Emanuel Derman looks at the “physics of an economic crisis” and explains the difference between economic theories and economic models. I had originally quoted a few passages from the article, but the site forbids re-use without written permission.
November 8, 2011
The difference between economic models and theories
September 6, 2011
Stephen Gordon: no case for stimulus in Canada (yet)
As he points out in the article, Canadians who are calling for the federal government to indulge in US-style stimulus spending are not paying attention to the Canadian economy:
Employment in the U.S. is far below its pre-recession levels, and employment in the construction sector has been hit particularly hard. So there is a strong case to be made for a U.S. program of infrastructure spending — and many U.S. observers are making that case.
Neither of these conditions holds in Canada. Although unemployment rates have yet to return to pre-recession levels [. . .], the number of jobs lost during the recession has been recovered, and July employment levels were 1 per cent above their pre-recession peak.
September 1, 2011
August 24, 2011
August 7, 2011
July 12, 2011
June 25, 2011
Taxes must rise to maintain “the overall size of government programs”
Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner was being as honest as he knows how in talking to the House Small Business Committee this week. Reducing the size of government is literally unthinkable:
[T]he Obama administration believes taxes on small business must increase so the administration does not have to “shrink the overall size of government programs.”
The administration’s plan to raise the tax rate on small businesses is part of its plan to raise taxes on all Americans who make more than $250,000 per year — including businesses that file taxes the same way individuals and families do.
[. . .]
Geithner, continuing, argued that if the administration did not extract a trillion dollars in new revenue from its plan to increase taxes on people earning more than $250,000, including small businesses, the government would in effect “finance” what he called a “tax benefit” for those people.
“We’re not doing it because we want to do it, we’re doing it because if we don’t do it, then, again, I have to go out and borrow a trillion dollars over the next 10 years to finance those tax benefits for the top 2 percent, and I don’t think I can justify doing that,” said Geithner.
Not only that, he argued, but cutting spending by as much as the “modest change in revenue” (i.e. $1 trillion) the administration expects from raising taxes on small business would likely have more of a “negative economic impact” than the tax increases themselves would.
May 29, 2011
May 17, 2011
Final legacy of the “Cash for Clunkers” program: higher used car prices
Remember the “Cash for Clunkers” program? It was supposed to give the auto industry a shot in the arm by buying up older vehicles, giving the owners vouchers toward (certain) new vehicles, then destroying the traded-in clunker. Even at the time, economists tried to point out that this was just an elaborate “broken window” fallacy.
Today, use car prices are indeed soaring:
As news outlets around the country are reporting, the price of used cars has lately soared to a modern-day record, with some cars commanding more used than they sold for when new. News accounts commonly finger the Japanese earthquake and high gas prices as reasons, but there are some problems fitting either reason to the case. While the earthquake affected the supply of new cars, it’s the previously driven kind that has scored the more impressive price jump. And while the rise in gas prices would explain a relative shift in buyer demand from SUVs and trucks toward smaller vehicles — which has indeed happened — the strength of the used-vehicle market lately has been such that even the thirstier vehicles have advanced in price, $4 gas or no.
No doubt there are multiple reasons for the price spike, including the severe general slump in new-auto sales in recent years, which has reduced the volume of newer cars coming onto the resale market. But — as Washington scrambles to take undeserved credit for whatever passes for normalization in the auto business these days — it’s worth remembering that an artificial scarcity of used cars isn’t just bad for the poor as a group: it’s bad in particular for the upwardly mobile poor, since in most of the country landing a job means needing to line up transportation to get to that job. When it suddenly costs $6,000 instead of $3,000 to get wheels, the move from unemployment to a paying job faces a new and discouraging barrier.
March 23, 2011
March 22, 2011
Why nobody takes conservative promises too seriously
Today is budget day, when federal Finance Minister Jim Flaherty will be introducing the Conservative budget for 2011. Unless something has suddenly changed in the government’s philosophy, don’t expect anything daring:
First and foremost, the budget should contain a plan for reducing federal spending in real terms over the next four or five years. Mr. Flaherty’s 2010 budget outlined how the federal government intended to restore balance to the federal books by 2015 by holding the line on spending increases to just over 1% a year while praying for a return to robust annual revenue increases. In fact, merely planning to hold the line on spending is never going to be enough. For one thing, the Conservatives have never proven themselves capable of pulling it off. Despite coming to power in 2006 on a message of fiscal restraint, the Tories raised federal program spending by an average of 6% in each of their first three budgets before the worldwide finance crisis of 2008. Since then, they have added $100-billion to the national debt, in large part thanks to stimulus spending of dubious worth.
According to the Canadian Taxpayers Federation, as of last Friday, Canada’s debt stood at nearly $563-billion. This means the debt repayments made over the 11 years before the recession began have been wiped out, and that the federal treasury is back to where it was before the Liberals’ then-finance minister Paul Martin brought down his austerity budget in 1995.
Since the Tories took power five years ago, program spending has expanded by nearly 40% and the federal civil service has grown by nearly 20%. We’re sorry, but we just don’t trust a government with a track record like the Tories’ to be able to regain budget balance simply by holding the line on new spending.
They can promise all sorts of things, but what they seem best at doing is pretending not to be “conservative” at all.
The government may fall, as the opposition are calling for even higher spending on “universities, home care, daycare, unemployment, seniors and Quebec”. This may work to the Conservatives’ advantage as they’re (temporarily) riding high in the opinion polls, so they might be able to win a majority if an election is forced on them over this budget. Of course, the opposition can read the polls too, so they may not be as eager to throw Stephen Harper an opportunity to win an easy victory.
Update: Well, the budget was tabled in the House, the opposition parties all rejected it “as it stands”, and the prime minister has stated they will not accept any amendments. For Thursday’s performance in the Ottawa Little Theatre, the budget will get first reading, which means the first opportunity for the government to be defeated . . . which means a May general election.
March 2, 2011
Why “Buy American” or “Buy Canadian” campaigns are bad economics
Daniel Ikenson takes ABC to task for their misleading propaganda against international trade:
Back in the “golden age” of 1960, when imports were oddities to marvel over in a disdainful way, the per-capita U.S. income was $2,914. In 2009, with imports ubiquitous, per-capita income was $46,411. (Economic Report of the President, 2010, Tables B-1 and B-34). In real, inflation-adjusted terms, even with a U.S. population increase from 181 million to 307 million, per-capita incomes in 2009 were almost triple what they were in 1960 ($42,277 vs. $15,669 in 2005 dollars — ERP, 2010, Tables B-2 and B-34). Oh, if only we could replicate the relative poverty, the limited consumer choices, the inefficient production processes, the massive trade barriers that compelled Americans to buy American, and the uneconomic work rules and wages commanded by once-powerful private sector labor unions. In 1960, before real economic liberalization spawned cultural and social liberalization, Diane Sawyer would never have dreamed of being a network news anchor, if she even dared to entertain the concept of working outside of the home. How can she pine for such an era?
It’s frustrating that so much research refuting the myth of manufacturing decline and supporting the conclusion that U.S. manufacturing is thriving — and is in fact leading the world in terms of value of output — is simply neglected by a media that is more committed to scaring than informing. Today Americans are less likely to find in their homes products manufactured in the United States because U.S. manufacturers have moved on to producing higher value products. American manufacturing isn’t focused on products that consumers find in retail stores, like furniture, hand tools, sporting goods, flatware, draperies, carpeting and clothes. American factories produce more value than any other country’s factories by focusing on producing the highest value products: pharmaceuticals, chemicals, airplanes, sophisticated componentry, technical textiles, and other items often sold directly to other businesses.
I and others have been making these points for several years, as U.S. manufacturing continues to thrive in every metric . . . except employment. Manufacturing employment peaked in 1979 and has been on a downward trajectory ever since. But that is the point that eludes ABC and everyone else who thinks U.S. manufacturing’s best days are in the past. Making more with less is the goal! That’s how an economy grows! The political imperative of “putting people back to work” regardless of the economic value of that work — remember the so-called stimulus? — spits in the face of economics. The fact that Americans are unemployed speaks to a mismatch of skills demanded and skills available, as well as to a business and regulatory environment that dissuades investment and hiring.
February 15, 2011
February 14, 2011
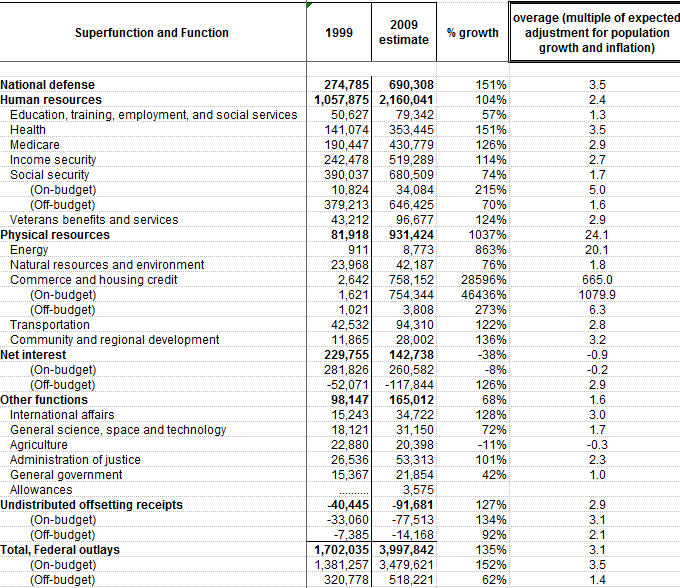
So, how big is the US federal debt, really?
H/T to Jon, my former virtual landlord, who asks:
Should “unfunded liabilities” be counted as the guy is counting them here? While some of those things are promised — such as Medicare and Medicaid — the amounts that will actually be paid out might be less. For example, many of those who are unemployed might starve to death before they rack up Medicare bills, so the actual Medicare costs will be less than the projected unfunded liability.
Whether they’re counted as he suggests or not, it’s still a freaking huge pile of bills.

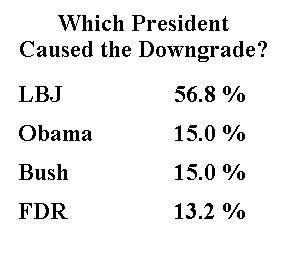 Well, it turns out that Social Security is a relatively minor part of the problem, so even though President Roosevelt’s policies exacerbated and extended the Great Depression, the program he created is only responsible for a small share of the fiscal crisis. To give the illusion of scientific exactitude, let’s assign FDR 13.2 percent of the blame.
Well, it turns out that Social Security is a relatively minor part of the problem, so even though President Roosevelt’s policies exacerbated and extended the Great Depression, the program he created is only responsible for a small share of the fiscal crisis. To give the illusion of scientific exactitude, let’s assign FDR 13.2 percent of the blame.