Railroad Street
Published 5 May 2023Whalebacks were a type of ship indigenous to the Great Lakes during the late 1890s and mid 1900s. They were invented by Captain Alexander McDougall, and revolutionized the way boats on the Great Lakes handled bulk commodities. Unfortunately, their unique design was one of the many factors which led to their discontinuation.
(more…)
August 11, 2023
The Weirdest Boats on the Great Lakes
November 4, 2021
Fallen Flag — the Milwaukee Road
 This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Milwaukee Road (MILW) by George Drury. As with most major US railways, the Milwaukee Road was a long-term collection of different railway lines, some merged for obvious economic benefit and others taken over to reduce competition, but the first of the components that eventually evolved into the Milwaukee Road system was the 1847 Milwaukee and Waukesha Railroad. This line was incorporated to connect the Wisconsin city of Milwaukee to the river traffic along the Mississippi River, and the corporate name was changed even before construction began to the Milwaukee and Mississippi Railroad to more adequately convey the purpose of the line. The first segment opened in November 1850 connecting Milwaukee and Wauwatosa, a distance of five miles, then to Waukesha a few months later, then to Madison, but not extending all the way to the river at Prairie du Chien until 1857.
This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Milwaukee Road (MILW) by George Drury. As with most major US railways, the Milwaukee Road was a long-term collection of different railway lines, some merged for obvious economic benefit and others taken over to reduce competition, but the first of the components that eventually evolved into the Milwaukee Road system was the 1847 Milwaukee and Waukesha Railroad. This line was incorporated to connect the Wisconsin city of Milwaukee to the river traffic along the Mississippi River, and the corporate name was changed even before construction began to the Milwaukee and Mississippi Railroad to more adequately convey the purpose of the line. The first segment opened in November 1850 connecting Milwaukee and Wauwatosa, a distance of five miles, then to Waukesha a few months later, then to Madison, but not extending all the way to the river at Prairie du Chien until 1857.
In that year, another of the frequent financial crises of the era struck and the company struggled on for two years, but eventually went into receivership in 1859. New owner the Milwaukee and Prairie du Chien Railroad took possession in 1861. After the Civil War, the company was merged with the Milwaukee and St. Paul and in 1874 the combined railroad became known as the Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul with the completion of a new line connecting with Chicago.
In the next few years the road built or bought lines from Racine, Wis., to Moline, Ill.; from Chicago to Savanna, Ill., and two lines west across southern Minnesota. The road reached Council Bluffs, Iowa, across the Missouri River from Omaha, in 1882, and reached Kansas City in 1887. In 1893 the CM&StP acquired the Milwaukee & Northern, which reached from Milwaukee into Michigan’s upper peninsula.
In 1900 the Chicago, Milwaukee & St. Paul was considered one of the most prosperous, progressive, and enterprising railroads in the U.S. Its lines reached from Chicago to Minneapolis, Omaha, and Kansas City. Secondary lines and branches covered most of the area between the Omaha and Minneapolis lines in Wisconsin, Iowa, and Minnesota. Lines covered much of eastern South Dakota and reached the Missouri River at three places in that state: Running Water, Chamberlain, and Evarts. Except for the last few miles into Kansas City and operation over Union Pacific rails from Council Bluffs to Omaha, the Missouri River formed the western boundary of the CM&StP. (“Milwaukee Road” as a name or nickname did not come into use until the late 1920s; “St. Paul Road” was sometimes used as a nickname, but the railroad’s advertising used the full name).
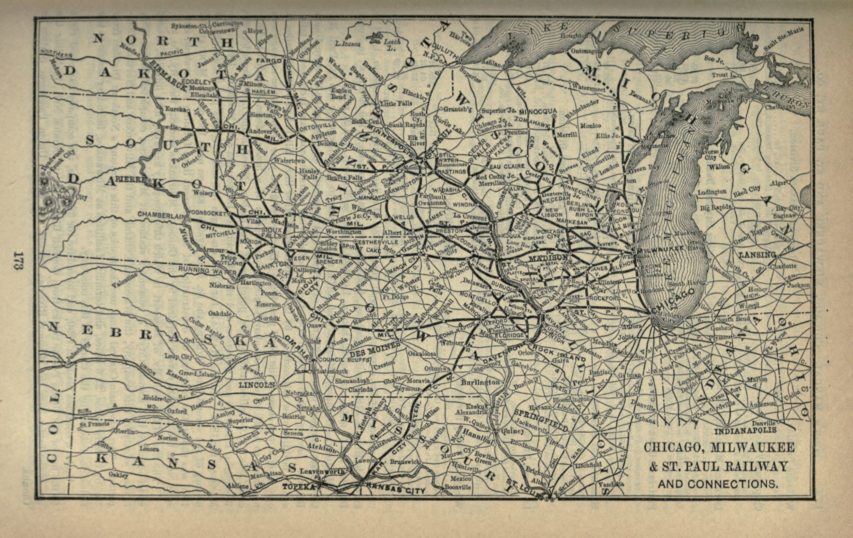
The Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul Railway in 1893.
Poor’s Manual of the Railroads of the United States via Wikimedia Commons.
The battle over control of the Northern Pacific and the Burlington in 1901 made the Milwaukee Road aware that without its own route to the Pacific it would be at its competitors’ mercy. At the same time the Milwaukee Road was experiencing a change in its traffic from dominance by wheat to a more balanced mix of agricultural and industrial products. Arguments against extension westward included the possibility of the construction of the Panama Canal and the presence of strong competing railroads: Union Pacific, Northern Pacific, and Great Northern. Arguments for the extension banked heavily on the growth of traffic to and from the Pacific Northwest.
In 1901 the president of the Milwaukee Road dispatched an engineer west to estimate the cost of duplicating Northern Pacific’s line. His figure was $45 million. Such an expenditure required considerable thought; not until November 1905 did Milwaukee’s board of directors authorize construction of a line west to Tacoma and Seattle.
In 1905 and ’06 the Milwaukee Road incorporated subsidiaries in South Dakota, Montana, Idaho, and Washington. The Washington company was renamed the Chicago, Milwaukee & Puget Sound Railway, and it took over the other three companies in 1908. It was absorbed by the CM&StP in 1912.
The extension began with a bridge across the Missouri River at Mobridge, 3 miles upstream from Evarts, S.D. Roadbed and rails pushed out from several points into unpopulated territory. The work went quickly, and the road was open to Butte, Mont., in August 1908.
Unfortunately for the Milwaukee, the Pacific extension was much more expensive to build than the initial estimates (it jumped from $45 million in the 1901 survey to $60 million in 1905), eventually weighing down the company books with $257 million in debt and worse, the traffic estimates for the new line turned out to be wildly optimistic. The difficulties of operating steam locomotives across the extension in winter pushed the railway toward electrification as an efficiency and cost-saving move. Beginning in 1914, sections of the line were converted to overhead catenary power until a total of 645 route-miles were being operated with electric locomotives, reportedly saving the company over a million dollars per year.
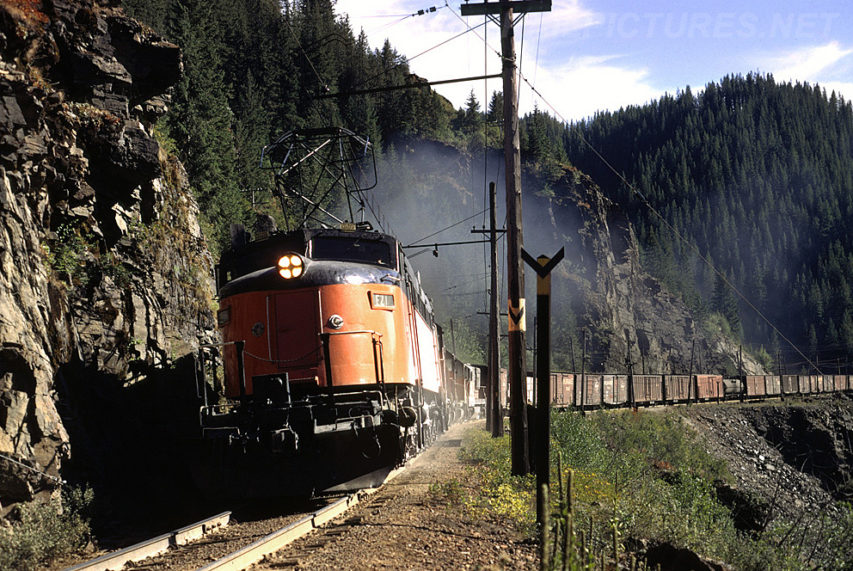

A Milwaukee “Little Joe” electric locomotive hauling a freight train along the Pacific extension in 1941. The “Little Joe” locomotives were originally built for the Soviet Union in the late 1940s but the US government cancelled the export license as relations with the Soviets deteriorated and the Cold War escalated. The Milwaukee Road bought 12 of the 20 from General Electric for $1 million during the Korean War.
Wikimedia Commons.
Despite the savings through electrification, the Pacific extension drove the company into bankruptcy in 1925, re-emerging as the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad, but the new company also had to declare bankruptcy during the Great Depression. Trustees ran the railroad for ten years until renewed civilian traffic after World War 2 allowed normal operations to resume. As with most North American railroads, the good times didn’t last and by the late 1950s, the Milwaukee’s management were looking for a merger partner to help cut costs and shed unprofitable branch lines. Unlike the rival merger of of Northern Pacific, Great Northern, Burlington Route, and the Spokane, Portland and Seattle Railway into Burlington Northern, the ICC blocked a merger between the Milwaukee Road and the Chicago and North Western. The ICC also blocked a later application for the Milwaukee to be included in the Union Pacific/Rock Island merger.
With declining business, deferred maintenance issues on most lines, and some self-induced financial issues caused by selling off rolling stock and leasing it back (which exacerbated car shortages leading to further reductions in business), the company had no funds to replace the failing “Little Joe” locomotives on the Pacific extension, so electrification was abandoned in 1974. George Drury sums up the mistakes that led to the end:
Over the decades, the road’s management had made too many wrong decisions: building the Pacific Extension, not electrifying between the two electrified portions, purchasing the line into Indiana, and in the 1960s choosing Flexivans (containers with separate wheels/bogies that required special flatcars) instead of conventional piggyback trailers.
After several money-losing years in the early 1970s, the Milwaukee voluntarily entered reorganization once again on December 19, 1977. The major result of the 1977 reorganization was the amputation of everything west of Miles City, Mont., to concentrate on what became known as the “Milwaukee II” system linking Chicago, Kansas City, Minneapolis-St. Paul, Duluth (on Burlington Northern rails from St. Paul), and Louisville (but no longer Omaha).
By 1983 the Milwaukee’s system consisted of the Chicago–Twin Cities main line; Chicago–Savanna–Kansas City; Chicago–Louisville (almost entirely on Conrail and Seaboard System rails), Milwaukee–Green Bay; New Lisbon–Tomahawk, Wis.; Savanna–La Crosse, along the west bank of the Mississippi; Marquette to Sheldon, Iowa, and Jackson, Minn.; Austin, Minn.–St. Paul; and St. Paul–Ortonville, Minn., plus a few branches.
Three roads vied for what remained of the Milwaukee: the Chicago & North Western, financially none too solid itself; Canadian National subsidiary Grand Trunk Western, with an eye toward creating a route between eastern and western Canada south of the Great Lakes; and Canadian Pacific subsidiary Soo Line.
May 6, 2021
Fallen Flag — the Northern Pacific Railway

Despite the vast land grants, the costs of building the railway eventually drove Jay Cooke, the original financial backer, into bankruptcy which was one of the major triggers of the financial disaster known as the Panic of 1873. The economic impact was widespread and was known — until the 1930s — as the “Great Depression”, and the US economy took several years to resume growth while other industrialized countries suffered the effects for longer.
NP reorganized by converting the bonds to stock, and the Lake Superior & Mississippi was reorganized as the St. Paul & Duluth. In 1881 control of the NP was purchased by Henry Villard, who also controlled the Oregon Railway & Navigation Co. and the Oregon & California Railroad. On Sept. 8, 1883, NP drove a last spike at Gold Creek, Mont., near Garrison, completing a line from Duluth to Wallula Junction, Wash. Northern Pacific trains continued on the rails of the OR&N to Portland, where NP’s own line to Tacoma resumed (it crossed the Columbia River by ferry from Goble, Ore., to Kalama, Wash.).
Even before completing the line at Gold Creek, NP began constructing a direct line from Pasco, Wash., over the Cascade Range to Tacoma. The Puget Sound area was beginning to grow, and NP wanted to reach it with its own line rather than rely on OR&N. Indeed, soon after the last-spike ceremonies, Villard’s empire collapsed and OR&N became part of Union Pacific (Southern Pacific got the Oregon & California). The Pasco–Tacoma line opened in 1887, with temporary switchbacks carrying trains over Stampede Pass until the opening of Stampede Tunnel in May 1888.
To help populate the railway’s claimed lands, colonization offices were established in northern Europe in the mid-1880s to attract immigrants to settle and farm along the right of way. Many Americans of German or Scandinavian ancestry can trace their roots back to these programs, which generally offered very cheap package deals for transportation to the United States along with parcels of land and other inducements.
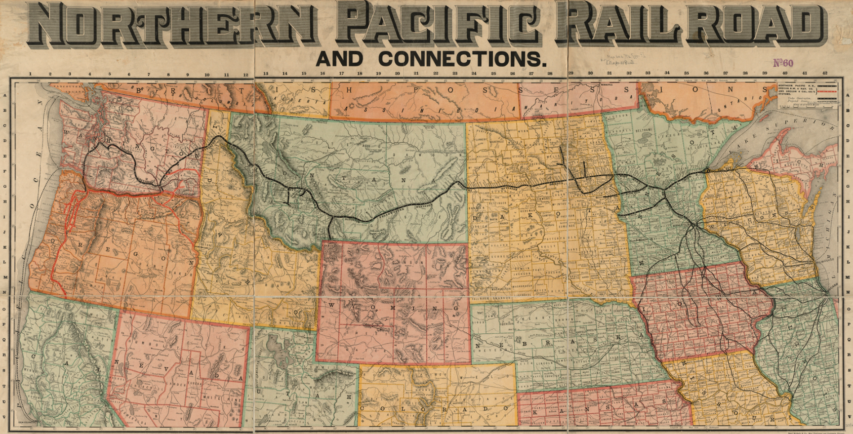
Detail from an 1885 Rand McNally publication showing a “Shipper’s Guide To All Points On And Connections To the Northern Pacific Railroad, Its Branches And Connecting Lines”
Original scan from the Norman B. Leventhal Map Center at the BPL via Wikimedia Commons.
In 1901 Northern Pacific and Great Northern gained control of the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy by jointly purchasing approximately 98 percent of its capital stock. That same year James J. Hill and J. P. Morgan formed the Northern Securities Co. as a holding company for NP and Great Northern. The U.S. Supreme Court dissolved Northern Securities in 1904. In 1905 the two roads organized the Spokane, Portland & Seattle, which was completed from Spokane through Pasco to Portland in 1908. GN and NP attempted consolidation in 1927, but the Interstate Commerce Commission made giving up control of the Burlington a requisite for approval, a condition the roads found unacceptable.
In October 1941 NP purchased the property of the Minnesota & International Railway (Brainerd to International Falls, Minn.), which it had controlled for a number of years.
In image, Northern Pacific was the most conservative of the three northern transcontinentals. (Great Northern was a prosperous, well-thought-out railroad; the Milwaukee Road was a brash newcomer.) Bulking large in NP’s freight traffic were wheat and lumber. In the 1920s and 1930s NP suffered from smaller than usual wheat crops and competition from ships for lumber moving to the East Coast. Ship competition decreased during World War II, and postwar prosperity brought an increase in building activity and population growth to the area NP served. NP was the oldest of the northern transcontinentals and had been instrumental in settling the northern plains. It served the populous areas of North Dakota, Montana, and Washington. Its slogan was “Main Street of the Northwest,” and its secondary passenger train of the 1950s and ’60s was the Mainstreeter. Its flagship was the North Coast Limited, launched in 1900.
In 1956 NP and Great Northern again studied merger of the two roads, the Burlington, and the Spokane, Portland & Seattle. In 1960 the directors of both roads approved the merger terms. On March 2, 1970, NP was merged into Burlington Northern along with Great Northern; Chicago, Burlington & Quincy; and Spokane, Portland & Seattle.
April 8, 2021
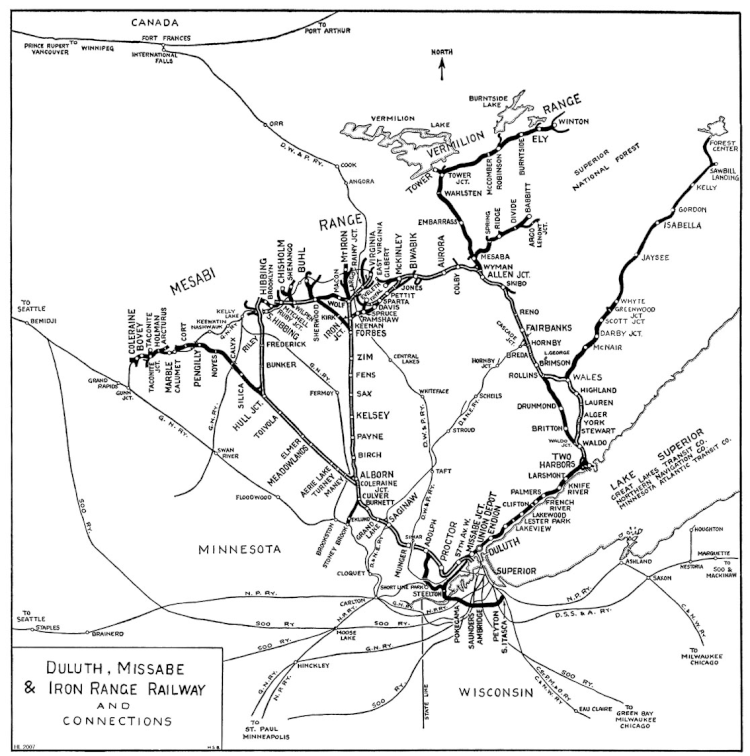
Fallen Flag — the Duluth, Missabe & Iron Range Railway

The Merritt family of Minnesota (known as the “Seven Iron Brothers“) discovered a large iron ore deposit in the Mesabi Range and created the largest iron ore mine in the world (as of the 1890s) and tried to persuade the DMN to build a 70-mile rail connection to get their ore to harbour and out to the iron and steel foundries around the Great Lakes. The DMN was unwilling to commit, so the Merritt family borrowed money to build the line from, among other financiers, John D. Rockefeller. The line — called the Duluth, Missabe and Northern — got built and began operations in 1892, but the Merritts expanded too quickly at the wrong moment — the financial panic of 1893 — losing financial control and leaving ownership of both the mine and the railway in Rockefeller’s hands by 1894.
Charlemagne Tower sold the Duluth & Iron Range to Illinois Steel in 1887, which was succeeded by Federal Steel, then U.S. Steel. By 1901, both the D&IR and DM&N were under U.S. Steel control. USS upgraded both railroads with heavy rail and double track, ordered bigger locomotives and larger cars, and built sizeable shops and roundhouses at Proctor and Two Harbors.
In 1915 DM&N leased the Spirit Lake Transfer Railway, a link between DM&N at Adolph, near Proctor, and the Interstate Transfer Railway at Oliver, Wis., across from Steelton, Minn. The Interstate Transfer ran from Oliver to Itasca, in eastern Superior, giving the DM&N connections with large railroads including Northern Pacific, Chicago & North Western’s “Omaha Road”, and three members of the Canadian Pacific family: Minneapolis, St. Paul & Sault Ste. Marie (“Soo Line”); Wisconsin Central; and Duluth, South Shore & Atlantic.
DM&N and D&IR remained separate until January 1, 1930, when the DM&N leased the D&IR and consolidated operations. Then on July 1, 1937, the DM&N merged with the Spirit Lake Transfer to form the Duluth, Missabe & Iron Range Railway. DM&IR then acquired ownership of D&IR and Interstate Transfer, and they became part of the new corporation on March 22, 1938. Reminders of the two big predecessors remained in the DM&IR’s two operating divisions, named Iron Range and Missabe, made up primarily of the predecessors’ tracks.
The Great Depression drastically reduced ore traffic. In 1932, not a single all-ore train was run — the small amount of ore that had to be shipped was carried in mixed freights. World War II reversed the road’s fortunes, of course, and the postwar boom resulted in an even higher demand for ore, with an all-time tonnage record being set in 1953.
Missabe had minimal passenger service. Into the 1950s, handsome Pacifics pulled heavyweight steel RPOs and coaches, two with solarium observation sections. At the end of World War II, the Missabe still provided service between Duluth and Ely (Winton), and Duluth and Hibbing, with the Hibbing train connecting with one from Iron Junction to Virginia.
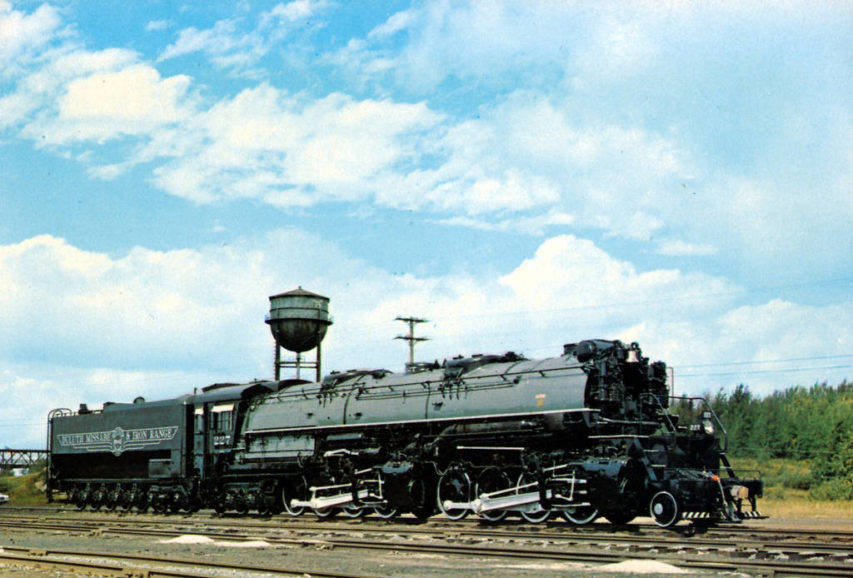

Duluth, Missabe & Iron Range M-3 locomotive no. 227.
Photo by “GavinTheGazelle” via Wikimedia Commons.
U.S. Steel spun off the DM&IR and its other ore railroads and shipping companies to subsidiary Transtar in 1988, selling majority control to the Blackstone Group. In 2001, DM&IR and other holdings were moved from Transtar to Great Lakes Transportation, fully owned by Blackstone, so for the first time in a century, DM&IR was no longer associated with U.S. Steel. On October 20, 2003, Canadian National announced it would buy Great Lakes Transportation, which also owned Bessemer & Lake Erie, Pittsburgh & Conneaut Dock Co. in Ohio, and Great Lakes Fleet, Inc. The purchase was finalized on May 10, 2004, and the independent Missabe Road vanished.
CN retired all but 10 of the SD40-3s, most of the SD38s, and all the rebuilt SD9s and 18s. Major locomotive work shifted from Proctor to other shops, and train dispatchers moved to Wisconsin, then Illinois. CN invested in new ore cars for the Missabe, gradually replacing those that dated to when steam still ruled the railroad. DM&IR existed on paper until December 31, 2011, when CN merged subsidiaries DM&IR and Duluth, Winnipeg & Pacific into Wisconsin Central.
December 17, 2020
Fallen Flag — the Ann Arbor Railroad
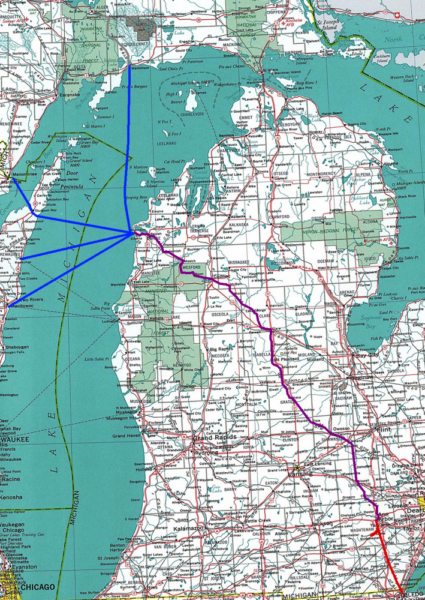
This month’s Classic Trains featured fallen flag is the Michigan-based Ann Arbor Railroad which operated rail services from Toledo, Ohio to Elberta and Frankfort, Michigan, along with lake ferry service across Lake Michigan to Manitowoc and Kewaunee, Wisconsin and Menominee and Manistique in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. Robert I. Warrick provides an outline of the history of the line:
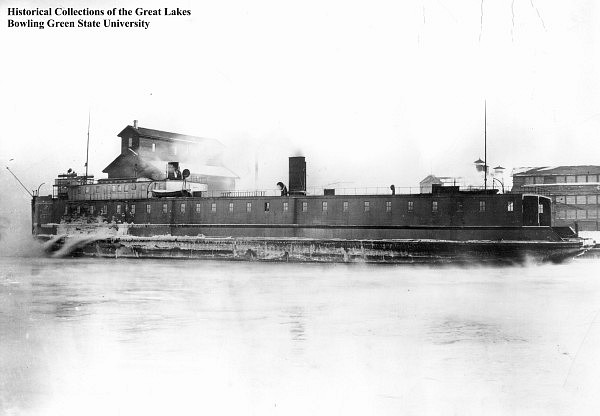

Ann Arbor No. 1, built in 1892 by Craig Shipbuilding Co. in Toledo, Ohio. She was destroyed in a fire on March 7, 1910 at Manitowoc, Wisconsin.
Photo from Bowling Green State University via Wikimedia Commons.
The Ann Arbor Railroad was as much a steamship line as a railroad. Built from Toledo, Ohio, northwest to Frankfort, Mich., it existed for one reason — to move freight in car ferries across Lake Michigan to bypass Chicago. From 1910 to 1968, “the Annie” operated 320 car ferry route-miles versus 292 miles of railroad. AA was at the forefront of car ferry design and innovation, from the first wooden-hulled vessels to the most advanced car ferry to ever sail Lake Michigan.
During the 1940s, up to six ferries made the round trip from Boat Landing, as AA called its yard in Elberta on the south side of Frankfort harbor, to two Wisconsin and two Michigan Upper Peninsula ports. The boats ran year-round on a tight schedule, timed to match with three pairs of scheduled Toledo freights, where AA interchanged with five trunk lines. Well-kept 2-8-2s powered those short, fast trains across AA’s rolling profile until 1950, when Alco FA2s took over.
[…]
The Eastern mergers of the 1960s ultimately doomed the old Ann Arbor. As planning for Penn Central went on, the Norfolk & Western merged with Wabash, Nickel Plate, and two smaller roads in 1964. N&W wanted no part of the Ann Arbor and its costly ferries, so AA was foisted off on DT&I, which was profitable by the 1960s.
With ICC approval, DT&I took over the Ann Arbor on August 31, 1963, and soon replaced the tired FA2s with 10 GP35s, riding on Alco trucks and painted in DT&I orange with large “Ann Arbor” lettering. DT&I’s GPs often mixed with the Annie’s.
DT&I had ferry Wabash refitted, changed her name to City of Green Bay, and loaned AA $2.5 million to rebuild Ann Arbor No. 7. The railroad renamed No. 7 Viking, lengthened it, installed four EMD 2,500 h.p. 567 diesels. But even with the bigger boats, capacity remained an issue as car sizes increased. AA was losing money. First the ferry route to Manistique, Mich. (and AA subsidiary Manistique & Lake Superior), was discontinued, then the one to Menominee, Mich.
Ann Arbor’s fate was sealed. A firm was hired to liquidate Pennsylvania Company assets, including AA and DT&I. Ann Arbor defaulted on the loan for the Viking on November 1, 1972, and filed for bankruptcy on October 15, 1973, leading to AA’s inclusion with other bankrupts in the Regional Rail Reorganization Act of 1973 that resulted in Conrail.
February 26, 2015
America’s not-so-hidden class structure
In The Federalist, Robert Tracinski looks at the recent brouhaha over Wisconsin governor Scott Walker’s lack of a university degree and what it reveals about America’s class structure:
On the surface, of course, it’s certainly about Scott Walker. The left-leaning mainstream media senses that he’s a potential danger. After all, he has won three straight elections in a swing state, while challenging the public employees’ unions head-on and significantly reducing their government privileges. (This is precisely what makes him interesting to those of us on the right.) The mainstream media feel that they need to disqualify him now, so they’re looking for anything they can use against him.
But behind that, there is a more visceral reaction. The real purpose of higher education is to learn the knowledge and skills required for success later in life. So if someone has already become a success, whether or not he went to college is irrelevant. If he has achieved the end, what does it matter that he didn’t do it by way of that specific means? But for the mainstream elites, particularly those at the top level in the media, a college education is not simply a means to an end. It is itself a key attainment that confers a special social status.
There are no real class divisions in America except one: the college-educated versus the non-college educated. It helps to think of this in terms borrowed from the world of a Jane Austen novel: graduating from college is what makes you a “gentleman.” (A degree from an Ivy League school makes you part of the aristocracy.) It qualifies you to marry the right people and hold the right kind of positions. It makes you respectable. And even if you don’t achieve much in the world of work and business, even if you’re still working as a barista ten years later, you still retain that special status. It’s a modern form of “genteel poverty,” which is considered superior to the regular kind of poverty.
If you don’t have a college degree, by contrast, you are looked down upon as a vulgar commoner who is presumptuously attempting to rise above his station. Which is pretty much what they’re saying about Scott Walker. This prejudice is particularly strong when applied to anyone from the right, whose retrograde views are easily attributed to his lack of attendance at the gentleman’s finishing school that is the university.
June 9, 2014
Indianapolis police “needed a mine-resistant vehicle to protect against a possible attack by veterans returning from war”
When you dress and act like an occupying army, eventually the citizenry will view you as just that:
Inside the municipal garage of this small lakefront city [Neenah, Wisconsin], parked next to the hefty orange snowplow, sits an even larger truck, this one painted in desert khaki. Weighing 30 tons and built to withstand land mines, the armored combat vehicle is one of hundreds showing up across the country, in police departments big and small.
The 9-foot-tall armored truck was intended for an overseas battlefield. But as President Obama ushers in the end of what he called America’s “long season of war,” the former tools of combat — M-16 rifles, grenade launchers, silencers and more — are ending up in local police departments, often with little public notice.
During the Obama administration, according to Pentagon data, police departments have received tens of thousands of machine guns; nearly 200,000 ammunition magazines; thousands of pieces of camouflage and night-vision equipment; and hundreds of silencers, armored cars and aircraft.
The equipment has been added to the armories of police departments that already look and act like military units. Police SWAT teams are now deployed tens of thousands of times each year, increasingly for routine jobs. Masked, heavily armed police officers in Louisiana raided a nightclub in 2006 as part of a liquor inspection. In Florida in 2010, officers in SWAT gear and with guns drawn carried out raids on barbershops that mostly led only to charges of “barbering without a license.”
[…]
The number of SWAT teams has skyrocketed since the 1980s, according to studies by Peter B. Kraska, an Eastern Kentucky University professor who has been researching the issue for decades.
The ubiquity of SWAT teams has changed not only the way officers look, but also the way departments view themselves. Recruiting videos feature clips of officers storming into homes with smoke grenades and firing automatic weapons. In Springdale, Ark., a police recruiting video is dominated by SWAT clips, including officers throwing a flash grenade into a house and creeping through a field in camouflage.
In South Carolina, the Richland County Sheriff’s Department’s website features its SWAT team, dressed in black with guns drawn, flanking an armored vehicle that looks like a tank and has a mounted .50-caliber gun.
Update: It’s not just Wisconsin or Indiana … even Maine feels the threat.
Cops must militarize because Maine foothills face previously unimagined threat from tourism — sorry, terrorism [NYT] http://t.co/gP3sxdhaco
— Walter Olson (@walterolson) June 9, 2014
August 19, 2013
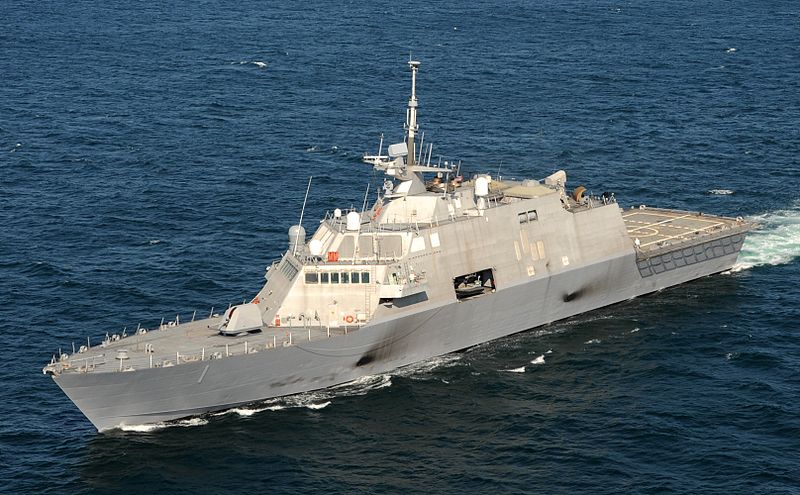
US Navy’s littoral combat ship (LCS) program under budget threat
The US Navy is betting big on the eventual success of their Littoral Combat Ship program despite the early teething troubles (earlier posts here and here). The more traditional hull design (there are two distinct designs in the same class) is being built by Wisconsin’s Marinette Marine, as a subcontractor to Lockheed-Martin. The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel reports on the latest political hitch in the program:
The littoral program has been dogged by problems, including early cost overruns. The completed ships have suffered from mechanical problems as well as from delays in producing switchable mission modules aimed at making the ships adaptable to varied types of warfare.
Testing has revealed deficiencies with “core ship systems,” according to the July 25 GAO report, which says Congress should consider restricting funding for additional littoral combat ships until the Navy completes technical and design studies.
Littoral combat ships are meant to be fast and capable of operating in shallow waters close to shore in places such as the Persian Gulf.
“We continue to believe that the acquisition approach for this program, with large quantities of ships and modules being bought ahead of key test events, is risky, especially for a new class of ship like LCS,” Paul Francis, a GAO official, said in recent testimony before a House of Representatives subcommittee looking into the program.
“The current LCS program is not the program envisioned over a decade ago,” Francis said, adding the Navy still doesn’t know how well the ships will perform their missions, how well the unique crew and maintenance concepts will work, or how much it will cost to equip and support the ships.
Further, the Navy is still considering changes to the ships and determining whether there are advantages to having two radically different designs — one built by Lockheed and Marinette, and the other by Austal USA in Mobile, Ala.
“These are things the Navy and Congress should know before contracting for more than half of the ships,” Francis said.
January 19, 2012
In spite of the large number of petitioners, recalling Wisconsin’s governor may not be a done deal
Christian Schneider in City Journal on the efforts underway in Wisconsin to recall Governor Scott Walker:
One morning last February, Wisconsin governor Scott Walker called his staff into his office. “Guys,” he warned, “it’s going to be a tough week.” Walker had recently sent a letter to state employees proposing steps — ranging from restricting collective bargaining to requiring workers to start contributing to their own pension accounts — to eliminate the state’s $3.6 billion deficit. That day in February was when Walker would announce his plan publicly.
It turned out to be a tough year. The state immediately erupted into a national spectacle, with tens of thousands of citizens, led by Wisconsin’s public-employee unions, seizing control of the capitol for weeks to protest the reforms. By early March, the crowds grew as big as 100,000, police estimated. Protesters set up encampments in the statehouse, openly drinking and engaging in drug use beneath the marble dome. Democratic state senators fled Wisconsin to prevent a vote on Walker’s plan. Eventually, the Senate did manage to pass the reforms, which survived a legal challenge and became law in July.
The unions aren’t done yet: they’re now trying to recall Walker from office. To do so, they will try to convince Wisconsin voters that Walker’s reforms have rendered the state ungovernable. But the evidence, so far, contradicts that claim—and Wisconsinites seem to realize it.
The fight between the Governor and the public unions matters more than it may seem: Wisconsin was the first state to allow civil service workers to unionize and has traditionally been seen as a strong union (and therefore also Democratic) state ever since. If unions can have some of their power trimmed back there, it will hearten the efforts of other state governments to follow suit.
September 28, 2011
“‘Sensitivity to hurt feelings’ is not, in fact, a First Amendment value or a justification for censorship”
Follow-up to Monday’s link to Popehat on bureaucratic censorship at the University of Wisconsin, Ken has a few words to say about the administration’s “justification”:
2. The problem with demanding a campus free of “implied threats” is illustrated by this case. Campus police first censored a poster of an imaginary space cowboy with a fan-pleasing quote. Next, just to say FUCK YOU IRONY they used threats of official retaliation against a poster condemning threats of official retaliation. No rational person could construe either poster as a threat, actual or implied, to commit violence against any person (although I suppose the second could be construed as a warning — a correct one — that thugs will act thuggishly when questioned.) If a rational person wouldn’t take it as an actual threat of violence, then it’s not a true threat that can be censored, however much the hysterical, irrational, nanny-stating, coddling, or professionally emo think about it, and however much university chancellors would like to believe otherwise.
3. Similarly, this case illustrates the problem with an approach to freedom of expression premised on “sensitivity” and making people feel “welcome, safe and secure.” “Sensitivity to hurt feelings” is not, in fact, a First Amendment value or a justification for censorship. In fact, stopping people from speaking because the speech hurts people’s feelings is the essence of censorship. A system in which what we can say is premised upon the likely reactions of the mentally ill and the undernourished pussywillows of the world is a system that encourages suppression of all unpopular, forceful, interesting, or challenging speech. The irrational and the morally and mentally weak are not entitled to have their feelings protected through the force of law, however prevalent they are on campus.
September 26, 2011
Gorram purplebelly censors
A Mal Reynolds poster falls victim to academic censorship:
Dateline: Wisconsin. At the University of Wisconsin-Stout, theater professor James Miller put up a poster on his door with an image of Nathan Fillon in the character of Captain Malcolm Reynolds with one of Mal’s better lines: “You don’t know me, son, so let me explain this to you once: If I ever kill you, you’ll be awake. You’ll be facing me. And you’ll be armed.”
In a better world, nothing would happen — except perhaps Firefly fans would geek out and people who roll their eyes at geek culture references would roll their eyes.
But this is modern America. In modern America, the Browncoats are people who like to use vigorous figurative language to speak their mind, and they are often outnumbered and outgunned by the Alliance, made up of silly, professionally frightened moral and intellectual weaklings who see expressions of dissent (particularly dissent rendered in vivid figurative terms) as upsetting and potentially all terroristy.
So naturally the campus police at University of Wisconsin-Stout went all Mrs.-Grundy-With-A-Gun-And-A-Badge on Professor Miller. They threatened Prof. Miller with criminal charges for disorderly conduct, taking a page from the cops at Sam Houston state. They also took the poster down. The redoubtable FIRE has the story and has sent the necessary letter asking the University to grow the fuck up and pull its shit together. (That might be kind of a paraphrase by me.)
March 18, 2011
Ignoring death threats to politicians (but only on the right)
An interesting article at the Huffington Post on the relative media silence on the spate of death threats against Wisconsin politicians:
Why isn’t the mainstream media talking about the death threats against Republican politicians in Wisconsin?
Try to set aside whatever biases or preconceptions you might have for a moment and ask yourself why death threats against politicians aren’t considered national news, especially in the wake of the all too fresh shooting of Rep. Gabrielle Giffords and other bystanders. And there hasn’t just been one death threat, but a number of them.
Here’s an example and it’s real. According to Wisconsin State Department of Justice, authorities have found a suspect who admitted to sending the following email:
I want to make this perfectly clear. Because of your actions today and in the past couple of weeks I and the group of people that are working with me have decided that we’ve had enough. We feel that you and your republican dictators have to die. This is how it’s going to happen: I as well as many others know where you and your family live, it’s a matter of public records. We have all planned to assult you by arriving at your house and putting a nice little bullet in your head. However, this isn’t enough. We also have decided that this may not be enough to send the message. So we have built several bombs that we have placed in various locations around the areas in which we know that you frequent. This includes, your house, your car, the state capitol, and well I won’t tell you all of them because that’s just no fun. Since we know that you are not smart enough to figure out why this is happening to you we have decided to make it perfectly clear to you. If you and your goonies feel that it’s necessary to strip the rights of 300,000 people and ruin their lives, making them unable to feed, clothe, and provide the necessities to their families and themselves then We will “get rid of” (in which I mean kill) the 8 of you. Please understand that this does not include the heroic Senator that risked everything to go aganist what you and your goonies wanted him to do. The 8 includes the 7 senators and the dictator. We feel that it’s worth our lives becasue we would be saving the lives of 300,000 people. Please make your peace with God as soon as possible and say goodbye to your loved ones we will not wait any longer. Goodbye ASSHOLE!!!!
After the Giffords shooting, authorities have to take this sort of threat seriously. The media should too, even if the disturbed person who sent that email was motivated by exactly the kind of rhetoric that’s been used by many liberals against GOP officials over and over again during the Madison protests. And there are more threats floating around the internet, in varying degrees of scary and credible.
The Google search for the string “Wisconsin death threats” only returned 704 results for me this morning, and the only major media outlets represented on the first page were the Chicago Sun-Times and Fox News.
March 17, 2011
Police and fire unions threaten to “boycott” businesses that support Wisconsin governor
You’ve got a nice office here, guv. Shame if anything were to happen to it, y’know?
Here is another reason public unions should not be allowed to collectively bargain with politicians running a local or state government. Union leadership — including those from law enforcement and firefighters — have sent letters out to local businesses demanding they publicly oppose the efforts of Wisconsin’s legislature and governor or face the consequences.
Not only are they suggesting they publicly oppose the fiscal-sanity measures in Wisconsin, they are flat out telling them they will publicly boycott businesses who do not proactively do so. From James Taranto’s opinion piece in the Wall Street Journal yesterday.
In the letter to Wisconsin businessmen, however, we see why so-called collective bargaining is particularly corrupting to the police. Although the letter explicitly threatens only an economic boycott, when it is written on behalf of the police — of those on whom all citizens depend to protect their safety — it invariably raises the prospect of another kind of boycott. Can a businessman who declines this heavy-handed “request” be confident that the police will do their job if he is the victim of a crime — particularly if the crime itself is in retaliation for his refusal to support “the dedicated public employees who serve our communities”?
LauraW clarifies the message here:
We’re the Police and Firefighters Unions.
If you don’t accede to our demand, we’ll put you on The Naughty List. And, um….boycott you. That’s our threat. We’ll boycott you. That’s all.
Right.
…did we forget to mention that we are cops and firefighters?
Just checking. Making sure you caught that.
H/T to Jon for the link.
February 27, 2011
QotD: Big government and big unions
The Times managed to get the salient feature of the story entirely wrong. They were not an “anti-government” mob, but a government mob, a mob of “public servants” objecting to austerity measures that would end, for example, the tradition of 14 monthly paychecks per annum. You read that right: the Greek public sector cannot be bound by anything so humdrum as temporal reality. So, when it was mooted that the “workers” might henceforth receive a mere 12 monthly paychecks per annum, they rioted. Their hapless victims — a man and two women — were a trio of clerks trapped in a bank when the mob set it alight and then obstructed emergency crews attempting to rescue them.
You don’t have to go to Athens to find “public servants” happy to take it out on the public. In Madison, politicized doctors provide fake sick notes for politicized teachers to skip class. In New York’s Christmas snowstorm, Sanitation Department plough drivers are unable to clear the streets, with fatal consequences for some residents. On the other hand, they did manage to clear the snow from outside the Staten Island home of Sanitation Dept head honcho John Doherty, while leaving all surrounding streets pristinely clogged. Three hundred Sanitation Department workers have salaries of over $100,000 per year. In retirement, you get a pension of 66 grand per annum plus excellent health benefits, all inflation proofed.
That’s what “collective bargaining” is about: It enables unions rather than citizens to set the price of government. It is, thus, a direct assault on republican democracy, and it needs to be destroyed. Unlovely as they are, the Greek rioters and the snarling thugs of Madison are the logical end point of the advanced social democratic state: not an oppressed underclass, but a spoiled overclass, rioting in defense of its privileges and insisting on more subsidy, more benefits, more featherbedding, more government.
Mark Steyn, “States of the Unions”, SteynOnline, 2011-02-26