… it’s easy to see what the evidence is (or would be): The well-documented awfulness of life under Stalin. There’s also plenty of evidence that the Wehrmacht certainly thought they’d be greeted as liberators, and while it’s hard to put too much weight on the anecdotes of individual soldiers and civilians (most recorded long after the fact), there seems to be a fair amount of evidence they actually were greeted as liberators …
… at least in some places, and at least initially. There’s a second inference here: “the exigencies of war led Germany to behave tactfully”. Here’s where our initial ground rules of evidence become extremely important. Those anecdotal reports of civilian / military interaction, above: What weight do we assign those? And why?
If I’m arguing for the “greeted as liberators” theory, I can use all those recollections of cordial civilian / military interaction. But I need to be consistent: If I say “You can trust those, even though they’re personal memories written down long after the fact, because XYZ”; then I can’t turn around and dismiss contrary evidence of the same type: “All those reports of brutality are just personal memories written down long after the fact.” That’s one of the ways you catch a propagandist: they constantly conflate the two.
Fortunately, in this case we’re dealing with two totally ideologized societies. Even better, one of those totally ideologized societies was German, with their well-documented love of paperwork. All armies generate scads of paperwork, and an ideologized army’s paperwork is full of ideology. So: How does the Army of Occupation’s paperwork tell the tale? That should give us some clues as to their future plans — obviously the occupiers would need to be part of it — and some insight as to the day-to-day.
As it turns out, the second part of your inference — “the exigencies of war led Germany to behave tactfully” — is false. We’ve got the paperwork on it, starting with the infamous “Commissar Order” and working down. Ideology trumps exigency. It seems clear from Wehrmacht paperwork that so long as military efficiency was maintained, you could do pretty much whatever you wanted out there.
[Interestingly, in a bit of meta-irony, the Wikipedia “thumbnail” — the little box you get on the side of the search results page — says of the Commissar Order: “Nazi conspiracy-enforcing unit of the Nazi military.” [Sic], of course — they really want you to know these guys were Nazis. Also, what’s a “conspiracy-enforcing unit”? One imagines a Q-tard goon squad, beating up people whose faith in the God-Emperor is wavering. Finally, it wasn’t a “conspiracy” — they were right out in the open with it. We’ve got lots of copies of the Commissar Order, because it was read out to the troops before the invasion. ALL the troops].1
That segues into the “Organizational Darwinism” thing. The paperwork shows us that “the Nazis” really did have grandiose plans for settling a whole bunch of Germans in the depopulated East. They even got a pilot program underway, as I recall — a whole bunch of ethnic Germans from Bohemia or someplace getting stuck in a transit camp in eastern Poland, or even Ukraine. But notice I put “the Nazis” in quotation marks. The guys with the grandiose plans were RuSHA, the Main Race and Settlement Office. And not even all of them: It was the fourth department, “Settlement”, inside RuSHA. And RuSHA was inside the SS, which was inside — but also outside, over, under, around, and through — the rest of the Nazis’ plate-of-spaghetti org chart.
And it’s actually way more complicated than that, because of course it is — these are the Nazis we’re talking about. I’m not going to dive into the details (not least because it all makes my head hurt), but if you were an ethnic German who wanted to get resettled in Ukraine for some reason — and this is all mostly theoretical, I hasten to add, very few actually moved so far as I know — you’d have to deal with a bewildering array of bizarrely-acronymed organizations. RuSHA, VOMI, the Generalgovernment (Occupied Poland), the SS (in general; over and above RuSHA), the army, the whole bewildering array of groups represented in Generalplan Ost, which was a “plan” in much the same way the “Holy Roman Empire” was holy, Roman, and an empire. Various Party goons would want to get their beaks wet, as would the Gestapo (hell yes they want to know if people are moving around the Reich, especially towards the front on military railroads), and so on.
As weird as this sounds, all this elaborate mishmash of ass-pulled “organization” was by largely by design. For one thing, it diffuses responsibility for really nasty shit — when it comes to certain events on the Eastern Front, even scrupulously neutral historians are often reduced to Ilhan Omar’s level: some people did some things. Who gave what order? Who was he reporting to? And in what capacity? Insufficient data.
Severian, “Organizational Darwinism”, Founding Questions, 2023-01-30.
1. Side note: Ideology really increases military efficiency, up to a point. Recalling that I’m not even an armchair general, it seems like the American military is really missing a trick there. Imagine what the Americans could’ve done in Vietnam if their regular forces had been better indoctrinated, instead of punting military-civilian relations off to CORDS. Properly indoctrinated, I mean, with an ideology that kinda sorta makes sense and is internally consistent and at least somewhat intersects with the real world. “Spreading democracy” would work ok, if they actually ideologized the ranks (instead of having the PR guys just parrot it to the cameras). The AINO military is of course fully indoctrinated, but see above: we’re talking combat efficiency here, not butt stuff.
July 7, 2023
QotD: Nazi Germany’s plans for Eastern Europe versus their actual implementation of those plans
July 2, 2023
Allies Liberate Cherbourg – WW2 – Week 253 – July 1, 1944
World War Two
Published 1 Jul 2023Several weeks after the invasion of Normandy began, the Allies finally take a port city there, though the actual harbor has been destroyed. On Saipan the Americans have the advantage, in Finland, the Soviets do, but the big news is the Soviet destruction of huge chunks of German Army Group Center, demolishing entire Army Corps, and surrounding tens of thousands of the enemy.
(more…)
June 27, 2023
“No one seems to understand what the hell just happened in Russia”
Discussing anything to do with the Russo-Ukraine war is difficult enough due to the signal-to-noise ratio in the information we get from both sides and (theoretically) disinterested observers. Trying to read the tea leaves in the events over the weekend was just an utter waste of time, despite the potentially earth-shaking possibilities being thrown up. The weekend dispatch from The Line doesn’t pretend to have any deep analysis to offer, which I think is by far the wisest approach:

“Sir Humphrey Appleby” tweeted this, saying it was “the intelligence update slide every DI analyst secretly dreams of producing …
As we write this, roughly a day has passed since the sudden end of what briefly looked like a massive event with the potential to reshape global politics for a generation … before it fizzled. The rebellion of Russia’s Wagner mercenary group and its bolt toward Moscow was a stunning story, until it wasn’t. And that itself is a stunning story. Yevgeny Prigozhin, former chef and now Wagner leader, suddenly called off his mutiny, and it just … ended.
Really?
When the mutiny began on Friday, and especially when Wagner seized the southern city of Rostov, home to a major Russian military headquarters overseeing the invasion of Ukraine as well as a million other people, we were surprised, but the more we thought about it, we weren’t particularly shocked. There had been obvious signs of an imminent rupture of some kind in recent months; Line editor Gurney had wondered on Twitter how long it could last before something snapped. That was about three hours before the entire country seemed to snap and Prigozhin marched into Rostov and began moving north.
Events proceeded at a fairly frantic pace after that, with Wagner troops advancing almost all the way to Moscow while Russian security forces fortified the city and tore up roads along the route. It wasn’t clear to us that Wagner had enough men to actually take the city and potentially capture key members of the government. But it wasn’t clear that he didn’t: there are two sides of that equation — the troops Prigozhin had and the troops Putin could count on to oppose Wagner. It was the latter group that captured our interest.
Wagner encountered some resistance along the way, but not much. Most of Russia’s army is deployed in Ukraine, of course, and much of what’s left is now of famously poor quality and morale. But even those military and security forces that were able to block Wagner’s advance didn’t seem that interested in the job. There are reports that some units went over to Prigozhin’s side, but it seems that most of them just did … nothing in particular. And waited to see what happened. For a few hours, we wondered if Prigozhin’s small force would be just large enough in the face of a Russian military that seemed to have no appetite for battle on its own soil.
We can’t pretend to explain the bizarre conclusion to this chaotic day and a half, with an apparent deal brokered by Belarus seeing Wagner’s advance on Moscow called off, a broad amnesty granted to all participants and Prigozhin apparently set to continue to oversee Wagner’s global operations from Belarus in some kind of exile. This is all just wildly unrealistic. Prigozhin cannot be the last person around to realize that he’s put a target on his back and that he’ll soon experience some kind of fatal medical emergency or tragic tumble out of an open window. The moment his mercenaries took Rostov, he had only one path forward: all the way to the Kremlin. What the hell he’s thinking is frankly beyond our ability to guess, and we have fairly vivid imaginations. It’s baffling.
Nor will we try to guess what this will mean for Russia. In a situation like this, your Line editors would normally simply confess that we don’t have the deep knowledge of Russian domestic politics to turn ourselves into credible instant-experts on this. We’d seek out someone with that knowledge. We could interview them, solicit a column from them, or even — as we’ve done in the past — allow someone with deep expertise but who isn’t permitted to speak on the record in public to provide a blurb for one of these dispatches, to run under our shared byline. But in this case, we had to reject all those options, because at least for right now, all the experts seem as baffled as we are. No one seems to understand what the hell just happened in Russia.
We can say with at least reasonable confidence that if you happen to be named Vladimir Putin, it isn’t good. When Prigozhin announced that he was ending his mutiny and began withdrawing his forces from Rostov, the locals cheered them like some kind of conquering heroes. That’s gotta be on Putin’s mind. Also on his mind: the apparent, ahem, reluctance of much of his military and domestic security force to rally to his side during the crisis. This has wounded Putin. Time will tell how badly. Time will also tell how many other people in Russia today have carefully watched recent events, have adjusted their understanding of the facts on the ground there, and are now pondering a variety of intriguing options accordingly.
And the last thing time will tell is what Putin feels he must now do to assert his authority, such as it is. We must recall that whatever Putin’s domestic troubles, he has problems on the battlefield, too. While we haven’t yet seen major breakthroughs by Ukrainian forces, they are not yet fully committed, and their counteroffensive does seem to be making gradual progress in multiple sectors. Events of recent days can only hurt Russia’s combat performance and morale.
We wish we could offer you all a more firm and decisive statement to wrap all this up. But the best we can honestly promise you is that we’ll keep pondering this, trying to figure out what the hell happened, and we’ll certainly be watching this. It’s been a strange war. And we suspect it might get stranger still before it finally ends.
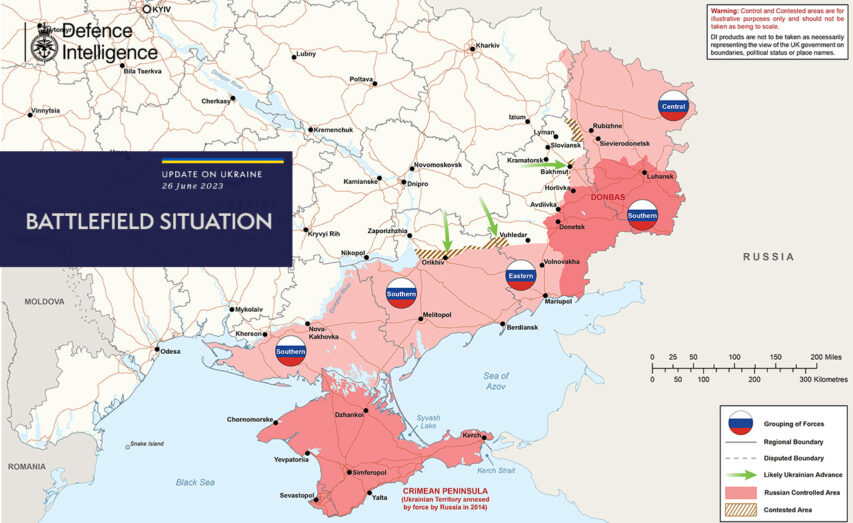
The most recent Defence Intelligence update map from the British Ministry of Defence shows what is thought to be a reasonably accurate representation of the battlefront in eastern Ukraine:
June 26, 2023
DShK-38: The Soviet Monster .50 Cal HMG
Forgotten Weapons
Published 10 Mar 2023In 1925 the USSR began a program to develop a heavy machine gun for antiaircraft use. After some initial experimentation with a converted Dreyse machine gun, they brought in Degtyarev to scale up his recently-adopted light machine gun to the task. Degtyarev’s first design was ready in 1930, and underwent testing until 1933. It was designated the DK, and used a 30-round drum magazine. This contributed to an unacceptably low rate of fire (~360 rpm), and the feed system was replaced by an ingenious development of Georgiy Shpagin to use belts instead.
Fitted with the Shpagin feed system, the DShK finished field testing in 1939 and was adopted as the model 1938. Production was slow, and the guns were not used on anything like the scale of American M2 use during World War Two. A total of about 9000 were in use at the end of the war, although the subsequent update to the DshKM (aka DShK 38/46) pattern would see it fitted to many armored vehicles, and total production eventually topped one million.
This example is a very early production 1939 example, most likely a Finnish capture piece from the Winter War or Continuation War.
(more…)
June 25, 2023
The Greatest Pincer Movement in Military History – WW2 – Week 252 – June 24, 1944
World War Two
Published 24 Jun 2023The Red Army surges forward in Operation Bagration, a mighty new offensive to destroy German Army Group Centre. Fighting continues in Normandy, Italy, and Finland. The United States Navy tears the heart out of the Imperial Japanese Navy in the Philippine Sea even as the Imperial Japanese Army has success in China. The British and Indian armies lift the siege of Kohima.
(more…)
June 23, 2023
June 22, 2023
QotD: Nuclear non-proliferation and the Russo-Ukraine war
The failure of the earlier League of Nations was crucial to preparing the way for the Second World War. Today, we see none of this, with most participants — excepting North Korea and Iran — still playing by the rules. This is where we return to Nevil Shute. Twice, using his technical expertise, Shute attempted to predict future war in a novel, and twice he got it wrong. With On the Beach, the author wrote of a 37-day war that “had flared all around the northern hemisphere”. Albania had dropped a “cobalt bomb” on Naples, which escalated into wider conflicts and eventually a Russo-Chinese exchange.
As one of Shute’s characters, a scientist, explained, “The trouble is, the damn things got too cheap. The original uranium bomb cost about fifty thousand quid towards the end. Every little pipsqueak country like Albania had a stockpile of them, and every little country that had that, thought it could defeat the major countries in a surprise attack”. Significantly, Shute’s future war, set in 1963, wasn’t triggered by the usual NATO-Warsaw Pact arsenals of nuclear weapons, but the proliferation of them elsewhere. Then, as now, it is not Russian or Chinese aggression that should worry those with nightmares of nuclear cataclysm, but that of other countries. Thanks to the NPT, IAEA and the UN, these possibilities are contained. Today, the world’s weapons of mass destruction stand at one tenth of their number during the Cold War.
Indeed, the very origins of the current Ukraine crisis illustrate how the international order has managed to contain potential proliferation. When the Soviet Union disintegrated in 1991, Ukraine possessed the world’s third largest nuclear arsenal, greater than those of Britain, France and China combined. Kyiv soon realised it couldn’t afford to maintain the warheads and remain a credible nuclear military power. A solution was found, whereby the weapons would be destroyed, but only in exchange for security assurances that the United States and Russia would respect Ukraine’s independence, sovereignty and territorial integrity.
What Ukraine signed on 5 December 1994 was the Budapest Memorandum of Security Assurances, in which Bill Clinton for the United States, Boris Yeltsin for Russia and John Major for Great Britain promised to protect Ukraine and its territorial integrity in recognition of Kyiv surrendering the protection of its nuclear arsenal. There was no mention of military guarantees, which Ukraine assumed were implied. Additionally, Kyiv promised to adhere to the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
After the annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014, the G7 nations complained that Russia had breached the Budapest Memorandum. Vladimir Putin replied evasively that since, in his view, a new regime had seized power from Ukraine’s previously pro-Moscow premier Viktor Yanukovych, “Russia has not signed any obligatory documents with this new state”. Since then, Russia has lied and prevaricated over its betrayal of Budapest. In 2016, Sergey Lavrov went so far as to claim, “Russia never violated Budapest memorandum. It contained only one obligation, not to attack Ukraine with nukes” — a gross distortion of the Memorandum’s many obligations.
However, the West responded in 2014 only with mild economic sanctions. Arguably, the apathy of the anti-interventionist Barack Obama and David Cameron, influenced by a London awash with Russian money, emboldened Vladimir Putin. Few experts disagree that had the West responded in 2014 as they did in 2022, Russia’s expansionist ambitions into Ukraine would have ended long ago. Yet, there is plenty of room for optimism. The Russo-Ukraine conflict has not spread because of the international order and its treaties. Apart from North Korea and Iran, neither of whom have quite perfected their devilish devices, nuclear proliferation of third parties has been held in check.
The Kremlin shows no sign of taking steps to escalate to a nuclear level. It is not in its interests, or those of its allies, to do so. None of the 32 nations who recently abstained from condemning Russia in the 24 February UN vote would welcome Vladimir Putin and his cronies flinging nukes around. The qualified support of major powers like China, India and Pakistan is attached to the cheap oil and arms procurements they have negotiated with Moscow. Any hint of Tsar Vladimir “going nuclear” would see their abstentions morph into support for the West. Putin, for all his rhetoric, cannot afford to go it alone with just the six who voted with him at the UN. In military terms, they offer nothing.
The world’s various international arms treaties provide plenty of optimism that this will remain a regional war. So far, Putin’s threats have melted away as the morning mist. The scenario he implies, akin that in On the Beach and other nuclear-war-scare novels and films, is so unlikely as to be discounted. They and all the rest of the post-apocalyptic genre are written as nail-biting entertainment, not history or current affairs.
Peter Caddick-Adams, “Putin, Shute and nukes”, The Critic, 2023-03-09.
June 18, 2023
Titanic Clash Looms In Pacific – WW2 – Week 251 – June 17, 1944
World War Two
Published 17 Jun 2023Japanese and American navies are heading for a showdown in the Philippine Sea, even as American forces land on Saipan in the Marianas in force. The Japanese have Changsha under siege in China, the Allies advance in both Normandy and Italy, the Soviets advance in Finland, and the massive Soviet summer operation is coming together and will begin in a matter of days.
(more…)
June 13, 2023
QotD: The purge of the Socialist Revolutionaries
Ideological revolutions follow a predictable pattern. At some point, you see what the Bolsheviks called “the Revolt of the Left SR’s.” “SR” stands for “socialist revolutionaries”, so their “left” was, of course, radical by all but Bolshevik standards. Nonetheless, they actually meant it when they said they were for “soviet power”, the “soviets” in this case being “assemblies made up of actual workers, not limpwristed eggheads like Lenin whose fathers were minor nobility”.
As Solzhenitsyn explained it, in the early days of the Bolshevik revolution, these SRs were part of a coalition government with the Bolsheviks. As such, they had to be given a certain amount of jobs in the ministries, including the justice ministry. They actually believed that stuff about The Workers, so they weren’t ready to send people to Siberia for twenty, thirty, forty years like Lenin demanded. They broke with Lenin (over other issues as well, obviously), the Bolsheviks crushed them, and once the Bolsheviks had power over all the ministries, there’s your gulag archipelago. Same as it ever was.
The Nazis had their “Left SR’s”, too. These were the Strasserites, led by brothers Otto and Gregor, the guys who put the “Socialist” in “National Socialism”. The Night of the Long Knives was a purge against both “left” and “right” — though Röhm and his butt boys get all the press, one of the Strasser brothers got his, too. That’s German efficiency for you!
And then there was the original Terror, in France, and even before that we had ours, too — the Whiskey Rebellion and Shays’ Rebellion aren’t usually taught as ideological (they’re usually not taught at all, of course), but they were. We’ve had two revolutions (before this week), in fact, and in both cases you had those pesky “we really believe this shit!” types causing all kinds of problems for the revolutionary government — see, for example, those state governors who made Jeff’s life hell in Richmond, objecting to the nationalization of their state militias on the grounds that the Confederacy is actually, you know, a confederacy, and that drafts and war production boards and taxes in kind and all the rest are exactly the kind of tyranny you’d expect from Abe’s gang in Washington …
Severian, “Speaking of Purges…”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-01-08.
June 11, 2023
The Invasion of Normandy begins! – WW2 – Week 250 – June 10, 1944
World War Two
Published 10 Jun 2023The Allies’ gigantic amphibious invasion of France begins and by the end of the week they’ve carved out a decent-sized beachhead. Meanwhile in Italy the Allied advance takes Rome. The Soviets are launching new attacks of their own — now against the Finns, and the Japanese at Kohima … have just plain had enough.
(more…)
June 2, 2023
Germany Adopts the PPSh in 9mm: the MP-41(r)
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 Feb 2023During World War Two, both German and Russian soldiers often thought that the other side’s weapons were better than their own. In particular, both sides often preferred their opponents’ SMGs. In late 1941, a group of German officers formally requested that Germany simply copy and produce the PPSh-41. This led to the HWA formally studying the question of PPSh-41 vs MP-40 … and they found that the German gun was better, but the Russian magazine was better.
Naturally, as a result of this finding, the German military chose to convert captured Russian PPSh-41s to use MP-40 magazines. The conversion used standard MP40 magazines, and required magazine well adapters and new 9mm barrels. Some 10,000 such conversions were made in total. Some used cast magwell adapters and some were stamped, and the barrels were made from standard MP40 barrels turned down to fit PPSh trunnions.
The standard 7.62mm PPSh-41 in German service was designated MP-717(r), while the ones changed to 9x19mm like this were designated MP-41(r). Many thanks to Limex for giving me access to film this one for you!
(more…)
May 30, 2023
Ban all the words!
Chris Bray reflects on the historical context of literature bans:
Before the Civil War, Southern states banned abolitionist literature. That ban meant that postmasters (illegally!) searched the mail, seized anti-slavery tracts, and burned them. And it meant that people caught with abolitionist pamphlets faced the likelihood of arrest. The District of Columbia considered a ban, then didn’t pass the thing, but Reuben Crandall was still arrested and tried for seditious libel in 1833 when he was caught with abolitionist literature. He was acquitted, then died of illness from a brutal pre-trial detention. Seizure, destruction, arrest: abolitionist literature was banned.
The Soviet writer Yevgeny Zamyatin wrote a 1924 novel, We, depicting a world in which an all-powerful government minutely controlled every aspect of life for an enervated population, finding as an endpoint for their ideological project a surgery that destroyed the centers of the brain that allowed ordinary people to have will and imagination. The Soviet government banned Zamyatin’s work: They seized and destroyed all known copies, told editors and publishers the author was no longer to allowed to publish, and sent Zamyatin into exile, where he died without ever seeing his own country again. Seizure, destruction, exile: Yevgeny Zamyatin’s work was banned.
During World War I, the federal government banned literature that discouraged military service, including tracts that criticized conscription. Subsequently, “socialists Charles Schenck and Elizabeth Baer distributed leaflets declaring that the draft violated the Thirteenth Amendment prohibition against involuntary servitude”. They were arrested, convicted, and imprisoned. The Supreme Court upheld the conviction. Anti-conscription literature was banned: It was seized and destroyed, and people caught distributing it were sent to prison.
In 2023, the tedious midwit poet Amanda Gorman posted on Twitter that she was “gutted” — the standard emotion for tedious midwits — to discover that one of her poems had been “banned” by a school in Florida. The news media raced to proclaim that Florida schools are banning books, the leading edge of the Ron DeSantis fascist wave.
As others have already said, Gorman’s boring poem was moved from an elementary school library shelf to a middle school library shelf, without leaving the library
May 28, 2023
Breakout from Anzio! – WW2 – Week 248 – May 27, 1944
World War Two
Published 27 May 2023After four months, the Allies breakout from their bridgehead at Anzio and meet with the advancing troops heading north after the fall of Monte Cassino last week. The Japanese begin phase two of their big operation in China, and both the Soviets and the Western Allies continue making plans for their massive June offensives to squeeze the Axis from both sides of Europe.
(more…)
May 21, 2023
The Fall of Monte Cassino – WW2 – Week 247 – May 20, 1944
World War Two
Published 20 May 2023In Italy, the Allies finally overcome Monte Cassino and break through the Gustav Line; in Burma Merrill’s Marauders surprise the Japanese and take Myitkyina Airfield; in China, it’s the Japanese who are playing offense, as Operation Ichi Go and the siege of Luoyang continue. That’s the field action, but there’s big planning behind the scenes for major June offensives going on by both the Western Allies and the Soviets.
(more…)
May 14, 2023
Victory at Sevastopol! – WW2 – Week 246 – May 13, 1944
World War Two
Published 13 May 2023The Soviets push the Axis out of the Crimea this week once and for all. In Italy, the Allies launch a major offensive, and the French make a breakthrough there by week’s end. In China, the Japanese are aiming at Luoyang, but in India at Kohima they’re slowly being pushed back.
(more…)