HardThrasher
Published 2 Feb 2023For more than 1,000 years British people have studied how to invade France, here then are the fruits of that wisdom.
1. Be German
2. Head for Sedan
March 23, 2025
How To Invade France
January 12, 2025
QotD: Kaiser Wilhelm II
Following the all-too brief reign of Frederick III, his son Wilhelm II, grandson of the first German Emperor, took power in 1888 (known as the “year of the three emperors”). From the start, the young Wilhelm was determined not to be the reserved figure of his grandfather and still less the liberal reformer that his ill-fated father had wished to be. Instead, Wilhelm believed it was his right and duty to be directly involved in the country’s governing.
This was completely incompatible with Bismarck’s system, which had centralized power upon his own person. With uncharacteristic focus and subtlety, Wilhelm sought to reclaim the power that his grandfather had ceded to the chancellor. This was not to prove especially difficult; Bismarck’s position had always relied upon his indispensability to the emperor. Thus, when Bismarck offered his resignation (as he often did during disputes) Wilhelm merely accepted it. The last great man of the wars of unification had now disappeared from the balance.
While the German Empire never became a true autocracy, Wilhelm succeeded in creating what historian, and biographer of the Kaiser, John C. Röhl called a “personalist” system.1 The Kaiser had significant power over personnel. Promotions in the officer corps required his assent. Advancement within civil service (from which civilian ministers were appointed) was also dependent on his favor. By exercising this power, Wilhelm was able to ensure the highest levels of the German government were men agreeable to his point of view. Though they were not mere “yes men”, Wilhelm ensured that they were knowingly dependent on his favor for their position. The Kaiser — even to the end of the monarchy — exercised considerable “negative power” (as Röhl termed it.)2 While Wilhelm’s ability to actively make policy was limited, anything he disapproved of was simply not proposed.
Wilhelm II’s reign marked a departure from the more restrained leadership of his predecessors, as he sought to assert direct influence over the German Empire’s governance and military affairs. This shift toward a more “personalist” system, where loyalty to the Kaiser outweighed true statesmanship, weakened the effectiveness of German leadership and contributed to its eventual strategic missteps. The rigid adherence to the Schlieffen Plan and the technocratic focus on material advantages, such as firepower and mobility, overshadowed the need for adaptable strategic thinking. These failures in both leadership and military planning set the stage for Germany’s disastrous involvement in World War I, where an empire led by personalities rather than policies was ill-prepared for the complexities of modern warfare. Ultimately, Wilhelm’s influence and the culture of sycophancy he fostered played a pivotal role in leading Germany down the path of ruin.
Kiran Pfitzner and Secretary of Defense Rock, “The Kaiser and His Men: Civil-Military Relations in Wilhelmine Germany”, Dead Carl and You, 2024-10-02.
1. John C. G. Röhl, Kaiser Wilhelm II: A Concise Life (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2014).
2. Negative power refers to the ability of an actor or group to block, veto, or prevent actions, decisions, or policies from being implemented, rather than directly initiating or shaping outcomes.
October 13, 2024
Bismarck, Moltke, and the Kaiser’s General Staff
From Bruce Gudmundsson’s weekly Milstack recommendations, here’s part of an essay on Kaiser Wilhelm and some of the important men in his government in the lead-up to the First World War:
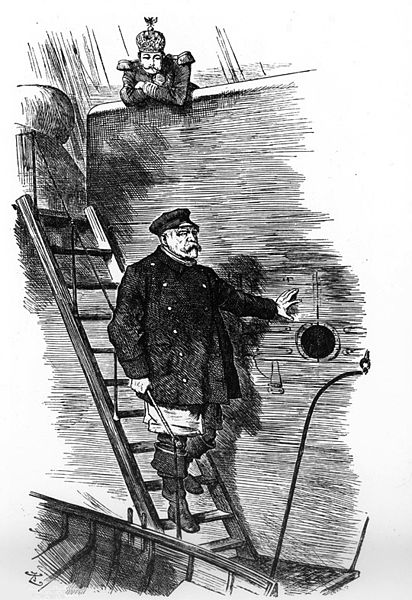

“Dropping the Pilot”. Caricature by Sir John Tenniel (1820-1914), first published in the British magazine Punch, March 1890. Showing German Emperor Wilhelm II and the departing Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
By the 1870s, Germany was the dominant land power in Europe. It had defeated the preeminent powers on the continent and seemed poised for an era of dominance not seen since Napoleon. However, how quickly Germany’s power was checked and ultimately fell is a cautionary tale about the limits and consequences of the predominance of the military profession. Victories in the war had propelled the Prussian Officer Corps to the status of “demigods” that now held “unquestioned authority and legitimacy” in German politics and society.1 But this status meant they had carte blanche over war planning and became increasingly influential in politics. This produced a civil-military relationship in which, “leaders subordinated political ends to military ends; considerations of war dominated considerations of politics”.2 The German General staff was rapidly departing from Clausewitz’s teachings regarding the primacy of policy.
By the 1880s, Otto von Bismarck and Helmuth von Moltke, the key architects of German unification both politically and militarily, were nearing the end of their distinguished careers. Now, a younger generation of German nationalists and military officers were chomping at the bit to further expand Germany’s power and formed the engine of what some have called, “a political doomsday machine”.3 The militarists believed preemptive war was the uniform solution to the rising power of Germany’s neighbors. Likewise, success in the wars of unification had led nationalists to dream of a greater Germany “from Berlin to Baghdad”.4 Even in his late career, Bismarck had the experience and gravitas to stymie attempts to initiate a “preventative” war. For instance, in 1887, the senior military leadership cooked up a scheme to convince the Kaiser to declare war on Russia on a whim; they also encouraged Austria-Hungary to do the same. Bismarck stopped it before it became a crisis. But it was a bad omen and showed how the military leadership was increasingly out of control.
Bismarck and Moltke had their issues, but they eventually built a strong relationship, leading the Chief of the General Staff to discuss prospective war plans with the Chancellor, something that had not occurred regularly before and a sign of good civil-military relations. Moltke continued to hold his role until 1888 when he retired. His thinking in his late career had evolved beyond the axiomatic focus on total victory.5 The Battle of Sedan was as complete a victory as one could imagine, yet it did not end the Franco-Prussian War. The ensuing experience of the Volkskrieg (“People’s War”) which encompassed fighting a tough insurgency in France had disillusioned him with the idea of a short war. In one of his final speeches in the Reichstag in 1890, he stated of the next war that,
If this war breaks out, then its duration and its end will be unforeseeable. The greatest powers of Europe, armed as never before, will be going into battle with each other; not one of them can be crushed so completely in one or two campaigns that it will admit defeat, be compelled to conclude peace under hard terms, and will not come back, even if it is a year later, to renew the struggle. Gentlemen, it may be a war of seven years or thirty years’ duration — and woe to him who sets Europe alight, who [first] puts the fuse to the powder keg!6
Moltke now conceded the need for diplomacy to find a resolution after the army did what it could. “Total victory” was no longer the objective. Unfortunately, by then, the aged Field Marshal was isolated in his work on operational plans and studies. The General Staff had been educated in his original concepts which had been inculcated in the official histories of the wars of unification. Moltke’s genius, shown in the breadth of his thinking, was never absorbed by the institution.
German military historian Gerhard Ritter would distinguish Moltke from his successors for his lack of fatalism. While the Elder Moltke often pressed for preventative war, he made the argument from the military point of view, i.e. that war would be more advantageous now rather than later.7 Moltke was not overly disturbed when Bismarck quashed proposals of preventative war. In contrast to his successors, Moltke was confident in his ability to meet the challenges of war whenever it arrived. He did not view the political situation as intractable. If the statesman did not want to utilize an opportunity for an easy victory in a preventative war, that was the business of the statesman. In other words, Moltke accepted Bismarck’s “right to be wrong”. A working relationship was therefore possible with the statesman who described his policy as “the most dangerous road last”.8
In the final years of their careers, both Bismarck and Moltke foresaw the dangers of a Germany where military prerogatives began to overshadow political ones. Bismarck, the architect of Germany’s rise, understood that the state’s survival hinged not just on military prowess but on the balancing of diplomatic relationships and restrained use of force. Moltke, though a staunch advocate of military autonomy, ultimately recognized the futility of unchecked military power in the context of modern warfare. Their eventual departures left a vacuum, filled by more aggressive military leaders, weak chancellors, and a feckless Kaiser. The political flexibility that had defined Germany’s rise came to be disregarded. As the officer corps grew more entrenched in its dominance, the military’s rigid and totalizing mindset contributed to Germany’s plunge into one of the most destructive conflicts in human history.9
1. Jack Snyder, “Civil-Military Relations and the Cult of the Offensive, 1914 and 1984”. International Security 9 (1) (1984).
2. Keir A. Lieber, “The New History of World War I and What It Means for International Relations Theory”. International Security 32 (2) (2007): 161.
3. Henry Kissinger, Diplomacy (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1995), 168.
4. For more on ultranationalist critique of the German government see Stig Förster, Der Doppelte Militarismus: Die Deutsche Heeresrüstungspolitik Zwischen Status-Quo-Sicherung Und Aggression, 1890-1913, Institut Für Europäische Geschichte Mainz: Veröffentlichungen Des (F. Steiner Verlag Wiesbaden, 1985).
5. For further detail, see Gerhard P. Gross, The Myth and Reality of German Warfare: Operational Thinking from Moltke the Elder to Heusinger.
6. Stig Förster, “Dreams and Nightmares: German Military Leadership and the Images of Future Warfare, 1871-1914”. In Anticipating Total War, The German and American experiences, 1871-1914, 343-376 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2013), 347.
7. A preventative war, in this context, is a conflict initiated to preemptively counter an anticipated future threat or to prevent a rival power from becoming stronger in the long term.
8. Gerhard Ritter, The Sword and the Scepter: The Problem of Militarism in Germany (Coral Gables: University of Miami Press, 1973), vol. 1 of 4, 243.
9. For more on Imperial German military culture, see Isabel Hull, Absolute Destruction: Military Culture and the Practices of War in Imperial Germany (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2005).
March 7, 2024
QotD: Helmuth von Moltke’s Kabinettskriege of 1870
[The Franco-Prussian War] is generally considered the magnum opus of the titanic Prussian commander, Field Marshal Helmuth von Moltke. Exercising deft operational control and an uncanny sense of intuition, Moltke orchestrated an aggressive opening campaign which sent Prusso-German armies streaming like a mass of tentacles into France, trapping the primary French field army in the fortress of Metz in the opening weeks of the war and besieging it. When the French Emperor, Napoleon III, marched out with a relief army (comprising the rest of France’s battle-worthy formations), Moltke hunted that army down as well, encircling it at Sedan and taking the entire force (and the emperor) into captivity.
From an operational perspective, this sequence of events was (and is) considered a masterclass, and a major reason why Moltke has become revered as one of history’s truly great talents (he is on this writer’s Mount Rushmore alongside Hannibal, Napoleon, and Manstein). The Prussians had executed their platonic ideal of warfare — the encirclement of the main enemy body — not once, but twice in a matter of weeks. In the conventional narrative, these great encirclements became the archetype of the German kesselschlacht, or encirclement battle, which became the ultimate goal of all operations. In a certain sense, the German military establishment spent the next half-century dreaming of ways to replicate its victory at Sedan.
This story is true, to a certain extent. My objective here is not to “bust myths” about blitzkrieg or any such trite thing. However, not everyone in the German military establishment looked at the Franco-Prussian War as an ideal. Many were terrified by what happened after Sedan.
By all rights, Moltke’s masterpiece at Sedan should have ended the war. The French had lost both of their trained field armies and their head of state, and ought to have given in to Prussia’s demand (namely, the annexation of the Alsace-Lorraine region).
Instead, Napoleon III’s government was overthrown and a National Government was declared in Paris, which promptly declared what amounted to a total war. The new government abandoned Paris, declared a Levee en Masse — a callback to the wars of the French Revolution in which all men aged 21 to 40 were to be called to arms. Regional governments ordered the destruction of bridges, roads, railways, and telegraphs to deny their use to the Prussians.
Instead of bringing France to its knees, the Prussians found a rapidly mobilizing nation which was determined to fight to the death. The mobilization prowess of the emergency French government was astonishing: by February, 1871, they had raised and armed more than 900,000 men.
Fortunately for the Prussians, this never became a genuine military emergency. The newly raised French units suffered from poor equipment and poor training (particularly because most of France’s trained officers had been captured in the opening campaign). The new mass French armies had poor combat effectiveness, and Moltke managed to coordinate the capture of Paris alongside a campaign which saw Prussian forces marching all over France to run down and destroy the elements of the new French Army.
Big Serge, “The End of Cabinet War”, Big Serge Thought, 2023-11-30.
January 20, 2024
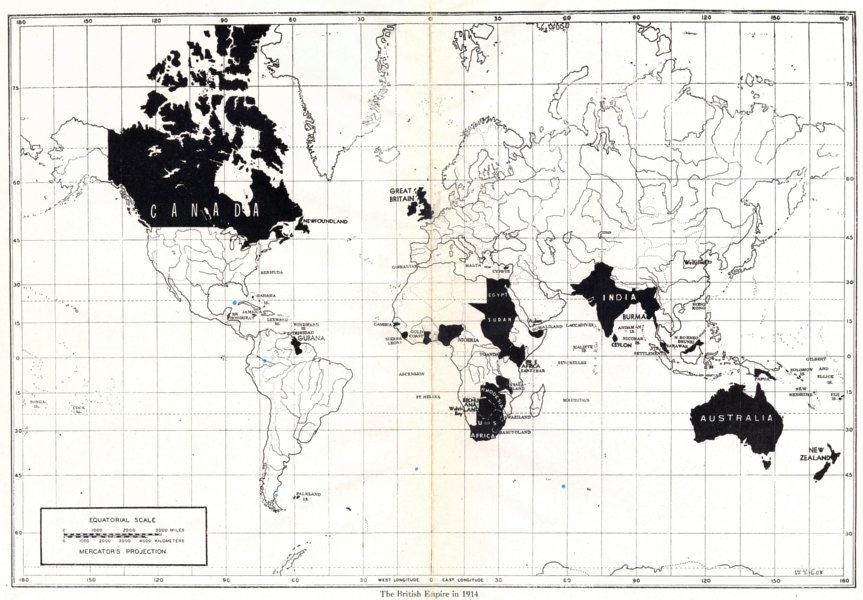
The British Empire would have failed a proper cost-benefit analysis
At the Institute of Economic Affairs, Kristian Niemietz is working on a paper on the economics of empire that, as he shows in this article, indicates that the empire was never a winning economic proposition for Britain as a whole, no matter how well certain well-connected individuals and companies benefitted:
But is it actually true that imperialism makes countries richer? Does imperialism make economic sense?
This question was already hotly debated at the heyday of imperialism. Adam Smith believed that the British Empire would not pass a cost-benefit test:
The pretended purpose of it was to encourage the manufactures, and to increase the commerce of Great Britain. But its real effect has been to raise the rate of mercantile profit, and to enable our merchants to turn into a branch of trade, of which the returns are more slow and distant than those of the greater part of other trades, a greater proportion of their capital than they otherwise would have done […]
Great Britain derives nothing but loss from the dominion which she assumes over her colonies.
He believed that Britain would be better off if it dissolved its Empire:
Great Britain would not only be immediately freed from the whole annual expense of the peace establishment of the colonies, but might settle with them such a treaty of commerce as would effectually secure to her a free trade, more advantageous to the great body of the people, though less so to the merchants, than the monopoly which she at present enjoys.
The liberal free-trade campaigner Richard Cobden agreed:
[O]ur naval force, on the West India station […], amounted to 29 vessels, carrying 474 guns, to protect a commerce just exceeding two millions per annum. This is not all. A considerable military force is kept up in those islands […]
Add to which, our civil expenditure, and the charges at the Colonial Office […]; and we find […] that our whole expenditure, in governing and protecting the trade of those islands, exceeds, considerably, the total amount of their imports of our produce and manufactures.
If imperialism was a loss-making activity – why did Britain and other European colonial empires engage in it for so long?
Smith and Cobden explained it in terms of clientele politics (or Public Choice Economics, as we would say today). Somebody obviously benefited, even if the nation as a whole did not. And the beneficiaries were politically better organised than those who footed the bill.
This proto-Public Choice case against imperialism was not limited to political liberals. Otto von Bismarck, the Minister President of Prussia and future Chancellor of the German Empire, hated liberals in the Smith-Cobden tradition, but he rejected colonialism in terms that almost make him sound like one of them:
The supposed benefits of colonies for the trade and industry of the mother country are, for the most part, illusory. The costs involved in founding, supporting and especially maintaining colonies […] very often exceed the benefits that the mother country derives from them, quite apart from the fact that it is difficult to justify imposing a considerable tax burden on the whole nation for the benefit of individual branches of trade and industry [translation mine].
In his writing about the economics of imperialism, even Michael Parenti, a Marxist-Leninist political scientist (who is, for obvious reasons, popular among Twitter hipsters), sounds almost like a Public Choice economist:
[E]mpires are not losing propositions for everyone. […] [T]he people who reap the benefits are not the same ones who foot the bill. […]
The transnationals monopolize the private returns of empire while carrying little, if any, of the public cost. The expenditures needed […] are paid […] by the taxpayers.
So it was with the British empire in India, the costs of which […] far exceeded what came back into the British treasury. […]
[T]here is nothing irrational about spending three dollars of public money to protect one dollar of private investment – at least not from the perspective of the investors.”
This leads us to a curious situation. Today’s woke progressives disagree with their comrade Parenti on the economics of empire, but they do agree with Britain’s old imperialists, who argued that the Empire was vital for Britain’s prosperity.
November 6, 2023
QotD: The “German Catastrophe”
The obvious frame for this book is what has been fittingly termed the German Catastrophe: the fate of Germany in the late 19th and early 20th century, as viewed from the perspective of German nationalists who were not Nazis — the perspective of people like Ernst Jünger.
Germany had entered modernity without democracy. The Kaiserreich (German Empire) had united the many small German states, aggressively worked to catch up with industrialization, built a state to rival France and Great Britain, and remained authoritarian throughout. Commoners had negligible political influence. They did get social insurance, but not through their own political power but granted top-down, as an appeasement to undermine socialist movements. Civil marriage, secularized state education, prospering state universities and a long series of modernizing laws kept increasing state power. And that meant executive power. There were parties, a parliament and a newly homogenized judiciary, but they had little power to check the executive.
And this entire development was accompanied by a lot of theorizing about this new German nation. Much of this theorizing ended up justifying authoritarianism, by making quickly-spreading myths about how obedience to authority, respect for aristocracy and love for tradition were uniquely German traits that set Germans apart from the French and the Jews and other dubious foreigners. Such myths, and opposition to them, colored the German population’s hard work to get accustomed to industrialization, urbanization, education, rapid population growth, militarization, national media and various culture wars.
This had seemed to work okay-ish while Bismarck, wielding both enormous ruthlessness and enormous political acumen, had navigated Germany through the trials and tribulations of the late 19th century, largely at the expense of France. But in 1890, Emperor Wilhelm II had taken over authority with less ruthlessness and much less political acumen. While his populace remained nearly unable to influence politics, Wilhelm II made critical political mistakes, especially in dealing with other European powers.
These mistakes culminated in the first World War. You know how that one went.
Germany’s defeat led into Germany’s first real democracy. Everyone was very obviously new to this. The right attacked the new state, falsely claiming it had needlessly capitulated. The left also attacked the new state, because it wasn’t Soviet-Union-like enough. There was a lot of political violence. The massive damage incurred in the war, and the restrictions and reparations Germany had accepted in the peace settlement, put massive strains on an already fragile political system. Elections were tumultuous and frequent. Hyperinflation caused a huge crisis in 1923, and the Great Depression of 1929 was another huge disaster for Germany. Overall, the abolition of authoritarianism was widely felt to be a mistake.
This seeming mistake was fixed when Hitler stepped in. And you know how that one went.
Anonymous, “Your Book Review: On the Marble Cliffs”, Astral Codex Ten, 2023-07-28.
September 27, 2022
The War That Made Germany Prussian – Austro-Prussian War 1866
Real Time History
Published 23 Sep 2022After settling the Schleswig-Holstein question in 1864, Austria and Prussia are uneasy allies. Both are the biggest players in the German confederation. In Bismarck’s dream of a united Germany, he sees Prussia as the only leader and wants to force the so called “small German solution” without Austria. And so, in 1866 a war between Austria and Prussia (plus other German states like Bavaria, Baden, Württemberg, Saxony, Hanover) breaks out to settle this question once and for all.
(more…)
August 27, 2022
Prussia’s Rise & Denmark’s Decline: The Schleswig Wars 1848-1864
Real Time History
Publisheed 26 Aug 2022The two Schleswig Wars of 1848-51 and 1864 mark an important period in European History. Intertwined with the 1848 revolutions, the First Schleswig War’s settlement tries to uphold the European status quo. But the unhappy belligerents soon find themselves at war again in 1864 when Prussian Prime Minister Otto von Bismarck uses the Second Schleswig War as a first step towards German unification.
(more…)
January 21, 2022
Why Wilhelm I Didn’t Want To Be German Emperor
Real Time History
Published 20 Jan 2022Get the Smartest Bundle in Streaming: https://smartbundle.com/thegreatwarsb
The proclamation of the German Empire on 18 January 1871 is usually portraited as a glorious ceremony. Most people associated it with the famous paintings from Anton von Werner. But the ceremony itself was far from well organized and the soon-to-be Emperor Wilhlem I himself was not to thrilled about the whole affair.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment, James Darcangelo, Jacob Carter Landt, Thomas Brendan, Kurt Gillies, Scott Deederly, John Belland, Adam Smith, Taylor Allen, Rustem Sharipov, Christoph Wolf, Simen Røste, Marcus Bondura, Ramon Rijkhoek, Theodore Patrick Shannon, Philip Schoffman, Avi Woolf,» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Bartmann, Dominik (Hrsg.): “Ausst.-Kat. DHM‚ Anton von Werner. Geschichte in Bildern.” Berlin 1993
Bauer, Gerhard u.a. (Hrsg.): Ausst.-Kat. MHM Dresden “Krieg – Macht – Nation. Wie das deutsche Kaiserreich entstand”. Dresden 2020
Bühl-Gramer, Charlotte: Anton von Werner – “Die Proklamierung des Deutschen Kaiserreichs 1871”, in: Der Europäische Bildersaal. Europa und seine Bilder, hrsg. v. Michael Wobring und Susanne Popp. Schwalbach/Ts. 2014. S. 86-97
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015
» SOURCES
Deuerlein, Ernst: Die Gründung des Deutschen Reichs 1870/71 in Augenzeugenberichten. Gerlingen 2011 (Neuauflage)Goncourt, Edmond de: Journal des Goncourts. II.1. 1870-1871. Paris 1890
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
Merkelbach, Thea (Hrsg.): Ferdinand Viebig. Der Krieg 1870/71. Aus den Erinnerungen eines preußischen Offiziers. Zell/Mosel 2021
N.N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Werner, Anton von: Erlebnisse und Eindrücke 1870-1890. Berlin 1913
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2022
January 7, 2022
French Ragtag Army’s Desperate Winter Battles 1871
Real Time History
Published 6 Jan 2022Support us on Patreon: https://patreon.com/realtimehistory
One of the last bastions of French resistance in the new year 1871 is Belfort. A ragtag army called “Army of the East” rushes to free the city near the Swiss border. Meanwhile the Germans prepare to announce their Empire in Versailles.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment, James Darcangelo, Jacob Carter Landt, Thomas Brendan, Kurt Gillies, Scott Deederly, John Belland, Adam Smith, Taylor Allen, Rustem Sharipov, Christoph Wolf, Simen Røste, Marcus Bondura, Ramon Rijkhoek, Theodore Patrick Shannon, Philip Schoffman, Avi Woolf» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Buk-Swienty, Tom: Schlachtbank Düppel. 18. April 1864. Die Geschichte einer Schlacht. Berlin 2011
» SOURCES
Klein, Karl: Fröschweiler Chronik. Arand, Tobias/Bunnenberg, Christian (Hrsg.). Hamburg 2021.Allorant, Salomé u.a. (Hrsg.): La République au défi de la guerre. Lettres et carnet de l’Année terrible (1870-1871). Amiens 2015
Fontane, Theodor: Der Krieg gegen Frankreich. Bd. 4. Berlin 1876
Goncourt, Edmond de: Journal des Goncourts. II.1. 1870-1871. Paris 1890
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
N. N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Pflugk-Harttung, Julius: Krieg und Sieg 1870-71. Berlin 1896
Sheridan, Philip H.: Von Gravelotte nach Paris. Erinnerungen aus dem deutsch-französischem Kriege. Leipzig 1889
Zeitz, Karl: Kriegserinnerungen eines Feldzugsfreiwilligen aus den Jahren 1870 und 1871. Altenburg 1905
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2022
December 31, 2021
German Artillery Shells Paris Into Submission I GLORY & DEFEAT
Real Time History
Published 30 Dec 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimeh…
The new year 1871 is about to bring upon a new German Empire. German leadership, especially Bismarck, is exceedingly frustrated with the dragged out Franco-Prussian War that the Germans have all but won for months now. The decision is finally made to bombard Paris into submission and the German guns surrounding Paris open fire.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment, James Darcangelo, Jacob Carter Landt, Thomas Brendan, Kurt Gillies, Scott Deederly, John Belland, Adam Smith, Taylor Allen, Rustem Sharipov, Christoph Wolf, Simen Røste, Marcus Bondura, Ramon Rijkhoek, Theodore Patrick Shannon, Philip Schoffman, Avi Woolf,» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Bourguinat, Nicolas and Gilles Vogt: La guerre franco-allemande de 1870. Une histoire globale. Paris 2020
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015
https://www.volksbund.de/nachrichten/… (zuletzt besucht am 21.11.2021)
» SOURCES
Allorant, Salomé u.a. (Hrsg.): La République au défi de la guerre. Lettres et carnet de lAnnée terrible (1870-1871). Amiens 2015Goncourt, Edmond de: Journal des Goncourts. II.1. 1870-1871. Paris 1890
Hérisson, Maurice d’: Journal d’un officier d’ordonnance. Paris 1885
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
N. N. (Htrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870-71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Pflugk-Hartung; Julius von: Krieg und Sieg 1870-71. Bd. I. Kulturgeschichte. Berlin 1896
Schikorsky, Isa (Hrsg.): “Wenn doch dies Elend ein Ende hätte”. Ein Briefwechsel aus dem Deutsch-Französischen Krieg 1870/71. Köln, Weimar, Wien 1999
Zeitz, Karl: Kriegserinnerungen eines Feldzugsfreiwilligen aus den Jahren 1870 und 1871. Altenburg 1905
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
December 17, 2021
German States Vote For Unity – Battle of Nuits-St. Georges 1870 I GLORY & DEFEAT Week 23
Real Time History
Published 16 Dec 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimeh…
While the German delegations arrive in Versailles to set in motion the unification of the German states into a German Reich, the people in nearby Paris are starving and their army is still fighting in the countryside.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment, James Darcangelo, Jacob Carter Landt, Thomas Brendan, Kurt Gillies, Scott Deederly, John Belland, Adam Smith, Taylor Allen, Rustem Sharipov, Christoph Wolf, Simen Røste, Marcus Bondura, Ramon Rijkhoek, Theodore Patrick Shannon, Philip Schoffman, Avi Woolf,» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015
» SOURCES
Hérisson, Maurice d’: Journal d’un officier d’ordonnance. Paris 1885Kriegsgeschichtliche Abteilung des Großen Generalstabs (Hrsg.): Der deutsch-französische Krieg 1870-71. 2.2. Berlin 1880
Kürschner, Joseph (Hrsg.): Der große Krieg 1870-71 in Zeitberichten. Leipzig o.J. (1895)
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
Pietsch, Ludwig: Von Berlin nach Paris. Kriegsbilder 1870-71. Berlin 1871
Schikorsky, Isa (Hrsg.): “Wenn doch dies Elend ein Ende hätte”. Ein Briefwechsel aus dem Deutsch-Französischen Krieg 1870/71. Köln, Weimar, Wien 1999
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
December 3, 2021
French Breakout Attempt During The Siege of Paris 1870 – Battle of Villiers-Champigny
Real Time History
Published 2 Dec 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimeh…
The Siege of Paris has been going on for months in November 1870 and the population is starving. The French Army has previously tried and failed to break out but this week they are starting their biggest attempt yet — not knowing that it has been doomed from the start.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan
James Giliberto
Kurt Gillies
Albert B. Knapp MD
Tobias Wildenblanck
Richard L Benkin
Scott Deederly
John Belland
Adam Smith
Taylor Allen
Jim F Barlow
Rustem Sharipov» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Ders.: “Rogerowski oder Rasumowsky? Überlegungen zur nationalen ‘Meistererzählung’ in Fontanes ‘Kriegsgefangen’“, in: Fontane-Blätter 105 (2018). S. 61-86
Ders.: “‘… dazu find ich keine Worte’ – Der Blick auf den Krieg von 1870/71 in Erinnerungsbüchern deutscher Veteranen“, in: Nation im Siegesrausch. Württemberg und die Gründung des Deutschen Reichs 1870/71, hrsg. u. bearb. von W. Mährle. Stuttgart 2020. S. 85-98
Bourguinat, Nicolas and Gilles Vogt: La guerre franco-allemande de 1870. Une histoire globale. 2020
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015
Lecaillon, Jean-François: Les Femmes et la Guerre de 1870/71. Histoire d’un engagement occulté. Paris 2020
» SOURCES
Hérisson, Maurice d’: Journal d’un officier d’ordonnance. Paris 1885De Trailles, Paul et Henry: Les femmes de France pendant la guerre et les deux sièges de Paris. Paris 1872
Fontane, Theodor: Der Krieg gegen Frankreich. Bd. 3. Berlin 1874
Fontane, Theodor: Kriegsgefangen. Erlebtes 1870. Briefe 1870/71. Berlin (Ost) 1984
Kühnhauser, Florian: Kriegs-Erinnerungen eines Soldaten des königlich bayerischen Infanterie Leibregiments. Partenkirchen 1898
N. N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Schikorsky, Isa (Hrsg.): “Wenn doch dies Elend ein Ende hätte”, Ein Briefwechsel aus dem Deutsch-Französischen Krieg 1870/71. Köln, Weimar, Wien 1999
Wöllwarth, Julie von: Unter den Verwundeten von 1870/71. Aufzeichnungen aus einer großen Zeit. o.O, o.J. (1890)
Zola, Émile: La Débacle. Paris 1892
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
November 26, 2021
The Battles of Amiens and Beaune-La-Rolande 1870 – Bismarck Wants His Kaiser
Real Time History
Published 25 Nov 2021Support us on Patreon: https://patreon.com/realtimehistory
After a brief break in the fighting, the Franco-Prussian War continues in late November with the Battles of Amiens and Beaune-La-Rolande. Both sides are exhausted and the casualties are mounting. In the meantime Bismarck is trying to convince the German states of a new German Emperor.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan
James Giliberto
Kurt Gillies
Albert B. Knapp MD
Tobias Wildenblanck
Richard L Benkin
Scott Deederly
John Belland
Adam Smith
Taylor Allen
Jim F Barlow
Rustem Sharipov» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Die Geschichte des Deutsch-Französischen Krieges erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Arand, Tobias: Gestorben für “Vaterland” und “Patrie”. Die toten Krieger aus dem Feldzug von 1870/71 auf dem “Alten Friedhof” in Ludwigsburg. Ludwigsburg 2012
Barry, Quintin: The Franco-Prussian War 1870-71. Vol 2 After Sedan. Solihull, 2007
Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015.
Howard, Michael: The Franco-Prussian War. London, 1961
» SOURCES
Braun, Lily (Hrsg.): Kriegsbriefe aus den Jahren 1870/71 von Hans von Kretschman. Berlin 1911Bundesgesetzblatt des Norddeutschen Bundes, Band 1867, Nr. 1, Seite 1–23
Fontane, Theodor: Kriegsgefangen. Erlebtes 1870. Briefe 1870/71. Berlin (Ost) 1984
Haus der Bayerischen Geschichte (Hrsg.): Gründung des Deutschen Kaiserreichs 1871. Unterrichtsmaterialien. o. O. 2011
Königliche Geheime Ober-Hof-Druckerei (Hrsg.): Verlust-Listen der Königlich-Preußischen Armee und der Großherzoglich Badischen Division aus dem Feldzuge 1870-1871. Berlin 1871
Kühnhauser, Florian: Kriegs-Erinnerungen eines Soldaten des königlich bayerischen Infanterie Leibregiments. Partenkirchen 1898
Kürschner, Joseph (Hrsg.): Der große Krieg in Zeitberichten. Leipzig o.J. (1895)
Moltke, Helmuth von: Geschichte des deutsch-französischen Krieges von 1870-71. Berlin 1891
Zeitz, Karl: Kriegserinnerungen eines Feldzugsfreiwilligen aus den Jahren 1870 und 1871. Altenburg 1905
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021
November 19, 2021
Bismarck Gets Closer To German Unification – A New Spanish King I GLORY & DEFEAT
Real Time History
Published 18 Nov 2021Sign up for Curiosity Stream and get Nebula bundled in and SAVE 26%: https://curiositystream.com/realtimeh…
While the Franco-Prussian War is continuing its messy guerilla phase, the German leaders are negotiating towards a united Germany. Hesse and Baden join the promptly renamed German Confederation — but Württemberg and Bavaria still want more concessions. Meanwhile the question of Spanish succession that started the war is solved in Madrid.
» THANK YOU TO OUR CO-PRODUCERS
John Ozment
James Darcangelo
Jacob Carter Landt
Thomas Brendan
James Giliberto
Kurt Gillies
Albert B. Knapp MD
Tobias Wildenblanck
Richard L Benkin
Scott Deederly
John Belland
Adam Smith
Taylor Allen
Jim F Barlow
Rustem Sharipov» OUR PODCAST
https://realtimehistory.net/podcast – interviews with historians and background info for the show.» LITERATURE
Arand, Tobias: 1870/71. Der Deutsch-Französische Krieg erzählt in Einzelschicksalen. Hamburg 2018Gouttman, Alain: La grande défaite. 1870-1871. Paris 2015
Koch, Roland : “Les canons à balles dans l’armée du Rhin en 1870” in Revue historique des armées, 255 (2009), p. 95-107.
» SOURCES
Braun, Lily (Hrsg): Kriegsbriefe aus den Jahren 1870/71 von Hans von Kretschman weiland General der Infanterie. Berlin 1911Carr, Raymond: Spain 1808–1939. Oxford: At the Clarendon Press, 1975
Deuerlein, Ernst: Die Gründung des Deutschen Reichs 1870/71 in Augenzeugenberichten. Düsseldorf 1970
Goncourt, Edmond de: Journal des Goncourts. II.1. 1870-1871. Paris 1890
Kühnhauser, Florian: Kriegs-Erinnerungen eines Soldaten des königlich bayerischen Infanterie Leibregiments. Partenkirchen 1898
Lowndes, Emma: Récits de femmes pendant la guerre franco-prussienne (1870-1871). Paris, 2013.
Meisner, Heinrich Otto (Hrsg.): Kaiser Friedrich III. Das Kriegstagebuch von 1870/71. Berlin, Leipzig 1926
N.N: + Amadeus von Savoyen in: Neue Presse v. 19. Januar 1890. S. 2
N. N. (Hrsg.): Bismarcks Briefe an seine Gattin aus dem Kriege 1870/71. Stuttgart, Berlin 1903
Schikorsky, Isa (Hrsg.). “Wenn doch dies Elend ein Ende hätte”. Ein Briefwechsel aus dem Deutsch-Französischen Krieg 1870/71. Köln, Weimar, Wien 1999
» OUR STORE
Website: https://realtimehistory.net»CREDITS
Presented by: Jesse Alexander
Written by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand, Jesse Alexander
Director: Toni Steller & Florian Wittig
Director of Photography: Toni Steller
Sound: Above Zero
Editing: Toni Steller
Motion Design: Philipp Appelt
Mixing, Mastering & Sound Design: http://above-zero.com
Maps: Battlefield Design
Research by: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias Arand
Fact checking: Cathérine Pfauth, Prof. Dr. Tobias ArandChannel Design: Battlefield Design
Contains licensed material by getty images
All rights reserved – Real Time History GmbH 2021