WW2TV
Published 19 Aug 2021One Day in August — Dieppe Anniversary Battlefield Event (Operation Jubilee) With David O’Keefe, Part 3 — Anniversary Battlefield Event.
David O’Keefe joins us for a third and final show about Operation Jubilee to explain how the plan unravelled and how the nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died. We will use aerial footage, HD footage taken in Dieppe last week and maps, photos, and graphics.
In Part 1 David O’Keefe talked about the real reason for the raid on Dieppe in August 1942. In Part 2 David talked about the plan for Operation Jubilee. The intentions of the raid and how it was supposed to unfold.
(more…)
August 19, 2023
One Day in August – Dieppe Anniversary Battlefield Event (Operation Jubilee)
August 21, 2015
Allocating the blame for “Operation Jubilee”
In a BBC post from a few years back, Julian Thompson looks at the Dieppe raid:
On 19 August 1942, a disastrous seaborne raid was launched by Allied forces on the German-occupied French port of Dieppe. Why was such a raid ever undertaken? Because, with Germany operating deep in the Soviet Union, the Russians were urging the Allies to relieve the pressure on them by opening a second front in north-west Europe.
At the same time the British Chief of Combined Operations, Rear Admiral Louis Mountbatten, was agitating for a practical trial beach landing, against real opposition, for his troops. In the face of this pressure, Churchill decided that Operation Rutter, a ‘hit and run’ raid on Dieppe, should go ahead.
[…]
Churchill and the Chiefs of Staff — the heads of the Navy, Army and Air Force, who met daily to discuss strategy and advise Churchill — were responsible for this disastrous misjudgement. But, because no written record exists of the Chiefs of Staff approving the raid in its final form, it has sometimes been suggested that it was really Mountbatten who remounted it without authorisation. This is almost certainly nonsense.
The Chiefs of Staff disliked Mountbatten, regarding him as an upstart foisted on them by Churchill, so any unauthorised action on his part would have given them the ammunition to recommend his removal. Since Mountbatten was not removed, and the Chief of the Imperial General Staff, General Sir Alan Brooke, in his frank and detailed diary, makes no mention of his having exceeded his authority, it seems unlikely that Mountbatten can be accused of mounting the raid without authority.
General Brooke was in the Middle East from 1 August 1942, returning on the 24th, after the event. This was unfortunate, for, as the most forceful and intelligent of the Chiefs of Staff, had he been in Britain in the days preceding the raid, he might have persuaded Churchill to call it off.
Much has been said since about the fact that the Dieppe raid was a necessary precursor to the great amphibious operations that were to follow, in terms of the lessons learned and experience gained. Mountbatten pursued that line all his life. But as Chief of Combined Operations, he did bear some of the responsibility for mounting the operation, so one can only comment, ‘he would say that, wouldn’t he?’
The disaster did point up the need for much heavier firepower in future raids. It was recognised that this should include aerial bombardment, special arrangements to be made for land armour, and intimate fire support right up to the moment when troops crossed the waterline (the most dangerous place on the beach) and closed with their objectives.
However, it did not need a debacle like Dieppe to learn these lessons. As judged by General Sir Leslie Hollis — secretary to the Chiefs of Staff Committee and deputy head of the Military Wing of the War Cabinet with direct access to Churchill — the operation was a complete failure, and the many lives that were sacrificed in attempting it were lost with no tangible result.
August 19, 2014
The Prime Minister’s statement on the 72nd anniversary of Operation Jubilee
It was a bloody shambles, but we still remember the bravery and sacrifice of the troops who went ashore at Dieppe in 1942:
On August 19, 1942, nearly 5,000 Canadian troops, along with British and American Allies, undertook a raid on Dieppe to test new equipment, probe the strength of German defences and gain the experience necessary for a larger amphibious assault.
The majority of the forces that attacked that day at five different points along the 16 km front encountered stiff resistance, unexpected obstacles, and a well-entrenched, well-prepared enemy. The Canadians fought on, through machine gun fire, mortar barrages, and sniper and air attacks.
The lessons learned at Dieppe and subsequent landings proved invaluable for the D-Day invasion and were instrumental in saving countless lives on June 6, 1944. Sadly, the Raid on Dieppe came at a steep price for Canadian participants, with 916 making the ultimate sacrifice and 1,900 taken as prisoners of war.
On this solemn day, let us remember the courage and sacrifice of the thousands of Canadians who fought with bravery and determination at Dieppe to free Europe from Nazi tyranny and ensure the peace and freedom that we enjoy today.
Lest we forget.
August 19, 2023
Dieppe Raid – 19 August, 1942
The History Chap
Published 15 Aug 2021The Dieppe Raid (codename Operation Jubilee) was a disastrous amphibious landing by the allies in France during World War 2. Nearly 4,000 allied soldiers (mainly Canadians) were killed, wounded or captured during the Battle of Dieppe.
1942 was turning out to be a bad year for the allies. The Nazis were sweeping forwards in Russia, the Japanese were sweeping though South East Asia. The British commonwealth troops were being pushed back by the Germans & Italians in North Africa and the Americans were still reeling from the attack on Pearl Harbour.
The British wanted to show that they were still willing to take the offensive in the war and were were being urged by Stalin to take some pressure off the Soviet Union. A plan was hatched to conduct a “smash & grab” raid on the port of Dieppe in northern France. The aim was to seize Dieppe and hold it for a limited time before evacuation, during which time the allied troops would collect intelligence and destroy German military infrastructure.
The Canadian government were keen to have their own troops play a role in the war and so the majority of the raiding force was made up of their troops. Initially planned for early July, Operation Jubilee was delayed for over a month due to bad weather and the need for a high tide at dawn. Eventually the Dieppe Raid took place just before 0400 on the 19th August 1942. 5,000 Canadians, 1,000 British and 50 US Rangers were to land at five different points along a 16km (10 mile front) either side of the port of Dieppe itself.
The result was a complete disaster. No major objectives were achieved, poor intelligence had not identified the strength of the German defences and the Germans were on high alert for a possible attack after the firefight at sea and the fact that there was high tide. Within less than 6 hours of the landing starting the order had been given to evacuate and by 1400 hours what remained of the allied force had been successfully removed.
The Dieppe Raid lasted 10 hours. They left behind 4,000 killed, wounded or prisoners of war — over 80% of whom were Canadians. The Royal Navy lost a destroyer and 33 landing craft whilst the RAF lost 106 planes.
The raid had sent a signal to the Germans that the Atlantic shoreline was not secure. That eventually they would have to fight the war on two fronts. It also raised morale within the population of occupied France. They were not alone. The best that can be said for the raid was that it taught the allies valuable lessons which were successfully implemented in the D-Day landings in Normandy in 1944. Maybe the sacrifice of the young men at Dieppe saved many more young men on D-Day.
(more…)
August 18, 2023
One Day in August – Dieppe – Part 2 – The Plan
WW2TV
Published 17 Jan 2021Part 2 – The Plan With David O’Keefe
David O’Keefe joins us again. In Part 1 he talked about the real reason for the raid on Dieppe in August 1942. In Part 2 we talk about the plan for Operation Jubilee and David will share his presentation about the intentions of the raid and how it was supposed to unfold.
A final show sometime in the summer will come live from Dieppe to explain how the plan unravelled and how the nearly 1,000 British, Canadian and American commandos died.
(more…)
July 10, 2018
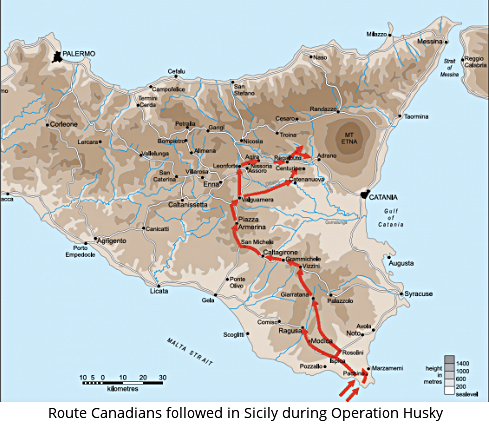
Operation Husky with the “D-Day Dodgers”
On this day in 1943, the Allies invaded Sicily as their first step toward knocking Italy out of the war. It was the first major allied operation (other than the abortive Operation Jubilee in 1942) in which a major formation of the Canadian Army took part. The 1st Canadian Infantry Division under the command of Major General Guy Simonds was part of General Montgomery‘s Eighth Army, which landed on the southeast coast of the island.
The Canada History Project describes the Canadian participation in Operation Husky:
The men were young, of course, many just 18 to 24 years old. The roads were narrow dirt tracks switchbacking over steep, volcanic mountains. Temperatures hovered around 37 degrees, turning water bottles into hot water bottles, as one soldier put it. Three dry and dusty weeks into the campaign, there was a five-hour downpour, and all the troops relished the chance to shower off the dirt caked to their skin. By this time they were well into the middle of the island where their enemy was the fierce Hermann Goering division of the German army.
For six weeks, from July 10th to August 17th 1943, the Canadians, fighting as an independent unit for the first time, slogged through the interior of Sicily as part of Operation Husky, the first stage of taking back Europe from the Nazis after four years of war. Meanwhile, the Americans skirted the more level western coastline of the island and the British came up the east side, each competing with the other for glory.
American General Patton wrote in a letter, “This is a horse race in which the prestige of the US Army is at stake…we must take Messina before the British.”
That may be the way the generals saw it. For the soldiers, pushing through, village by village, mountaintop by mountaintop, it was no game.
Sicily, a rural mountainous island known for its orange groves and almond orchards, olives and the Mafia, sits strategically in the Mediterranean off the foot of Italy. The Canadian contingent was 25,000 strong. All men and materials were brought in by sea, making it the largest amphibious operation yet, though D-Day, a year later, would be bigger still.
In the first few days the Canadians passed through an area that is now a Unesco World Heritage site. Today tourists come to this southeast corner of Sicily to see the restored baroque architecture. But the young Canadian lads were eyeing the pillboxes, watching for snipers and lookouts. In the early days many Italian soldiers surrendered without too much resistance and the local people gave them grapes and oranges to quench their thirst in the scorching heat.
[…]
Operation Husky did succeed in gaining back the first European soil for the Allies. In the midst of it, Mussolini resigned and soon after Italy surrendered, another goal of the campaign. It started a second front forcing Hitler to back off his aggressive attack on our ally, Russia. And it provided a rehearsal for the larger amphibious landing on the beaches of Normandy, France in June of 1944. As well, it was the first time Canadians had fought as an independent unit. Their young commander was Guy Simonds. 1200 Canadians were wounded in Sicily and 562 died there. 490 of them are buried in the Canadian cemetery at Agira.
For their efforts, the soldiers fighting in Sicily and Italy became known as the “D-Day Dodgers”, a careless epithet supposedly delivered by Lady Astor, but embraced by the soldiers themselves who, with some sarcastic humour, turned it into the song, “We are the D-Day Dodgers, in sunny Italy…”
The Canadian part of the campaign from canadiansoldiers.com:
Sailing secretly at the end of June, the Division took its place on the left flank of General Bernard Montgomery’s famed Eighth Army for the Sicilian landings. The amphibious attack against Pachino peninsula was an unqualified success. The defenders were surprised and overrun with very few Allied casualties, and so began a controversial 38-day campaign. General Simonds’ troops advanced inland under difficulties:
The weather was extremely hot, the roads extremely dusty, and there was little transport; the troops were fresh from a temperate climate and a long voyage in crowded ships; and even though for a time there was scarcely any opposition, mere marching was a very exhausting experience under these conditions.
Continuing over the rocky terrain, they had their first fight with the Germans at Grammichele on 15 July. Three days later they captured Valguarnera. Both were rear-guard actions by a withdrawing enemy, and the first real tests came on the July 20 at Assoro and Leonforte. At the former, the 1st Brigade launched a surprise attack at night against an ancient Norman stronghold on the summit of a lofty peak. They seized and held their place in the face of fierce counter attacks, the records for the 15th Panzer Grenadier Division afterwards revealing generous tributes to the fieldcraft (Indianerkrieg) of the Canadians. Leonforte, an equally difficult situation, was captured by the 2nd Brigade after a bitter fight. These three days cost the Division about 275 casualties.
The advance then turned the east towards Adrano, at the base of Mount Etna. In their path stood Agira, “one of the most imposing of Sicily’s innumerable hill-towns,” and in the neighbouring hills the enemy put up a stubborn resistance. Both the 1st and 2nd Brigades were heavily engaged during the last week of July. The operations were, however, effectively supported by Canadian tanks and by the divisional artillery, reinforced by units of the Royal Artillery. General Simonds also had temporarily under his command the 231st British Infantry Brigade (the Malta Brigade), which threatened German communications from the south. After a bitter struggle Agira was captured on the 28th. Between Agira and Adrano the Hermann Goering Division made a stand at Regalbuto, using tanks as pillboxes in the debris of the town. While part of the 1st Division loosened the enemy’s grip on this town, the 3rd Brigade, temporarily under the command of the British 78th Infantry Division, assisted that formation in the Dittaino Valley.
American encircling operations in the western and northern districts of the island, combined with steady British pressure north of the Catania Plain, forced the enemy out of the defences based on Etna, and the campaign ended when the Allies entered Messina on 16-17 Aug. The 1st Division had performed all of its allotted tasks and had acquired valuable battle experience at a total cost of 2,155 casualties. The measure of the achievement was contained in General Montgomery’s statement: “I now consider you one of my veteran Divisions.”
The Division passed from XXX Corps to XIII Corps on 10 Aug, and moved to a concentration area in the rear on 11-13 Aug, relieved of operational responsibilities. Divisional headquarters moved to Francofonte. During the battle of Sicily they had travelled 120 miles, over largely rough and mountainous terrain.
August 31, 2017
The Dieppe raid and the failure of the Churchill tank
Published on 15 Oct 2010
The Dieppe Raid, also known as the Battle of Dieppe, Operation Rutter and, later, Operation Jubilee, was a Second World War Allied attack on the German-occupied port of Dieppe. The raid took place on the northern coast of France on 19 August 1942. The assault began at 5:00 a.m. and by 10:50 a.m. the Allied commanders were forced to call a retreat. Over 6,000 infantrymen, predominantly Canadian, were supported by a Canadian Armoured regiment and a strong force of Royal Navy and smaller Royal Air Force landing contingents. It involved 5,000 Canadians, 1,000 British troops, and 50 United States Rangers.
Objectives included seizing and holding a major port for a short period, both to prove that it was possible and to gather intelligence. Upon retreat, the Allies also wanted to destroy coastal defences, port structures and all strategic buildings. The raid had the added objectives of boosting morale and demonstrating the firm commitment of the United Kingdom to open a western front in Europe.
Virtually none of these objectives were met.
October 26, 2015
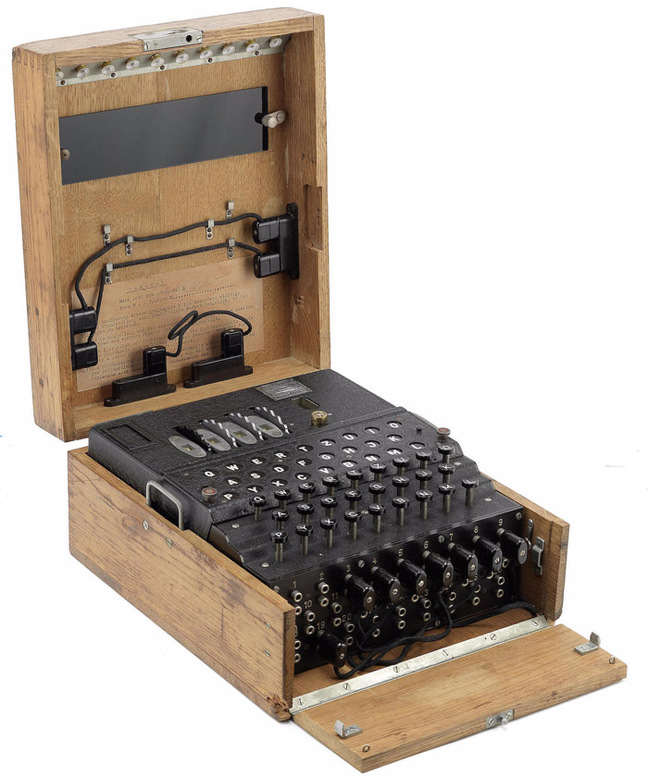
Going price for a working Enigma machine – $365,000
Lester Haines reports on a recent record auction price for an Enigma machine:
A fully-functioning four-rotor M4 Enigma WW2 cipher machine has sold at auction for $365,000.
The German encryption device, as used by the U-Boat fleet and described as “one of the rarest of all the Enigma machines”, went under the hammer at Bonham’s in New York last night as part of the “Conflicts of the 20th Century” sale.
The M4 was adopted by the German Navy, the Kriegsmarine, in early 1942 following the capture of U-570 in August 1941*. Although the crew of U-570 had destroyed their three-rotor Enigma, the British found aboard written material which compromised the security of the machine.
The traffic to and from the replacement machines was dubbed “Shark” by codebreakers at Bletchley Park. Decryption proved troublesome, due in part to an initial lack of “cribs” (identified or suspected plaintext in an encrypted message) for the new device, but by December 1942, the British were regularly cracking M4 messages.
I recently read David O’Keefe’s One Day in August, which seems to explain the otherwise inexplicable launch of “Operation Jubilee”, the Dieppe raid … in his reading, the raid was actually a cover-up operation while British intelligence operatives tried to snatch one or more of the new Enigma machines (like the one shown above) without tipping off the Germans that that was the actual goal. Joel Ralph reviewed the book when it was released:
One Day in August, by David O’Keefe, takes a completely different approach to the Dieppe landing. With significant new evidence in hand, O’Keefe seeks to reframe the entire raid within the context of the secret naval intelligence war being fought against Nazi Germany.
On February 1, 1942, German U-boats operating in the Atlantic Ocean switched from using a three-rotor Enigma code machine to a new four-rotor machine. Britain’s Naval Intelligence Division, which had broken the three-rotor code and was regularly reading German coded messages, was suddenly left entirely in the dark as to the positions and intentions of enemy submarines. By the summer of 1942, the Battle of the Atlantic had reached a state of crisis and was threatening to cut off Britain from the resources needed to carry on with the war.
O’Keefe spends nearly two hundred pages documenting the secret war against Germany and the growth of the Naval Intelligence Division. What ties this to Dieppe and sparked O’Keefe’s research was the development of a unique naval intelligence commando unit tasked with retrieving vital code-breaking material. As O’Keefe’s research reveals, the origins of this unit were at Dieppe, on an almost suicidal mission to gather intelligence they hoped would crack the four-rotor Enigma machine.
O’Keefe has uncovered new documents and first-hand accounts that provide evidence for the existence of such a mission. But he takes it one step further and argues that these secret commandos were not simply along for the ride at Dieppe. Instead, he claims, the entire Dieppe raid was cover for their important task.
It’s easy to dismiss O’Keefe’s argument as too incredible (Zuehlke does so quickly in his brief conclusion [in his book Operation Jubilee, August 19, 1942]). But O’Keefe would argue that just about everything associated with combined operations defied conventional military logic, from Operation Ruthless, a planned but never executed James Bond-style mission, to the successful raid on the French port of St. Nazaire only months before Dieppe.
Clearly this commando operation was an important part of the Dieppe raid. But, while the circumstantial evidence is robust, there is no single clear document that directly lays out the Dieppe raid as cover for a secret “pinch by design” operation to steal German code books and Enigma material.
August 19, 2013
The Dieppe Raid
The Laurier Centre for Military Strategic and Disarmament Studies has a two-part post on the Dieppe raid and the decision-making process that led up to the operation:
Professor Emeritus Terry Copp, director of the Laurier Centre for Military Strategic and Disarmament Studies presents “The Dieppe Raid: A Decision-Making Exercise – Part 1: Operation Rutter.” This lecture, which explores Operation Rutter – the precursor to Operation Jubilee (the Dieppe Raid) – is the first in a series of two videos which will make up this decision-making exercise. The next video (Part Two) focuses entirely on Operation Jubilee and can be found here.
This decision-making exercise is offered as part of the outreach activities of the Laurier Centre for Military Strategic and Disarmament Studies at Wilfrid Laurier University, Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The exercise is based on the one we use to engage students in critical historical thinking at the strategic and operational level without the benefit of hindsight.
The main question we would like you to consider while watching these lectures is:
After being presented with the same information that decision-makers had in 1942, would you still launch the Dieppe Raid?
Additional information will pop up throughout the video through the “Annotations” feature, so please do not disable this option while viewing.
June 6, 2013
D-Day 1942 or 1943
At Military History Now, there’s a look at a few of the allied plans for invading France before the actual June 6, 1944 operation:
IKE’S SLEDGEHAMMER
Almost as soon as America entered the war with Nazi Germany, generals Dwight Eisenhower and George Marshall were both lobbying for a strike across the English Channel into France. One plan foresaw a joint British and American assault on either of the French port cities of Cherbourg or Brest as early as the fall of 1942. The operation, codenamed Sledgehammer, would see a force of just six divisions attack, capture and hold either one of the two strategically-vital, deep-water harbours. The force, which likely would have totalled no more than 60,000 men, would have been expected to withstand the inevitable Nazi counterattacks until spring when more reinforcements could arrive. Despite the fact that the Germans would have been free to throw as many as 30 divisions at the invaders, the U.S. Joint Chiefs (as well as the Soviets) endorsed Sledgehammer wholeheartedly. The American commanders seemed to favour any plan that would bring U.S. forces into action in Europe quickly, while Stalin was thrilled at the prospect of an Allied offensive in Western Europe — anything to divert German forces away from the Russian front. Oddly enough, while the mission called for the heavy use of American air and sea power, at the time there was still only a handful of combat-ready U.S. Army units in England. As such, the ground portion of the invasion would be left entirely up to the British military. Cooler heads, namely Prime Minister Churchill, convinced Eisenhower to shelve Sledgehammer – Britain was already stretched thin in Egypt and America still had yet to fully mobilize for the war in Europe. An invasion of France would simply have to wait.OPERATION ROUNDUP
Later in 1942, the Allies roughed out a second plan to put troops ashore in Western Europe the following spring. This operation, dubbed Roundup, called for 18 British and 30 American divisions to hit a series of landing zones along a 200 km stretch of coastline between Boulogne-sur-Mer near Calais and the port of Le Harve. Overhead, more than 5,700 Allied aircraft were to sweep the skies of the Luftwaffe clearing the way for a series of airborne drops. D-Day was set for some time in April or May of 1943. The British, already strained by three years of total war against the Axis, were understandably reluctant to throw their army headlong into the teeth of Germany’s Channel fortifications. They pushed instead to attack Sicily and Italy – what Churchill called the “soft underbelly of Europe” — by way of North Africa. A sober appraisal of British and American fleet strength, air assets and manpower ultimately convinced the Allied high command that no invasion could be mounted until 1944 at the earliest. For one thing, American factories had yet to manufacture enough of the landing craft needed for such a massive undertaking. Washington and London turned their attention instead towards a late 1942 invasion of Tunisia – Operation Torch. The rest is, as they say, history.
As any Canadian military historian would probably have said to either of these proposals … I have two words: Operation Jubilee.
The Dieppe Raid, also known as the Battle of Dieppe, Operation Rutter and, later, Operation Jubilee, was a Second World War Allied attack on the German-occupied port of Dieppe. The raid took place on the northern coast of France on 19 August 1942. The assault began at 5:00 a.m. and by 10:50 a.m. the Allied commanders were forced to call a retreat. Over 6,000 infantrymen, predominantly Canadian, were supported by a Canadian Armoured regiment and a strong force of Royal Navy and smaller Royal Air Force landing contingents.
The objective of the raid was discussed by Winston Churchill in his war memoirs:
“I thought it most important that a large-scale operation should take place this summer, and military opinion seemed unanimous that until an operation on that scale was undertaken, no responsible general would take the responsibility of planning the main invasion…
In discussion with Admiral Mountbatten it became clear that time did not permit a new large-scale operation to be mounted during the summer (after Rutter had been cancelled), but that Dieppe could be remounted (with the new code-name “Jubilee”) within a month, provided extraordinary steps were taken to ensure secrecy. For this reason no records were kept but, after the Canadian authorities and the Chiefs of Staff had given their approval, I personally went through the plans with the C.I.G.S., Admiral Mountbatten, and the Naval Force Commander, Captain J. Hughes-Hallett.”
Objectives included seizing and holding a major port for a short period, both to prove it was possible and to gather intelligence from prisoners and captured materials, including naval intelligence in a hotel in town and a radar installation on the cliffs above it. Although the primary objective was not met and secondary successes were relatively few, some knowledge was gained while assessing the German responses. The Allies also wanted to destroy coastal defences, port structures and all strategic buildings. Due to the failure to secure Dieppe this objective was not met in any systematic sense. The raid had the added objective of providing a morale boost to the troops, Resistance, and general public, while assuring the Soviet Union of the commitment of the United Kingdom and the United States.
A total of 3,623 of the 6,086 men (almost 60%) who made it ashore were either killed, wounded, or captured. The Royal Air Force failed to lure the Luftwaffe into open battle, and lost 96 aircraft (at least 32 to flak or accidents), compared to 48 lost by the Luftwaffe.[2] The Royal Navy lost 33 landing craft and one destroyer. The events at Dieppe later influenced preparations for the North African (Operation Torch) and Normandy landings (Operation Overlord).
Operation Jubilee clearly showed that the plans for both Sledgehammer and Roundup would have been bloody failures.