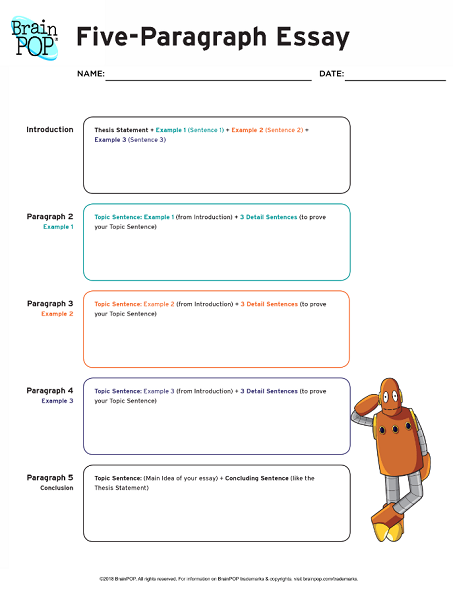
In Aeon, David Labaree discusses the good intent and terrible results of forcing students to rigidly follow the “five paragraph” model of essay writing:
Schools and colleges in the United States are adept at teaching students how to write by the numbers. The idea is to make writing easy by eliminating the messy part – making meaning – and focusing effort on reproducing a formal structure. As a result, the act of writing turns from moulding a lump of clay into a unique form to filling a set of jars that are already fired. Not only are the jars unyielding to the touch, but even their number and order are fixed. There are five of them, which, according to the recipe, need to be filled in precise order. Don’t stir. Repeat.
So let’s explore the form and function of this model of writing, considering both the functions it serves and the damage it does. I trace its roots to a series of formalisms that dominate US education at all levels. The foundation is the five-paragraph essay, a form that is chillingly familiar to anyone who has attended high school in the US. In college, the model expands into the five-section research paper. Then in graduate school comes the five-chapter doctoral dissertation. Same jars, same order. By the time the doctoral student becomes a professor, the pattern is set. The Rule of Five is thoroughly fixed in muscle memory, and the scholar is on track to produce a string of journal articles that follow from it. Then it’s time to pass the model on to the next generation. The cycle continues.
Edward M White is one participant in the cycle who decided to fight back. It was the summer of 2007, and he was on the plane home from an ordeal that would have crushed a man with a less robust constitution. An English professor, he had been grading hundreds of five-paragraph essays drawn from the 280,000 that had been submitted that June as part of the Advanced Placement Test in English language and composition. In revenge, he wrote his own five-paragraph essay about the five-paragraph essay, whose fourth paragraph reads:
The last reason to write this way is the most important. Once you have it down, you can use it for practically anything. Does God exist? Well you can say yes and give three reasons, or no and give three different reasons. It doesn’t really matter. You’re sure to get a good grade whatever you pick to put into the formula. And that’s the real reason for education, to get those good grades without thinking too much and using up too much time.
White’s essay – “My Five-Paragraph-Theme Theme” – became an instant classic. True to the form, he lays out the whole story in his opening paragraph:
Since the beginning of time, some college teachers have mocked the five-paragraph theme. But I intend to show that they have been mistaken. There are three reasons why I always write five-paragraph themes. First, it gives me an organisational scheme: an introduction (like this one) setting out three subtopics, three paragraphs for my three subtopics, and a concluding paragraph reminding you what I have said, in case you weren’t paying attention. Second, it focuses my topic, so I don’t just go on and on when I don’t have anything much to say. Three and only three subtopics force me to think in a limited way. And third, it lets me write pretty much the same essay on anything at all. So I do pretty well on essay tests. A lot of teachers actually like the five-paragraph theme as much as I do.
Note the classic elements of the model. The focus on form: content is optional. The comfortingly repetitive structure: here’s what I’m going to say, here I am saying it, and here’s what I just said. The utility for everyone involved: expectations are so clear and so low that every writer can meet them, which means that both teachers and students can succeed without breaking a sweat – a win-win situation if ever there was one. The only thing missing is meaning.
For students who need a little more structure in dealing with the middle three paragraphs that make up what instructors call the “body” of the essay, some helpful tips are available – all couched in the same generic form that could be applicable to anything. According to one online document by a high-school English teacher:
The first paragraph of the body should contain the strongest argument, most significant example, cleverest illustration, or an obvious beginning point. The first sentence of this paragraph should include the “reverse hook” which ties in with the transitional hook at the end of the introductory paragraph. The topic for this paragraph should be in the first or second sentence. This topic should relate to the thesis statement in the introductory paragraph. The last sentence in this paragraph should include a transitional hook to tie into the second paragraph of the body.
You probably won’t be surprised that the second paragraph “should contain the second strongest argument, second most significant example, second cleverest illustration, or obvious follow-up to the first paragraph …” And that the third paragraph “should contain the third strongest argument …” Well, you get the picture.