At Astral Codex Ten, Scott Alexander discusses some of the ideas from Bryan Caplan’s book The Case Against Education:
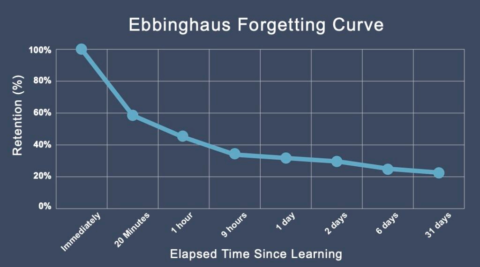
Source here. Note deranged horizontal axis.
Education isn’t just about facts. But it’s partly about facts. Facts are easy to measure, and they’re a useful signpost for deeper understanding. If someone has never heard of Chaucer, Dickens, Melville, Twain, or Joyce, they probably haven’t learned to appreciate great literature. If someone can’t identify Washington, Lincoln, or either Roosevelt, they probably don’t understand the ebb and flow of American history. So what facts does the average American know?
In a 1999 poll, only 66% of Americans age 18-29 knew that the US won independence from Britain (as opposed to some other country). About 47% of Americans can name all three branches of government (executive, legislative, and judicial). 37% know the closest planet to the sun (Mercury). 58% know which gas causes most global warming (carbon dioxide). 44% know Auschwitz was the site of a concentration camp. Fewer than 50% (ie worse than chance) can correctly answer a true-false question about whether electrons are bigger than atoms.
These results are scattered across many polls, which makes them vulnerable to publication bias; I can’t find a good unified general knowledge survey of the whole population. But there’s a great survey of university students. Keeping in mind that this is a highly selected, extra-smart population, here are some data points:
- 85% know who wrote Romeo and Juliet (Shakespeare)
- 56% know the biggest planet (Jupiter)
- 44% know who rode on horseback in 1775 to warn that the British were coming (Paul Revere)
- 33% know what organ produces insulin (pancreas)
- 31% know the capital of Russia (Moscow)
- 30% know who discovered the Theory of Relativity (Einstein)
- 19% know what mountain range contains Mt. Everest (Himalayas)
- 19% know who wrote 1984 (George Orwell)
- 16% know what word the raven says in Poe’s “The Raven” (“Nevermore!”)
- 10% know the captain’s name in Moby Dick (Ahab)
- 7% know who discovered, in 1543, that the Earth orbits the sun (Copernicus)
- 4% know what Chinese religion was founded by Lao Tse (Taoism)
- <1% know what city the general Hannibal was from (Carthage)
Remember, these are university students, so the average person’s performance is worse.
Most of these are the kinds of facts that I would expect school to teach people. Some of them (eg the branches of government) are the foundations of whole subjects, facts that I would expect to get reviewed and built upon many times during a student’s career. If most people don’t remember them, there seems to be little hope that they remember basically anything from school. So what’s school even doing?
Maybe school is why at least a majority of people know the very basics – like that the US won independence from Britain, or that Shakespeare wrote Romeo and Juliet? I’m not sure this is true. Here are some other questions that got approximately the same level of correct answers as “Shakespeare wrote Romeo and Juliet“:
- What is the name of the rubber object hit by hockey players? (Puck, 89%)
- What is the name of the comic strip character who eats spinach to increase his strength? (Popeye, 82% correct)
- What is the name of Dorothy’s dog in The Wizard of Oz? (Toto, 80% correct)
I don’t think any of these are taught in school. They’re absorbed by cultural osmosis. It seems equally likely that Romeo and Juliet could be absorbed the same way. Wasn’t there an Academy-Award-winning movie about Shakespeare writing Romeo and Juliet just a decade or so before this study came out? Sure, 19% of people know that Orwell wrote 1984 – but how many people know the 1984 Calendar Meme, or the “1984 was not an instruction manual!” joke, or have heard of the reality show Big Brother? Nobody learned those in school, so maybe they learned Orwell’s name the same place they learned about the other 1984-related stuff.
Okay, so school probably doesn’t do a great job teaching facts. But maybe it could still teach skills, right?
According to tests, fewer than 10% of Americans are “proficient” at PIIAC-defined numeracy skills, even though in theory you need to know algebra to graduate from most public schools.
I took a year of Spanish in middle school, and I cannot speak Spanish today to save my life; that year was completely wasted. Sure, I know things like “Hola!” and “Adios!”, but I also know things like “gringo” and “Yo quiero Taco Bell” – this is just cultural osmosis again.
So it seems most people forget almost all of what they learn in school, whether we’re talking about facts or skills. The remaining pro-school argument would be that even if they forget every specific thing, they retain some kind of scaffolding that makes it easier for them to learn and understand new things in the future; ie they keep some sort of overall concept of learning. This is a pretty god-of-the-gaps-ish hypothesis, and counterbalanced by all the kids who said school made them hate learning, or made them unable to learn in a non-fake/rote way, or that they can’t read books now because they’re too traumatized from years of being forced to read books that they hate.
It’s common-but-trite to encounter people who say things like “I love learning, but I hated school” — I’ve undoubtedly said that myself many times. A weird experience was having to study a book in school that I’d already read on my own: it was like an early form of aversion therapy … here’s something you loved once, let’s make you hate it now.






