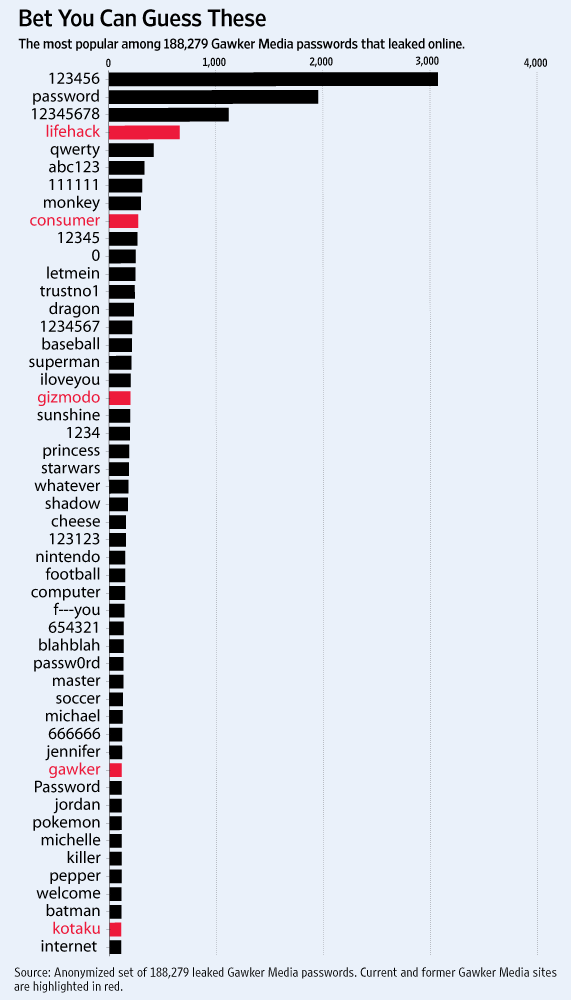
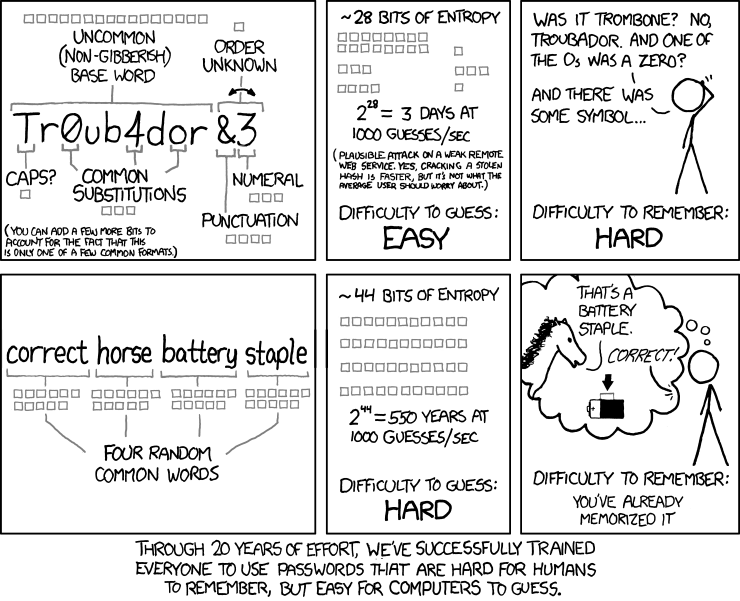
An interesting article at Strategy Page discussing online espionage:
Firms with the most to lose, like financial institutions, guard their data most successfully. They do this the old-fashioned way, with layers and layers of security, implemented by the best (and most highly paid) people and pushed by senior managers who take the time to learn about what they are dealing with, and what it will take to stay on top of the problem.
It’s different in the defense business. If the Chinese steal data on some new weapon, there might be a problem years down the road, when the Chinese offer a cheaper alternative to an American weapon, for the export market. But even that problem has a silver lining, in that you can get away with insisting that those clever Chinese developed your technology independently. Meanwhile, everyone insists that there was no espionage, cyber or traditional, involved. As a further benefit, the American firm will get more money from a terrified government, in order to maintain the American technical edge. It’s the same general drill for military organizations. But for financial institutions, especially those that trade in fast moving currency, derivatives and bond markets, any information leaks can have immediate, and calamitous consequences. You must either protect your data, or die.
It’s not exactly a secret that China has been active in this area, but the extent of their official activity is hard to state. However, just as non-state actors take advantage of individuals who fail to use anti-virus software on their computers, ignorance and apathy are tools for state actors:
But the biggest problem, according to military Cyber War commanders, is the difficulty in making it clear to political leaders, and non-expert (in Internet matters) military commanders, what the cyber weapons are, and the ramifications of the attacks. Some types of attacks are accompanied by the risk of shutting down much, or all, of the Internet. Other types of operations can be traced back to the source. This could trigger a more conventional, even nuclear, response. Some attacks use worms (programs that, once unleashed, keep spreading by themselves.) You can program worms to shut down after a certain time (or when certain conditions are met). But these weapons are difficult, often impossible, to test “in the wild” (on the Internet). By comparison, nuclear weapons were a new, very high-tech, weapon in 1945. But nukes were easy to understand; it was a very powerful bomb. Cyber weapons are much less predictable, and that will make them more difficult for senior officials to order unleashed.
So the first order of business is to develop reliable techniques to quickly, and accurately, educate the senior decision makers about what they are about to unleash. This would begin with the simplest, and cheapest, weapons, which are botnets, used for DDOS attacks. In plain English, that means gaining (by purchase or otherwise) access to hundreds, or thousands, of home and business PCs that have had special software secretly installed. This allows whoever installed the software that turned these PCs into zombies, to do whatever they want with these machines. The most common thing done is to have those PCs, when hooked up to the Internet, to send as many emails, or other electronic messages, as it can, to a specified website. When this is done with lots of zombies (a botnet), the flood of messages becomes a DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack that shuts the target down. This happens because so much junk is coming in from the botnet, that no one else can use the web site.