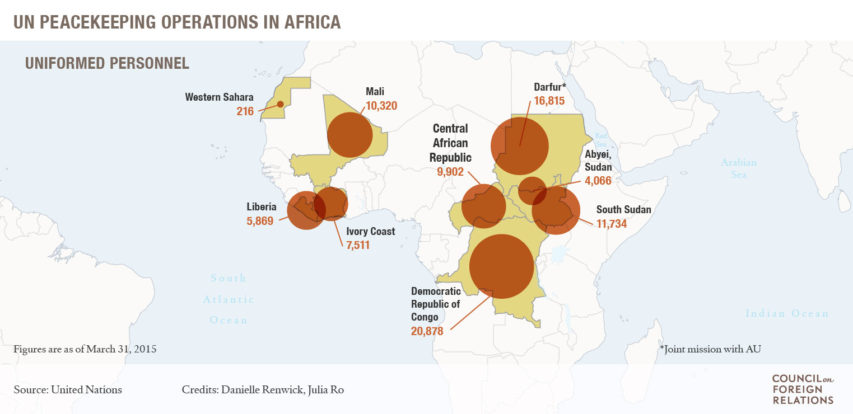
Ted Campbell explains why it would not be a good thing for Canada to send a peacekeeping force to Mali (or to anywhere else in Africa right now):
The Globe and Mail, in an editorial, asks the key question:
“Is there a Canadian national interest in sending troops to Mali?”I suggest that unless and until the Trudeau government can say, “yes,” and can explain that vital interest to most Canadians that sending Canadian soldiers off to Africa on a United Nations operation is problematical. “The Canadian Armed Forces shed blood and lost lives during the decade-long mission in Afghanistan,” the Globe‘s editorial says, “Sending them into a similar campaign in Mali may further Liberal political interests. But does it serve the national interest?“
Now, I believe that I can make a sensible, mid to long term case for Canada to be “engaged,” politically, economically and militarily in Africa:
- Africa will be, after Asia, the “next big deal” for economic growth, trade and, therefore, profits;
- Canada will want to be involved as a trusted friend when Africa is ready to “blossom” and have an economic “boom” of its own; and
- Despite Chinese and French incursions there are still plenty of opportunities for Canadian engagement.
In other words, we have interests in Africa; even, perhaps, in the mid to long term, we have vital interests, at that.
I cannot make a case for getting involved in any United Nations mission in Africa. I cannot, even with rose coloured glasses, see one single United Nations mission in Africa that is working, much less succeeding and doing some good.
I’m not opposed to the UN. In fact, I’m one of those who says that if it didn’t exist we’d have to invent it. The current UN is better than the old League of Nations, and some UN agencies, like the International Telecommunications Union, for example, do good work for the whole world and are, alone, worth our entire UN contribution, but we ask too much of the UN and it is neither well enough designed or led or organized or funded to do even a small percentage of what is asked of it. Peacekeeping is one of the things that the UN cannot do well in the 21st century. Peacekeeping was fine when it was ‘invented’ (circa 1948, by Ralph Bunche, and American and Brian Urquhart, a Brit, not by Lester Pearson in 1957, no matter what your ill-educated professors may have told you) but it could not be adapted to situations in which there is:
- No peace to be kept;
- A plethora of non-state actors who are not amenable to UN sanctions.
A few days ago I wrote about the risks involved in sending soldiers to Africa. The Globe and Mail‘s editorial just adds some more fuel to that fire.