Chris Dalla Riva, guest-posting at Ted Gioia’s Honest Broker, considers how instrumental hits used to be far more popular before (among other factors) microphone technology let vocalists compete with orchestras and guitar amplifiers let the strings dominate the pop music market:
Clarinet players aren’t sex symbols. I say this with no disrespect for those that play the single-reeded woodwind. But if you asked a random person on the street to name a clarinet player, I suspect most people couldn’t come up with one, let alone one known for their good looks. Then again, this isn’t a particular indictment of clarinetists. If you asked that same person to name a sexy musician, I’d bet a large sum of money they’d name a vocalist.
This wasn’t always the case, though. In Kelly Schrum’s book Some Wore Bobby Sox: The Emergence of Teenage Girls’ Culture, 1920-1945, she notes that in high school yearbooks in the 1930s some students expressed a passion for “Benny Goodman while other girls had a ‘weakness’ for Artie Shaw or were classified as Glenn Miller ‘fanatics’, faithful fans of Tommy Dorsey, or ‘Happy while listening to Kay Kyser’. Cab Calloway, Xavier Cugat, and Harry James were also popular favorites.” Of those musicians, only Calloway was a singer. Goodman, Shaw, and Kyser played the clarinet. Miller and Dorsey played the trombone. Cugat played violin. James played trumpet.
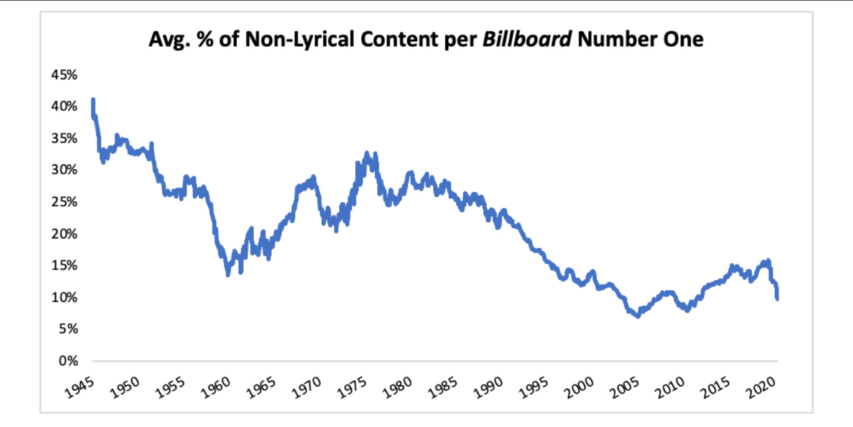
Given that our contemporary musical world is dominated by vocalists, this seems bizarre. It feels like if you have a musical group it must be centered around the vocalist. If we measure the average percent of instrumental content per Billboard number hit between 1940 and 2021, we see demonstrable evidence for not just the decline of the instrumental superstar but the instrumentalist generally, with the sharpest declines beginning in the 1950s and the 1990s.
NOTE: Data from July 1940 to August 1958 comes from Billboard‘s Best Sellers in Stores chart. After August 1958, Billboard deprecated that chart in favor of the Hot 100, which initially aggregated sales, jukebox, and radio data. The Hot 100 remains the premiere pop chart, though it has come to include many more sources, like streams and digital downloads. The above displays a 50-song rolling average.
What’s going on here? How could throngs of high schoolers long for the clarinet-wielding Artie Shaw 80 years ago when most teenagers today would struggle to name a musician who isn’t also a singer. I believe it comes down to four factors: improved technology, the 1942 musicians’ strike, WWII, television, and hip-hop.
Improved Technology
In the VH1-produced documentary The Brian Setzer Orchestra Story, Dave Kaplan, Setzer’s manager, recounts a conversation he had with Setzer before assembling a guitar-fronted big band in the 1990s: “Nobody had ever fronted a big band with an electric guitar … I asked Brian, ‘Why wouldn’t somebody have tried it?’ [Setzer replied,] ‘Well there weren’t amps.'” Albeit a simplification, Setzer’s quip is pretty accurate.
While there were some famous guitar players among the big bands of the first half of the 20th century, we don’t see the guitar become a driving force in popular music until amplification improved. This was not only a boon for the guitarists but also vocalists. Unlike brass and wind instruments, you can sing while you play the guitar. Thus, it’s not shocking that the rise of the guitar coincided with the rise of the vocalist.
But it wasn’t just guitar amplification technology that was vital. It was also microphone technology. Again, microphones had to improve so vocalists could compete with the cacophony of a loud band. On top of this, recording had to change to capture more subtlety in the human voice.