The demands for reparations from Britain over the slave trade are not based on the actual history as much as emotion and selective blindness to the facts:

The Official Medallion of the British Anti-Slavery Society, by Josiah Wedgwood 1795.
British Abolition Movement via Wikimedia Commons.
No, no, stop squealing. Yes, slavery was appalling, vile, we’re all damn glad we don’t do it any more. But slave labour was not free.
We could — possibly should — look at the difference between that subsistence level that the slaves got and what free labour — not free as in at no cost, free as in free to choose — got at the same time. The answer being not much difference in fact. If we’re to believe Jason Hickel (which, of course, we shouldn’t) free labour in England got below subsistence incomes. To be Marxist, what was the expropriation from those slaves, from the value of their labour? And, well, not a hugely different amount from that of free labour at the time.
While imperial Britain soared to sustainable economic development and global military superpower status, the enslaved and their descendants were left to this day with enduring pain, persistent poverty and systemic suffering.
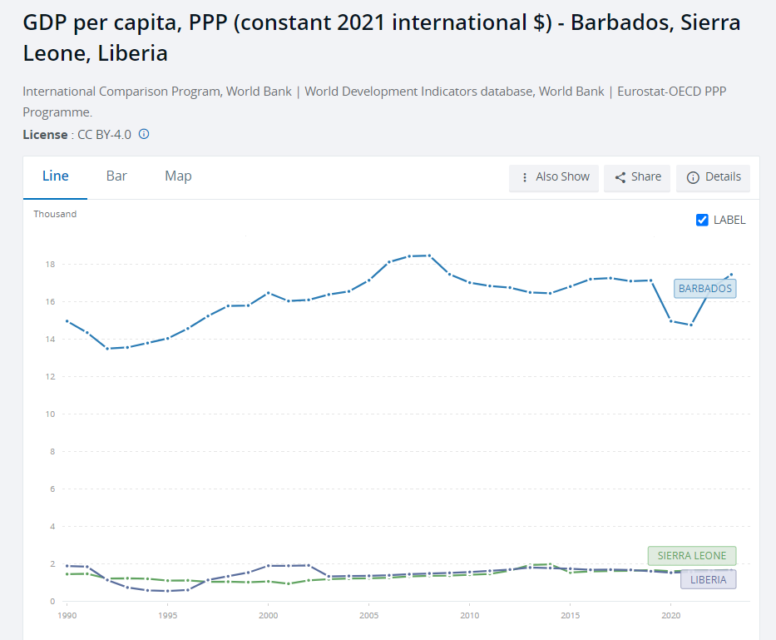
This is, as the cool kids say, problematic. Beckles is from Barbados. So, let us use Barbados numbers. And compare them to Sierra Leone and Liberia. The places that slaves not transported across to their servitude were freed into.
So, Hils, Matey, what is this poverty and pain you’re condemned to?
An obvious point — it’s not possible for us to compensate a man for having made him better off.
But we need to go further too. Britain did not benefit from this labour anyway. We did not then have a state controlled economy, we do not now have a state controlled economy. Britain didn’t own the slaves so it’s not Britain that — even if you can prove that there should be reparations — which should pay for owning the slaves it didn’t.
This does then rather leave the reparations argument being that Barbados — or whoever — needs to go around suing, individually, the estates of those who owned slaves. Good luck with that one.
The so-called Slavery Abolition Act, the most racist legislation ever passed in the British parliament,
Aha, have you ever in your puff seen such a perfect perisher of an argument? That abolition of slavery itself was the most racist legislation ever?
Aha, aha, aha. Becks must have practised that one in the mirror a lot for no audience would be able to hear that without screaming in laughter.
compensation of £20m in cash paid as reparations to the enslavers. The enslaved were valued at £47m, and the remaining amount was paid off with labour in kind for four extra years of enslavement after they were freed. They received no compensation for the theft of their labour or the denial of their human identity.
A £20 million bribe and cheap at twice the price. For that’s what it was. A bribe. One we’re still paying off today — no, Osborne did not pay it off, he issued more gilts to pay off the old ones — and I’m wholly happy to be paying my mite of that amount. Absolute damn bargain, freeing 700k people from slavery for such a trivial sum. As to the slaves, well, they gained their freedom. Which is of value. Actually, that’s rather the point, freedom has value, no?