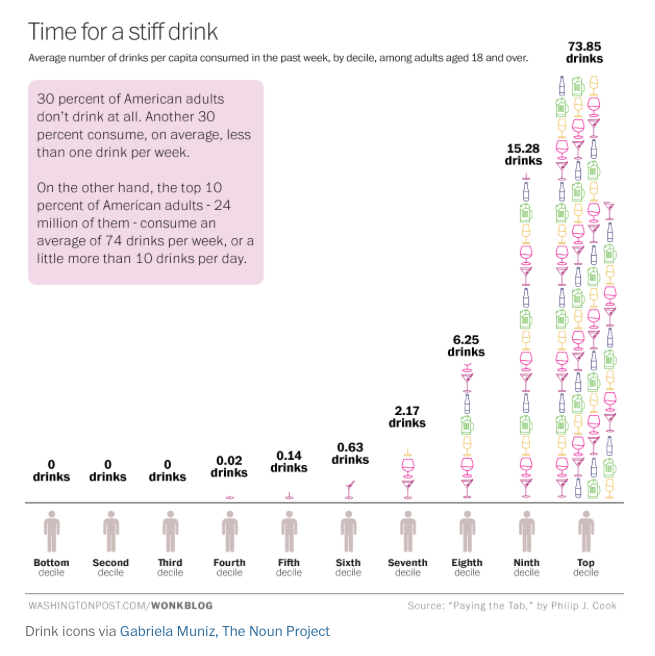
Defence With A “C” summarizes the tale of how we got to the current suite of modern military small arms. It’s a long story, but if you’re interested in firearms, it’s a fascinating one.
To understand why we’ve arrived where we are now with the NATO standard 5.56mm calibre round you have to go all the way back to the war of 1939-1945. Much study of this conflict would later inform decision making surrounding the adoption of the 5.56, but for now there was one major change that took place which would set the course for the future.
The German Sturmgewehr 44 is widely accepted as the worlds first true assault rifle. Combining the ability to hit targets out to around 500 yards with individual shots in a semi-automatic mode, as well as the ability to fire rapidly in fully automatic mode (almost 600 rounds per minute) the StG 44 represented a bridge between short ranged sub-machine guns and longer ranged bolt action rifles.
[…]
After the second world war the US army began conducting research to help it learn the lessons of its previous campaigns, as well as preparing it for potential future threats. As part of this effort it began to contract the services of the Operations Research Office (ORO) of the John Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, for help in conducting the scientific analysis of various aspects of ground warfare.
On October 1st, 1948, the ORO began Project ALCLAD, a study into the means of protecting soldiers from the “casualty producing hazards of warfare“. In order to determine how best to protect soldiers from harm, it was first necessary to investigate the major causes of casualties in war.
After studying large quantities of combat and casualty reports, ALCLAD concluded that first and foremost the main danger to combat soldiers was from high explosive weapons such as artillery shells, fragments from which accounted for the vast majority of combat casualties. It also determined that casualties inflicted by small arms fire were essentially random.
Allied troops in WW2 had been generally armed with full-sized bolt action rifles (while US troops were being issued the M1 Garand), optimized to be accurate out to 600 yards or more, yet most actual combat was at much shorter ranges than that. Accuracy is directly affected by the stress, tension, distraction, and all-around confusion of the battlefield: even at such short ranges, riflemen required many shots to be expended in hopes of inflicting a hit on an enemy. The ORO ran a series of tests to simulate battle conditions for both expert and ordinary riflemen and found some unexpected results:
A number of significant conclusions were thus drawn from these tests. Firstly, that accuracy — even for prone riflemen, some of them expert shots, shooting at large static targets — was poor beyond ranges of about 250 yards. Secondly, that under simulated conditions of combat shooting an expert level marksman was no more accurate than a regular shot. And finally that the capabilities of the individual shooters were far below the potential of the rifle itself.
This in turn — along with the analysis of missed shots caught by a screen behind the targets — led to three further conclusions.
First, that any effort to try and make the infantry’s general purpose weapon more accurate (such as expensive barrels) was largely a waste of time and money. The weapon was, and probably always would be, inherently capable of shooting much tighter groups than the human behind it.
Second, that there was a practical limit to the value of marksmanship training for regular infantry soldiers. Beyond a certain basic level of training any additional hours were of limited value*, and the number of hours required to achieve a high level of proficiency would be prohibitive. This was particularly of interest for planning in the event of another mass mobilisation for war.