement about the Roman army of this period, but on the other hand once again beyond that basic idea, most of this is wrong. Once again there’s an issue of verisimilitude here: the appearance of strange catapults and the true fact that the Romans used a lot of unusual catapults is likely to lead the viewer to assume some research has been done here and thus that these are the right catapults. For the most part, they are not.
We can start with the easy one, the larger single-armed pot-throwers. These are onagers, a late-Roman simplified single-arm torsion catapult, named for their fearsome “kick” (like an ass, an onager). These are popular favorites for Roman artillery, for instance showing up in both Rome: Total War and Total War: Rome II (both of which have main campaigns set during the Late Republic). There’s only one problem, which is that Gladiator (much less the even earlier Total War games) is set substantially too early for an onager to appear. Our first attestation of the onager is in Ammianus Marcellinus, writing in the last two decades of the 300s AD about the events of 353-378 (his work was broader than this, but only the back end survives). Vegetius, writing roughly contemporary with Ammianus also mentions them. But before the late fourth century, we don’t have any evidence for this design and it doesn’t show up on the Columns of Trajan or Marcus. So this isn’t just a little bit too early for these catapults but, given the evidence we have, around 150 years too early, the equivalent of having a line of M1 Abrams show up in a film about the Battle of Gettysburg.
What we do have are a number of twin-armed bolt or arrow-throwing machines and the Romans certainly had those, though what we see doesn’t match up well with what the Romans used. What we see is a single size of fairly large arrow-throwing engines, aimed upward to fire in fairly high arcs and built with large metal cases containing the torsion springs (generally made of hair or sinew, tightly coiled up; it is the coiling of these springs which stores the energy of the machine).
These two-armed torsion catapults came in a wide range of sizes and could be designed to throw either arrows/bolts or stones (the latter carved into spheres of rather precise caliber for specific machines). And we ought to see a pretty wide range of sizes here, from massive one-talent engines, which threw a 1 talent (26kg) stone and stood about three times the height of a man, to much smaller anti-personnel weapons (scorpiones) that were more like a “crew served” weapon than a large artillery piece. By Trajan’s time, the Romans had even taken to mounting these smaller crew-served engines on mule-drawn carts (called carroballistae) to allow them to be rapidly repositioned, something like early modern “horse artillery” (they were not meant to fire on the move; when we see them on Trajan’s Column, at least one of the operators is usually standing on the ground outside of the cart to winch the machine). These smaller machines, which would have made up the bulk of those deployed in a field battle, seem mostly absent in the sequence.
The result of all of this is that the Roman army presented in the opening moments of Gladiator manages to strike a remarkably unhappy balance: having just enough of the appearance of accuracy to decisively influence two decades of subsequent depictions of the Roman army without actually being particularly correct about anything beyond a very surface level. But subsequent pop-culture (again, I think Rome: Total War played a significant role here) would codify this vision of the Roman army – fire-throwing onagers, lots of auxilia archers, legionary rather than auxiliary cavalry, uniform use of the lorica segmentata – as the dominant model for quite some time.
But the army isn’t the only thing that’s wrong.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Nitpicking Gladiator’s Iconic Opening Battle, Part I”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2025-06-06.
- See figures in P. Holder, Auxiliary Deployment in the Reign of Hadrian (2003).
- There’s some complexity here because some infantry auxilia cohorts had small attached cavalry contingents too.
- I suppose I should note that is an odd exception for a type of very fine armor sometimes called lorica plumata (“feathered armor”) by modern writers where metal scales were mounted on mail armor (typically with extremely fine, small rings), rather than on a textile backing. This armor type seems to have been rare and must have been very expensive.
December 16, 2025
QotD: Arms and the (pre-modern) man (at arms)
… how much value might a heavily armored fighter or warrior be carrying around on their backs in the real world? Because I think the answer here is informative.
Here we do have some significant price data, but of course its tricky to be able to correlate a given value for arms and armor with something concrete like wages in every period, because of course prices are not stable. But here are some of the data points I’ve encountered:
We don’t have good Roman price data from the Republic or early/high Empire, unfortunately (and indeed, the reason I have been collecting late antique and medieval comparanda is to use it to understand the structure of earlier Roman costs). Hugh Elton1 notes that a law of Valens (r. 364-378) assessed the cost of clothing, equipment and such for a new infantry recruit to be 6 solidi and for a cavalryman, 13 solidi (the extra 7 being for the horse). The solidus was a 4.5g gold coin at the time (roughly equal to the earlier aureus) so that is a substantial expense to kit out an individual soldier. For comparison, the annual rations for soldiers in the same period seem to have been 4-5 solidi, so we might suggest a Roman soldier is wearing something like a year’s worth of living expenses.2
We don’t see a huge change in the Early Middle Ages either. The seventh century Lex Ripuaria,3 quotes the following prices for military equipment: 12 solidi for a coat of mail, 6 solidi for a metal helmet, 7 for a sword with its scabbard, 6 for mail leggings, 2 solidi for a lance and shield for a rider (wood is cheap!); a warhorse was 12 solidi, whereas a whole damn cow was just 3 solidi. On the one hand, the armor for this rider has gotten somewhat more extensive – mail leggings (chausses) were a new thing (the Romans didn’t have them) – but clearly the price of metal equipment here is higher: equipping a mailed infantryman would have some to something like 25ish solidi compared to 12 for the warhorse (so 2x the cost of the horse) compared to the near 1-to-1 armor-to-horse price from Valens. I should note, however, warhorses even compared to other goods, show high volatility in the medieval price data.
As we get further one, we get more and more price data. Verbruggen (op. cit. 170-1) also notes prices for the equipment of the heavy infantry militia of Bruges in 1304; the average price of the heavy infantry equipment was a staggering £21, with the priciest item by far being the required body armor (still a coat of mail) coming in between £10 and £15. Now you will recall the continental livre by this point is hardly the Carolingian unit (or the English one), but the £21 here would have represented something around two-thirds of a year’s wages for a skilled artisan.
Almost contemporary in English, we have some data from Yorkshire.4 Villages had to supply a certain number of infantrymen for military service and around 1300, the cost to equip them was 5 shillings per man, as unarmored light infantry. When Edward II (r. 1307-1327) demanded quite minimally armored men (a metal helmet and a textile padded jack or gambeson), the cost jumped four-fold to £1, which ended up causing the experiment in recruiting heavier infantry this way to fail. And I should note, a gambeson and a helmet is hardly very heavy infantry!
For comparison, in the same period an English longbowman out on campaign was paid just 2d per day, so that £1 of kit would have represented 120 days wages. By contrast, the average cost of a good quality longbow in the same period was just 1s, 6d, which the longbowman could earn back in just over a week.5 Once again: wood is cheap, metal is expensive.
Finally, we have the prices from our ever-handy Medieval Price List and its sources. We see quite a range in this price data, both in that we see truly elite pieces of armor (gilt armor for a prince at £340, a full set of Milanese 15th century plate at more than £8, etc) and its tricky to use these figures too without taking careful note of the year and checking the source citation to figure out which region’s currency we’re using. One other thing to note here that comes out clearly: plate cuirasses are often quite a bit cheaper than the mail armor (or mail voiders) they’re worn over, though hardly cheap. Still, full sets of armor ranging from single to low-double digit livres and pounds seem standard and we already know from last week’s exercise that a single livre or pound is likely reflecting a pretty big chunk of money, potentially close to a year’s wage for a regular worker.
So while your heavily armored knight or man-at-arms or Roman legionary was, of course, not walking around with the Great Pyramid’s worth of labor-value on his back, even the “standard” equipment for a heavy infantryman or heavy cavalryman – not counting the horse! – might represent a year or even years of a regular workers’ wages. On the flipside, for societies that could afford it, heavy infantry was worth it: putting heavy, armored infantry in contact with light infantry in pre-gunpowder warfare generally produces horrific one-sided slaughters. But relatively few societies could afford it: the Romans are very unusual for either ancient or medieval European societies in that they deploy large numbers of armored heavy infantry (predominately in mail in any period, although in the empire we also see scale and the famed lorica segmentata), a topic that forms a pretty substantial part of my upcoming book, Of Arms and Men, which I will miss no opportunity to plug over the next however long it takes to come out.6 Obviously armored heavy cavalry is even harder to get and generally restricted to simply putting a society’s aristocracy on the battlefield, since the Big Men can afford both the horses and the armor.
But the other thing I want to note here is the social gap this sort of difference in value creates. As noted above with the bowman’s wages, it would take a year or even years of wages for a regular light soldier (or civilian laborers of his class) to put together enough money to purchase the sort of equipment required to serve as a soldier of higher status (who also gets higher pay). Of course it isn’t as simple as, “work as a bowman for a year and then buy some armor”, because nearly all of that pay the longbowman is getting is being absorbed by food and living expenses. The result is that the high cost of equipment means that for many of these men, the social gap between them and either an unmounted man-at-arms or the mounted knight is economically unbridgeable.7
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday, January 10, 2025”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2025-01-10.
- Warfare in Roman Europe AD 350-425 (1996), 122.
- If you are wondering why I’m not comparing to wages, the answer is that by this point, Roman military wages are super irregular, consisting mostly of donatives – special disbursements at the accession of a new emperor or a successful military campaign – rather than regular pay, making it really hard to do a direct comparison.
- Here my citation is not from the text directly, but Verbruggen, The Art of War in Western Europe during the Middle Ages (1997), 23.
- From Prestwich, Armies and Warfare in the Middle Ages (1996).
- These prices via Hardy, Longbow: A Social and Military History (1992).
- Expect it no earlier than late this year; as I write this, the core text is actually done (but needs revising), but that’s hardly the end of the publication process.
- Man-at-arms is one of those annoyingly plastic terms which is used to mean “a man of non-knightly status, equipped in the sort of kit a knight would have”, which sometimes implies heavy armored non-noble infantry and sometimes implies non-knightly heavy cavalry retainers of knights and other nobles.
October 4, 2025
Warner Carbine
Forgotten Weapons
Published 8 Sept 2015The Warner carbine was another of the weapons used in small numbers by the Union cavalry during the Civil War. It is a pivoting breechblock action built on a brass frame. These carbines were made in two batches, known as the Greene and Springfield. The first guns were chambered for a proprietary .50 Warner cartridge, which was replaced with .56 Spencer in the later versions (for compatibility with other cavalry arms).
This particular Warner shows some interesting modification to its breechblock, which has been converted to use either rimfire or centerfire ammunition. This was not an uncommon modification for .56 Spencer weapons, as the centerfire type of Spencer ammunition could be reloaded (unlike the rimfire cartridges). With this modification, the firing pin can be switched from rimfire to centerfire position fairly easily.
August 28, 2025
QotD: The rise and fall of the chariot in combat
Horses had been domesticated long before the Scythians. Horses, along with dogs and reindeer, are the only animals domesticated by foragers, rather than farmers. The first significant use of horses in battle was to draw chariots. Chariot archers could shoot, and javelins could be thrown, further from a chariot than a horse.
The classic chariot was driver and archer or spearmen. A friend describes them as being like a pilot and a navigator (or bomb-aimer) on a bombing run. The pilot/charioteer concentrates on getting the pair of you where you need to be (or not to be). The archer/spearmen/navigator/bomb-aimer concentrates on killing the enemy.
The most famous driver/warrior pairing in myth and literature is Krishna and Prince Arjuna in the Mahabharata and, specifically, the Bhagavad Gita. (Normally, the driver serves the warrior, but if your driver is an incarnation of Vishnu, things work differently.) The warriors of the Iliad are also chariot-driving warriors — hence scenes such as Achilles dragging Hector‘s dead body behind his chariot. Chariots were a major element in Chinese warfare up to the Warring States period. New Kingdom Egypt was very much a chariot empire, as were their great rivals, the Hittites.
Once recurve bows able to match chariot archery from horseback arrived, chariots largely disappeared from combat in the major Eurasian civilisations. This began to occur around the time of the Assyrians — who were a transitional case using both chariots and cavalry — about a thousand years before the invention of the stirrup and even longer before the stirrup’s arrival in the Mediterranean world. Lancers — the heavily armoured version of which was the cataphract — then developed as a way of dealing with horse archers.
Lorenzo Warby, “Stirrups, a rant”, Lorenzo from Oz, 2025-02-28.
August 27, 2025
M1922 BAR Cavalry Light Machine Gun
Forgotten Weapons
Published 21 Apr 2025After World War One, there was a lot of tinkering with the BAR by the US military. It was recognized as being a very good platform, but the original M1918 configuration left a lot to be desired. It was deemed too heavy to use effectively from the shoulder, but also not really well suited to sustained fire. In an effort to optimize it for use as a dynamic support weapon by a small squad, the Infantry & Cavalry Board requested a model with a heavier barrel and lightweight bipod in 1920. Six experimental examples were made form existing BARs, and the design was formalized two years later as the Model 1922.
This pattern of BAR has a heavy finned barrel to give it more sustained fire capacity and a folding bipod and rear monopod for more accurate use prone. The Board also experimented with larger magazines, and ended up recommending a 30-round size — although this was never put into production. In total, 500 of the Model 1922 guns were made, all converted from existing BARs. Experimentation continued slowly, and eventually in 1937 a lighter pattern was adopted as the M1918A1. The Model 1922 was formally declared obsolete in April 1941, and virtually all of them were rebuilt to the new M1918A2 pattern for use in World War Two. Surviving examples like this one are extremely rare — this is the only known example in private hands.
(more…)
August 11, 2025
Speed vs Armour: The Unexpected History of Fast Tanks
The Tank Museum
Published 21 Mar 2025Would you rather go to war in a tank that was quick but lightly armoured – or heavily armoured but slow?
The concept of fast tanks has existed since the First World War, but making a tank fast is easier said than done. You can increase the speed, but only by compromising the other two sides of The Iron Triangle.
Whilst a good power to weigh ratio is key to making a tank go fast, there are other factors that need to be considered. J Walter Christie pioneered the innovative helicoil spring suspension system – an invention that allowed tanks to cope with travelling at high speeds across country. Although not picked up by the US Army, the brilliance of Christie’s suspension was recognised by the Soviets and soon made an appearance on the BT-Series of tanks – and most effectively on the T-34.
Back in the UK, the newly mechanised cavalry was making use of some brand-new Cruiser tanks. Whilst these were fast vehicles, this was coming at the cost of effective protection. Some military thinkers advocated for the concept of “speed as armour” but results were mixed – with the Crusader and Cromwell both proving to be capable tanks.
After the war, the British Army finally moved on from “speed as armour” and settled on sacrificing a bit of speed for the sake of better protection. This was incorporated first into the concept of Universal Tanks and remains a fixture in the modern Main Battle Tank.
So, we’ll ask again. Would you rather go to war in a tank that was quick but lightly armoured – or heavily armoured but slow?
00:00 | Introduction
00:51 | What Makes it a Fast Tank?
02:39 | What is a Fast Tank For?
04:39 | Suspension of Disbelief
06:34 | Speedy Soviets
08:29 | Cruisers Replace Cavalry
11:20 | The Second Wave
13:19 | Cruising in Europe
19:08 | One Tank to Do It All
(more…)
August 2, 2025
The Bloody Battle of Cannae | Animated(ish) Episode
The Rest Is History
Published 5 Jun 2025This is the final episode of our series on Hannibal, which is the second season on Carthage, the whole series is here: Rome Vs Cathage
Part 1 of our series on Hannibal is here: Hannibal: The Rise of Rome’s Greatest Nemesis
How did the Battle of Cannae — one of the most important battles of all time for Ancient Rome, with a whole Empire at stake, and a reputation that had reverberated across the centuries — in 216 BC, unfold? What brilliant tactics did Hannibal adopt in order to overcome the Roman killing machine, with its vast numbers and relentless soldiers? Why did so many men die in such horrific circumstances? And, what would be the outcome of that bloody, totemic day, for the future of both Carthage and Rome?
Join Tom and Dominic for the climax of their epic journey through the rise of Hannibal, and his world-shaking war against Rome, in one of the deadliest rivalries of all time.
00:00 Context to the battle
08:30 Prelude to the battle and their plans of attack
37:28 The battle
(more…)
July 23, 2025
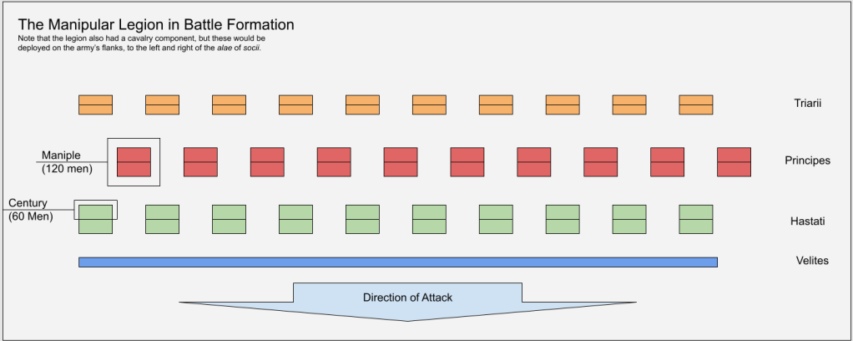
QotD: The legion of the Middle Republic
The basic building blocks of Roman armies in the Middle Republic are the citizen legion and the socii alae or “wing”. A “standard” Roman army generally consisted of two legions and two matching alae. but larger and smaller armies were possible by stacking more legions or enlarging the alae. We’re not nearly so well informed as to the structure of the alae of socii (the socii being Rome’s “allied” – really, subject – peoples in Italy), except that they seem to have been tactically and organizationally interchangeable with legions. Combined with the fact that they don’t seem archaeologically distinctive (that is, we don’t find different non-Roman weapons with them), the strong impression is that at least by the mid-third century – if not earlier – the differences were broadly ironed out and these formations worked much the same way.1 So, for the sake of simplicity, I am going to discuss the legion here, but I want you to understand (because it will matter later) that for every legion, there is a matching ala of socii which works the same way, has effectively the same equipment, fights in the same style and has roughly the same number of troops.
With that said, we reach the first and arguably most important thing to know about the legion: the Roman legion (and socii ala) of the Middle Republic is an integrated combined arms unit. That is to say, unlike a Hellenistic army, where different “arms” (light infantry, heavy infantry, cavalry, etc.) are split into different, largely homogeneous units, these are “organic” to the legion, that is to say they are part of its internal structure (we might say they are “brigaded together” into the legion as well). Consequently, whereas the Hellenistic army aims to have different arms on the battlefield in different places doing different things to produce victory, the Roman legion instead understands these different arms to be functioning in a fairly tightly integrated fashion with a single theory of victory all operating on the same “space” in the enemy’s line.
And you may well ask, before we get to organization, “What is that theory of victory?” As we saw, the Hellenistic army aims to fix the enemy with its heavy infantry center, hold the flanks with lighter, more mobile infantry (to protect that formation) and win the battle with a decisive cavalry-led hammer-blow on a flank. By contrast, the Romans seem to have decided that the quickest way to an enemy’s vulnerable rear was through their front. The legion is thus not built for flanking, its cavalry component – while ample in numbers – is distinctly secondary. Instead, the legion is built to sandpaper away the enemy’s main battle line in the center through attrition, in order to produce a rupture and thus victory.
To do that, you need to create a lot of attrition and this is what the manipular legion is built to do.
The legion of the Middle Republic is built out of five components: three lines of heavy infantry (hastati, principes and triariivelites), and a cavalry contingent (the equites). Specifically, a normal legion has 1200 each of velites, hastati and principes, 600 triarii and 300 equites, making a total combined unit of 4,500. Organizationally, the light infantry velites were packaged in with the heavy infantry (Polyb. 6.24.2-5) for things like marching and duties in camp, but in battle they typically function separately as a screening force thrown forward of the legion.
So to take the legion as an enemy would experience them, the first force were the velites. These seem to have been deployed in open order in front of the legion to screen its advance. These fellows had lighter javelins, the hasta velitaris (Livy notes they carried seven, Livy 39.21.13), no body armor and a “simple headcovering” (λιτός περικεφάλαιος, Polyb. 6.22.3), possibly hide or textile; they also carried a smaller round shield, the parma, and the gladius Hispaniensis for close-in defense (Livy 38.21.13). These are, all things considered, fairly typical ancient javelin troops, aiming to use the mobility their light equipment offers them to stay out of close-combat.
Behind the velites was the first line of the heavy infantry, the hastati. These fellows were organized into units called maniples (lit: “a handful”) of 120, which in turn are divided into centuries of 60 each. The maniples are their own semi-independent maneuvering units (note how much smaller they are than the equivalent taxeis in the phalanx, this is a more flexible fighting system), each with its own small standard (Polyb. 6.24.6) to enable it to maintain coherence as it maneuvers. That said, they normally form up in a quincunx (5/12ths, after a Roman coin with the symbol of five punches, like on dice) formation with the rear ranks, as you can see above.
The hastati (and the principes, who are equipped the same way) have the large Roman shield, the scutum, two heavy javelins (pila), the gladius Hispaniensis sword, a helmet (almost always a Montefortino-type in bronze in this period) and body armor. Poorer soldiers, we’re told, wore a pectoral, wealthier soldiers (probably post-225, though we cannot be certain) wore mail. That is, by the standards of antiquity, quite a lot of armor, actually – probably more armor per-man than any other infantry formation on their contemporary battlefield. That relatively higher degree of protection – big shield, stout helmet (Montefortino’s in this period range from 1.5-2.5kg, making them unusually robust), and lots of body armor – makes sense because these fellows are going to aim to grind the enemy down.
Note that a lot of popular treatments of this assume that the hastati were worse equipped than the principes; there’s no reason to assume this is actually true. The principes are older than the hastati, but the way to understand this formation is that the velites are young or poor, whereas for the upper-classes of the infantry (probably pedites I-IV) after maybe the first year or so, they serve in the heavy infantry (hastati, principes, triarii) based on age, not on wealth (and then the equites are the truly rich, regardless of what age they are; the relevant passage here is Polyb. 6.21.7-9, which is, admittedly, not entirely clear on what is an age distinction and what is a wealth distinction).
We’ve discussed the combat width these guys fight with already – somewhat wider spacing than most, so that each man covers the other’s flanks but they all have room to maneuver. It seems like the standard depth in the Middle Republic was either base-3 (so 3 deep on close order, 6 deep for “fighting” open order) or base-4 (so 4 and 8). Even in open-order with the maniples stretched wide (possibly by having rear centuries move forward), there would have been open intervals (10-20m) between maniples, which reinforces the role of a maniple as a potentially independent maneuvering unit – it has the space to move.2
Behind the hastati are the principes, with the same equipment and organization, slightly off-set to cover the intervals between the hastati, with a gap between the two lines (we do not know how large a gap). These men are slightly older, though not “old”. The whole field army generally consists of iuniores (men under 46) and given how the Romans seem to like to conscript, the vast majority of men will be in their late teens and 20s. So we might imagine the velites to be poorer men, or men in their late teens (17 being the age when one become liable for conscription) or so, while the hastati are early twenties, the principes mid-twenties and the handful of triarii being men in their late twenties or perhaps early 30s. The positioning of the principes isn’t to spare older men the rigors of combat, but rather to put more experienced veterans in a position where they can steady the less experienced hastati.3
Finally, behind them are the triarii, who trade the pila for a thrusting spear, the hasta, the Roman version of the Mediterranean omni-spear. These men are, as noted, the oldest and so likely the calmest under pressure and thus form a reserve in the rear. The three-line system here is what the Romans call a triplex acies (“three battle lines”). This wasn’t the only way these armies engaged and they could sometimes be formed up into a single solid line, but the triplex acies seems to have been the standard. We don’t know exactly how deep such a formation would run, but we have fairly good evidence that a legion might occupy a space around 400m wide (with some variation), meaning a whole Roman army’s core heavy infantry component (the two legions and two alae) might be some 1.6km (about a mile) across.
The equites, while organic to the legion organizationally, will be tactically grouped in battle to form cavalry screens on the edges of the army, not as a grand flanking cavalry “hammer”, but as flank-protection for the advancing infantry body (as a result, they tend to fight more cautiously). The equites in this period are heavy cavalry, with armored riders (after c. 225, that would be mail), using a shield and a hasta, along with a gladius as a backup weapon and thus serving as “shock” cavalry. Roman cavalry, if we look at their deployments, is generally ample in numbers, but the Romans seem to have been well aware it wasn’t very good, and sought allied cavalry (especially non-Italian allied cavalry) whenever they could get it. But the cavalry, Roman or not, was almost never the decisive part of the army.
Polybius tells us that the socii supplies more cavalry than the Romans and implies that there was a standard rule of three socii cavalrymen to every Roman equites, while socii infantry matched Roman infantry numbers (Polyb. 6.26.7). Looking at actual deployments though, we see that the socii tend to outnumber the Romans modestly, on about a 2:3 ratio, with socii cavalry only modestly outnumbering Roman cavalry.4 Consequently a normal Roman consular field army (of which the Romans generally had at least two every year) was 8,400 Roman infantry, around 12,600 socii infantry, 600 Roman cavalry and perhaps a thousand or so socii cavalry, for a combined force of 21,000 infantry (c. 5,000 light 16,000 heavy, so that’s a lot of heavy infantry) and 1,600 cavalry. That somewhat undersells the cavalry force the Romans might bring, as Roman armies also often move with auxilia externa (allied forces not part of the socii), which are very frequently cavalry-heavy (especially, after 203, that really good Numidian cavalry).5 By and large, it’s not that the Romans bring a lot less cavalry (as a percentage of army size), but that Italian cavalry tends to perform poorly and the as a result the Romans do not built their battle plans around their weakest combat arm.
Perhaps ironically, the Romans used their cavalry like Alexander and Hellenistic armies used their light infantry: holding forces designed to keep the flanks of the battlefield busy while the decisive action happened somewhere else.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Phalanx’s Twilight, Legion’s Triumph, Part IIa: How a Legion Fights”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-02-09.
1. On this, see Burns, M. T. “The Homogenisation of Military Equipment under the Roman Republic”. In Romanization? Digressus Supplement I. London: Institute of Archaeology, University College London, 2003.
2. On this, M.J. Taylor, “Roman Infantry Tactics in the Mid-Republic: A Reassessment”, Historia 63.3 (2014): 301-322.
3. To expound at some length on my own thoughts on how I think the wealth/age issue was probably managed, Dionysius (4.19.2) claims that the Romans recruited by centuries in the comitia centuriata such that the wealthy, divided into fewer voting blocks, served more often, and we know from Polybius that the maximum period of service for the infantry was sixteen years and from some math done by N. Rosenstein in Rome at War (2004) that the average service must have been around seven years. My suspicion, which I cannot prove is that the very poorest Roman assidui (men liable for conscription) might have only been serving fewer years on average and so it wasn’t a problem having them do all of their service as velites (the only role they can afford), whereas wealthier Romans (my guess is pedites IV and up) are the ones who age into the heavy infantry, with pedites I, whose members probably serve more than the seven-year average (perhaps around 10?) might make up close to 40% of the actual heavy infantry body (which is their balance in the comitia centuriata). The velites thus serves two important functions: a place to “blood” wealthier young Roman men to prepare them to stand firm in the heavy infantry line, as well as a place for poorer Romans to contribute militarily in a way they could afford. But I think that, once in the heavy infantry, the division between hastati, principes and triarii was – as Polybius says (6.21.7-9 and 6.23.1) – an age division, not a wealth division. Instead, the next wealth line is for the equites.
4. The data on this is compiled by Taylor, Soldiers & Silver (2020), 26-28.
5. Taylor, op. cit., 54-7 compiles examples.
June 11, 2025
QotD: “Pike and Shot” in the early gunpowder era
… this is why the pike[-armed infantry] fought in squares: it was assumed the cavalry was mobile enough to strike a group of pikemen from any direction and to whirl around in the empty spaces between pike formations, so a given pike square had to be able to face its weapons out in any direction or, indeed, all directions at once.
Instead, pike and shot were combined into a single unit. The “standard” form of this was the tercio, the Spanish organizational form of pike and shot and one which was imitated by many others. In the early 16th century, the standard organization of a tercio – at least notionally, as these units were almost never at full strength – was 2,400 pikemen and 600 arquebusiers. In battle, the tercio itself was the maneuver unit, moving as a single formation (albeit with changing shape); they were often deployed in threes (thus the name “tercio” meaning “a third”) with two positioned forward and the third behind and between, allowing them to support each other. The normal arrangement for a tercio was a “bastioned square” with a “sleeve of shot”: the pikes formed a square at the center, which was surrounded by a thin “sleeve” of muskets, then at each corner of the sleeve there was an additional, smaller square of shot. Placing those secondary squares (the “bastions” – named after the fortification element) on the corner allowed each one a wide potential range of fire and would mean that any enemy approaching the square would be under fire at minimum from one side of the sleeve and two of the bastions.
That said, if drilled properly, the formation could respond dynamically to changing conditions. Shot might be thrown forward to provide volley-fire if there was no imminent threat of an enemy advance, or it might be moved back to shelter behind the square if there was. If cavalry approached, the square might be hollowed and the shot brought inside to protect it from being overrun by cavalry. In the 1600s, against other pike-and-shot formations, it became more common to arrange the formation linearly, with the pike square in the center with a thin sleeve of shot while most of the shot was deployed in two large blocks to its right and left, firing in “countermarch” (each man firing and moving to the rear to reload) in order to bring the full potential firepower of the formation to bear.
Indeed it is worth expanding on that point: volley fire. The great limitation for firearms (and to a lesser extent crossbows) was the combination of frontage and reloading time: the limited frontage of a unit restricted how many men could shoot at once (but too wide a unit was vulnerable and hard to control) and long reload times meant long gaps between shots. The solution was synchronized volley fire allowing part of a unit to be reloading while another part fired. In China, this seems to have been first used with crossbows, but in Europe it really only catches on with muskets – we see early experiments with volley fire in the late 1500s, with the version that “catches on” being proposed by William Louis of Nassau-Dillenburg (1560-1620) to Maurice of Nassau (1567-1625) in 1594; the “countermarch” as it came to be known ends up associated with Maurice. Initially, the formation was six ranks deep but as reloading speed and drill improved, it could be made thinner without a break in firing, eventually leading to 18th century fire-by-rank drills with three ranks (though by this time these were opposed by drills where the first three ranks – the front kneeling, the back slightly offset – would all fire at once but with different sections of the line firing at different times (“fire-by-platoon”)).
Coming back to Total War, the irony is that while the basic components of pike-and-shot warfare exist in both Empire: Total War and for the Empire faction in Total War: Warhammer, in both games it isn’t really possible to actually do pike-and-shot warfare. Even if an army combines pikes and muskets, the unit sizes make the kind of fine maneuvers required of a pike-and-shot formation impossible and while it is possible to have missile units automatically retreat from contact, it is not possible to have them pointedly retreat into a pike unit (even though in Empire, it was possible to form hollow squares, a formation developed for this very purpose).
Indeed if anything the Total War series has been moving away from the gameplay elements which would be necessary to make representing this kind of synchronized discipline and careful formation fighting possible. While earlier Total War games experimented with synchronized discipline in the form of volley-fire drills (e.g. fire by rank), that feature was essentially abandoned after Total War: Shogun 2‘s Fall of the Samurai DLC in 2012. Instead of firing by rank, musket units in Total War: Warhammer are just permitted to fire through other members of their unit to allow all of the soldiers in a formation – regardless of depth or width – to fire (they cannot fire through other friendly units, however). That’s actually a striking and frustrating simplification: volley fire drills and indeed everything about subsequent linear firearm warfare was focused on efficient ways to allow more men to be actively firing at once; that complexity is simply abandoned in the current generation of Total War games.
Bret Devereaux, “Collection: Total War‘s Missing Infantry-Type”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-04-01.
May 5, 2025
The Bloody Battle of Agincourt | Animated Episode
The Rest Is History
Published 30 Nov 2024“We few, we happy few, we band of brothers”.
The Battle of Agincourt in 1415 endures as perhaps the most totemic battle in the whole of English history. Thanks in part to Shakespeare’s masterful Henry V, the myths and legends of that bloody day echo across time, forever enshrining the young Henry as the greatest warrior king England had ever known. So too the enduring idea of the English as plucky underdogs, facing down unfavourable odds with brazen grit. And though the exact numbers of men who fought in the two armies is hotly contested, the prospect was certainly intimidating for the English host looking down upon the vast French force amassed below them the day before the battle. Hungry and weary after an unexpectedly long march, and demoralised by the number of French that would be taking to the field, the situation certainly seemed dire for the English. One man amongst them, however, held true to his belief that the day could still be won: Henry V. An undeniably brilliant military commander, he infused his men with a sense of patriotic mission, convincing them that theirs was truly a divinely ordained task, and therefore in this — and his careful strategic planning the night before the battle — he proves a striking case of one individual changing the course of history. However, the French too had plans in place for the day ahead: total warfare. In other words, to overwhelm the English in a single devastating moment of impact, sweeping the lethal Welsh archers aside. So it was that dawn broke on the 25th of October to the site of King Henry wearing a helmet surmounted by a glittering crown and bearing the emblems of both France and England, astride his little grey horse, and riding up and down his lines of weathered silver clad men, preparing them to stride into legend … then, as the French cavalry began their charge, the sky went black as 75,000 arrows blocked out the sun. What else would that apocalyptic day hold in store?
Join Tom and Dominic as they describe the epochal Battle of Agincourt. From the days building up to it, to the moment that the two armies shattered together in the rain and mud of France. It is a story of courage and cowardice, kings and peasants, blood and bowels, tragedy and triumph.
00:00 What is to come …
00:50 Shakespeare and Henry V
02:53 Agincourt is exceptional
04:15 The battle is a test of God’s favour
05:27 The English see the French forces …
09:30 The French aren’t offering battle
10:40 Why the French delay
11:13 The French think they’re going to win
11:35 An ominous silence
12:35 Henry’s plan
20:50 The French plan
24:28 How big were the armies
28:49 The lay of the land
34:50 Henry makes the first move
37:00 The French charge into darkness
38:57 The French army advances
45:50 Reaction to the slaughter
(more…)
March 8, 2025
Joslyn M1862 and M1864 Carbines
Forgotten Weapons
Published 15 Jun 2015While US infantry forces during the Civil War had only limited access to the newest rifle technology, cavalry units adopted a wide variety of new carbines in significant numbers. Among these were a design by Benjamin Joslyn. It first appeared in 1855 designed to use paper cartridges, but by the time the US Army showed an interest Joslyn had updated the weapon to use brass rimfire ammunition. The first version purchased by the government was the 1862 pattern carbine, of which about a thousand were obtained. Many more were ordered, but it took Joslyn a couple years to really get his manufacturing facility and processes worked out. By the time he had this all straightened out, the design had been updated again to the 1864 pattern, addressing several minor problems with the earlier version. Ultimately more than 11,000 of the 1864 pattern carbines were purchased by the Union, chambered for the same .56-.52 cartridge as the Spencer carbines also in service.
March 1, 2025
QotD: Roman Republic versus Seleucid Empire – the Battle of Magnesia
Rome’s successes at sea in turn set conditions for the Roman invasion of Anatolia, which will lead to the decisive battle at Magnesia, but of course in the midst of our naval narrative, we rolled over into a new year, which means new consuls. The Senate extended Glabrio’s command in Greece to finish the war with the Aetolians, but the war against Antiochus was assigned to Lucius Cornelius Scipio, one of the year’s consuls and brother of Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, the victor over Hannibal at Zama (202). There’s an exciting bit of politics behind Scipio getting the assignment (including his famous brother promising to serve as one of his military tribunes), but in a sense that’s neither here nor there. As we’ve seen, Rome has no shortage of capable generals. From here on, if I say “Scipio”, I mean Lucius Cornelius Scipio; if I want his brother, I’ll say “Scipio Africanus”.
Scipio also brought fresh troops with him. The Senate authorized him to raise a supplementum (recruitment to fill out an army) of 3,000 Roman infantry, 100 Roman cavalry, 5,000 socii infantry and 200 socii cavalry (Livy 37.2.1) as well as authorizing him to carry the war into Asia (meaning Anatolia or Asia Minor) if he thought it wise – which of course he will. In addition to this, the two Scipios also called for volunteers from Scipio Africanus’ veterans and got 5,000 of them, a mix of Romans and socii (Livy 37.4.3), so all told Lucius Cornelius Scipio is crossing to Greece with reinforcements of some 13,000 infantry (including some battle-hardened veterans), 300 cavalry and one Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus.1 That said, a significant portion of this force is going to end up left in Greece to handle garrison duty and the Aetolians. Antiochus III, for his part, spends this time raising forces for a major battle, while dispatching his son Seleucus (the future Seleucus IV, r. 187-175) to try to raid Pergamum, Rome’s key ally in the region.
Once the Romans arrive (and join up with Eumenes’ army), both sides maneuvered to try and get a battle on favorable terms. Antiochus III’s army was massive with lots of cavalry – 62,000 infantry and 12,000 cavalry, an army on the same general order of magnitude as the one that fought at Raphia – so he sought an open area, setting up his fortified camp near Magnesia, with fairly formidable defenses – a ditch with a double-rampart (Livy 37.37.9-11). Unsurprisingly, the Romans, with a significant, but smaller force, preferred a fight in more confined quarters and for several days the armies sat opposite each other with minor skirmishes (Livy 37.38).
The problem Scipio faced was a simple one: the year was coming to a close, which meant that soon new consuls would be elected and he could hardly count on his command being extended. Consequently, Scipio calls together his war council – what the Romans call a consilium – to ask what he should do if Antiochus III couldn’t be lured into battle on favorable terms. The answer he got back was to force a battle and so force a battle Scipio did, advancing forward onto the ground of Antiochus’ choosing, leading to the Battle of Magnesia.
We have two accounts of this battle which mostly match up, one in Livy (Livy 37.39-44) and another in Appian’s Syrian Wars (App. Syr. 30-36). Livy here is generally the better source and chances are both authors are relying substantially on Polybius (who would be an even better source), whose account of the battle is lost.
Antiochus III’s army was enormous, with a substantial superiority in cavalry. From left to right, according to Livy (Livy 37.40), Antiochus III deployed: Cyrtian slinger and Elymaean archers (4,000), then a unit of caetrati (4,000; probably light infantry peltasts), then the contingent of Tralli (1,500; light infantry auxiliaries from Anatolia), then Carian and Cilicians equipped like Cretans (1,500; light archer infantry), then the Neo-Cretans (1,000; light archer infantry), then the Galatian cavalry (2,500; mailed shock cavalry), then a unit of Tarantine cavalry (number unclear, probably 500; Greek light cavalry), a part of the “royal squadron” of cavalry (1,000; Macedonian shock cavalry), then the ultra-heavy cataphract cavalry (3,000), supported by a mixed component of auxiliaries (2,700; medium thureophoroi infantry?) along with his scythed chariots and Arab camel troops.
That gets us to the central component of the line (still reading left to right): Cappadocians (2,000) who Livy notes were similarly armed to the Galatian infantry (1,500, unarmored, La Tène infantry kit, so “mediums”) who come next. Then the main force of the phalanx, 16,000 strong with 22 elephants. The phalanx was formed 32 ranks deep, with the intervals between the regiments covered by the elephants deployed in pairs, creating an articulated or enallax phalanx like Pyrrhus had, but using elephants rather than infantry to cover the “hinges”. This may in fact, rather than being a single phalanx 32 men deep be a “double” phalanx (one deployed behind the other) like we saw at Sellasia. Then on the right of the phalanx was another force of 1,500 Galatian infantry. Oddly missing here is the main contingent of the elite Silver Shields (the Argyraspides); some scholars2 note that a contingent of them 10,000 strong would make Livy’s total strength numbers and component numbers match up and he has just forgotten them in the main line. We might expect them to be deployed to the right of the main phalanx (where Livy will put the infantry Royal Cohort (regia cohors), confusing a subunit of the argyraspides with the larger whole unit. Michael Taylor in a forthcoming work3 has suggested they may also have been deployed behind the cavalry we’re about to get to or otherwise to their right.
That gets us now to the right wing (still moving left to right; you begin to realize how damn big this army is), we have more cataphracts (3,000, armored shock cavalry), the elite cavalry agema (1,000; elite Mede/Persian cavalry, probably shock), then Dahae horse archers (1,200; Steppe horse archers), then Cretan and Trallian light infantry (3,000), then some Mysian Archers (2,500) and finally another contingent of Cyrtian slinger and Elymaean archers (4,000).
This is, obviously, a really big army. But notice that a lot of its strength is in light infantry: combining the various archers, slingers and general light infantry (excluding troops we suspect to be “mediums”) we come to something like 21,500 lights, plus another 7,700 “medium” infantry and then 26,000 heavy infantry (accounting for the missing argyraspides). That’s 55,200 total, but Livy reports a total strength for the army of 62,000; it’s possible the missing remainder were troops kept back to defend the camp, in which case they too are likely light infantry. A Roman army’s infantry contingent is around 28% “lights” (the velites), who do not occupy any space in the main battle line. Antiochus’ infantry contingent, while massive, is 39% “lights” (and another 14% “mediums”), some of which do seem to occupy actual space in the battle line.
Of course Antiochus also has a massive amount of cavalry ranging from ultra-heavy cataphracts to light but highly skilled horse archers and massive cavalry superiority covereth a multitude of sins.
But the second problem with this gigantic army is one that – again, in a forthcoming work – Michael Taylor has pointed out. The physical space of the battlefield at Magnesia is not big enough to deploy the whole thing […]
Now Livy specifies that the flanks of Antiochus’ army curve forward, describing them as “horns” (cornu) rather than “wings” (alae) and noting they were “a little bit advanced” (paulum producto), which may be an effort to get more of this massive army actually into the fight […]. So while this army is large, it’s also unwieldy and difficult to bring properly into action and it’s not at all clear from either Livy or Appian that the whole army actually engaged – substantial portions of that gigantic mass of light infantry on the wings just seem to dissolve away once the battle begins, perhaps never getting into the fight in the first place.
The Roman force was deployed in its typical formation, with the three lines of the triplex acies and the socii flanking the legions (Livy 37.39.7-8), with the combined Roman and socii force being roughly 20,000 strong (the legions and alae being somewhat over-strength). In addition Eumenes, King of Pergamum was present and the Romans put his force on their right to cover the open flank, while he anchored his left flank on the Phrygios River. Eumenes’ wing consisted of 3,000 Achaeans (of the Achaean League) that Livy describes as caetrati and Appian describes as peltasts (so, lights), plus nearly all of Scipio’s cavalry: Eumenes’ cavalry guard of 800, plus another 2,200 Roman and socii cavalry, and than some auxiliary Cretan and Trallian light infantry, 500 each. Thinking his left wing, anchored on the river, relatively safe, Scipio posted only four turmae of cavalry there (120 cavalry). He also had a force of Macedonians and Thracians mixed together – so these are probably “medium” infantry – who had come as volunteers, who he posts to guard the camp rather than in the main battleline. I always find this striking, because I think a Hellenistic army would have put these guys in the front line, but a Roman commander looks at them and thinks “camp guards”. The Romans also had some war elephants, sixteen of them, but Scipio assesses that North African elephants won’t stand up to the larger Indian elephants of the Seleucids (which is true, they won’t) and so he puts them in reserve behind his lines rather than out front where they’d just be driven back into him. All told then, the Roman force is around 26,000 infantry and 3,000 cavalry – badly outnumbered by Antiochus, but of a relatively higher average quality and a bit more capable of actually fitting its entire combat power into the space.
The Battle
Because the armies are so large, much like as happened at Raphia, the battle that results is almost three battles running in parallel: the two wings and the center. Antiochus III commanded from his right wing, where – contrary to the expectations of Scipio who thought the river would secure his flank there – he intended his main attack. His son Seleucus commanded the left. Livy reports a light rain which interfered with both with visibility and some of Antiochus’ light troops’ weapons, as their bows and slings reacted poorly to the moisture (as composite bows will sometimes do; Livy 37.41.3-4, note also App. Syr. 33).Antiochus opens the battle on his left with his scythed chariots, a novel “gimmick” weapon (heavy chariots with blades all over them, used to shock infantry out of position). This may have been a nasty surprise for the Romans, but given the dispositions of the army, it was Eumenes, not Scipio who faces the chariots and as Livy notes, Eumenes was well aware how to fight them (Livy 37.41.9), using his light troops – those Cretan archers and Trallian javelin-troops. Deployed in loose order, they were able to move aside to avoid the chariots better than heavy infantry in close-order (similar tactics are used against elephants) and could with their missiles strike at chariot drivers and horses at range (Livy 37.41.10-12). Turning back this initial attack seems to have badly undermined the morale of the Seleucid left-wing, parts of which fled, creating a gap between the extreme left-wing and the heavy cavalry contingent. Eumenes then, with the Roman cavalry, promptly hammered the disordered line, hitting first the camel troops, then in the confusion quickly overwhelming the rest of the cavalry, including the cataphracts, leading Antiochus’ left wing to almost totally collapse, isolating the phalanx in the center. It’s not clear what the large mass of light infantry on the extreme edge of the battlefield was doing.
Meanwhile on the other side of the battle, where Scipio had figured a light screen of 120 equites would be enough to hold the end of the line, Antiochus delivered is cavalry hammer-blow successfully. Obnoxiously, both of our sources are a lot less interested in describing how he does this (Livy 37.42.7-8 and App. Syr. 34), which is frustrating because it is a bit hard to make sense of how it turns out. On the one hand, the constricted battlefield will have meant that, regardless of how they were positioned, those argyraspides are going to end up following Antiochus’ big cavalry hammer on the (Seleucid) right. They then overwhelm the cavalry and put them to flight and then push the infantry of that wing (left ala of socii and evidently a good portion of the legion next to it) back to the Roman camp.
On the other hand, the Roman infantry line reaches its camp apparently in good order or something close to it. Marcus Aemilius, the tribune put in charge of the camp is able to rush out, reconstitute the infantry force and, along with the camp-guard, halt Antiochus’ advance. The thing is, infantry when broken by cavalry usually cannot reform like that, but the distance covered, while relatively short, also seems a bit too long for the standard legionary hastati-to-principes-to-triarii retrograde. Our sources (also including a passage of Justin, a much later source, 31.8.6) vary on exactly how precipitous the flight was and it is possible that it proceeded differently at different points, with some maniples collapsing and others making an orderly retrograde. In any case, it’s clear that the Roman left wing stabilized itself outside of the Roman camp, much to Antiochus’ dismay. Eumenes, having at this point realized both that he was winning on his flank and that the other flank was in trouble dispatched his brother Attalus with 200 cavalry to go aid the ailing Roman left wing; the arrival of these fellows seem to have caused panic and Antiochus at this point begins retreating.
Meanwhile, of course, there is the heavy infantry engagement at the center. Pressured and without flanking support, Appian reports that the Seleucid phalanx first admitted what light infantry remained and then formed square, presenting their pikes tetragonos, “on all four sides” (App. Syr. 35), a formation known as a plinthion in some Greek tactical manuals. Forming this way under pressure on a chaotic battlefield is frankly impressive (though if they were formed as a double-phalanx rather than a double-thick single-phalanx, that would have made it easier) and a reminder that the core of Antiochus’ army was quite capable. Unable in this formation to charge, the phalanx was showered with Roman pila and skirmished by Eumenes’ lighter cavalry; the Romans seem to have disposed of Antiochus’ elephants with relative ease – the Punic Wars had left the Romans very experienced at dealing with elephants (Livy 37.42.4-5). Appian notes that some of the elephants, driven back by the legion and maddened disrupted the Seleucid square, at which point the phalanx at last collapsed (App. Syr. 35); Livy has the collapse happen much faster, but Appian’s narrative here seems more plausible.
What was left of Antiochus’ army now fled to their camp – not far off, just like the Roman one – leading to a sharp battle at the camp which Livy describes as ingens et maior prope quam in acie cades, “a huge slaughter, almost greater than that in the battle” (Livy 37.43.10), with stiff resistance at the camp’s gates and walls holding up the Romans before they eventually broke through and butchered the survivors. Livy reports that of Antiochus’ forces, 50,000 infantry and 3,000 cavalry were killed, another 1,500 captured; these seem really high as figures go, but Appian reports almost the exact same. Interesting, Livy doesn’t report the figure in his own right or attribute it to Polybius but instead simply notes “it is said that”, suggesting he may not be fully confident of the number either. Taylor supposes, reasonably I think, that this oversized figure may also count men who fled from the battlefield, reflecting instead that once Antiochus III could actually reconstitute his army, he had about 19,000 men, most of the rest having fled.4 Either way, the resulting peace makes clear that the Seleucid army was shattered beyond immediate repair.
Roman losses, by contrast, were shockingly light. Livy reports 300 infantry lost, 24 Roman cavalry and 25 out of Eumenes’ force; Appian adds that the 300 infantry were “from the city” – meaning Roman citizens – so some socii casualties have evidently been left out (but he trims Eumenes’ losses down to just fifteen cavalry) (Livy 37.44.2-3; App. Syr. 36). Livy in addition notes that many Romans were wounded in addition to the 300 killed. This is an odd quirk of Livy’s casualty reports for Roman armies against Hellenistic armies and I suspect it reflects the relatively high effectiveness of Roman body armor, by this point increasingly dominated by the mail lorica hamata: good armor converts lethal blows into survivable wounds.5 It also fits into a broader pattern we’ve seen: Hellenistic armies that face Roman armies always take heavy casualties, winning or losing, but when Roman armies win they tend to win lopsidedly. It is a trend that will continue.
So why Roman victory at Magnesia? It is certainly not the case that the Romans had the advantage of rough terrain in the battle: the battlefield here is flat and fairly open. It should have been ideal terrain for a Hellenistic army.
A good deal of the credit has to go to Eumenes, which makes the battle a bit hard to extrapolate from. It certainly seems like Eumenes’ quick thinking to disperse the Seleucid chariots and then immediately follow up with his own charge was decisive on his flank, though not quite battle winning. Eumenes’ forces, after all, lacked the punch to disperse the heavier phalanx, which did not panic when its wing collapsed. Instead, the Seleucid phalanx, pinned into a stationary, defensive position by Eumenes’ encircling cavalry, appears to have been disassembled primary by the Roman heavy infantry, peppering it with pila before inducing panic into the elephants. It turns out that Samnites make better “glue” for an articulated phalanx than elephants, because they are less likely to panic.
Meanwhile on the Seleucid right (the Roman left), the flexible and modular nature of the legion seems to have been a major factor. Antiochus clearly broke through the Roman line at points, but with the Roman legion’s plethora of officers (centurions, military tribunes, praefecti) and with each maniple having its own set of standards to rally around, it seems like the legion and its socii ala managed to hold together and eventually drive Antiochus off, despite being pressured. That, in and of itself, is impressive: it is the thing the Seleucid center fails to do, after all.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Phalanx’s Twilight, Legion’s Triumph, Part IVb: Antiochus III”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-04-05.
1. I enjoy this joke because the idea of bringing Scipio Africanus along as a junior officer is amusing, but I should note that in the event, he doesn’t seem to have had much of a role in the campaign.
2. E.g. Bar Kockva, The Seleucid Army: Organization and Tactics in the Great Campaigns (1979)
3. “A Commander Will Put an End to his Insolence: the Battle of Magnesia, 190BC” to appear in The Seleucids at War: Recruitment, Organization and Battles (forthcoming in 2024), eds. Altay Coşkun and Benhamin E. Scolnic.
4. Taylor, Antiochus the Great (2013), 143.
5. On this, see, uh, me, “The Adoption and Impact of Roman Mail Armor in the Third and Second Centuries B.C.” Chiron 52 (2022).
February 23, 2025
QotD: The Hellenistic army system as a whole
I should note here at the outset that we’re not going to be quite done with the system here – when we start looking at the third and second century battle record, we’re going to come back to the system to look at some innovations we see in that period (particularly the deployment of an enallax or “articulated” phalanx). But we should see the normal function of the components first.
No battle is a perfect “model” battle, but the Battle of Raphia (217BC) is handy for this because we have the two most powerful Hellenistic states (the Ptolemies and Seleucids) both bringing their A-game with very large field armies and deploying in a fairly standard pattern. That said, there are some quirks to note immediately: Raphia is our only really good order of battle of the Ptolemies, but as our sources note there is an oddity here, specifically the mass deployment of Egyptians in the phalanx. As I noted last time, there had always been some ethnic Egyptians (legal “Persians”) in the phalanx, but the scale here is new. In addition, as we’ll see, the position of Ptolemy IV himself is odd, on the left wing matched directly against Antiochus III, rather than on his own right wing as would have been normal. But this is mostly a fairly normal setup and Polybius gives us a passably good description (better for Ptolemy than Antiochus, much like the battle itself).
We can start with the Seleucid Army and the tactical intent of the layout is immediately understandable. Antiochus III is modestly outnumbered – he is, after all, operating far from home at the southern end of the Levant (Raphia is modern-day Rafah at the southern end of Gaza), and so is more limited in the force he can bring. His best bet is to make his cavalry and elephant superiority count and that means a victory on one of the wings – the right wing being the standard choice. So Antiochus stacks up a 4,000 heavy cavalry hammer on his flank behind 60 elephants – Polybius doesn’t break down which cavalry, but we can assume that the 2,000 with Antiochus on the extreme right flank are probably the cavalry agema and the Companions, deployed around the king, supported by another 2,000 probably Macedonian heavy cavalry. He then uses his Greek mercenary infantry (probably thureophoroi or perhaps some are thorakitai) to connect that force to the phalanx, supported by his best light skirmish infantry: Cretans and a mix of tough hill folks from Cilicia and Caramania (S. Central Iran) and the Dahae (a steppe people from around the Caspian Sea).
His left wing, in turn, seems to be much lighter and mostly Iranian in character apart from the large detachment of Arab auxiliaries, with 2,000 more cavalry (perhaps lighter Persian-style cavalry?) holding the flank. This is a clearly weaker force, intended to stall on its wing while Antiochus wins to the battle on the right. And of course in the middle [is] the Seleucid phalanx, which was quite capable, but here is badly outnumbered both because of how full-out Ptolemy IV has gone in recruiting for his “Macedonian” phalanx and also because of the massive infusion of Egyptians.
But note the theory of victory Antiochus III has: he is going to initiate the battle on his right, while not advancing his left at all (so as to give them an easier time stalling), and hope to win decisively on the right before his left comes under strain. This is, at most, a modest alteration of Alexander-Battle.
Meanwhile, Ptolemy IV seems to have anticipated exactly this plan and is trying to counter it. He’s stacked his left rather than his right with his best troops, including his elite infantry (the agema and peltasts, who, while lighter, are more elite) and his best cavalry, supported by his best (and only) light infantry, the Cretans.1 Interestingly, Polybius notes that Echecrates, Ptolemy’s right-wing commander waits to see the outcome of the fight on the far side of the army (Polyb. 6.85.1) which I find odd and suggests to me Ptolemy still carried some hope of actually winning on the left (which was not to be). In any case, Echecrates, realizing that sure isn’t happening, assaults the Seleucid left.
I think the theory of victory for Ptolemy is somewhat unconventional: hold back Antiochus’ decisive initial cavalry attack and then win by dint of having more and heavier infantry. Indeed, once things on the Ptolemaic right wing go bad, Ptolemy moves to the center and pushes his phalanx forward to salvage the battle, and doing that in the chaos of battle suggests to me he always thought that the matter might be decided that way.
In the event, for those unfamiliar with the battle: Antiochus III’s right wing crumples the Ptolemaic left wing, but then begins pursuing them off of the battlefield (a mistake he will repeat at Magnesia in 190). On the other side, the Gauls and Thracians occupy the front face of the Seleucid force while the Greek and Mercenary cavalry get around the side of the Seleucid cavalry there and then the Seleucid left begins rolling up, with the Greek mercenary infantry hitting the Arab and Persian formations and beating them back. Finally, Ptolemy, having escaped the catastrophe on his left wing, shows up in the center and drives his phalanx forward, where it wins for what seem like obvious reasons against an isolated Seleucid phalanx it outnumbers almost 2-to-1.
But there are a few structural features I want to note here. First, flanking this army is really hard. On the one hand, these armies are massive and so simply getting around the side of them is going to be difficult (if they’re not anchored on rivers, mountains or other barriers, as they often are). Unlike a Total War game, the edge of the army isn’t a short 15-second gallop from the center, but likely to be something like a mile (or more!) away. Moreover, you have a lot of troops covering the flanks of the main phalanx. That results, in this case, in a situation where despite both wings having decisive actions, the two phalanxes seem to be largely intact when they finally meet (note that it isn’t necessarily that they’re slow; they seem to have been kept on “stand by” until Ptolemy shows up in the center and orders a charge). If your plan is to flank this army, you need to pick a flank and stack a ton of extra combat power there, and then find a way to hold the center long enough for it to matter.
Second, this army is actually quite resistive to Alexander-Battle: if you tried to run the Issus or Gaugamela playbook on one of these armies, you’d probably lose. Sure, placing Alexander’s Companion Cavalry between the Ptolemaic thureophoroi and Gallic mercenaries (about where he’d normally go) would have him slam into the Persian and Medean light infantry and probably break through. But that would be happening at the same time as Antiochus’ massive 4,000-horse, 60-elephant hammer demolished Ptolemaic-Alexander’s left flank and moments before the 2,000 cavalry left-wing struck Alexander himself in his flank as he advanced. The Ptolemaic army is actually an even worse problem, because its infantry wings are heavier, making that key initial cavalry breakthrough harder to achieve. Those chunky heavy-cavalry wings ensure that an effort to break through at the juncture of the center and the wing is foolhardy precisely because it leaves the breakthrough force with heavy cavalry to one side and heavy infantry to the other.
I know this is going to cause howls of pain and confusion, but I do not think Alexander could have reliably beaten either army deployed at Raphia; with a bit of luck, perhaps, but on the regular? No. Not only because he’d be badly outnumbered (Alexander’s army at Gaugamela is only 40,000 infantry and 7,000 cavalry) but because these armies were adapted to precisely the sort of army he’d have and the tactics he’d use. Even without the elephants (and elephants gave Alexander a hell of a time at the Hydaspes), these armies can match Alexander’s heavy infantry core punch-for-punch while having enough force to smash at least one of his flanks, probably quite quickly. Note that the Seleucid Army – the smaller one at Raphia – has almost exactly as much heavy infantry at Raphia as Alexander at Gaugamela (30,000 to 31,000), and close to as much cavalry (6,000 to 7,000), but of course also has a hundred and two elephants, another 5,000 more “medium” infantry and massive superiority in light infantry (27,000 to 9,000). Darius III may have had no good answer to the Macedonian phalanx, but Antiochus III has a Macedonian phalanx and then essentially an entire second Persian-style army besides (and his army at Magnesia is actually more powerful than his army at Raphia).
This is not a degraded form of Alexander’s army, but a pretty fearsome creature of its own, which supplements an Alexander-style core with larger amounts of light and medium troops (and elephants), without sacrificing much, if any, in terms of heavy infantry and cavalry. The tactics are modest adjustments to Alexander-Battle which adapt the military system for symmetrical engagements against peer armies. The Hellenistic Army is a hard nut to crack, which is why the kingdoms that used them were so successful during the third century, to the point that, until the Romans show up, just about the only thing which could beat a Hellenistic army was another Hellenistic army.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Phalanx’s Twilight, Legion’s Triumph, Part Ib: Subjects of the Successors”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2024-01-26.
1. You can tell how much those Cretans are valued, given that they get placed in key positions in both armies.
December 30, 2024
QotD: The auxilia troops of the Imperial Roman armies
As we’ve seen, there had always been non-Romans fighting alongside Roman citizens in the army, for as long as we have reliable records to judge the point. In the Republic (until the 80s BC) these had consisted mostly of the socii, Rome’s Italian allies. These were supplemented by troops from whatever allies Rome might have at the time, but there was a key difference in that the socii were integrated permanently into the Roman army’s structure, with an established place in the “org. chart”, compared to the forces of allies who might fight under their own leaders with an ad hoc relationship to the Roman army they were fighting with. The end of the Social War (91-87BC) brought the Italians into the Roman citizen body and thus their soldiers into the legions themselves; it marked the effective end of the socii system, which hadn’t been expanded outside of Italy in any case.
But almost immediately we see the emergence of a new system for incorporating non-Romans, this time provincial non-Romans, into the Roman army. These troops, called auxilia (literally, “helpers”) first appear in the Civil Wars, particularly with Caesar‘s heavy reliance on Gallic cavalry to support his legions (which at this time seem not to have featured their own integrated cavalry support, as they had earlier in the republic and as they would later in the empire). The system is at this point very ad hoc and the auxiliaries here are a fairly small part of Roman armies. But when Augustus sets out to institutionalize and stabilize the Roman army after the Battle of Actium (31BC) and the end of the civil wars, the auxilia emerge as a permanent, institutional part of the Roman army. Clearly, they were vastly expanded; by 23 AD they made up half of the total strength of the Roman army (Tac. Ann. 4.5) a rough equivalence that seems to persist at least as far as the Constitutio Antoniniana in 212.
Of course it was no particular new thing for the Romans to attempt to use their imperial subjects as part of their army. The Achaemenid army had incorporated a bewildering array of subject peoples with their own distinctive fighting styles, a fact that Achaemenid rulers liked to commemorate […] The Seleucid army at Magnesia (189) which the Romans defeated also had numerous non-Macedonian supporting troops: Cappadocians, Galatians, Carians, Cilicians, Illyrians, Dahae, Mysians, Arabs, Cyrtians and Elamites. At Raphia (217) the Ptolemaic army incorporated Egyptian troops into the phalanx for the first time, but also included Cretans, Greek mercenaries, Thracians, Gauls and Libyans, inter alia. Most empires try to do this.
The difference here is the relative performance that Rome gets out of these subject-troops (both the socii and the auxilia). Take those examples. Quite a number of the ethnicities on Xerxes monument both served in the armies of Darius III fighting against Alexander but then swiftly switched sides to Alexander after he won the battles – the Ionians, Egypt, and Babylon greeted Alexander as a liberator (at least initially) which is part of why the Achaemenid Empire could crumble so fast so long as Alexander kept winning battles. Apart from Tyre and Gaza, the tough sieges and guerilla resistance didn’t start until he reached the Persian homeland. The auxiliaries in the Seleucid army at Magnesia famously fell apart under pressure, whereas the Roman socii stuck in the fight as well as the legions; our sources give us no sense at any point that the socii were ever meaningfully weaker fighters than the legions (if anything, Livy sometimes represents them as more spirited, though he has an agenda here, as discussed). And the Ptolemaic decision to arm their Egyptian troops in the Macedonian manner won the battle (turns out, Egyptians could fight just as well as Greeks and Macedonians with the right organization and training) but their subsequent apparent decision not to pay or respect those troops as well as their Macedonians seems to have led quite directly to the “Great Revolt” which crippled the kingdom (there is some scholarly argument about this last point, but while I think Polybius’ pro-Greek, anti-Egyptian bias creeps in to his analysis, he is fundamentally right to see the connection (Plb. 5.107). Polybius thinks it was foolish to arm non-Greeks, but the solution here to saving the Ptolemaic kingdom would have been arming the Egyptians and then incorporating them into the system of rule rather than attempting to keep up the ethnic hierarchy with a now-armed, angry and underpaid underclass. The Greek-speakers-only-club system of Ptolemaic rule was unsustainable in either case, especially with Rome on the horizon).
By contrast, the auxilia were mostly very reliable. The one major exception comes from 69 AD – the “Year of the Four Emperors” to give some sense of its chaos – when the Batavian chieftain Julius Civilis (himself an auxiliary veteran and a Roman citizen) revolted and brought one ala and eight cohorts drawn from the Batavi (probably around 4,500 men or so) with him, out of an empire-wide total of c. 150,000 auxilia (so maybe something like 3.3% of the total auxilia). Indeed, the legions had worse mutinies – the mutiny on the Rhine (Tac. Ann. 1.16ff in 14AD) had involved six legions (c. 30,000 troops, nearly a quarter of Rome’s 25 legions at the time). This despite the fact that the auxilia were often deployed away from the legions, sometimes in their own forts (you’ll see older works of scholarship suggest that the auxilia were kept logistically dependent on the legions, but more recent archaeology on exactly where they were has tended to push against this view). Indeed, the auxilia were often the only military forces (albeit in small detachments) in the otherwise demilitarized “senatorial” provinces (which comprised most of the wealthy, populous “core” of the empire); they could be trusted with the job, provided they weren’t the only forces in their own home provinces (and after 69, they never were). And the auxilia fought hard and quite well. The Romans occasionally won battles with nothing but the auxilia, was with the Battle of Mons Graupius (83 AD, Tac. Agricola 35ff) where the legions were held in reserve and never committed, the auxilia winning the battle effectively on their own. Viewers of the Column of Trajan’s spiral frieze have long noted that the auxilia on the monument (the troop-types are recognizable by their equipment) do most of the fighting, while the legions mostly perform support and combat engineering tasks. We aren’t well informed about the training the auxilia went through, but what we do know points to long-service professionals who were drilled every bit as hard as the famously well-drilled legions. Consequently, they had exactly the sort of professional cohesion that we’ve already discussed.
Why this difference in effectiveness and reliability? The answer is to be found in the difference in the terms under which they served. Rather than being treated as the disposable native auxiliaries of other empires, the Romans acted like the auxilia mattered … because they did.
First of all, the auxilia were paid. Our evidence here is imperfect and still much argued about, but it seems that auxilia were paid 5/6ths of the wages of the legionary counterparts, with the cavalry auxilia actually paid more than the infantry legionaries. While it might sound frustrating to be systematically paid 1/6th less than your legionary equivalent, the legions were paid fairly well. The auxilia probably made in wages about as much as a normal day-laborer, but the wage was guaranteed (something very much not the case for civilian laborers) and while the cost of their rations was deducted from their pay, that deduction was a fixed amount that seems to have been set substantially below the market value of their rations, building in another subsidy. Most auxiliaries seem to have been volunteers, because the deal in being an auxiliary was good enough to attract volunteers looking to serve a full tour of duty (around 20 years; this was a long-service professional army now so joining it meant making a career out of it).
And most importantly, eventually (perhaps under Tiberius or shortly thereafter) the auxilia began to receive a special grant of citizenship on finishing that tour of duty, one which covered the soldier, and any children he might have had by his subsequent spouse (including children had, it seems, before he left the army; Roman soldiers in this period were legally barred from contracting legal marriages while serving, so the grant is framed so that it retroactively legitimizes any children produced in a quasi-marriage when the tour of service is completed). Consequently, whereas a soldier being dragooned or hired as a mercenary into other multi-ethnic imperial armies might end his service and go back to being an oppressed subject, the Roman auxiliary, by virtue of his service, became Roman and thus essentially joined the ruling class at least in ethnic status. Auxiliaries also clearly got a share of the loot when offensive warfare happened and while there is a lot of debate as to if they also received the praemia (the large retirement bonus legionaries got), epigraphically it is pretty clear that auxiliaries who were careful with their money could establish themselves fairly well after their service. I should also note that what we see of auxiliaries suggests they were generally well armed (with some exceptions, which may have more to do with stereotyped depictions of certain kinds of “barbarians” than anything else): metal helmets, mail shirts (an expensive and high quality armor for the period), oval shields, a spear and the spatha – a Roman version of the classic Gallic one-handed cutting sword – are the standard visual indicator in Roman artwork for generic “auxiliaries”. That is actually a fairly high-end kit; it is no surprise that the auxilia could win battles with it.
The attentive should already be noting many of the components of the old socii system now in a new form: the non-Roman troops serve under similar conditions with the Romans, get similar pay and rations (forts occupied by the auxilia show no deviation from the standard Roman military diet), a share of loot and glory and can finally be rewarded for loyal service by being inducted into the Roman citizen body itself (which could mean their sons might well enroll in the legions, a thing which does seem to have happened, as we do see a fair bit of evidence for “military families” over multiple generations).
(For those looking for more detail on the auxilia, a lot of this is drawn from a book I have already recommended, Ian Haynes, Blood of the Provinces: The Roman auxilia and the Making of Provincial Society from Augustus to the Severans (2013). Also still useful for the history of the development of the auxilia is D.B. Saddington, The Development of the Roman auxiliary Forces from Caesar to Vespasian (1982); this is, alas, not an easy book to find as it is – to my knowledge – long out of print, but your library may be able to track down a copy.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Queen’s Latin or Who Were the Romans, Part V: Saving and Losing and Empire”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-07-30.