
The Western Pacific company magazine Mileposts included this historical snippet in their 50th anniversary issue (courtesy of the Western Pacific Railroad Museum):
Virgil Bogue had become George Gould’s consulting engineer and recalling his surveys for the Union Pacific in the ’80’s, recommended Beckwourth Pass and the Feather River route. Remembering also an unhappy experience he had once had in locating any other road, only to find the whole route plastered with mining claims of dubious mineral value but through which rights of way must be negotiated, he advised Gould to form a “mining company” first. Accordingly the North California Mining Company was organized and soon nearly 600 placer claims were staked out, blanketing the entire proposed route across the mountains.
Gould turned the job over to the Denver and Rio Grande and its president, E.T. Jeffery, sent a field party under H.H. Yard west to locate the line. It was all top secret. The transit men and stake artists were forbidden even to let their wives know where they were. Letters could only be exchanged through the Denver office of the railroad. Two California corporations, the Butte and Plumas Railway and the Indian Valley Railway, were set up to be the figureheads.
[…]
George Gould still remained completely out of the picture and denied all connection with the project. Although he financed the new surveying parties that were immediately sent out to make the final location, he was forced, in the interests of this secrecy, to keep the Rio Grande engineers in the field as well. The absurd result was two hostile groups struggling to outwit each other and often on the point of exchanging pot shots, though both were actually on the same payroll.
After much chicanery and effort, the railway’s right of way through the Feather River Canyon, the next historically significant fight was securing access to the waterfront along San Francisco Bay, where the legal department of the Southern Pacific believed they had an ironclad monopoly of all the potentially useful access routes to salt water:
… the S.P. was fully confident that it would have but little difficulty in isolating the Western Pacific from a practical outlet on the Bay. The Santa Fe, only a few years before, had built its ferry slip way up at Point Richmond rather than attempt to crack the S.P. stronghold. Bartnett, after a hard struggle against the older railroad’s influence, did secure a small site on the mudflats of the Oakland Estuary. It would have made a miserably cramped ferry terminal but, from all appearances, the WP promoters had concluded it was the best they could do. Harriman’s forces sneered and relaxed. Gould’s were just beginning. Every move was carefully rehearsed and logistics figured to the last detail.
As the Oakland tidelands had gradually been filled in, the Government had extended the banks of San Antonio Estuary with rock quays called “training walls” in order to prevent silt from washing into the Oakland inner harbor channel. A dredger was often necessary to prevent the formation of a bar at the entrance of the channel. This dredger became the Trojan horse of the Gould attack.
On the night of January 5, 1906, the Western Pacific forces under Bartnett struck.
With 200 workmen and 30 guards armed with carbines and sawed-off shotguns, he used the dredging company as a front, and seizing the north training wall, began feverishly to lay a rough track. Most of the guards took up positions at the shore end of the U. S. training wall and maintained them night and day. Laborers snatched their sleep in shelter tents on the wave-washed rocks and the WP commissary department fed them. Scows rushed more rails and ties across the Bay to the end of the wall. Soon there was a mile of track on top of the rock wall.
Of course the Southern Pacific did not quietly accept this outrageous trespassing on domains it had held undisputed for more than half a century. Its legal department, fairly in convulsions, was whipping out the necessary papers for immediate appeal to the law. This was exactly what Bartnett had told Gould would happen and exactly what they both desired. For the courts, as Bartnett had felt sure they would, held that the Southern Pacific title to the waterfronts had not progressed westward with the shoreline as the tidelands and marshes had been filled in, but was valid only to the low tide line of 1852. The S.P.’s “waterfront” therefore was by now well inland, and the new marginal land surrounding it was the property of the city.
The city government was duly grateful to the new railway for almost literally liberating the city’s shoreline from the grip of the Southern Pacific. With most of the legal complications (and paramilitary solutions) out of the way, construction of the full line began in earnest, as Arthur L. Lloyd picks up the story:
Construction started in Salt Lake City. The line would be all 90-lb. rail and have no curve exceeding 10 degrees. To keep to the 1-percent maximum grade, the full-circle Williams Loop was built between Massack and Spring Garden, Calif., and another partial one, Arnold Loop, west of Wendover, Nev.
Work also went from Oakland eastward, and the last spike marking completion was driven on the bridge over Spanish Creek at Keddie, Calif., on Nov. 1, 1909. There was no ceremony. Section foreman Leonardo de Tomasso, age 25, did the honors with a standard steel spike. Arthur Keddie was still around, though. He rode WP’s first passenger train, and he spoke from the Plumas County Courthouse steps in Quincy, Calif., on Nov. 21, 1910.
WP was dispatched completely by train orders and timetable; its only block signals were on the paired track between Weso (Winnemucca) and Alazon (Wells) in Nevada, where eastbound WP and Southern Pacific trains used WP, while both roads’ westbounds used SP.
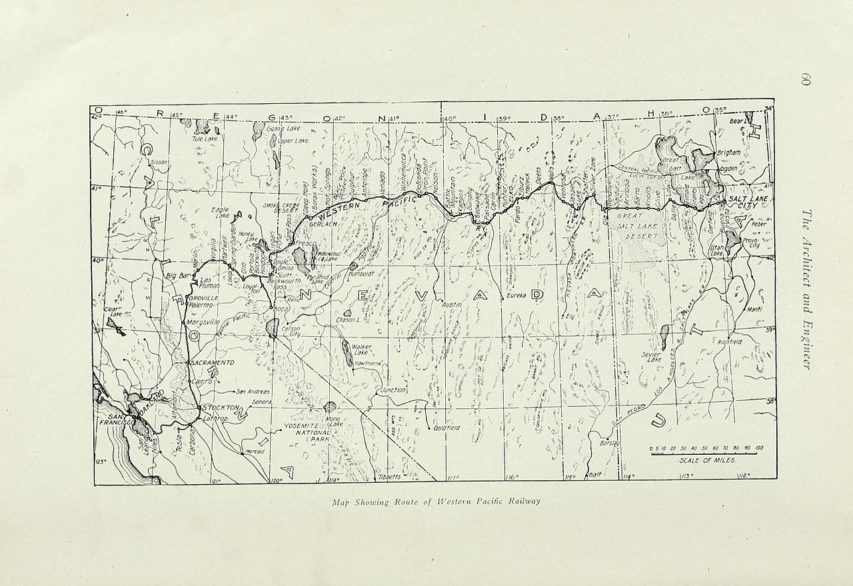
Route map of the Western Pacific, published in The Architect & Engineer of California and the Pacific Coast, 1905.
WP’s map was simplicity itself, highlighted by a main line from San Francisco Bay to Salt Lake City and a connection with the Rio Grande. The branch to Bieber, Calif., completed in the 1930s, connected to a Great Northern line.

 Click to see full size image at RR Picture Archives
Click to see full size image at RR Picture Archives

