seangabb
Published 28 Dec 2024This is the eighth video in my series on Everyday Life in the Roman Empire. In this, I wander about at the beginning, with talk of poetry and philosophy, before realising that the real theme is the extent of ancient literacy. The whole of the remainder is given over to this, and how it enabled a literary civilisation wholly different from our own.
Introduction – 00:00:00
Our perceptions of culture in the Ancient world – 00:01:40
Virgil – 00:03:45
Catullus – 00:05:17
Philosophy in Rome – 00:06:23
The Romans and Stoicism – 00:08:40
The Romans and Epicureanism – 00:10:27
Pretty silver things from Roman Britain – 00:16:25
Broad-based cultural participation in the Ancient World? – 00:19:26
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (no spectacles) – 00:28:27
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (expensive education, expensive books) – 00:35:40
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (economic imperatives) – 00:42:35
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (expensive writing materials) – 00:44:44
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (difficulties of reading) – 00:49:16
The Ancient memory – 00:53:14
The primacy of oral communication – 00:55:23
The Ancient World: a largely illiterate civilisation (the Second Sophistic and linguistic change) – 00:59:53
Bibliography – 01:08:10
(more…)
May 4, 2025
Everyday Life in the Roman Empire – Culture and Literacy in the Roman Empire
April 10, 2025
QotD: Epicurus on death
If it is to succeed, Epicureanism must deliver us not only from physical pain but also from anxiety and mental anguish. The prospect of death, Epicurus knew, upset many people. Hence he and his followers expended a great deal of effort trying to remove the sting, the fear, from the prospect of death.
Epicurus offered two things to battle the fear of death: an attitude and an argument. The attitude was one of mild contempt: the right sort of people, he implies, do not get in a tizzy about things, not even about death. The argument is equally compelling. “Get used to believing,” he says, “that death is nothing to us.”
Why?
Because all good and bad consist in sense experience. Death is the absence of sense experience. Therefore, “when we exist, death is not yet present, and when death is present, then we do not exist. Therefore it is relevant neither to the living nor to the dead, since it does not affect the former, and the latter do not exist.”
How convincing is this?
Not very. Even if one were to grant the materialism that Epicureanism assumes, one might object that what one resents about death is not the simple absence of sense experience but the loss of the world: one’s friends, engagements, duties, involvements, as well as the panoply of sense experience that attends living.
Death also brings with it the prospect of pain and suffering: few of us can count on a pain-free exit, and that fact also helps to account for the bad reputation death has among non-Epicureans.
Finally, Epicurus and his followers say “death is nothing to us,” but they leave out of account the fact that human beings exist not simply as individuals but as part of a network of family, friends, and a larger community.
Epicurus taught that “self-sufficiency is a great good”. But who, really, is self-sufficient? Let’s say you are married with young children. Your death, quite apart from the inconvenience it might be thought to cause you, would also gravely affect your spouse and children.
There is not much room from children or spouses in the Epicurean philosophy. Why? Because they threaten to compromise the ideal of self-sufficiency. At bottom, Epicureanism is a workable philosophy only for a small subset of people. You must be unafflicted by life’s tragedies: grave poverty or illness or oppression makes being an Epicurean difficult. You must also be largely unafflicted by deep passions. A profound love of life is incompatible with Epicureanism, as is a profound love of one’s children.
The true Epicurean is more of a spectator of than a participant in life. The Roman poet Lucretius (c. 99-c. 55 BC) was one of Epicurus’ greatest disciples. In his long paean to Epicureanism “De Rerum Natura” (“On The Nature of Things”), Lucretius extolled the great sweetness of disengagement, of becoming a spectator rather than a participant in life. In a famous passage, Lucretius warns that “medio de fonte leporum surgit aliquid amari quod in ipsis floribus angat” — “even in the midst of the fountain of pleasure there is something bitter that torments us in the midst of our flowering”. Hence it is better to step back, to watch “the clash of battle / Across the plains, yourself immune to danger”.
One is left with two questions. The first is whether the immunity that Lucretius (like Epicurus) promises is real or illusory. Can we really remain mere spectators of our lives? The second question is whether, even if possible, such disengagement is finally desirable. Perhaps some battles can only be won by engaging with the enemy.
Roger Kimball, “Coronavirus, Flynn and Epicureanism”, American Greatness, 2020-05-02.
November 29, 2024
Greek History and Civilization, Part 8 – The Hellenistic Age
seangabb
Published Jul 17, 2024This eighth lecture in the course covers the Hellenistic Age of Greece — from the death of Alexander in 323 BC to about the death of Cleopatra in 30 BC.
(more…)
October 27, 2024
Reading the Herculaneum Papyri
Toldinstone Footnotes
Published Jul 5, 2024On this episode of the Toldinstone Podcast, Dr. Federica Nicolardi and I discuss the challenges of reading scrolls charred and buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD.
Chapters:
00:00 Discovery of the scrolls
03:23 Opened and unopened
05:17 How to handle charred papyrus
09:11 New texts
13:17 Philodemus of Gadara
16:04 Epicurean philosophy
20:20 The library in the Villa of the Papyri
24:05 The Vesuvius Challenge
25:56 Progress so far …
28:44 The newest text
30:06 What comes next
34:20 What’s still buried?
October 26, 2024
Secrets of the Herculaneum Papyri
toldinstone
Published Jul 5, 2024The Herculaneum papyri, scrolls buried and charred by Vesuvius, are the most tantalizing puzzle in Roman archaeology. I recently visited the Biblioteca Nazionale in Naples, where most of the papyri are kept, and discussed the latest efforts to decipher the scrolls with Dr. Federica Nicolardi.
My interview with Dr. Nicolardi: https://youtu.be/gs1Z-YN1aQMChapters:
0:00 Introduction
0:40 Opening the scrolls
1:47 A visit to the library
2:38 A papyrologist at work
4:00 The Vesuvius Challenge
4:46 What the scrolls say
5:40 Contents of the unopened scrolls
6:28 The other library
7:12 An interview with Dr. Nicolardi
(more…)
February 9, 2024
The (so-far limited) ability to read the Herculaneum Papyri may vastly increase our knowledge about the Roman world
Colby Cosh on the achievement of the three young researchers who were awarded the Vesuvius Challenge prize earlier this month, and what it might mean for classicists and other academics:
On Monday morning, Farritor and two other young Vesuvius Challenge notables, Youssef Nader and Julian Schillinger, were announced as winners of the grand prize. Nader and Schillinger had, like Farritor, already won Vesuvius Challenge prizes for smaller technical discoveries, and Nader had in fact been a mere heartbeat behind Farritor in producing the same “porphyras” from the same scan. After Farritor nabbed his US$40,000 “first letters” prize, the three decided to combine their efforts to net the big fish.
The result is a text that represents about five per cent of one of the thousands of scrolls recovered — and there may be more not yet recovered — from the Villa of the Papyri. The enormous villa was owned by an unknown Roman notable, but there are clues that one of its librarians was the Epicurean philosopher Philodemus of Gadara, who lived from around 110 to 35 BC. Until his identity was connected with the library, Philodemus did not receive too much attention even from classicists. But the Vesuvius Challenge efforts have now yielded fragments of what has to be an Epicurean text — one which discusses the delights of music and food, and condemns an unnamed adversary, possibly a Stoic, for failing to give a philosophical account of sensual pleasure.
The recovery of dozens more of the works of Philodemus would be — one might now say “will be” — a world-changing event for the classics. We know Philodemus was close to Calpurnius Piso (101-43 BC), the father-in-law of Julius Caesar and a likely owner of the doomed villa. He almost certainly had a front-row seat for the prelude to the end of the Roman Republic. We know he wrote works on religion, on natural philosophy and on history: even his thoughts on music and poetry would be of marked interest.
But nobody knows what else, what copies of older works, may be lurking in Philodemus’s library. At this moment antiquarians know the titles of dozens of lost plays by Aeschylus and Sophocles and Euripides and Aristophanes; we are missing major works of Aristotle and Euclid and Archimedes and Eratosthenes. We know that Sulla wrote his memoirs and that Cato the Elder wrote a seven-book history of Rome. Any of these old writings, or others of equal significance, may materialize suddenly out of oblivion now, thanks to the Vesuvius Challenge. It’s an impressive triumph for the idea of prize-giving as an approach to solving scientific problems, and the news release from the challenge offers a discussion of what the funding team got right and where the project will go next.
February 5, 2024
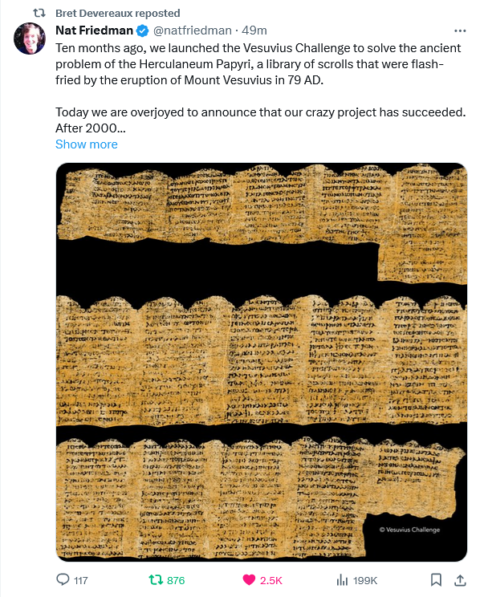
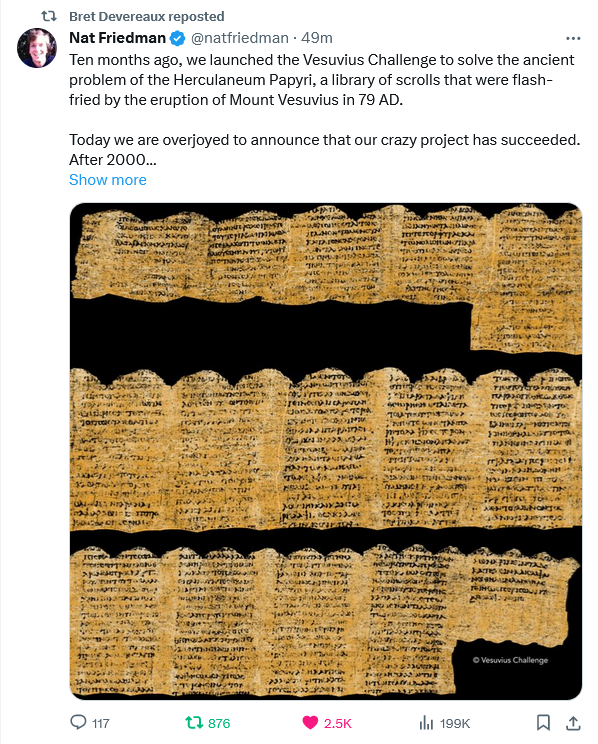
The Vesuvius Challenge prize has been awarded!
Scrolling through Twit-, er, I mean “X” this morning brought me this amazing piece of news for classical scholars:
We received many excellent submissions for the Vesuvius Challenge Grand Prize, several in the final minutes before the midnight deadline on January 1st.
We presented these submissions to the review team, and they were met with widespread amazement. We spent the month of January carefully reviewing all submissions. Our team of eminent papyrologists worked day and night to review 15 columns of text in anonymized submissions, while the technical team audited and reproduced the submitted code and methods.
There was one submission that stood out clearly from the rest. Working independently, each member of our team of papyrologists recovered more text from this submission than any other. Remarkably, the entry achieved the criteria we set when announcing the Vesuvius Challenge in March: 4 passages of 140 characters each, with at least 85% of characters recoverable. This was not a given: most of us on the organizing team assigned a less than 30% probability of success when we announced these criteria! And in addition, the submission includes another 11 (!) columns of text — more than 2000 characters total.
The results of this review were clear and unanimous: the Vesuvius Challenge Grand Prize of $700,000 is awarded to a team of three for their excellent submission. Congratulations to Youssef Nader, Luke Farritor, and Julian Schilliger!
Much more information at the Vesuvius Challenge site.
July 18, 2022
QotD: The basis of belief in pre-modern polytheistic societies
 For the Roman (or most any ancient polytheist) there is never much question of if the gods exist. True atheism was extremely rare in the pre-modern world – the closest ancient philosophy gets to is Epicureanism, which posits that the gods absolutely do exist, but they simply do not care about you (the fancy theological term here is immanence (the state of being manifest in the material world). Epicureans believed the gods existed, but were not immanent, that they did not care about and were little involved with the daily functioning of the world we inhabit). But the existence of the gods was self-evident in the natural phenomena of the world. Belief was never at issue.
For the Roman (or most any ancient polytheist) there is never much question of if the gods exist. True atheism was extremely rare in the pre-modern world – the closest ancient philosophy gets to is Epicureanism, which posits that the gods absolutely do exist, but they simply do not care about you (the fancy theological term here is immanence (the state of being manifest in the material world). Epicureans believed the gods existed, but were not immanent, that they did not care about and were little involved with the daily functioning of the world we inhabit). But the existence of the gods was self-evident in the natural phenomena of the world. Belief was never at issue.
(This is, as an aside, much the world-view we might expect from a universe – as is often the case in speculative fiction or high fantasy – where divine beings are not merely immanent, but obviously so, intervening in major, visibly supernatural ways. The point at which this or that supernatural, divine being brings someone back to life, grants them eternal youth or makes swords light on fire ought to be a pretty substantial theological awakening for everyone there. Even for other polytheists, such displays demand the institution of cult and ritual.)
This, of course, loops back to one of my favorite points about history: it is generally safe to assume that people in the past believed their own religion. Which is to say that polytheists genuinely believe there are many gods and that those gods have power over their lives, and act accordingly.
In many ways, polytheistic religions, both ancient and modern (by modern polytheisms, I mean long-standing traditional religious structures like Hinduism and Shinto, rather than various “New Age” or “Neo-pagan” systems, which often do not follow these principles), fall out quite logically from this conclusion. If the world is full of gods who possess great power, then it is necessary to be on their good side – quite regardless of it they are morally good, have appropriate life philosophies, or anything else. After all, such powerful beings can do you or your community great good or great harm, so it is necessary to be in their good graces or at the very least to not anger them.
Consequently, it does not matter if you do not particularly like one god or other. The Greeks quite clearly did not like Ares (the Romans were much more comfortable with Mars), but that doesn’t mean he stopped being powerful and thus needing to be appeased.
So if these polytheistic religions are about knowledge, then what do you need to know? There are two big things: first you need to know what gods exist who pertain to you, and second you need to know what those gods want.
Two things I want to pull out here. First: the exact nature and qualities of the gods do not really matter, because remember, the goal is practical results. Crops need to grow, ships need to sail, rain needs to fall and the precise length of Zeus’ beard is profoundly unimportant to those objectives, but getting Zeus to bring storms at the right times is indispensable. The nature of the gods largely does not matter – what matters is what you need to do to keep them happy.
Second, you may be saying – you keep ramming home the idea that you have to cultivate all of the gods – what is this “pertaining to you” business? What I mean by this is that while the polytheist typically accepts the existence of vast numbers of gods (often vast beyond counting), typically only a subset of those gods might be immediately relevant. Some gods are tied to specific places, or specific families, or jobs, or problems – if you don’t live in that place, belong to that family, hold that job, etc., then you don’t need to develop a relationship with that god.
Nevertheless, everyone typically needs to develop a relationship with the big gods – the sort whose name you know from a high school or college class – that control big parts of life we all share, along with a bunch of smaller gods which pertain to smaller parts of our lives or perhaps only to select groups of people (we’ll talk more about these “little” gods later in this series, because they are fascinating).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: Practical Polytheism, Part I: Knowledge”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-10-25.
August 4, 2020
QotD: Epicureans are not hedonists
… for now I am tempted amidst the “darling buds of May” to ponder with affection the proverbial injunction “Eat drink and be merry!”
Many people consider that a fair summary of the Epicurean philosophy, named for its founder, the Athenian philosopher Epicurus who lived from 341-270 B.C., a few generations after Plato. It is a natural mistake. After all Epicurus did say that “Pleasure is the starting-point and goal of living blessedly.”
A common Greek word for pleasure is “hedone,” whence our word “hedonism.” A hedonist, we know, is someone who devotes himself to sensual pleasure. Add that to the fact that Epicureanism is a deeply materialistic philosophy — “all good and bad,” Epicurus says, “consists in sense experience” — and it is easy to see why people often conclude that Epicureanism advocates sensual abandon.
Easy, but mistaken.
For in fact, Epicureanism is a deeply ascetic philosophy. It preaches the gospel of pleasure. But it defines pleasure in such a way that no hedonist worth his salt would embrace it.
A hedonist is someone devoted to pleasure in the positive sense: he seeks to gratify his senses.
An Epicurean is devoted to pleasure in the negative sense: he seeks to avoid pain. “We do everything we can,” Epicurus wrote, “for the sake of being neither in pain nor terror.”
It is a melancholy fact that the human frame, while capable of great joy and pleasure, is susceptible to even greater pain and misery. The pleasures afforded us are delicate blossoms; the pains we are susceptible to are like a raging wildfire in comparison. Epicurus and his followers took note of this fact. Indeed, it was a fact that mesmerized their imaginations.
Epicurus says that pleasure is the goal of life. But what he taught was immunity to pain. “The removal of all feeling of pain,” he wrote, “is the limit of the magnitude of pleasures.” There was a core of common sense about the Epicurean approach to life. He advised his followers to live simple, healthy lives, to shun extravagances of all sorts. Of course, that is something many philosophers, indeed many friends and parents, would also advise. There is nothing distinctively Epicurean about the injunction to live simply and soberly.
There are three things distinctive about Epicureanism. One is its identification of pleasure with the absence of pain. Another is its emphasis on sense experience as the ultimate reality. The third is its identification of tranquillity as the aim or goal of life. (The Greek word is “ataraxia,” i.e., not troubled, not disturbed: note the privative character of the Epicurean ideal.)
If it is to succeed, Epicureanism must deliver us not only from physical pain but also from anxiety and mental anguish. The prospect of death, Epicurus knew, upset many people. Hence he and his followers expended a great deal of effort trying to remove the sting, the fear, from the prospect of death.
Epicurus offered two things to battle the fear of death: an attitude and an argument. The attitude was one of mild contempt: the right sort of people, he implies, do not get in a tizzy about things, not even about death. The argument is equally compelling. “Get used to believing,” he says, “that death is nothing to us.”
Roger Kimball, “Coronavirus, Flynn and Epicureanism”, American Greatness, 2020-05-02.
April 19, 2020
QotD: Early Greek philosophers
The greatest name in this succession of first researchers was that of Democritus, who became known as the laughing philosopher. In his ethical teaching great store was set by cheerfulness.
Democritus was still living when the new scientific movement suffered a violent reverse. It was in Athens, a center of conservatism, that the opposition arose and it was brilliantly headed. The leader was no other than Socrates, who despaired of the possibility of scientific knowledge. Even Aristotle, who pioneered in some branches of science, rejected the atomic theory. Between these two great names came that of Plato, who believed the ultimate realities to be not atoms but triangles, cubes, spheres and the like. By a kind of analogy he extended this doctrine to the realm of abstract thought. If, for example, perfect spheres exist, why should not perfect justice exist also? Convinced that such perfect justice did exist, he sought in his own way to find it. The ten books of his Republic record only part of his searchings of the mind. At the core of all this thinking lies the doctrine that the eternal, unchangeable things are forms, shapes, models, patterns, or, what means the same thing in Greek, “ideas.” All visible things are but changing copies of unchanging forms.
The Epicurean Revival
After the great triumvirate of Socrates, Plato and Aristotle had passed away the scientific tradition was revived with timely amendments by Epicurus. In his time it was the prevalent teaching that the qualities of compound bodies must be explained by the qualities of the ingredients. If the compound body was cold, then it must contain the cold element air, if moist, water, if dry, earth, and if hot, fire. Even Aristotle sanctioned this belief in the four elements. Epicurus, on the contrary, maintained that colorless atoms could produce a compound of any color according to the circumstances of their combination. This was the first definite recognition of what we now know as chemical change.
The Stoic Reaction
Epicurus was still a young man when Athenian conservatism bred a second reaction to the new science. This was headed by Zeno, the founder of Stoicism. His followers welcomed a regression more extreme than that of Aristotle in respect to the prime elements. For the source of their physical theories they went back to Heracleitus, who believed that the sole element was fire. This was not a return to the Stone Age but it was a longish way in that direction.
This Heracleitus had been a doleful and eccentric individual and became known, in contrast to the cheerful Democritus, as the weeping philosopher. His gloom was perpetuated in Stoicism, a cheerless creed, of which the founder is described as “the sour and scowling Zeno.” Epicurus, on the contrary, urged his disciples to “wear a smile while they practiced their philosophy.”
Running parallel to these contrasting attitudes toward life and physical theories was an equally unbroken social divergence. Platonism as a creed was always aristocratic and in favor in royal courts. “I prefer to agree with Plato and be wrong than to agree with those Epicureans and be right,” wrote Cicero, and this snobbish attitude was not peculiar to him. Close to Platonism in point of social ranking stood Stoicism, which steadily extolled virtue, logic, and divine providence. This specious front was no less acceptable to hypocrites than to saints. Aptly the poet Horace, describing a pair of high-born hypocrites, mentions “Stoic tracts strewn among the silken cushions.” Epicureanism, on the contrary, offered no bait to the silk-cushion trade. It eschewed all social distinction. The advice of the founder was to have only so much regard for public opinion as to avoid unfriendly criticism for either sordidness or luxury. This was no fit creed for the socially or politically ambitious.
Norman W. DeWitt, “Epicurus: Philosophy for the Millions”, The Classical Journal, 1947-01.
November 25, 2019
How to Be an Epicurean
In City Journal, Michael Gibson reviews a recent book on Epicureanism by Catherine Wilson:
The Atomic Age had its anxieties, but Hugh Hefner believed he had a good diversion. “We aren’t a family magazine,” he announced in the first issue of Playboy in 1953. “We enjoy mixing up cocktails, an hors d’oeuvres or two, putting a little mood music on the phonograph, and inviting in a female acquaintance for a quiet discussion on Picasso, Nietzsche, jazz, sex.” By the 1960s, the music had grown louder, the colors more lurid, the conversations steamier. When Hefner died in 2017, he was considered either a hero of hedonism or an object lesson in the period’s squalid obsessions. Run a Google search today on Hefner, and you’ll often find the word “Epicurean” to describe him. Is this fair to Epicurus, the man who set forth the philosophy starting in 306 BC?
Marble bust of Epicurus. Roman copy of Greek original, 3rd century BC/2nd century BC. On display in the British Museum, London.
Photo by ChrisO via Wikimedia Commons.For 23 centuries now, Epicureans have struggled mightily against variations of the Hefner caricature. If pleasure is the highest good, the goal of the best life, must we all strive to live in pajamas, smoking a pipe in a decadent Hollywood Hills estate? Though he didn’t live in a mansion off Sunset Boulevard, at the end of the fourth century BC, at the age of 32, the philosopher Epicurus founded the Garden, a school removed from Athens’s monuments of power and politics. An inscription at the entrance read: “Stranger, here you will do well to stay; here our highest good is pleasure.” (In Chicago, Hefner’s door bore an inscription: Si Non Oscillas, Noli Tintinnare, or “If you don’t swing, don’t ring.”)
Leading life in a modern Garden is the subject of Catherine Wilson’s latest book, How to Be an Epicurean: The Ancient Art of Living Well. There was always an air of Peter Pan-like anarchy at the Playboy Mansion, but as Wilson shows us, life in the Garden was quite different. Her book is a spirited tour and defense of Epicurean philosophy, as reconstructed by the fragments Epicurus left behind in tattered papyrus and as set forth in the epic poem De Rerum Natura, “On the Nature of Things,” by the Roman poet Lucretius.
What did these pleasure-seekers believe? They start with the elementary particles, atoms — tiny, colorless, without smell, shaped this way and that, indestructible, reshuffling themselves infinitely into all the marvelous forms we see, including ourselves. Their forms get swept away by time, only to recombine again into something new — possibly another universe. Blurred in this haze of metaphysics, most atoms fall straight downward into the void, but a few swerve, and from these deviations arise our free will and all that we see. At the California Institute of Technology, physicist Richard Feynman began his lectures by wondering what single sentence would be passed on to future generations, if, in a cataclysm, all scientific knowledge was destroyed. His answer: “The atomic hypothesis that all things are made of atoms.”
With the Epicureans, we have a historical test of Feynman’s thought. The world is made of nothing more than atoms in the void, but where did that take the ancient Greeks and Romans who believed it? Wilson begins with these basic building blocks because she asserts that mistaken beliefs about nature are the source of our deepest fears and hang-ups: death, punishment in an afterlife, failure in this one, lust for power, greed, jealousy, unrequited love, and status-jockeying. “Epicurean philosophy might be said to be based on the notion of the limit,” Wilson writes. By understanding the atom and the void, by knowing that the soul is mortal and the gods indifferent, that all things pass and are forgotten, we might then liberate ourselves from the grinding weight of superstition and the vanity of ambition and pursue pleasure without guilt.
October 5, 2018
QotD: Thomas Jefferson, Epicurean
As you say of yourself, I too am an Epicurean. I consider the genuine (not the imputed) doctrines of Epicurus as containing everything rational in moral philosophy which Greece and Rome have left us. Epictetus indeed, has given us what was good of the stoics; all beyond, of their dogmas, being hypocrisy and grimace. Their great crime was in their calumnies of Epicurus and misrepresentations of his doctrines; in which we lament to see the candid character of Cicero engaging as an accomplice. Diffuse, vapid, rhetorical, but enchanting. His prototype Plato, eloquent as himself, dealing out mysticisms incomprehensible to the human mind, has been deified by certain sects usurping the name of Christians; because, in his foggy conceptions, they found a basis of impenetrable darkness whereon to rear fabrications as delirious, of their own invention. These they fathered blasphemously on him who they claimed as their founder, but who would disclaim them with the indignation which their caricatures of his religion so justly excite. Of Socrates we have nothing genuine but in the Memorabilia of Xenophon; for Plato makes him one of his Collocutors merely to cover his own whimsies under the mantle of his name; a liberty of which we are told Socrates himself complained. Seneca is indeed a fine moralist, disguising his work at times with some Stoicisms, and affecting too much of antithesis and point, yet giving us on the whole a great deal of sound and practical morality. But the greatest of all the reformers of the depraved religion of his own country, was Jesus of Nazareth. Abstracting what is really his from the rubbish in which it is buried, easily distinguished by its lustre from the dross of his biographers, and as separable from that as the diamond from the dunghill, we have the outlines of a system of the most sublime morality which has ever fallen from the lips of man; outlines which it is lamentable he did not live to fill up. Epictetus and Epicurus give laws for governing ourselves, Jesus a supplement of the duties and charities we owe to others. The establishment of the innocent and genuine character of this benevolent moralist, and the rescuing it form the imputation of imposture, which has resulted from artificial systems, **** invented by ultra-Christian sects, and unauthorized by a single word ever uttered by him, is a most desirable object, and one to which Priestley has successfully devoted his labors and learning. It would in time, it is to be hoped, effect a quiet euthanasia of the heresies of bigotry and fanaticism which have so long triumphed over human reason, and so generally and deeply afflicted mankind; but this work is to be begun by winnowing the grain form the chaff of the historians of his life. I have sometimes thought of translating Epictetus (for he has never been tolerably translated into English) by adding the genuine doctrines of Epicurus from the Syntagma of Gassendi, and an abstract from the Evangelists of whatever has the stamp of the eloquence and fine imagination of Jesus. The last I attempted too hastily some twelve or fifteen years ago. It was the work of two or three nights only, at Washington, after getting through the evening task of reading the letters and papers of the day. But with one foot in the grave, these are now idle projects for me. My business is to beguile the wearisomeness of declining life, as I endeavor to do, by the delights of classical reading and of mathematical truths, and by the consolations of a sound philosophy, equally indifferent to hope and fear.
I take the liberty of observing that you are not a true disciple of our master Epicurus, in indulging the indolence to which you say you are yielding. One of his canons, you know, was that “that indulgence which prevents a greater pleasure, or produces a greater pain, is to be avoided.” Your love of repose will lead, in its progress, to a suspension of healthy exercise, a relaxation of mind, an indifference to everything around you, and finally to a debility of body, and hebetude of mind, the farthest of all things from the happiness which the well-regulated indulgences of Epicurus ensure; fortitude, you know is one of his four cardinal virtues. That teaches us to meet and surmount difficulties; not to fly from them, like cowards; and to fly, too, in vain, for they will meet and arrest us at every turn of our road. Weigh this matter well; brace yourself up; take a seat with Correa, and come and see the finest portion of your country, which, if you have not forgotten, you still do not know, because it is no longer the same as when you knew it. It will add much to the happiness of my recovery to be able to receive Correa and yourself, and prove the estimation in which I hold you both. Come, too, sand see your incipient University, which has advanced with great activity this year. By the end of the next, we shall have elegant accommodations for seven professors, and the year following the professors themselves. No secondary character will be received among them. Either the ablest which America or Europe can furnish, or none at all. They will give us the selected society of a great city separated from the dissipations and levities of its ephemeral insects.
I am glad the bust of Condorcet has been saved and so well placed. His genius should be before us; while the lamentable, but singular act of ingratitude which tarnished his latter days, may be thrown behind us.
I will place under this a syllabus of the doctrines of Epicurus, somewhat in the lapidary style, which I wrote some twenty years ago; a like one of the philosophy of Jesus of nearly the same age, is too long to be copied. Vale, et tibi persuade carissimum te esse mihi.
**** e. g. The immaculate conception of Jesus, his deification, the creation of the world by him, his miraculous powers, his resurrection and visible ascension, his corporeal presence in the Eucharist, the Trinity; original sin, atonement, regeneration, election, orders of Hierarchy, &c.
Thomas Jefferson, letter to William Short, 1819-10-31.
Syllabus of the doctrines of Epicurus
Physical
The Universe eternal.
Its parts, great and small, interchangeable
Matter and Void alone.
Motion inherent in matter, which is weighty & declining
eternal circulation of the elements of bodies.
Gods, an order of beings next superior to man.
enjoying in their sphere their own felicities,
but not meddling with the concerns of the scale of beings below them
Moral
Happiness the aim of life
Virtue the foundation of happiness
Utility the test of virtue.
Pleasure active and in-dolent.
In-dolence is the absence of pain, the true felicity
Active, consists in agreeable motion
it is not happiness, but the means to produce it.
thus the absence of hunger is an article of felicity; eating the means to produce it.
The summum bonum is to be not pained in body, nor troubled in mind
i.e. In-dolence of body, tranquility of mind.
to procure tranquility of mind we must avoid desire & fear, the two
principal diseases of the mind.
Man is a free agent.
Virtue consists in: 1. Prudence 2. Temperance 3. Fortitude 4. Justice
to which are opposed: 1. Folly 2. Desire 3. Fear 4. Deceit
September 22, 2018
QotD: Epicurean influences on Marx
… what’s also interesting is that our friends the Marxists also thought Epicurus was a great philosopher. Marx himself did his doctoral dissertation on the differences between the atomism of Epicurus and his forerunner Democritus.
Most books on Epicureanism published in France in the 20th century were written by Marxists. (Well, I suppose you could say that of most books published in France on any topics in the 20th century…!) I have a booklet on Lucretius at home published in France in the 1950s in a collection called Les classiques du peuple – The classics of the people. In the Acknowledgement section, the author thanks all the Soviet specialists of Epicureanism and materialism for any original insight that might appear in the book.
Marx found in Epicureanism a materialist conception of nature that rejected all teleology and all religious conceptions of natural and social existence.
Martin Masse, “The Epicurean roots of some classical liberal and Misesian concepts“, speaking at the Austrian Scholars Conference, Auburn Alabama, 2005-03-18.
September 8, 2018
QotD: Reactions to, and criticisms of, Epicureanism
Hedonism has always been a controversial doctrine, so far as it is opposed to the teachings of the explicitly altruistic philosophies and religious systems. There are difficulties with hedonism when it comes to the exact comparison of pleasures. We do not have any of the more detailed works in which Epicurus might have attempted what Jeremy Bentham later called a “felicific calculus”. But, bearing in mind the difficulties that Bentham and the 19th century utilitarians found when they tried to move from principles to details, there is no reason to suppose he was more successful.
However, it is hard to see anything so scandalous in the pursuit of happiness through moderation and through friendship that should have brought on a flood of often hysterical denunciation and misrepresentation in antiquity that began in his own lifetime and did not end even with the loss of virtually the whole body of Epicurean writings.
The early accusations are very detailed, and are cited by Diogenes Laertius. Among much else, it is alleged:
- That he wrote 50 obscene letters;
- That one of his brothers was a pimp;
- That his understanding of philosophy was small and his understanding of life even smaller;
- That he put forward as his own the doctrines of Democritus about atoms and of Aristippus about pleasure;
- That in his On Nature Epicurus says the same things over and over again and writes largely in sheer opposition to others, especially against his former teacher Nausiphanes;
- That he was not a genuine Athenian;
- That he vomited twice a day from over-indulgence.
Three centuries after his death, Plutarch (46-127 AD) wrote against him in almost hysterical tone. He says:
Epicurus… actually advises a cultivated monarch to put up with recitals of stratagems and with vulgar buffooneries at his drinking parties sooner than with the discussion of problems in music and poetry.
And again:
Colotes himself, for another, while hearing a lecture of Epicurus on natural philosophy, suddenly cast himself down before him and embraced his knees; and this is what Epicurus himself writes about it in a tone of solemn pride: ‘You, as one revering my remarks on that occasion, were seized with a desire, not accounted for by my lecture, to embrace me by clasping my knees and lay hold of me to the whole extent of the contact that is customarily established in revering and supplicating certain personages. You therefore caused me,’ he says, ‘to consecrate you in return and demonstrate my reverence.’ My word! We can pardon those who say that they would pay any price to see a painting of that scene, one kneeling at the feet of the other and embracing his knees while the other returns the supplication and worship. Yet that act of homage, though skillfully contrived by Colotes, bore no proper fruit: he was not proclaimed a Sage. Epicurus merely says: ‘Go about as one immortal in my eyes, and think of me as immortal too.’
Now, all this and more was said against Epicurus when the whole body of his writings was still available, and by men who had access to those writings. It is unlikely, bearing in mind their general ability, that they were incapable of understanding plain Greek. So what could have been their motivation for misrepresenting him in defiance of the evidence, or in repeating personal libels irrelevant to his philosophy?
A possible answer is that they hated his philosophy for other reasons that they were not able or did not wish fully to discuss.
What does make Epicurus and his philosophy so controversial is one further piece of advice on the pursuit of happiness. It is impossible to be happy, he insists, unless we understand the nature of the universe and our own place within the universe.
Sean Gabb, “Epicurus: Father of the Enlightenment”, speaking to the 6/20 Club in London, 2007-09-06.
August 26, 2018
QotD: Epicurus and the gods
… [Ludwig von] Mises ridicules the naïve anthropomorphism that consists in applying human characteristics to deities defined as perfect and omnipotent. How could such a being be understood to be planning and acting, or be angry, jealous, and open to bribing, as he is shown in many religious traditions? As he writes in Human Action again, “An acting being is discontented and therefore not almighty. If he were contented, he would not act, and if he were almighty, he would have long since radically removed his discontent.”
In an article on the implications of human action published on Mises.org two years ago, Gene Callahan discusses this and asserts that Mises’ insight into the relationship of praxeology to any possible supreme being is quite original, at least as far as he knows. Well, in fact, this insight is straight out of Epicureanism. Epicurus declared that since Gods were perfect and completely contented, they could not be involved in any way in human affairs. It was silly to be afraid of them, and useless to try to propitiate them. For this of course, he was suspected of being an atheist, and this is a major reason why he has been so vilified by Christian writers for centuries.
Martin Masse, “The Epicurean roots of some classical liberal and Misesian concepts“, speaking at the Austrian Scholars Conference, Auburn Alabama, 2005-03-18.