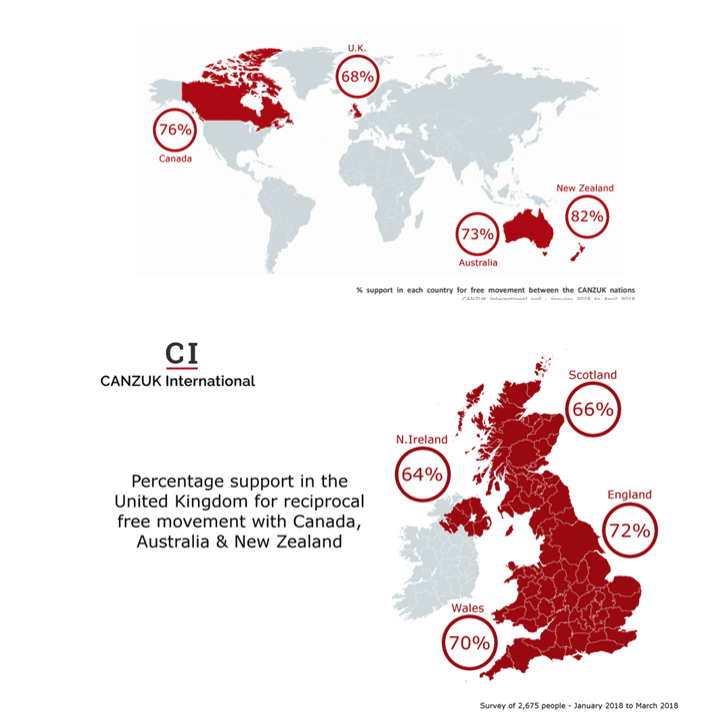
Ted Campbell is a big fan of the CANZUK scheme (Canada-Australia-New Zealand-United Kingdom) to create an “anglosphere” power alongside the current economic big-hitters on the world stage like the United States, China and the European Union. I agree it has historical, nostalgic appeal, but as Aris Roussinos points out, geography is a big stumbling block to it ever being much more than an idea:
Since losing the empire, Britain has notoriously struggled to find a role on the world stage. Initial attempts to piggyback on the power of our successor as global hegemon, the United States, by acting as a guiding force — a Greece to America’s Rome, in Harold Macmillan’s phrase — faltered due to the total absence of interest ever shown in this arrangement by any American administration.
The subsequent attempt to remould Britain as a European power acting in concert with its continental neighbours through the European Union was an unhappy marriage, and has ended in a rancorous divorce whose final settlement is still to be determined. Adrift on the world stage, we are in need of good ideas.
Instead, we are offered CANZUK, a reheated Edwardian fantasy of a globe-spanning Anglosphere acting as a world power which excites the enthusiasm of a small coterie of neoliberal and neoconservative ideologues, if no one else.
In a recent piece for the Wall Street Journal, the historian and Churchill biographer Andrew Roberts argued that the CANZUK nations — Canada, Australia, New Zealand and the UK — ought to establish “some form of federation among them” as a “second Anglospheric superpower” combining “free trade, free movement of people, a mutual defense organization and combined military capabilities” , which would “create a new global superpower and ally of the U.S., the great anchor of the Anglosphere”.
One cannot fault Roberts for the grandeur of his vision, even if the details of how this would actually work are left to others to fill in. Instead, we are reassured, this would not be a centralising project like the hated EU; rather, “its program for a loose confederal state linking the Westminster democracies would be clearly enunciated right from the start.” Already, we see the harsh hand of reality ready to crush this initially appealing vision. On the one hand, CANZUK is a globe-spanning superpower ready to be born; on the other, it is merely a loose grouping of separate national governments, which would, like all national governments, act according to their own interests above all.
By totting up the different GDP figures of the various CANZUK nations, Roberts claims that his proposed Empire 2.0 “would have a combined GDP of more than $6 trillion, placing it behind only the U.S., China and the EU,” while “with a combined defense expenditure of over $100 billion, it would also be able to punch above its weight”.
Yet the flaws of this argument are obvious. As other critics have noted, only a minuscule proportion of the CANZUK nations’ trade is with each other, save New Zealand, an economic satellite of Australia. Australia is a great East Asian trading power, and will remain so. Canada is enmeshed in the greater North American trading sphere, as are we with Europe, whatever Brexiteers may wish. As always, the simple matter of geography trumps the affective bonds between far-flung kith and kin, whatever their emotional appeal.