Union Pacific is the ideal lab rat for Precision Scheduled Railroading, practiced by the late Hunter Harrison on four Class I railroads, with great rewards for shareholders and mixed results for customers. UP, which will begin recasting itself October 1, is ideal for the role because it has too many employees, too many unproductive route miles, and too many expensive toys. Plus, it is less interested in increasing market share than in maximizing freight rates, which makes right-sizing the railroad easier. Let’s start by running the numbers.
Employees. At the peak of the last railroad cycle in 2006, Union Pacific had already been lapped by its western competitor, BNSF Railway, in both cars originated and revenue ton miles. Since then, through 2017, UP’s originations and revenue ton miles both fell 17 percent, while BNSF RTMs actually set a record in 2017. Yet at 44,146 employees last year, UP’s employee count was still 7 percent higher than that of BNSF. To put this another way, for UP’s productivity per employee (revenue ton miles per worker) to equal its competitor’s, it would need to slice the headcount by 16,000. A place to start might be headquarters in Omaha. UP counted 3,678 executives, officials and staff assistants in 2017 versus BNSF’s 1,511.
Barren route miles. Salina, Kan., to Provo, Utah, is becoming a traffic wasteland. That didn’t stop UP from laying welded rail and concrete ties and from covering the almost 1,000 miles with centralized traffic control. Meanwhile, one train a day (plus Amtrak) operates In Missouri between St. Louis and Poplar Bluff, Ark. And the railroad has effectively ceased freight service between Watsonville Junction and San Luis Obispo, Calif., and is close to doing so over the rest of the Coast Line to Los Angeles. All of these routes and perhaps many others you can identify contribute little revenue but buckets of costs, inflating the operating ratio (which is the percentage of revenues eaten up by operating costs). They would constitute Hunter Harrison’s first target.
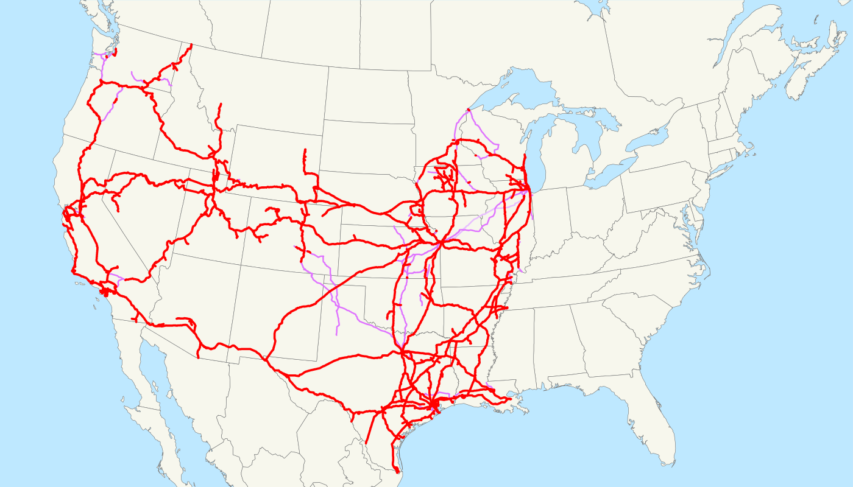
Map of the Union Pacific Railroad as of 2008, with trackage rights in purple (the special Chicago-Kansas City intermodal trackage rights are lighter).
Image via Wikimedia Commons.
[…]
Moreover, there are aspects to PSR as practiced by Hunter Harrison that customers won’t like. At the core of Precision Scheduled Railroading is intense use of assets: Run as many trains every day one direction as you do the other, fill them to maximum designed length and operate them at similar speeds. This isn’t how the commercial world works, and the Hunter Harrison way to make customers ship seven days a week was to discount rates on slow days and slap on surcharges on busy days. This keeps your crews and equipment fleet in motion at all times, and those cars and locomotives not continually used can be retired. Goodbye to growth and increased market share, which is a messy process requiring you to accede to the needs of customers rather than the other way around. But it is efficient.
However, if Union Pacific is serious about serving its customers better and delivering individual cars rather than trains to their destinations on schedule, I have an idea that I guarantee will achieve that result: Base salaried bonuses and stock grants on UP’s success in getting cars to customers on the right day and time and on the right train. UP has scheduled individual cars for decades, but there have never been monetary consequences for achieving those plans. People do follow the money. And when Union Pacific does for customers what it says it will do, calling the process Precision Scheduled Railroading or whatever you wish, I will be leading the applause.





