Invicta
Published 13 Mar 2020Support the channel by downloading Rise of Kingdoms: http://patron.me/Invicta, New users can use the code
seyfpw6fxuand claim these prizes: GEM 200, Silver Key x2, 50000 Food x2, 50000 Wood x2Today Carthage is remembered only in the context of its dramatic fall at the end of the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage. We all know about Hannibal and the Battle of Cannae but how about the daily life of Carthage. There is much more to this ancient civilization than the dust and ashes left to us by history. Today we will be exploring the Rise of Carthage and dive into the fascinating details of their civilization.
The history documentary begins by covering the ancient Phoenicians who planted colonies across the Mediterranean. Carthage emerged from this trade network to become the leader of the Phoenicians in the west and eventually come to forge an empire when its mother colony Tyre declined. The history documentary then turns to cover the government, economy, culture, and military of ancient Carthage.
Sources and Suggested Reading:
Carthage: A History by Serge Lancel
The Carthaginians by Dexter Hoyos
Carthage’s Other Wars by Dexter Hoyos
Carthage Must be Destroyed by Richard Miles#History
#Documentary
#Carthage
August 10, 2020
The Rise of Carthage
Russia in Asia (for now)
Ted Campbell looks at some long-frozen geopolitical forces that may become more active in coming years:
The Jamestown Foundation, which some experts describe as mainly non-partisan and relatively unbiased, has published an interesting article by Paul Goble in which he reminds us that “Russia east of the Urals comprises more than two-thirds of the Russian Federation but has only about one-fifth of that country’s population. It is where most of Russia’s natural resources are to be found, though the earnings from their extraction largely go to Moscow and not to local people. The region is located three to ten time zones east of Moscow and is linked to the center by few roads or rail lines. Its people are far closer to China and other Pacific rim countries — including the United States — than to the core of the Russian Federation. Because of their roots in explorers, those fleeing oppression, and those sent there by the state for punishment, eastern Russians have always been more independent minded and entrepreneurial than Russians in central and western Russia. Perhaps the most important measure of this cultural divide is that Protestant faiths dominate the religious scene there, not the Russian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate.”
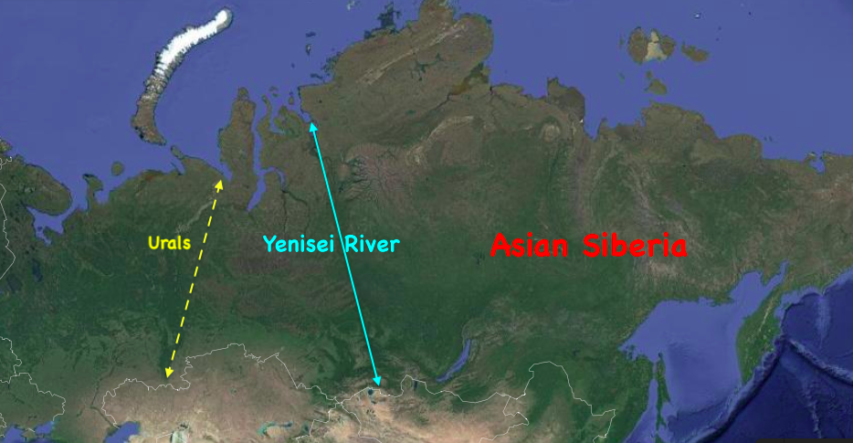
It is related to something I have been saying for a long time: Siberia (essentially everything East of the Yenisei River (some say everything East of the Urals) is Asia …
… while Russia, per se, is an Eastern European country.
[…]
A few years ago a couple of middle-ranked Chinese officials suggested to me that one of China’s long-term strategic plans was (and I’m guessing still is) to encourage separatist movements in Siberia which, they hoped, will succeed in creating three or four (maybe even five or six) “autonomous” states in Siberia which will, like Mongolia, look, primarily to China for trade and support.
China
covetsneeds the resources, including water, that Siberia has. I have, in the past, forecast a Sino-Russian “Water War” in Siberia. But, speaking broadly and generally, the Chinese don’t like wars: they are expensive and unpredictable. They would much rather play a modest, behind the scenes role in creating a handful of weak, independent Siberian states with which they can trade to their advantage. They do not, I was told, wish to annex Siberia ~ some Chinese feel that the Qing Dynasty (1644 to 1912) went too far when it annexed what is now the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (新疆维吾尔自治区) in 18th century.(Tibet is a different matter and most of the Chinese people I know who might wish that Xinjiang was a more autonomous place, more like Kyrgyzstan, for example, believe that Tibetans are Chinese (and Uighurs are not) and Tibet is a “natural” part of China.)
I said a couple of days ago, that “Russia is a pariah state that is flailing about as it withers and dies.” But Putin is flailing about in the wrong directions. The Chinese are, I believe, cultivating and fertilizing Siberian separatist movements with a view to dismembering Russia and “liberating” Siberia. When that happens, and I’m confident that it is NOT an IF, the world will be a much different place.
Donald MacLean: The First of the Cambridge Five
The Cold War
Published 22 Jun 2020Our historical documentary series on the history of the Cold War continues with a video on the famous Cambridge Five and Donald Maclean in particular — a real Cold War-era spy story
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thecoldwar or Paypal: http://paypal.me/TheColdWar
✔ Merch store ► https://teespring.com/stores/thecoldwar
✔ Instagram ► http://www.instagram.com/thecoldwartv#ColdWar #Maclean #CambridgeFive
FDR’s “New Deal” and the Great Depression
The Great Depression began with the collapse of the stock market in 1929 and was made worse by the frantic attempts of President Hoover to fix the problem. Despite the commonly asserted gibe that Hoover tried laissez faire methods to address the economic crisis, he was a dyed-in-the-wool progressive and a life-long control freak (the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act which devasted world trade was passed in 1930). Franklin D. Roosevelt won the 1932 election by promising to undo Hoover’s economic interventions, yet once in office he turned out to be even more of a control freak than Hoover. His economic and political plans made Hoover’s efforts seem merely a pale shadow.
For newcomers to this issue, “New Deal” is the term used to describe the various policies to expand the size and scope of the federal government adopted by President Franklin Delano Roosevelt (a.k.a., FDR) during the 1930s.
And I’ve previously cited many experts to show that his policies undermined prosperity. Indeed, one of my main complaints is that he doubled down on many of the bad policies adopted by his predecessor, Herbert Hoover.
Let’s revisit the issue today by seeing what some other scholars have written about the New Deal. Let’s start with some analysis from Robert Higgs, a highly regarded economic historian.
… as many observers claimed at the time, the New Deal did prolong the depression. … FDR and Congress, especially during the congressional sessions of 1933 and 1935, embraced interventionist policies on a wide front. With its bewildering, incoherent mass of new expenditures, taxes, subsidies, regulations, and direct government participation in productive activities, the New Deal created so much confusion, fear, uncertainty, and hostility among businessmen and investors that private investment, and hence overall private economic activity, never recovered enough to restore the high levels of production and employment enjoyed in the 1920s. … the American economy between 1930 and 1940 failed to add anything to its capital stock: net private investment for that eleven-year period totaled minus $3.1 billion. Without capital accumulation, no economy can grow. … If demagoguery were a powerful means of creating prosperity, then FDR might have lifted the country out of the depression in short order. But in 1939, ten years after its onset and six years after the commencement of the New Deal, 9.5 million persons, or 17.2 percent of the labor force, remained officially unemployed.
Writing for the American Institute for Economic Research, Professor Vincent Geloso also finds that FDR’s New Deal hurt rather than helped.
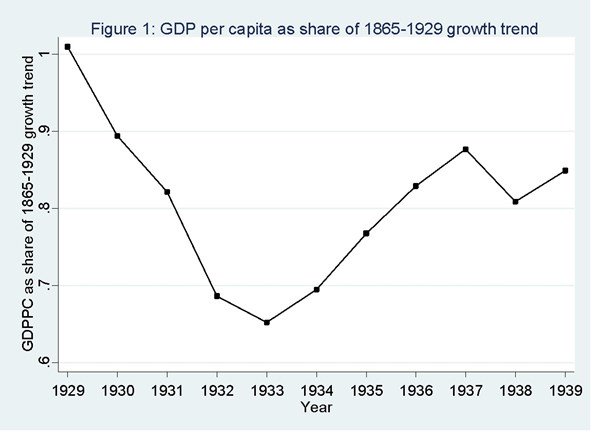
… let us state clearly what is at stake: did the New Deal halt the slump or did it prolong the Great Depression? … The issue that macroeconomists tend to consider is whether the rebound was fast enough to return to the trendline. … The … figure below shows the observed GDP per capita between 1929 and 1939 expressed as the ratio of what GDP per capita would have been like had it continued at the trend of growth between 1865 and 1929. On that graph, a ratio of 1 implies that actual GDP is equal to what the trend line predicts. … As can be seen, by 1939, the United States was nowhere near the trendline. … Most of the economic historians who have written on the topic agree that the recovery was weak by all standards and paled in comparison with what was observed elsewhere. … there is also a wide level of agreement that other policies lengthened the depression. The one to receive the most flak from economic historians is the National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA). … In essence, it constituted a piece of legislation that encouraged cartelization. By definition, this would reduce output and increase prices. As such, it is often accused of having delayed recovery. … other sets of policies (such as the Agricultural Adjustment Act, the National Labor Relations Act and the National Industrial Recovery Act) … were very probably counterproductive.
Here’s one of the charts from his article, which shows that the economy never recovered lost output during the 1930s.
How to Safely Unload & Clear the Four Most Common Rifles
Forgotten Weapons
Published 10 Sep 2016http://www.armamentresearch.com
This is a basic instructional video on unloading and clearing the four most common types of rifles that will be encountered by journalists, aid workers, and other non-combatants in conflict zones today.
Armament Research Services (ARES) is a specialist technical intelligence consultancy, offering expertise and analysis to a range of government and non-government entities in the arms and munitions field. ARES fills a critical market gap, and offers unique technical support to other actors operating in the sector. Drawing on the extensive experience and broad-ranging skillsets of our staff and contractors, ARES delivers full-spectrum research & analysis, technical review, training, and project support services. Our services are often delivered in support of national, regional, and international initiatives, and can be conducted in both permissive and non-permissive environments.
ARES is an apolitical, policy-neutral organisation, providing technical assessments to legitimate customers. We reserve the right to decline any engagement we deem ethically problematic.
United Nations Global Marketplace (UNGM) number: 358103
QotD: Gandhi’s legacy
Some Indians feel that after the early 1930s, Gandhi, although by now world-famous, was in fact in sharp decline. Did he at least “get the British out of India”? Some say no. India, in the last days of the British Raj, was already largely governed by Indians (a fact one would never suspect from this movie), and it is a common view that without this irrational, wildly erratic holy man the transition to full independence might have gone both more smoothly and more swiftly. There is much evidence that in his last years Gandhi was in a kind of spiritual retreat and, with all his endless praying and fasting, was no longer pursuing (the very words seem strange in a Hindu context) “the public good.” What he was pursuing, in a strict reversion to Hindu tradition, was his personal holiness. In earlier days he had scoffed at the title accorded him, Mahatma (literally “great soul”). But toward the end, during the hideous paroxysms that accompanied independence, with some of the most unspeakable massacres taking place in Calcutta, he declared, “And if … the whole of Calcutta swims in blood, it will not dismay me. For it will be a willing offering of innocent blood.” And in his last days, after there had already been one attempt on his life, he was heard to say, “I am a true Mahatma.”
We can only wonder, furthermore, at a public figure who lectures half his life about the necessity of abolishing modern industry and returning India to its ancient primitiveness, and then picks a Fabian socialist, already drawing up Five-Year Plans, as the country’s first Prime Minister. Audacious as it may seem to contest the views of such heavy thinkers as Margaret Bourke-White, Ralph Nader, and J.K. Galbraith (who found the film’s Gandhi “true to the original” and endorsed the movie wholeheartedly), we have a right to reservations about such a figure as a public man.
I should not be surprised if Gandhi’s greatest real humanitarian achievement was an improvement in the treatment of Untouchables — an area where his efforts were not only assiduous, but actually bore fruit. In this, of course, he ranks well behind the British, who abolished suttee — over ferocious Hindu opposition — in 1829. The ritual immolation by fire of widows on their husbands’ funeral pyres, suttee had the full sanction of the Hindu religion, although it might perhaps be wrong to overrate its importance. Scholars remind us that it was never universal, only “usual.” And there was, after all, a rather extensive range of choice. In southern India the widow was flung into her husband’s fire-pit. In the valley of the Ganges she was placed on the pyre when it was already aflame. In western India, she supported the head of the corpse with her right hand, while, torch in her left, she was allowed the honor of setting the whole thing on fire herself. In the north, where perhaps women were more impious, the widow’s body was constrained on the burning pyre by long poles pressed down by her relatives, just in case, screaming in terror and choking and burning to death, she might forget her dharma. So, yes, ladies, members of the National Council of Churches, believers in the one God, mourners for that holy India before it was despoiled by those brutish British, remember suttee, that interesting, exotic practice in which Hindus, over the centuries, burned to death countless millions of helpless women in a spirit of pious devotion, crying for all I know, Hai Rama! Hai Rama!
Richard Grenier, “The Gandhi Nobody Knows”, Commentary, 1983-03-01.