Fortissax thinks that the rest of Canada has lessons to be learned from Quebec:
If you are a Canadian born at any point in the Post-WWII era, you have been subjected to varying degrees of liberal “Cultural Mosaic” propaganda. This narrative exploits the historic presence of three British Isles ethnic groups (which had already been intermixing for millennia) and the predominantly Norman French settlers to justify the unprecedented mass migration of people from the Third World into Canada. This process only began in earnest in the 1990s before accelerating rapidly in the 2010s.
The Great Canadian Lie is the claim that we’ve “always been multicultural”, as though the extremely small and inconsequential presence of “Black Loyalists” or the historically hostile Indigenous groups (making up only 1% of the population at Canada’s founding in 1867) played any serious role in shaping the Canadian nation, its identity, institutions, or culture. Inspired by Dr. Ricardo Duchesne’s book Canada in Decay: Mass Immigration, Diversity, and the Ethnocide of Euro-Canadians (2017), which chronicled the emergence of two ethnic groups uniquely born of the New World, I delved into the 2021 Census data collected by the Canadian government to explore the ethnic breakdown of White Canadians in greater detail
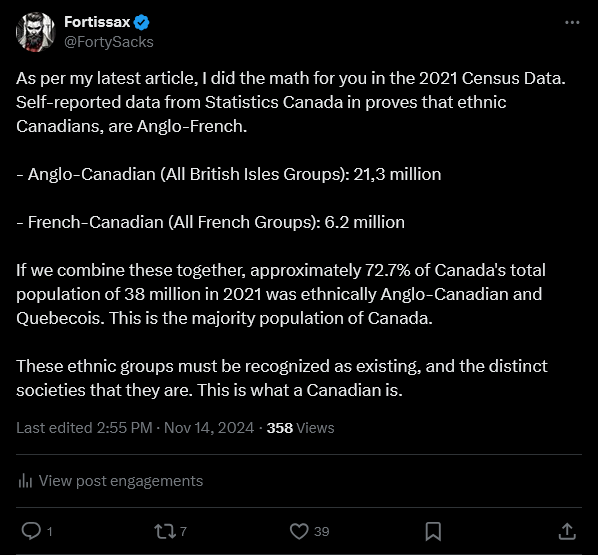
The evidence is clear. In 2021, just four years ago, 72.7% of the entire Canadian population was not just White, but Anglo-Canadian and French-Canadian, representing an overwhelming presence compared to visible minorities and other White ethnic groups, such as the small populations of Germans and Ukrainians.
In the space last night, I highlighted this historical fact and explained to the audience the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Canadian and its significance. While we all recognize that the Québécois are a homogeneous group descended predominantly from Norman French settlers — such as the Filles du Roi and Samuel de Champlain’s 1608 expedition, which established Quebec City with a single-minded purpose — the Anglo-Canadian story also deserves similar recognition for its role in shaping Canada’s identity.
But what is less known is that Anglo-Canadians are just as ethnically homogeneous as the Québécois, from Nova Scotia to British Columbia. Anglo-Canadian identity emerged from Loyalist Americans in the 1750s, beginning with the New England Planters in Nova Scotia — “continentals” with a culture distinct from both England and the emergent Americans. After the American Revolutionary War, they marched north with indomitable purpose, like Aeneas and the Trojans, to rebuild their Dominion. Author Carl Berger, in his influential work The Sense of Power: Studies in the Ideas of Canadian Imperialism, demonstrates that the descendants of Loyalists were the one ethnic group that nurtured “an indigenous British Canadian feeling.” The following passage from Berger’s work is worth citing:
The centennial arrival of the loyalists in Ontario coincided with the fiftieth anniversary of the incorporation of the City of Toronto and, during a week filled with various exhibitions, July 3 was set aside as “Loyalist Day”. On the morning of that day the platform erected at the Horticultural Pavilion was crowded with civic and ecclesiastical dignitaries and on one wall hung the old flag presented in 1813 to the York Militia by the ladies of the county. Between stirring orations on the significance of the loyalist legacy, injunctions to remain faithful to their principles, and tirades against the ancient foe, patriotic anthems were sung and nationalist poetry recited. “Rule Britannia” and “If England to Herself Be True” were rendered “in splendid style” and evoked “great enthusiasm”. “A Loyalist Song”, “Loyalist Days”, and “The Maple Leaf Forever”, were all beautifully sung
The 60,000 Loyalist Americans, who arrived in two significant waves, were soon bolstered by mass settlement from the British Isles. However, British settlers assimilated into the Loyalist American culture rather than imposing a British identity on the new Canadians. The first major wave of British settlers after the Loyalists primarily consisted of the Irish. Before Confederation in 1867, approximately 850,000 Irish immigrants settled in Canada. Between 1790 and 1815, an estimated 6,000 to 10,000 settlers, mainly from the Scottish Highlands and Ireland, also made their way to Canada.
Another large-scale migration occurred between 1815 and 1867, bringing approximately 1 million settlers from Britain to Canada, specifically to Ontario, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. New Brunswick was carved out from the larger province of Nova Scotia to make room for the influx of Loyalists. During this time, settlers from England, Scotland, and Ireland intermingled and assimilated into the growing Anglo-Canadian culture. Scottish immigrants, who constituted 10–15% of this wave, primarily spoke Gaelic upon arrival but adopted English as they integrated.
All settlers from the British Isles spoke English (small numbers spoke Gaelic in case of Scots), were ethnically and culturally similar, and had much more in common with each other than with their continental European counterparts.
Settlement would slow down in the years immediately preceding Confederation in 1867 but surged again during the period between 1896 and 1914, with an estimated 1.25 million settlers yet again from Britain moving to Canada as part of internal migration within the British Empire. These settlers predominantly also [went] to Ontario and the Maritimes, further forging the Anglo-Canadian identity.
A common misconception among Canadians is that Canada “was a colony” of Britain, subordinate to, or a “vassal state”. This is wrong. Canadians were the British, in North America. There were no restrictions on what Canadians could or could not do in their own Dominion. From the first wave of Loyalists onward, Canadians were regularly involved in politics and governance, actively participating in shaping the nation.
Like the ethnogenesis of the English, which saw Angles, Saxons, Jutes, and Frisians converge into a new people and ethnicity (the Anglo-Saxons), Anglo-Canadians are a combination of 1.9 million English, 850,000 Irish (from both Northern and Southern Ireland), and 200,000 Scots, converging with 60,000 Loyalist Americans from the 13 Colonies. These distinct yet similar ethnic groups no longer exist as separate peoples in Canada. Anglo-Canadians are the fusion of the entire British Isles. The Arms of Canada, the favourite symbol of Canadian nationalists today, represents this new ethnic group with the inclusion of the French:
It’s no coincidence that, once rediscovered, the Arms of Canada exploded in popularity as the emblem of Canadian nationalists. Unlike more controversial symbols that appeal to pan-White racial unity, such as the Sonnenrad or Celtic cross, the Arms of Canada resonate as a distinctly Canadian icon, deeply rooted in the nation’s true heritage and history — a heritage that cannot be bought, sold, or traded away. This is an immutable bloodline stretching into the ancient past. If culture is downstream from race, and deeper still, ethnicity, then Canadian culture, values, and identity are fundamentally tied not just its race, but its ethnic composition. The ethnos defines the ethos. Canadians are not as receptive to the abstract idea of White nationalism for the same reason Europeans aren’t — because they possess a cohesive ethnic identity, unlike most White Americans.