Trust me on this: “impostor syndrome” is very real. It is, in fact — and obviously — the source of the benzo bottle in every egghead’s medicine cabinet. And the reason all eggheads feel like frauds is equally obvious: Nothing you do can possibly justify your paycheck.
There are no Dead Poets Society teachers in real life in any case, and even if there were, and even if you were one of them, well … congrats, buddy, you’ve managed to reach one student, one time, out of the hundreds, thousands, tens of thousands you taught before reaching tenure, the hundreds, thousands, tens of thousands more who will drift through your classroom, fish-eyed and phone-addled, for the rest of your academic career. One kid, one time, and meanwhile you live a life that 90% of Americans would be ecstatic to have. (As for your “research”, […] please. Unless your book revolutionizes a field — good luck with that — maybe twenty people will read it, and fifteen of them will hate it). You’re a fucking fraud, pal, that’s all there is to it …
Which leaves you with two options, if you want to avoid the kind of crushing cognitive dissonance that turns a guy like Todd into a gutter drunk: You embrace the make-believe, or you quit. Todd quit. Becoming a gutter drunk was a spectacularly gaudy, self-destructive way of quitting, but it was quitting nonetheless. I quit too, as y’all know … but the funny thing was, I didn’t quit drinking until I did. I didn’t go out and get wrecked every night like I used to do with Todd, but I was still a drinker, often quite a heavy one. I just did it in private. It was only when I quit the ivory tower for good that I stopped drinking.
This, I suggest, is the ultimate source of the Poz: The crushing impostor syndrome that all Americans feel, who haven’t built their lives up from scratch. Unless your day-to-day is a struggle, a real one — a “need to choose between buying food and making rent” one — you can’t help but feel, at some level, that you’re a fraud, a sham. You don’t deserve this, because no one deserves this who didn’t earn it, didn’t hew it out of the wilderness himself. And the more “white collar” you are, the stronger your latent impostor syndrome. Is it any surprise that Karen, who has never earned anything in her entire life, is the most pozzed? That “Human Resources” is just the Poz Gestapo?
Severian, “On the Poz”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2020-11-16.
May 24, 2023
QotD: Impostor Syndrome in academia
May 23, 2021
QotD: The psychological impact of extended lockdowns
Claudio Grass (CG): A lot has been said and written about the economic and financial impact of the covid crisis and all the lockdowns and restrictions that came with it. However, the mental health implications haven’t really received the attention they arguably merit, at least not by mainstream media or government officials. Over the last year, we saw self-reported depression rates creep up in many Western nations, while excessive alcohol consumption and the abuse of prescription drugs also jumped. Do such trends raise concerns over longer-term problems or will we all simply snap back to normal once the crisis is over?
Theodore Dalrymple (TD): The first thing to say is that I do not like the term “mental health.” Was Isaac Newton mentally healthy, or Michelangelo? I think part of the problem is very concept of mental health. It implies that there is some state or condition of mind deviation from which is analogous to illness. Once this idea takes hold, it is clearly up to an expert to cure the person, or better still prevent him from getting ill in the first place. This expectation cannot be met, but the idea that it can be makes people more fragile.
Second, people clearly vary much in their response to confinements, lockdowns, closures of resorts of entertainment, etc. For myself, I have reached the age of misanthropy or self-sufficiency when these things make comparatively little difference to my life. I have plenty of space and plenty of things to do, in essence reading and writing. But that does not make me mentally healthier than a young man who is frustrated because he cannot play football with his friends and becomes ratty – moreover living in a very confined space.
Depression is so loosely defined a term that it has become almost valueless as a diagnosis. How often have you heard someone say “I’m unhappy” rather than “I’m depressed?” The semantic shift is very important. The proper response to someone who says that he is depressed is to give him antidepressants, even though these don’t work in the majority of cases, except as a placebo, and have potential side-effects. It is always tempting for people who are unhappy to drink alcohol – to drown their sorrows, as we say. Of course, if you drink too much, you might become really and truly depressed. A person who did not respond to the current situation with a little gloom would be odd.
Claudio Grass, “Theodore Dalrymple: Self-Control And Self-Respect Have Become Undervalued”, The Iconoclast, 2021-02-17.
May 16, 2021
Gambling machines have come a long way from the “one-armed bandit” days
This is another reader book review for Scott Alexander’s Astral Codex Ten, looking at Addiction by Design: Machine Gambling in Las Vegas by Natasha Dow Schüll. I’m incredibly risk-averse, so I’ve never even set foot in a casino, but from this review I do not regret my aversion one tiny little bit:

“Hiking the Las Vegas casinos” by davduf is licensed under CC BY-ND 2.0
Sometimes employees at Netflix think, “Oh my god, we’re competing with FX, HBO, or Amazon” … [W]e actually compete with sleep.
Reed Hastings
Randomness is addictive, in rats. B. F. Skinner learned that when he created his eponymous rat boxes. The boxes had levers that, when pressed, dispensed food pellets. Rats in boxes where one press resulted in one pellet pressed the lever when hungry. But rats in boxes where one press randomly resulted in no, one, or many pellets, became addicted to pressing the lever. That mammalian attraction to randomness lies at the heart of all gambling.
But machine gambling is not like other kinds of gambling. The book overflows with metaphors straining to describe how machine gambling is the supercharged version of table games like poker, blackjack, and roulette. Machine gambling is deforestation ruining the rainforest of diverse table games. Machines are invasive kudzu outcompeting and killing the native table games. Machine gambling is the crack cocaine to table games’ cocaine.
In about two decades, machine gambling went from being a side attraction to keep wives busy while their husbands played table games to the source of 85% of casino profits. You know how shopping malls have benches for husbands to sit on while their wives shop in stores? Imagine that those benches became the mall. (If you’re reading this in 2025, shopping malls were, uh, a collection of permanent pop-up stores under the same roof.)
The first time I went to Vegas, I knew a few tricks casinos would use to encourage me to gamble too much. I knew the hotel rooms were purposefully cheap, to entice me to visit Vegas. I knew casinos would have neither windows nor clocks, to help me lose my sense of time. I knew they would be full of bright lights and loud sounds, to overstimulate me. I knew nothing. Those tricks are old hat, as quaint as doilies. Machine gambling is a brave new world.
Machine gambling comes in the form of many games, but one example is enough to illustrate the pattern, so let’s discuss slot machines. Slot machines are games with reels with a variety of symbols on them, like cherries, diamonds, or the number 7. (Fun fact: fruit symbols were initially used on slot machines during the prohibition era to disguise them as gum vending machines.) The game is simple. The player spins the reels. If they land to show symbols in a row, the player wins. Because of their simplicity, these machines are favored by new gamblers and tourists.
Back when Moore’s Law was just Moore’s Prediction, slot machines were mechanical devices. The player would pull on a mechanical lever, which caused reels to spin. The reels would eventually slow down and then stop. The symbols in the middle of the screen when the reels stopped dictated whether the player won or lost.
Now, slot machines are digital. The lever, the reels, the symbols — they are all ones and zeros untethered from reality. This gives machine designers a terrifying amount of flexibility. They can optimize the game to maximize its addictivity.
March 4, 2021
QotD: Accounting for the long-term fall in the crime rate
Any criminologist will tell you that criminals as a group are also highly deviant in ways that are not criminal. They have very high rates of accidental injury, alcoholism, nicotine addiction, and involvement in automobile collisions. They have poor impulse control. They have high time preference (that is, they find it difficult to defer gratification or regulate their own behavior in light of distant future consequences). And they’re stupid, well below the whole-population average in IQ or whatever other measure of reasoning capacity you apply. I’m going to revive a term from early criminology and refer to these dysfunctional deviants as “jukes”.
One clue to the long-term fall in crime rates may be that most of the juke traits I’ve just described are heritable. Note that this is not exactly the same thing as genetically transmitted; children may to a significant extent acquire them from their families by imitation and learning.
The long-term fall in crime rates suggest that something may have been disrupting the generational transmission of traits associated with criminal deviance. Are there plausible candidates for that something? Are there selective pressures operating against jukeness that have become more pressing since the 1960s?
I think I can name three: ready availability of intoxicants, contraception, and automobiles.
Once I got this far in my thinking I realized that the authors of Freakonomics got there before me on one of these; they argued for a strong forward influence from availability of abortion to decreased crime rates two decades later. And yes, I know that a couple of conservative economists (Steve Sailer and John Lott) think they’ve found fatal flaws in the Levitt/Dubner argument; I’ve read the debate and I think Levitt/Dubner have done an effective job of defending their insight.
But I’m arguing a more general case that subsumes Levitt/Dubner. That is, that modern life makes juke traits more dangerous to reproductive success than they used to be. Automobiles are a good example. Before they became ubiquitous, most people didn’t own anything that they used every single day and that so often rewarded a moment’s inattention with injury or death.
Ready availability of cheap booze and powerful drugs means people with addictive personalities can kill themselves faster. Easy access to contraception and abortion means impulse fucks are less likely to actually produce offspring. More generally, as people gain more control over their lives and faster ways to screw up, the selective consequences from bad judgment and the selective premium on good judgment both increase.
Eric S. Raymond, “Beyond root causes”, Armed and Dangerous, 2010-01-12.
September 27, 2020
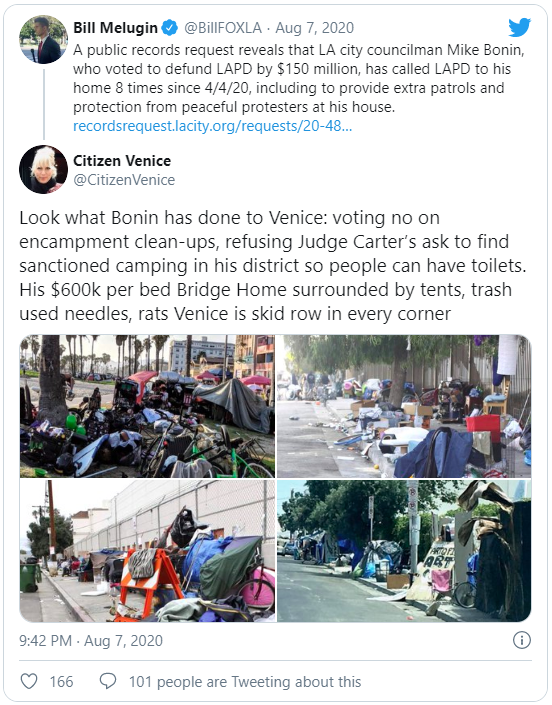
Homelessness in Los Angeles
In Quillette, Amy Alkon talks about the homeless crisis in LA, particularly her own immediate experience with a couple who “camped out” in front of her house.
Throughout [Los Angeles Mayor Eric] Garcetti’s seven years as Mayor, Los Angeles has witnessed a shocking explosion of homelessness. When he took office in 2013, the city had about 23,000 residents classified as homeless, two thirds of whom were unsheltered, living on the streets. By mid-2019, the figure was about 36,000, and three-quarters of them were living on the streets. Currently, there are 41,000 homeless. Garcetti’s pet plan to alleviate the homelessness crisis was the construction of permanent supportive housing. In 2016, compassionate voters approved $1.2 billion in new spending to fund these units. Three years later, only 72 apartments had been built, at a cost of about $690,000 apiece. Meanwhile, an El Salvador-based company has come up with nifty $4,000 3D-printed houses that look like great places to live and can be put up in a single day.
There’s also been a failure to admit that housing alone isn’t the solution. As urban-policy researcher Christopher Rufo explains, only about 20 percent of the homeless population are people down on their luck, who just need housing and a few supportive services to get back on their feet. Approximately 75 percent of the unsheltered homeless have substance-abuse disorders and 78 percent have mental-health disorders. Many have both.
As a bleeding-heart libertarian, I feel personally compelled to try to help people who are struggling. I do this by volunteering as a mediator, doing free dispute resolution to provide “access to justice” to people who can’t afford court. And since about 2009, I personally have given support to one of those easily helpable 20 percent Rufo refers to, getting him paying work and a bank account, and storing his stuff in my garage. He is a good man and a hard worker — sober for many years — who simply seems to have issues in the “front-office” organizational parts of his brain that help most of us get our act together to, say, pay bills on time. He just needs somebody to back him up on the bureaucratic aspects of life. I’m happy to say he now has a roof over his head. He lives in a motel across the country, and all I still do for him is provide him with a permanent address. I receive his Veterans Administration and Social Security mail at my house, which I mail to him with smiley faces and hearts on the envelopes, colored in with pink and orange highlighter.
This success story would not be possible for most homeless people, the nearly 80 percent who are addicted and/or mentally ill. As Rufo writes:
Progressives have rallied around the slogan “Housing First,” but haven’t confronted the deeper question: And then what? It’s important to understand that, even on Skid Row, approximately 70 percent of the poor, addicted, disabled, and mentally ill residents are already housed in the neighborhood’s dense network of permanent supportive-housing units, nonprofit developments, emergency shelters, Section 8 apartments, and single room-occupancy hotels.
When I toured the area with Richard Copley, a former homeless addict who now works security at the Midnight Mission, he explained that when he was in the depths of his methamphetamine addiction, he had a hotel room but chose to spend the night in his tent on the streets to be “closer to the action.” Copley now lives … at the Ward Hotel — which he calls the “mental ward” — where he says there are frequent fights and drugs are available at all hours of the day. The truth is that homelessness is not primarily a housing problem but a human one. Mayors, developers, and service providers want to cut ribbons in front of new residential towers, but the real challenge is not just to build new apartment units but to rebuild the human beings who live inside them.
The situation is especially tragic for those who are so mentally ill that they cannot take care of themselves, and are often a danger to both themselves and others. And I sometimes wonder which movie star or other famous person needs to be stabbed or bludgeoned before politicians take meaningful action.
It’s fashionable in progressive circles to demonize law enforcement, but Rufo explains that in 2006, then-L.A. police chief Bill Bratton implemented a “Broken Windows” policing initiative on Skid Row. It led to a 42 percent reduction in felonies, a 50 percent reduction in deaths by overdose, and a 75 percent reduction in homicides. The overall homeless population was reduced from 1,876 people to 700 — a huge success. Activists filed lawsuits and ran publicity campaigns, slowly killing Bratton’s program, on the grounds that it “criminalizes homelessness.” As a libertarian, I’m opposed to drug laws and forced behavior — but only to a point. It is not compassion to leave people to be victimized by criminals simply because they are unhoused, nor is leaving mentally and physically disabled people strewn across the streets amidst piles of garbage a form of freedom.
Mayor Garcetti, in lieu of admitting the real challenges — the first step to taking meaningful action to alleviate the homelessness crisis — has simply ignored the human results of his failed policy. As a result, whole sections of the city, including formerly livable streets in my beloved Venice, have been turned into Skid Row by the Sea.
July 29, 2020
QotD: Grog in the Royal Navy
More generally, though, do we have any historical evidence of groups whose alcohol consumption was documented with any confidence, to see how they fared?
Actually, we do, at least as a floor: we know the quantity of the Royal Navy’s spirit ration, which until 1823 was based on half a pint of rum (284 millilitres in foreign) per man per day. We also know its minimum strength, since it was tested by trying to ignite gunpowder soaked in it: it had to be over 57% alcohol by volume (“proof strength”) to pass. That’s sixteen units of alcohol – not per week, but per day – or north of a hundred units a week, just for the issued ration before sailors bought any extra from the purser. (No wonder Jack Tar was jolly back in those days!)
But clearly, we would expect a body of men consuming such suicidally destructive quantities of booze to be physical wrecks, raddled by cirrhosis and disease? As Dr James Lind (he of the discovery that citrus fruits were a sovereign remedy for scurvy) put it,
It is an observation, I think, worthy of record that fourteen thousand persons, pent up in ships, should continue, for six or seven months, to enjoy a better state of health upon the watery element, than it can well be imagined so great a number of people would enjoy, on the most healthful spot of ground in the world.
(For context, around this point the Navy won the battle of Quiberon Bay, with twenty ships – who had less than one man sick per ship).
The ration was halved in 1823, and again in 1850, but for a hundred and twenty years until Black Tot Day in 1970, the Navy still issued nearly thirty units of alcohol a week to everyone on the lower deck (junior rates got theirs diluted, seniors got neat rum). Either folk were hardier back then, or Britannia managed to rule the waves and keep her sailors reasonably healthy despite being a pack of hopelessly addicted alcoholics.
Jason Lynch, “How Much Is ‘Too Much’?”, Continental Telegraph, 2018-05-08.
October 19, 2019
Churchill Was a Drunk… or Was He? – Doped WW2 Leaders Part 2
World War Two
Published 17 Oct 2019Winston Churchill was one of the most influential figures of World War Two. But as a heavy drinker he must have been under influence of constant drunkenness, right?
Watch Part 1 about Hermann Göring here: https://youtu.be/8H7arcUi7zQ
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Francis van Berkel
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Francis van Berkel
Edited by: Michal Drzewiecki
Map animations: Eastory
Sound design: Marek KaminskiColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.Sources:
– IWM: A 11590
– Wine and whiskey icons by Made by Made, papers icon by Pauline, Breakfast icon by shashank singh, Champagne icons by Made by Made and Jenie Tomboc, Heart icon by Sophia Bai, alcohol icon by Flatart, beef icon by Igé Maulana, Beer by Valeriy, Cheese by Erin Agnoli, red wine by sasha willins, Brandy by NAS, all – the Noun Project
– Royalty free music of BensoundA TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
22 hours ago (edited)
We make an effort to approach history as unbiased as possible. The result is what we think is a balanced videos on Churchill’s alcohol (ab)use. For those of you who are new here, we are following World War Two Week by Week, in which we do pay a lot of attention to all those smaller but still significant events. If you would like to watch the series, make sure to subscribe and to click here to start watching from episode one: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3-A1gVm9T0A&list=PLsIk0qF0R1j4Y2QxGw33vYu3t70CAPV7XCheers,
The TimeGhost team.
October 12, 2019
Göring, the Stoned Nazi Nut – Doped WW2 Leaders Part 1
World War Two
Published 10 Oct 2019Hermann Göring was one of the most powerful leaders of the Third Reich. He was also a drug addict with some serious problems and a remarkable lifestyle.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow WW2 day by day on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Joram Appel
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Research by: Joram Appel
Edited by: Iryna Dulka
Map animations: EastoryColorisations by Norman Stewart and Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
Eastory’s channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEly…
Archive by Screenocean/Reuters https://www.screenocean.com.Sources:
Klimbim Colorizations – https://klimbim2014.wordpress.com/A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
31 minutes ago (edited)
Though this episode is mostly about the lifestyle of Hermann Göring, we will certainly get back to his more serious impact on the Nazi party, Germany and World War Two. For those of you who are new here, we are following World War Two Week by Week, in which we do pay a lot of attention to all those smaller but still significant events. If you would like to watch the series, make sure to subscribe and to click here to start watching from episode one: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3-A1gVm9T0A&list=PLsIk0qF0R1j4Y2QxGw33vYu3t70CAPV7XCheers,
The TimeGhost team.
July 24, 2019
Wait, you mean there might be a downside to cannabis legalization?
As a libertarian of long standing, I’m on the record as being in favour of legalizing cannabis since long before it was cool (geeky and perpetually uncool libertarians probably helped keep it from being cool for at least a few years longer). I’m not enthused to hear that we may have been undersold on the risks of cannabis use … not that the government didn’t try telling is it was deadly, deadly poison (they did, repeatedly, and at great length), but they institutionalized the role of the boy who cried wolf, and every illegal narcotic got basically the same description. I’m actually not kidding here: the first health class I got in middle school included a lecture and a pamphlet on the dangers of pot; the second class covered the dangers of cocaine; the third warned against LSD; and so on … but they used a copy/paste to discuss the physical and mental risks of the different drugs, and they all read the same way. All those evil drugs are evil, bad, and rot your brain. Knowing that the pothead (“Hi, Gary!”) at the back of the class hadn’t suddenly had a psychotic break and tried to fly off the top of the school was the first hint that we were being oversold on the real world risks of (some) illegal drug use. The declared fact that some illegal narcotics actually are deadly, deadly poison ran up against the observed fact that a significant majority of people over the age of fifteen had tried cannabis and found it somewhat less scary than advertised.
Along with the beginnings of doubt that the government was being honest with us, and the clear understanding that even if using drugs wasn’t as dangerous as we were told, we shared a growing awareness that being caught with drugs by the police was significantly more dangerous and possibly deadly. Officer Friendly would shoot you down like a mad dog if he thought you were one’o’them drug-crazed hippies. It certainly changed the social dynamics of any interaction with Officer Friendly’s fellow heavily armed co-workers…
In the National Post, Barbara Kay suggests that not all the dangers of cannabis use were mere government propaganda:
Some years ago, in conversation with his wife, a forensic psychiatrist specializing in mentally ill criminals, former New York Times reporter Alex Berenson observed that the perpetrator of a recent violent crime had been high at the time, and had smoked pot regularly all his life. Her response — “Yeah, they all do” — jolted him. The result was his book, Tell Your Children: The Truth About Marijuana, Mental Illness and Violence.
Much of the referenced material in Berenson’s book had not yet been published a decade ago. But more recent studies only confirm what a few intrepid researchers were already warning about then.
Indeed, as I noted in a 2008 column, the head of the Medical research Council in the U.K., Professor Colin Blakemore, who in 1997 had been the moral authority behind a pot-legalization campaign, unequivocally reversed his pot-friendly stance in 2007, stating: “The link between cannabis and psychosis is quite clear now; it wasn’t 10 years ago.”
If you haven’t energy for a whole book, but would invest in 16 pages on the subject, you will be well rewarded by Steven Malanga’s in-depth article, “The Marijuana Delusion,” in City Journal‘s June issue. Here you will find debunked the blithe claim, still received as gospel by progressives and libertarians, that pot is virtually harmless and even therapeutic.
Unlike marijuana, real medications are deeply researched before coming on the market, and may attest to proven benefits, but are obligated to admit potential harms. Is pot a medicinal drug or a placebo? Nobody really knows. One may argue “who cares, as long as it works” (anecdotally I hear that pot works, and also that it doesn’t work), but that isn’t the point, since the legalization movement made medical claims for pot in order to bring the public onside politically. There was no will on the movement’s side to discover even radically fortified pot’s downsides.
The knowledge was out there for those interested. In 1987 a study of nearly 50,000 Swedish military conscripts followed for drug use over 15 years found that frequent pot use in teenhood was linked to a six-fold risk of schizophrenia as compared with non-usage. A 2004 meta-analysis of studies on pot use came to a similar conclusion. These studies, and others, are suggestive that heavy marijuana consumption, particularly in youth, may cause serious mental health problems. Yes, it is possible that the link isn’t entirely causal; people with mental health issues may be more likely to use marijuana heavily. But at the very least, this ought to be an issue of ongoing concern, particularly now that marijuana is legal in Canada and in an increasing number of U.S. states.
July 17, 2019
QotD: “The United States government [became] the greatest and most potent maker of criminals in any recent century”
For most of the history of the United States, drugs were legal. People could buy opiates and cocaine-based products from their local pharmacy. An opiate-laced brew called Mrs. Winslow’s Soothing Syrup, for example, was particularly popular with housewives. One person who viewed this legal system with skepticism was a Los Angeles doctor named Henry Smith Williams. When a small number of his patients became addicted, he was disgusted, and he came to see them as despicable “weaklings.” So when opiates and cocaine were banned in 1914, he welcomed this first birth-pang of the drug war with glee.
But then he noticed what happened to his addicted patients. They didn’t stop using. Instead, “here were tens of thousands of people, in every walk of life, frantically craving drugs that they could in no legal way secure,” he wrote in one of his books. “They craved the drugs, as a man dying of thirst craves water. They must have the drugs at any hazard, at any cost.”
At the same time, Smith Williams realized that the drug war was “in effect ordering a company of drug smugglers into existence.” Because pharmacists could no longer sell these drugs, the Mafia and other criminal organizations stepped in, selling a vastly inferior product at extortionate prices. In the pharmacies, morphine had cost two or three cents a grain, but the criminal gangs charged a dollar.
The death rate among addicts rose, and those who survived began to behave very differently. An official government study had found that, before the drug war kicked in, three-quarters of self-described addicts had steady and respectable jobs: some 22% were wealthy, while only 6% were poor. They were more sedate as a result of their addiction, but they were rarely out of control or criminal. Yet faced with the need to meet these extortionate new prices, many of the men started to commit property crimes, and many of the women started to steal or prostitute themselves.
So Smith Williams watched as the drug war created two waves of crime: first a wave of violent criminal drug-dealers, and then a wave of criminality among addicts. “The United States government,” Henry wrote in shock, had become “the greatest and most potent maker of criminals in any recent century.”
Johann Hari, “A 1930s California story shows why the war on drugs is a failure”, Los Angeles Times, 2017-06-16.
June 18, 2019
Blitzkrieg on Speed – Nazis on Crystal Meth Part 2 – WW2 SPECIAL
World War Two
Published on 17 Jun 2019While many armies use performance enhancing drugs during WW2, the Wehrmacht takes it to extremes in 1940, with more than debatable consequences.
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvJoin our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesHosted by: Indy Neidell
Written by: Astrid Deinhard, Joram Appel and Spartacus Olsson
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Post Production Director: Wieke Kapteijns
Research by: Joram Appel and Astrid Deinhard
Edited by: Spartacus Olsson
Sound Engineering: Joakim BrodénColorisations by Spartacus Olsson
Archive by Reuters/Screenocean http://www.screenocean.com
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
1 hour ago
Read before you comment; “it wasn’t just the Germans” This video treats the use of methamphetamine by the German Wehrmacht and its cultural background. The purpose of this video is not to attribute any atrocities that the Nazis perpetrated to that they were simply on drugs – we know that this was not a contributing factor to what they did, although it perhaps influenced how they did it. It is also not the purpose of this video to single out Germany as the only belligerent to use drugs in WW2. As we point out in the video, many belligerents (to not say all) used drugs, especially amphetamines during WW2. In fact amphetamines are still in official, monitored used by for instance the US Army in some situations to this day. However, the Wehrmacht and a few of the Axis allies used methamphetamine which is different than amphetamine as the effects of meth is unpredictable and comes on faster and harder. These unpredictable effects include hallucinations and delusions, which amphetamines do not induce, or at least to a lesser and more predictable degree. Methamphetamine metabolizes into amphetamine in the body, but in that process it creates a number of side effects that contribute to its unstable effects. Of course this was poorly understood in 1940 and meth was also available commercially over the counter in many places like the US and Australia, mostly as a dieting pill and (somewhat ironically) an anti-depressant. While amphetamines like Benzedrine are still administered by doctors for certain conditions, methamphetamine is now known to be a very dangerous, potentially lethal, drug that only has recreational use, and in 2019 it is therefore illegal almost everywhere in the world. Last but not least, the Wehrmacht was singular in how liberal they were in distributing drugs to the troops, at least to begin with. It is important to also point out that beside the official use of drugs, many soldiers throughout the ages have resorted to intoxicating themselves to deal with the unfathomable horrors of war, and in this respect WW2 was no different. We will cover drug use by other belligerents and in general during the war in future videos.
June 12, 2019
High Hitler! – Nazis on Crystal Meth Part 1 – WW2 SPECIAL
World War Two
Published on 11 Jun 2019You might have heard he a was vegetarian. You might have heard that he shunned alcohol. You might have heard he was anti-tobacco. Then you might think he was against hard drugs as well, but you’d be wrong…
Join us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory
Or join The TimeGhost Army directly at: https://timeghost.tvFollow World War Two on Instagram @World_war_two_realtime https://www.instagram.com/world_war_t…
Join our Discord Server: https://discord.gg/D6D2aYN.
Between 2 Wars: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list…
Source list: http://bit.ly/WW2sourcesWritten and Hosted by: Indy Neidell
Produced and Directed by: Spartacus Olsson and Astrid Deinhard
Executive Producers: Bodo Rittenauer, Astrid Deinhard, Indy Neidell, Spartacus Olsson
Creative Producer: Joram Appel
Research by: Spartacus Olsson
Edited by: Wieke Kapteijns
Sound design: Joakim BrodénColorisations by Julius Jääskeläinen https://www.facebook.com/JJcolorization/
A TimeGhost chronological documentary produced by OnLion Entertainment GmbH.
From the comments:
World War Two
2 hours ago (edited)
This is the first of our specials on drug use in the Third Reich, and this episode is about the drug addiction of Adolf Hitler himself. As Indy mentions in the video, YouTube regularly demonetises our content. Instead, we fully rely on our Patreon supporters to finance these series and this special. What doesn’t help, is that YouTube algorithm recommends demonetised episodes less, even further limiting our efforts. So, please share this video with your brothers and sisters, your friends, neighbours, your grandma and your history teacher. And make sure to turn on your notifications! And if you really like what we do – please consider supporting us on https://www.patreon.com/TimeGhostHistory or at https://timeghost.tv.
April 10, 2019
Theodore Dalrymple on obesity
His latest in the New English Review:
It hardly requires me to point out that obesity has become a greater threat to the health of the human population in most parts of the world than famine. There was a wonderful cartoon recently in the British magazine, The Oldie, which captured this perfectly. A mother is taking a plate of food away from her child, who is protesting. “Think of the obese millions!” she says to him. When I was young, of course, we were told to finish what was on our plate and to think of the starving millions. Being a precocious little brat, I used to ask how eating what I did not want would help them. Let us just say that the reply was seldom well-reasoned, either in form or content.
It has now become an almost unassailable orthodoxy, at least in medical journals, that obesity is an illness in and of itself: that is to say, it does not merely have medical consequences, but — even without those consequences — is a disease. To be fat is, ipso facto, to be ill, in the same sense as to have Parkinson’s disease is to be ill.
Nor, according to the modern orthodoxy, is obesity to be considered the natural consequence of bad or foolish individual choices, a lack of self-control. That would be to blame the victim. The fat person is in effect the vector of forces that play upon him or her, without any contribution on his or her part.
This is an idea of long gestation. Reading an old text on obesity, published in 1975, and edited by one of my medical mentors, I came across the following quote from a paper written in 1962:
I wish to propose that obesity is an inherited disorder and due to a genetically determined defect in an enzyme: in other words that people who are fat are born fat, and nothing much can be done about it.
This is like saying that addicted people are born to be addicted, and until doctors discover a technical means of stopping their addiction, they might as well make no efforts on their own behalf. No doubt the people who adhere to this view – that obesity and addiction are illnesses simpliciter – think they are being generous but in fact they are forging psychological manacles. No doubt the fat woman in the bakery was at some level trying to prove to herself that obesity was a fatality and not under any possible individual control.
But is the theory in accord with the scene I have described above? In fact, the scene might lead us to a more nuanced or less categorical view of the problem of obesity (and, by extension, of other social problems) than we might at first adopt.
March 4, 2019
December 29, 2018
QotD: Booze, smokes, and heroin
It is now impolite to refer to habitual drunkards. They are “alcoholics,” supposedly suffering from a complaint that is not their fault. The curious variable ambiguity of Alcoholics Anonymous on this point has added to the confusion. AA, to begin with, asked its adherents to admit they had no control over themselves, as a preliminary to giving that power to God. Somehow I suspect that God plays less of a part in modern AA doctrine, but the idea of powerlessness remains. Members of the organization quietly moved from calling alcoholism an “illness” or a “malady” to describing it as a “disease,” round about the time that the medical profession began to do the same thing.
We are ceaselessly told that cigarettes are “addictive.” Most powerfully, most of us believe that the abusers of the illegal drug heroin are “addicted” to it. Once again, the public, the government, and the legal and medical systems are more or less ordered to believe that users of these things are involuntary sufferers. A British celebrity and alleged comedian, Russell Brand, wrote recently, “The mentality and behaviour of drug addicts and alcoholics is wholly irrational until you understand that they are completely powerless [my emphasis] over their addiction and, unless they have structured help, they have no hope.”
Brand is a former heroin abuser who has by now rather famously given up the drug. But how can that be, if what he says about addiction is true? The phrase “wholly irrational” simply cannot withstand the facts of Brand’s own life. It will have to be replaced by something much less emphatic — let us say, “partly irrational.” The same thing happens to the phrase “completely powerless.” Neither the adverb nor the adjective can survive. Nor can the word “addiction” itself, which is visibly evaporating. We have to say “they struggle over their compulsion.”
Peter Hitchens, “The Fantasy of Addiction”, First Things, 2017-02.