In the latest installment of his Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes explores the very early steam age in England:
Why was the steam engine invented in England? An awful lot hinges on this question, because the answer often depends on our broader theories of what caused the British Industrial Revolution as a whole. And while I never tire of saying that Britain’s acceleration of innovation was about much, much more than just the “poster boy” industries of cotton, iron, and coal, the economy’s transition to burning fossil fuels was still an unprecedented and remarkable event. Before the rise of coal, land traditionally had to be devoted to either fuel, food, or clothing: typically forest for firewood, fields for grain, and pastures for wool-bearing sheep. By 1800, however, English coal was providing fuel each year equivalent to 11 million acres of forest — an area that would have taken up a third of the country’s entire surface area, and which was many times larger than its actual forest. By digging downward for coal, Britain effectively increased its breadth.
And coal found new uses, too. It had traditionally just been one among many different fuels that could be used to heat homes, alongside turf, gorse, firewood, charcoal, and even cow dung. When such fuels were used for industry, they were generally confined to the direct application of heat, such as in baking bricks, evaporating seawater to extract salt, firing the forges for blacksmiths, and heating the furnaces for glass-makers. Over the course of the seventeenth century, however, coal had increasingly become the fuel of choice for both heating homes and for industry. Despite its drawbacks — it was sooty, smelly, and unhealthy — in places like London it remained cheap while the price of other fuels like firewood steadily increased. More and more industries were adapted to burning it. It took decades of tinkering and experimentation, for example, to reliable use coal in the smelting of iron.
Yet with the invention of the steam engine, the industrial uses of coal multiplied further. Although the earliest steam engines generally just sucked the water out of flooded mines, by the 1780s they were turning machinery too. By the 1830s, steam engines were having a noticeable impact on British economic growth, and had been applied to locomotion. Steam boats, steam carriages, steam trains, and steam ships proliferated and began to shrink the world. Rather than just a source of heat, coal became a substitute for the motive power of water, wind, and muscle.
So where did this revolutionary invention come from? There were, of course, ancient forms of steam-powered devices, such as the “aeolipile”. Described by Hero of Alexandria in the 1st century, the aeolipile consisted of a hollow ball with nozzles, configured in such a way that the steam passing into the ball and exiting through the nozzles would cause the ball to spin. But this was more like a steam turbine than a steam engine. It could not do a whole lot of lifting. The key breakthroughs came later, in the late seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries, and instead exploited vacuums. In a steam engine the main force was applied, not by the steam itself pushing a piston, but by the steam within the cylinder being doused in cold water, causing it to rapidly condense. The resulting partial vacuum meant that the weight of the air — the atmospheric pressure — did the real lifting work. The steam was not there to push, but to be condensed and thus pull. It saw its first practical applications in the 1700s thanks to the work of a Devon ironmonger, Thomas Newcomen.
Science was important here. Newcomen’s engine could never have been conceived had it not been for the basic and not at all obvious observation that the air weighed something. It then required decades of experimentation with air pumps, barometers, and even gunpowder, before it was realised that a vacuum could rapidly be created through the condensation of steam rather than by trying to suck the air out with a pump. And it was still more decades before this observation was reliably applied to exerting force. An important factor in the creation of the steam engine was thus that there was a sufficiently large and well-organised group of people experimenting with the very nature of air, sharing their observations with one another and publishing — a group of people who, in England, formalised their socialising and correspondence in the early 1660s with the creation of the Royal Society.
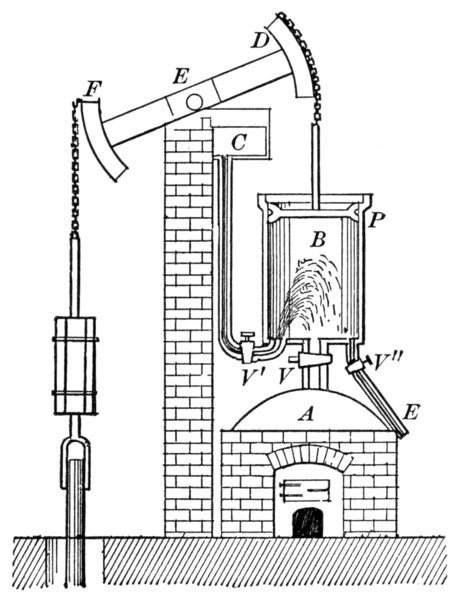
Newcomen’s Atmospheric Steam Engine. The steam was generated in the boiler A. The piston P moved in a cylinder B. When the valve V was opened, the steam pushed up the piston. At the top of the stroke, the valve was closed, the valve V’ was opened, and a jet of cold water from the tank C was injected into the cylinder, thus condensing the steam and reducing the pressure under the piston. The atmospheric pressure above then pushed the piston down again.
Original illustration from Practical Physics for Secondary Schools. Fundamental principles and applications to daily life, by Newton Henry Black and Harvey Nathaniel Davis, 1913, via Wikimedia Commons.