This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Central Railroad of New Jersey (CNJ) by Peter Brill. The first of the two original lines that merged to become the CNJ was granted a charter as the Elizabethtown and Somerville Railroad to create a connection from Elizabeth, New Jersey to Somerville, including a ferry into New York City. The charter was dated 9 February, 1831 and the line was completed in 1842. The Somerville and Easton received a charter in 1847 to connect the existing Elizabethtown line to Easton, Pennsylvania and the new connecting line was leased by the Elizabethtown and Somerville in 1848 and then purchased outright in 1849. The combined railroads merged as the Central Railroad of New Jersey in February of that year.
This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Central Railroad of New Jersey (CNJ) by Peter Brill. The first of the two original lines that merged to become the CNJ was granted a charter as the Elizabethtown and Somerville Railroad to create a connection from Elizabeth, New Jersey to Somerville, including a ferry into New York City. The charter was dated 9 February, 1831 and the line was completed in 1842. The Somerville and Easton received a charter in 1847 to connect the existing Elizabethtown line to Easton, Pennsylvania and the new connecting line was leased by the Elizabethtown and Somerville in 1848 and then purchased outright in 1849. The combined railroads merged as the Central Railroad of New Jersey in February of that year.
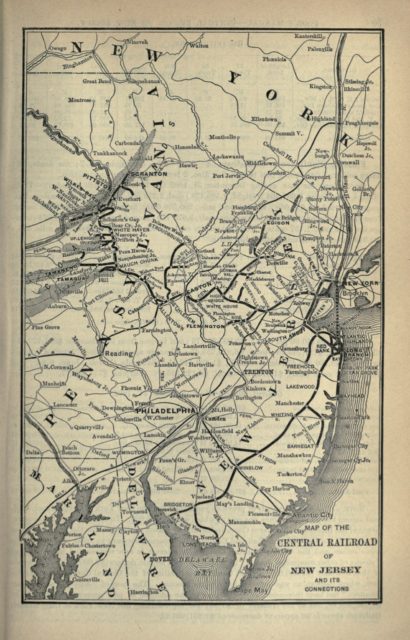
Map of the extent and connections of the Centrail Railroad of New Jersey in 1893.
Poor’s Manual of the Railroads of the United States via Wikimedia Commons.
Click to see full-size image.At its peak, the Central Railroad of New Jersey, the self-proclaimed “Big Little Railroad”, operated only about 700 route-miles, but in keeping with its densely populated region, totaled over 1,900 miles of track, two-thirds in New Jersey. CNJ’s Central Division extended from Jersey City to Phillipsburg, on the Delaware River. The Lehigh & Susquehanna Division (later Central Railroad of Pennsylvania, then the Penn Division) went west from Easton, Pa., to Allentown, then north to Wilkes-Barre and Scranton. The Southern Division, from Red Bank to Bridgeton/Bayside, was reached from Elizabethport via CNJ’s Perth Amboy Branch and the New York & Long Branch.
Although “little” in geographic span — it’s just 191 miles from Jersey City to Scranton — CNJ was “big” in traffic density. Between Jersey City and Raritan, 35 miles of commuter territory, four to six main tracks handled 300 daily commuter trains carrying 35,000 riders plus local freights, longer-distance passenger and freight trains, and, east of Bound Brook Junction, through Baltimore & Ohio/Reading traffic from Philadelphia and beyond.
[…]
CNJ’s evolution from tidewater connection to competing anthracite road coincided with LV [Lehigh Valley] and DL&W [Delaware, Lackawanna & Western] developing their own routes to New York Harbor. CNJ originally based its Pennsylvania operations in Mauch Chunk (now called Jim Thorpe). Narrow-gauge “lokies” worked the Wanamie Colliery on the Nanticoke Branch until 1967, and CNJ hauled the anthracite to Ashley’s Huber Breaker. In 1892, Central States Dispatch, a fast freight route on B&O, Western Maryland, RDG [Reading], CNJ, Lehigh & Hudson River, and New Haven, commenced via Allentown Yard.
In 1893, America’s first automatic, motor-operated semaphore signal was installed on CNJ at Black Dan’s Cut east of Phillipsburg. Installation of twin McMyler car dumpers at Pier 18 in Jersey City in 1919 created CNJ’s foremost destination for anthracite and bituminous coal into the 1960s. In 1925, what is regarded as America’s first successful commercial diesel locomotive, CNJ 1000, a 300 h.p. box-cab, began a 27-year assignment at Bronx Terminal. The bridge over Newark Bay was replaced in 1926 by a 1.4-mile, 4-track, 2-span, lift-type drawbridge. In the 1930s, one of the country’s most modern traffic control towers was installed at Elizabethport to control the convergence of the multi-track Central Division main with the Newark and Perth Amboy branches. E’port also hosted CNJ’s main shops.
Two Blue Comet consists, Packard blue with gold lettering and window bands of Jersey cream, in 1929 introduced luxury coach service at no extra charge between Jersey City and Atlantic City. Later that year, The Bullet debuted similar service between Jersey City and Wilkes-Barre. Specially painted Pacifics handled both: royal and Packard blue with gold striping and lettering for the Comet and dark olive with gold striping and chromium trim for The Bullet. The latter ran only two years, but the Comet lasted until 1941.
CNJ entered a 10-year bankruptcy in 1939 while controlled by the Reading, which in turn was controlled by B&O. During World War II, the German submarine menace diverted eastbound oil products from tanker to tank car, and CNJ delivered up to 1,000 loads a day, half the New York area’s requirement, until pipelines were built. In 1944 CNJ became “Jersey Central Lines” and adopted the Statue of Liberty emblem.