We want to start with asking what the distinction is between soldiers and warriors. It is a tricky question and even the U.S. Army sometimes gets it badly wrong ([author Steven] Pressfield, I should note, draws a distinction which isn’t entirely wrong but is so wrapped up with his dodgy effort to use discredited psychology that I think it is best to start from scratch). We have a sense that while both of these words mean “combatant”, that they are not quite equivalent.
[…]
But why? The etymologies of the words can actually help push us a bit in the right direction. Warrior has a fairly obvious etymology, being related to war (itself a derivative of French guerre); as guerre becomes war, so Old French guerreieor became Middle English werreior and because that is obnoxious to say, modern English “warrior” (which is why it is warrior and not “warrer” as we might expect if it was regularly constructed). By contrast, soldier comes – it has a tortured journey which I am simplifying – from the sold/sould French root meaning “pay” which in turn comes from Latin solidus, a standard Late Roman coin. So there is clearly something about pay, or the lack of pay involved in this distinction, but clearly it isn’t just pay or the word mercenary would suit just as well.
So here is the difference: a warrior is an individual who wars, because it is their foundational vocation, an irremovable part of their identity and social position, pursued for those private ends (status, wealth, place in society). So the core of what it is to be a warrior is that it is an element of personal identity and also fundamentally individualistic (in motivation, to be clear, not in fighting style – many warriors fought with collective tactics, although I think it fair to say that operation in units is much more central to soldiering than the role of a warrior, who may well fight alone). A warrior remains a warrior when the war ends. A warrior remains a warrior whether fighting alone or for themselves.
By contrast, a soldier is an individual who soldiers (notably a different verb, which includes a sense of drudgery in war-related jobs that aren’t warring per se) as a job which they may one day leave behind, under the authority of and pursued for a larger community which directs their actions, typically through a system of regular discipline. So the core of what it is to be a soldier is that it is a not-necessarily-permanent employment and fundamentally about being both in and in service to a group. A soldier, when the war or their term of service ends, becomes a civilian (something a warrior generally does not do!). A soldier without a community stops being a soldier and starts being a mercenary.
Incidentally, this distinction is not unique to English. Speaking of the two languages I have the most experience in, both Greek and Latin have this distinction. Greek has machetes (μαχητής, lit: “battler”, a mache being a battle) and polemistes (πολεμιστής, lit: “warrior”, a polemos being a war); both are more common in poetry than prose, often used to describe mythical heroes. Interestingly the word for an individual that fights out of battle order (when there is a battle order) is a promachos (πρόμαχος, lit: “fore-fighter”), a frequent word in Homer. But the standard Greek soldier wasn’t generally called any of these things, he was either a hoplite (ὁπλίτης, “full-equipped man”, named after his equipment) or more generally a stratiotes (στρατιώτης, lit: “army-man” but properly “soldier”). That general word, stratiotes is striking, but its root is stratos (στρατός, “army”); a stratiotes, a soldier, for the ancient Greeks was defined by his membership in that larger unit, the army. One could be a machetes or a polemistes alone, but only a stratiotes in an army (stratos), commanded, presumably, by a general (strategos) in service to a community.
Latin has the same division, with similar shades of meaning. Latin has bellator (“warrior”) from bellum (“war”), but Roman soldiers are not generally bellatores (except in a poetic sense and even then only rarely), even when they are actively waging war. Instead, the soldiers of Rome are milites (sing. miles). The word is related to the Latin mille (“thousand”) from the root “mil-” which indicates a collection or combination of things. Milites are thus – like stratiotes, men put together, defined by their collective action for the community (strikingly, groups acting for individual aims in Latin are not milites but latrones, bandits – a word Roman authors also use very freely for enemy irregular fighters, much like the pejorative use of “terrorist” and “insurgent” today) Likewise, the word for groups of armed private citizens unauthorized by the state is not “militia”, but “gang”. The repeated misuse by journalists of “militia” which ought only refer to citizens-in-arms under recognized authority, drives me to madness).
(I actually think these Greek and Latin words are important for understanding the modern use of “warrior” and “soldier” even though they don’t give us either. Post-industrial militaries – of the sort most countries have – are patterned on the modern European military model, which in turn has its foundations in the Early Modern period which in turn (again) was heavily influenced by how thinkers of that period understood Greek and Roman antiquity (which was a core part of their education; this is not to say they were always good at understanding classical antiquity, mind). Consequently, the Greek and Roman understanding of the distinction probably has significant influence on our understanding, though I also suspect that we’d find distinctions in many languages along much the same lines.)
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: The Universal Warrior, Part I: Soldiers, Warriors, and …”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-01-29.
October 17, 2024
QotD: Soldiers and warriors
October 16, 2024
Many of the posh pro-trans activists are objectively anti-gay
It’s starting to be a true wedge issue in the LGBT community, as the logic of the pro-trans activists leads quite directly to the suppression of the gay and lesbian parts of that community:
It was hardly a plague of locusts, but it was disruptive nonetheless. During the annual LGB Alliance conference at the Queen Elizabeth II centre in Westminster on Friday afternoon, teenage activists unleashed thousands of crickets into the auditorium. The inconvenience was only temporary. The crowd simply relocated to another room and the event went on as before.
As those responsible were apprehended, many people were struck by just how young and posh they were. By this point, it should surprise precisely no-one that anti-gay activism in its current form is a predominately bourgeois pursuit. The symbolism of the crickets was, of course, deliberate. It was an attempt to dehumanise those in attendance, to suggest that they were akin to parasites, vermin, spreaders of disease, a common trope of those who seek to demonise minorities.
The perpetrators were children, and so it would be unwise to speculate too much on their motives. It is likely they were being manipulated by the group that has claimed responsibility, calling itself “Trans Kids Deserve Better”. As Bev Jackson, co-founder of LGB Alliance said on my show last night:
Trans kids do deserve better. They deserve better than to be told lies that that they might have been born in the wrong body. They deserve better than to be told that these hormones and surgeries that they are clambering for will somehow solve all their problems. Many are on the autism spectrum. Many are struggling with their sexual orientation. We know that. They deserve better than to be told that we hate them. And they deserve better than to be labelled trans when they’re going through all the turbulence of adolescence, when your feelings about yourself are in constant flux.
Irrespective of the intentions of the teenagers involved, this was anti-gay activism. To attack a group of lesbian, gay and bisexual people who have assembled to discuss the ongoing threats to their civil rights could hardly be defined in any other way. Likewise, to refer to groups such as LGB Alliance as “anti-trans”, “transphobic” or “hateful” – as activist media outlets such as the Metro and the Guardian have been known to do — is also an anti-gay strategy. In order to address a problem, one needs to label it accurately.
Gender identity ideologues are, by definition, anti-gay. They are campaigning to force their pseudo-religious belief-system onto the rest of society, one that claims that same-sex attraction is a myth, and that a mysterious spiritual sense of “gender” is the defining feature of homosexuality. Even if they have convinced themselves that they are “pro-trans” and “compassionate” and “progressive”, the implementation of their demands would result directly in the demolition of gay rights. And so “anti-gay activism” is not only an accurate description, it also cuts to the heart of what is at stake.
The Korean War 017 – The Americans invade North Korea! – October 15, 1950
The Korean War by Indy Neidell
Published 15 Oct 2024The American forces — and British Commonwealth ones — join the South Koreans in crossing the 38th parallel and invading North Korea this week, though large scale resistance by the North Korean forces has to a large extent dissolved. This means that the planned Allied amphibious operation against the port of Wonsan — already delayed by minefields — is no longer really useful, since the South Koreans take the port already this week. And even as American brass meets on Wake Island and discounts the thought of Communist Chinese troops helping the North Koreans, Mao Zedong is preparing for an invasion of his own.
(more…)
The last few weeks of the US Presidential race moves only a tiny fraction of voters’ opinions
Niccolo Soldo explains why he’s not been writing very much about the last phase of the US Presidential election:

“Polling Place Vote Here” by Scott Beale is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 .
95% of Americans who intend to vote already decided who they were going to vote for two years ago, no matter who would be running on the Dem ticket (Trump was always going to win the GOP nomination). It’s been all noise ever since, with the two assassination attempts the only real stories coming out of this election. Vice-Presidents don’t matter, unless you are Dick Cheney, so the amount of media attention given over to Vance and Walz is another sign of over-saturation.
This election was always going to be a referendum on what we call the “Deep State”, even though Trump is aligned with the Deep State on so many issues, China being the best example. I wager that future historians are going to have difficulty understanding why the powers-that-be were so stridently opposed to him beyond elements of his personality.
No matter who moves into the White House next year, 90% of what is happening in the USA will remain the same. Four years is a short time in US politics, and the American system is designed for compromise and hostage to gridlock via the balances and checks built into it. Biden’s foreign policy is a continuation of Trump’s, which was a continuation of Obama’s, which was a continuation of Dubya’s. Only certain touches were different, with Dubya’s being more unilateral in nature than Obama’s for example, as his administration sought to achieve the same goals via multilateralist approaches. I still don’t know why they fear Trump and any policy that he would pursue regarding Russia or NATO. To me, it’s nonsensical; Trump is a wheeler-dealer, not a revolutionary. In his first go at office he was more than happy to give the US Armed Forces anything that they wanted, for example.
This leaves immigration as the only big ticket issue where real change can come about. But I have to raise the question about how much can be done in four years if Trump enters the White House and has to deal with Congress, and deal with lawfare trying to halt any changes that he would seek regarding immigration. Does his team have a strategy in place that will allow them to hit the ground running right away? Is there a strategy to avoid legal challenges? How much can be done via executive actions?
Steve Bannon said something in either late 2015 or 2016 that has stuck with me ever since: that it would take 20 years of consecutive victories in order to reform the system. This means 20 years of wins at the highest level in order to be able to gut the federal bureaucracy/Deep State and make actual change possible. This makes perfect sense to me. I am aware of the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025, but is it doable?
I can only speak for myself when I say that fatigue with this election cycle set in months ago. I just want to see who wins because a Kamala win means business as usual, and a Trump win means that we will see if he has actually learned anything from his time in office.
If it were up to me, the media coverage of the US Election cycle would last longer than those in the UK or France, as the USA is the world’s most important country. I think that it should last no longer than four months at the maximum. This, of course, is pie-in-the-sky from me, as there are too many interests involved, and too much money to be had in covering this long, drawn-out torture.
Roman Historian Rates 10 Ancient Rome Battles In Movies And TV | How Real Is It? | Insider
Insider
Published Jun 18, 2024Historian Michael Taylor rates depictions of ancient Rome in Gladiator, Spartacus, and Indiana Jones and the Dial of Destiny.
(more…)
QotD: Technical differences between ground-attack and air-defence missiles
Russians claim the missile that struck the Okhmatdyt Children’s Hospital in Kiev yesterday was an American-made air defense missile. It wasn’t; video footage clearly shows that it was a Russian KH-101.
To help everybody not get fooled again, I’m going to explain some basic differences between ground-attack and air-defense missiles, and why nobody should have been fooled by this propaganda for a second.
The top-line thing here is that ground attack missiles can be large and have heavy warheads, while air defense missiles have to be smaller and have lighter warheads.
Air defense missiles have to intercept a target traveling at high speed. They have to be as fast and agile as possible in order to do that; every gram of weight is a penalty. That means you’re going to make the warhead no heavier than you have to in order to kill a plane. And it doesn’t take much kaboom to kill a plane.
Even if we didn’t have footage of the missile and wreckage to examine, it would be obvious that the damage to that hospital wasn’t done by an air defense missile because there’s too much of it. You can’t get that much blast shock out of the smallish warheads they put in those things.
The weight penalty for a big warhead is much less in something like a KH-101. It’s not designed to be agile, it’s designed to get from point A to point B on a least-time course and then blow up real good.
You can use an air defense missile for ground attack with some hacking of the guidance software, but you can’t use a ground-attack missile for air defense; the physics are against you.
The problem with using an AD missile for ground attack is it it won’t give you much of a kaboom when it gets there. They’re just not very effective.
Nevertheless, the Russians have actually been doing this in Ukraine, throwing S-300s and S-400s at ground targets. Only because they were short on ground attack missiles to start with, and their capacity to manufacture them is limited by Western sanctions on the electronics they need.
So the next time the Russians try to deflect blame for one of their missile strikes on civilian cities by claiming the explosion was from a failed Ukrainian intercept, treat the assertion with the contempt it deserves. If whatever went boom actually was an air defense missile, it was almost certainly a repurposed Russian one.
Eric S. Raymond, X(the social media platform formerly known as Twitter, 2024-07-11.
October 15, 2024
Czech Sa vz. 26 SMG
Forgotten Weapons
Published Aug 10, 2015The Czech Samopal vz. 26 was one of a family of submachine guns (the vz 23-26) that pioneered the use of bolts telescoped out forward over the barrel, allowing guns to have much better ratios of barrel to receiver length than before. The guns actually have quite a few interesting mechanical details, although in my opinion they fail to make it a particularly desirable gun for actual shooting.
QotD: The Mandela Effect
Do you remember where you were when you heard that planes had struck the World Trade Center? That the Challenger shuttle had exploded? Or that Nelson Mandela had been released?
Your memories may be different from mine, but not as different as Fiona Broome’s. I remember watching the live TV footage of Nelson Mandela walking to freedom after 27 years in captivity, while Broome, an author and paranormal researcher, remembers Nelson Mandela dying in prison in the 1980s.
When Broome discovered that she was not the only person to remember an alternative version of events, she started a website about what she dubbed “the Mandela Effect”. On it, she collected shared memories that seemed to contradict the historical record. (The site is no longer online but, never fear, Broome has published a 15-volume anthology of these curious recollections.)
Mandela, of course, did not die in prison. On a recent trip to South Africa, I visited Robben Island, where he and many others were incarcerated in harsh conditions, to speak to former prisoners and former prison guards, and to wander around a city emblazoned with images of the smiling, genial, elderly statesman. How could it be that anyone remembers differently?
The truth is that our memories are less reliable than we tend to think. The cognitive psychologist Ulric Neisser vividly remembered where he was when he heard that the Japanese had launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7 1941. He was listening to a baseball game on the radio when the broadcast was interrupted by the breaking news, and he rushed upstairs to tell his mother. Only later did Neisser realise that his memory, no matter how vivid, must be wrong. There are no radio broadcasts of baseball in December.
On January 28 1986, the Challenger space shuttle exploded shortly after launch; a spectacular and highly memorable tragedy. The morning after, Neisser and his colleague Nicole Harsch asked a group of students to write down an account of how they learnt the news. A few years later, Neisser and Harsch went back to the same people and made the same requests. The memories were complete, vivid and, for a substantial minority of people, completely different from what they had written down a few hours after the event.
What’s stunning about these results is not that we forget. It’s that we remember, clearly, in detail and with great confidence, things that simply did not happen.
Tim Harford, “The detours on memory lane”, Tim Harford, 2024-06-20.
October 14, 2024
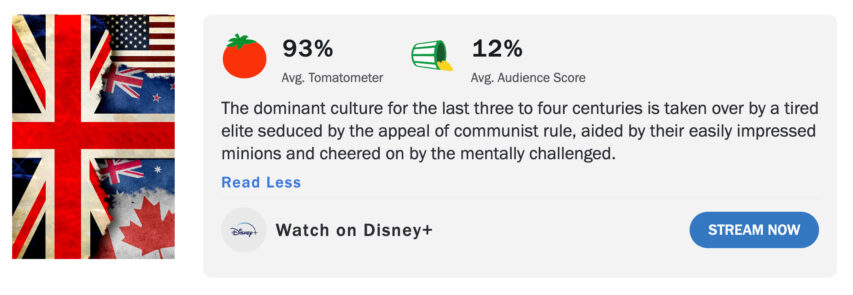
The reviews are in for this season of The West and it’s as bad as you think
Spaceman Spiff has been a longstanding fan of The West, but the current season is doing much more than giving him the sadz:
The current season of The West is a disappointing mishmash of bad writing, wooden acting and implausible plot lines.
Critics have known the show has been in decline for years although have been reluctant to say openly.
But with cancellation rumours growing it is difficult to see how it can survive. If the current season is any measure they simply don’t have the writers even if the producers hadn’t lost their minds.
The plot thickens
The West has always been known for its compelling plots. Epoch-defining inventions, new technologies and globe-spanning empires. Even grand moral crusades no one else would consider such as ending slavery or elevating women to equal status.
Just some of the storylines they said would never work and yet we were glued to our screens as they unfolded.
Unfortunately, more recent seasons have shown none of the flair of the past.
The latest drama is the threat of another plague. It is difficult to know how this got the go ahead so soon after the Covid storyline.
The original pandemic idea got off to a roaring start since it was then a novel idea. But as the drama unfolded the plot became increasingly contrived. The writers became carried away and eventually struggled to get out of the hole they had dug themselves.
It ended in absurdity with obvious conflicts between the original lockdown plot and the later mask and vaccine subplots.
It was almost as if different teams of writers were competing with each other instead of cooperating on the story arc, exactly the kind of mistake audiences are increasingly complaining about.
The latest version is a species-jumping virus and is already facing criticism for lazy writing and reheating ideas from last time. Audiences are unimpressed. Time will tell if they can pull it off again.
The second plot they seem to be exploring is even more implausible, war with China.
After the last few seasons mired in the Ukraine storyline it beggars belief the writers went in this direction.
There were rumours of production overruns and expensive reshoots as the Ukraine storyline dragged on. We will never know the full extent of their production woes but tough decisions were clearly made as well as a shakeup of the production team.
Critics had warned wars were rarely popular. People like the drama of course, but audiences quickly get bored. None of this stopped the producers and the writers dutifully did as asked.
Now it is China.
Many are saying this is just a sign the producers have been there too long. It is time for another clear out.
At least war is exciting. But after numerous attempts to sell immigration storylines they are trying it again despite its unpopularity.
Previous attempts to promote immigration plots failed to resonate with audiences although it has always been popular with a small, loud minority.
Most found it too farfetched, millions of young foreign men just wandering into Western nations as if no one would stop them. The critics had a field day.
But this season they are going with climate migration. People moving around because of the weather.
This is partly to shore up their failing climate plot. It was obvious several seasons ago this long running theme, a strong favourite with the showrunners, was no longer popular.
Rumours of a caucus revolt against Justin Trudeau
The polls are historically bad, but Justin Trudeau seems determined to hang on until he has to call an election which is reported to be generating panic among Liberal backbenchers. Any Liberal Party leader is tough to unseat, but especially Trudeau after the most recent changes to the party’s operating rules instituted after he became party leader.
Could the season of Thanksgiving see the fall of Justin Trudeau?
Unlikely, but there will be no Happy Thanksgiving for the prime minister as he contemplates rebellious Liberal MPs trying to engineer a palace coup.
Such news may not surprise Trudeau, but the fact that it is now public is a starting gun. It is at times such as these that Sherlock Holmes tells trusty sidekick Watson, “The game’s afoot”.
As Trudeau returns from a trip to Asia, he is likely to hunker down with his faithful entourage to plot strategy while plotting of another kind will be on the minds of the Gang of 20 (the approximate number of Liberal MPs said to have signed a document in support of replacing the prime minister before the next election.)
The Toronto Star first reported on Friday that “anxious Liberals” were worried about the state of the party under Trudeau. People were saying on the doorstep that “your guy’s gotta go,” while one party source said two dozen sitting MPs were deciding whether to run again at the next election.
Fast exits and furry rodents are all associated with sinking ships.
The Star quoted Wayne Long, the only serving Liberal so far to publicly call for Trudeau to quit as leader, saying, “The status quo is leading us to obliteration”.
Party leaders never want to hear the word obliteration when it refers to their own electoral fortunes and certainly not when it comes from the mouth of one of their own MPs.
But Trudeau probably isn’t even listening to the shrill chorus of the caucus. Why now, after nine years, should he start listening to his members?
Meanwhile, the CBC reported that Liberal MPs were meeting in rooms across Parliament Hill to sign a document that pledged them to call on Trudeau to resign. They were signing their own names and “in ink”, said CBC’s David Cochrane, making it sound like a Faustian bargain rather than a parliamentary coup.
Perhaps it is?
Quality v Quantity? | Panzer IV v M4 Sherman | Tank V Tank – Normandy, 1944
The Tank Museum
Published Jun 14, 2024Normandy, 1944: in the dense bocage countryside, two tanks, the US-built M4 Sherman and the German PzKpfw IV go head-to-head in the fighting around the Allied bridgehead. Both are similar in capabilities but which will prevail?
In this film, Chris Copson compares the armour protection, firepower and mobility of the two designs, and we recount the events of a specific engagement fought at Mouen near Caen on 28th June, 1944.
00:00 | Intro
01:45 | Meet the Tanks
03:08 | Armour
07:37 | Firepower
12:19 | Mobility & Operation
13:29 | Tank Crews
16:37 | Summary
17:15 | Mouen, Normandy, 28 June 1944
23:10 | ConclusionThis video features archive footage courtesy of British Pathé.
#tankmuseum
QotD: Americans and their cars
Given that, for “Americans”, cars are a pretty good proxy for personality. What you drive, and more importantly how you drive, shows everyone else on the road the state of your soul. There are entire models of car — Toyota Priuses (Prii?), Subaru Outbacks — that are only driven by SJWs. Karen drives a late-model SUV, almost universally, but if she’s forced to drive a minivan or, God help us all, a standard four-door, she’ll festoon it with a thousand of those “passive-aggressive” (or whatever we end up calling them) bumper stickers: My broomstick is in the shop. Stick-figure families in rainbow colors. Hate is not a family value (often juxtaposed, with brain-breaking obtuseness, next to one wishing that various “conservatives” would die in fires). And so on.
Severian, “Cars, Bikes, Motorcycles”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-07-25.
October 13, 2024
The Soviet Union’s surplus of math nerds
The most recent review from Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf is John Psmith’s musings on Math from Three to Seven: The Story of a Mathematical Circle for Preschoolers by Alexander Zvonkin, and he starts by talking about something the Soviets did better than the west:
To me, one of the greatest historical puzzles is why the Cold War was even a contest. Consider it a mirror image of the Needham Question: Joseph Needham famously wondered why it was that, despite having a vastly larger population and GDP, Imperial China nevertheless lost out scientifically to the West. (I examined this question at some length in this review.) Well, with the Soviets it all went in the opposite direction: they had a smaller population, a worse starting industrial base, a lower GDP, and a vastly less efficient economic system. How, then, did they maintain military and technological parity1 with the United States for so long?
The puzzle was partly solved for me, but partly deepened, when those of us who grew up in the ‘90s and ‘00s encountered the vast wave of former Soviet émigrés that washed up in the United States after the fall of communism. Anybody who played competitive chess back then, or who participated in math competitions, knows what I’m talking about: the sinking feeling you got upon seeing that your opponent had a Russian name. These days, the same scenes are dominated by Chinese and Indian kids. But China and India have large populations — the Russians were punching way above their weight, demographically speaking. Today, those same Russians are all over Wall Street and Silicon Valley and Ivy League math departments, still overrepresented in technical fields. What explains it? Are Russians just naturally better at math and physics?
When I related these questions to an Ashkenazi-supremacist friend of mine, he immediately suggested that “maybe it’s because they’re all Jewish”. (I’ve noticed that the most philosemitic people and the most antisemitic people sometimes have curiously similar models of the world, they just disagree on whether it’s a good thing.) My friend’s question wasn’t crazy, since there are definitely times when asking “were they all Jewish?” yields an affirmative answer. But in this case I had to disappoint him with the knowledge that many of these Russian math and chess superstars were gentiles.2 What’s more, by the ’60s and ’70s the Soviets had an entire discriminatory apparatus dedicated to keeping Jews out of the scientific establishment, so it would be impressive indeed if they were the foundation of its success.
Another possible explanation actually hinges on the relative poverty of the Soviet Union. Assume there are a lot of people out there with natural mathematical talent, but who given their druthers would major in underwater basket-weaving instead. The United States, because it’s so wealthy, can afford to “waste” a huge proportion of our talented population on humanities, arts, and other stuff that doesn’t involve you sitting in the school library until 3am. In other words, not going into a technical field is a form of luxury, which America can afford to consume. The Soviets, rather like the Chinese today, were forced by their underdog status to allocate human capital more efficiently (and had the authoritarian means to do so by force if necessary). This theory is related to the curious fact that, on average, the more feminist your society, the fewer women there are in math and science — which makes total sense if you assume that on average women are good at math but uninterested in it.
The thing is, the émigré superstars I encountered didn’t seem at all grudging or resentful about their studies. If anything it was the opposite. I’ve previously complained about how much I hate Russian mathematician Edward Frenkel’s3 book, but one thing it gets across well is just how important passion is to being a great mathematician, and passion was the thing the émigrés seemed to have a surfeit of. In college, the joke was that seminars by American professors would last an hour, whereas seminars by Russian professors would turn into boisterous debates lasting all night. People have been writing for centuries about Russians having a tendency towards “maximalism” — whether aesthetic or ideological or anything else. Maybe a culture-wide commitment to not doing anything by half-measures explains it?
1. There are scientific sub-disciplines where even at the end the Soviets had a clear lead, including several fields of math. Even crazier, there are sub-disciplines where we have not yet gotten back to where the Soviets were (for instance phage therapy).
2. Undeterred, my friend pointed out that many modern Russian gentiles have significant Jewish ancestry. The Soviets actively promoted mixed marriages, to the point where in some cities the average urban gentile Russian is as much as 25% Jewish. I still don’t think this explains Soviet scientific prowess, but it’s an interesting data point because the most highly urbanized areas are the ones where most of the mathematicians (and most of the émigrés) came from.
3. Before you ask, I looked it up and Frenkel is half Jewish, half gentile. I will leave it to you whether you count that as evidence for or against my friend’s theory.
Occupation of Germany, Plunder and Enslavement?
World War Two
Published 12 Oct 2024The Allies’ occupation of Germany was marked by competing visions for its future, ranging from France’s focus on security to the Soviet push for reparations. This episode dives into the complex negotiations that determined Germany’s borders, industrial disarmament, and economic management, all of which would shape Europe’s post-war order and fuel the East-West divide.
(more…)
Bismarck, Moltke, and the Kaiser’s General Staff
From Bruce Gudmundsson’s weekly Milstack recommendations, here’s part of an essay on Kaiser Wilhelm and some of the important men in his government in the lead-up to the First World War:
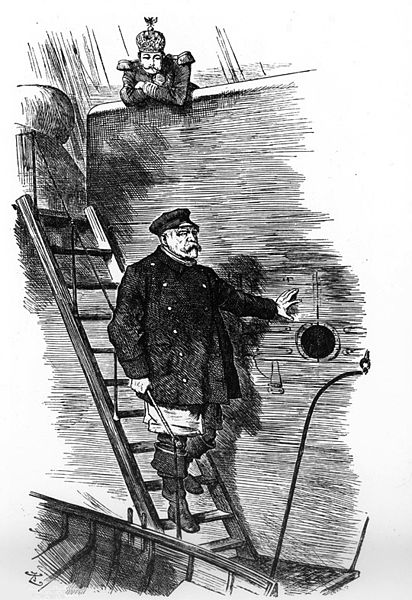

“Dropping the Pilot”. Caricature by Sir John Tenniel (1820-1914), first published in the British magazine Punch, March 1890. Showing German Emperor Wilhelm II and the departing Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
By the 1870s, Germany was the dominant land power in Europe. It had defeated the preeminent powers on the continent and seemed poised for an era of dominance not seen since Napoleon. However, how quickly Germany’s power was checked and ultimately fell is a cautionary tale about the limits and consequences of the predominance of the military profession. Victories in the war had propelled the Prussian Officer Corps to the status of “demigods” that now held “unquestioned authority and legitimacy” in German politics and society.1 But this status meant they had carte blanche over war planning and became increasingly influential in politics. This produced a civil-military relationship in which, “leaders subordinated political ends to military ends; considerations of war dominated considerations of politics”.2 The German General staff was rapidly departing from Clausewitz’s teachings regarding the primacy of policy.
By the 1880s, Otto von Bismarck and Helmuth von Moltke, the key architects of German unification both politically and militarily, were nearing the end of their distinguished careers. Now, a younger generation of German nationalists and military officers were chomping at the bit to further expand Germany’s power and formed the engine of what some have called, “a political doomsday machine”.3 The militarists believed preemptive war was the uniform solution to the rising power of Germany’s neighbors. Likewise, success in the wars of unification had led nationalists to dream of a greater Germany “from Berlin to Baghdad”.4 Even in his late career, Bismarck had the experience and gravitas to stymie attempts to initiate a “preventative” war. For instance, in 1887, the senior military leadership cooked up a scheme to convince the Kaiser to declare war on Russia on a whim; they also encouraged Austria-Hungary to do the same. Bismarck stopped it before it became a crisis. But it was a bad omen and showed how the military leadership was increasingly out of control.
Bismarck and Moltke had their issues, but they eventually built a strong relationship, leading the Chief of the General Staff to discuss prospective war plans with the Chancellor, something that had not occurred regularly before and a sign of good civil-military relations. Moltke continued to hold his role until 1888 when he retired. His thinking in his late career had evolved beyond the axiomatic focus on total victory.5 The Battle of Sedan was as complete a victory as one could imagine, yet it did not end the Franco-Prussian War. The ensuing experience of the Volkskrieg (“People’s War”) which encompassed fighting a tough insurgency in France had disillusioned him with the idea of a short war. In one of his final speeches in the Reichstag in 1890, he stated of the next war that,
If this war breaks out, then its duration and its end will be unforeseeable. The greatest powers of Europe, armed as never before, will be going into battle with each other; not one of them can be crushed so completely in one or two campaigns that it will admit defeat, be compelled to conclude peace under hard terms, and will not come back, even if it is a year later, to renew the struggle. Gentlemen, it may be a war of seven years or thirty years’ duration — and woe to him who sets Europe alight, who [first] puts the fuse to the powder keg!6
Moltke now conceded the need for diplomacy to find a resolution after the army did what it could. “Total victory” was no longer the objective. Unfortunately, by then, the aged Field Marshal was isolated in his work on operational plans and studies. The General Staff had been educated in his original concepts which had been inculcated in the official histories of the wars of unification. Moltke’s genius, shown in the breadth of his thinking, was never absorbed by the institution.
German military historian Gerhard Ritter would distinguish Moltke from his successors for his lack of fatalism. While the Elder Moltke often pressed for preventative war, he made the argument from the military point of view, i.e. that war would be more advantageous now rather than later.7 Moltke was not overly disturbed when Bismarck quashed proposals of preventative war. In contrast to his successors, Moltke was confident in his ability to meet the challenges of war whenever it arrived. He did not view the political situation as intractable. If the statesman did not want to utilize an opportunity for an easy victory in a preventative war, that was the business of the statesman. In other words, Moltke accepted Bismarck’s “right to be wrong”. A working relationship was therefore possible with the statesman who described his policy as “the most dangerous road last”.8
In the final years of their careers, both Bismarck and Moltke foresaw the dangers of a Germany where military prerogatives began to overshadow political ones. Bismarck, the architect of Germany’s rise, understood that the state’s survival hinged not just on military prowess but on the balancing of diplomatic relationships and restrained use of force. Moltke, though a staunch advocate of military autonomy, ultimately recognized the futility of unchecked military power in the context of modern warfare. Their eventual departures left a vacuum, filled by more aggressive military leaders, weak chancellors, and a feckless Kaiser. The political flexibility that had defined Germany’s rise came to be disregarded. As the officer corps grew more entrenched in its dominance, the military’s rigid and totalizing mindset contributed to Germany’s plunge into one of the most destructive conflicts in human history.9
1. Jack Snyder, “Civil-Military Relations and the Cult of the Offensive, 1914 and 1984”. International Security 9 (1) (1984).
2. Keir A. Lieber, “The New History of World War I and What It Means for International Relations Theory”. International Security 32 (2) (2007): 161.
3. Henry Kissinger, Diplomacy (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1995), 168.
4. For more on ultranationalist critique of the German government see Stig Förster, Der Doppelte Militarismus: Die Deutsche Heeresrüstungspolitik Zwischen Status-Quo-Sicherung Und Aggression, 1890-1913, Institut Für Europäische Geschichte Mainz: Veröffentlichungen Des (F. Steiner Verlag Wiesbaden, 1985).
5. For further detail, see Gerhard P. Gross, The Myth and Reality of German Warfare: Operational Thinking from Moltke the Elder to Heusinger.
6. Stig Förster, “Dreams and Nightmares: German Military Leadership and the Images of Future Warfare, 1871-1914”. In Anticipating Total War, The German and American experiences, 1871-1914, 343-376 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2013), 347.
7. A preventative war, in this context, is a conflict initiated to preemptively counter an anticipated future threat or to prevent a rival power from becoming stronger in the long term.
8. Gerhard Ritter, The Sword and the Scepter: The Problem of Militarism in Germany (Coral Gables: University of Miami Press, 1973), vol. 1 of 4, 243.
9. For more on Imperial German military culture, see Isabel Hull, Absolute Destruction: Military Culture and the Practices of War in Imperial Germany (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2005).