Ted Campbell outlines how the Battle of the Atlantic was fought between the Kriegsmarine and the Royal Navy (and the Royal Canadian Navy and, eventually, the United States Navy) in World War 2:
… there is a rather thick, and quite blurry line between naval strategy and naval tactics. One Army.ca member used the Battle of the Atlantic to distinguish between two doctrines:
- Sea control ~ which was practised by the 2nd World War allies ~ mostly British Admirals Percy Noble and Max Horton in Britain and Canadian Rear Admiral Leonard Murray in St John’s and Halifax; and
- Sea denial ~ which was practised by German Admiral Karl Dönitz.
The difference between the two tactical doctrines was very clear. The strategic aims were equally clear:
- Admiral Dönitz wanted to knock Britain out of the war ~ something that he (and Churchill) understood could be done by starving Britain into submission by preventing food, fuel and ammunition from reaching Britain from North America. (We can be eternally grateful that Adolph Hitler did not share Dönitz’ strategic vision and listened, instead, to lesser men and his own, inept, instincts); and
- Prime Minister Churchill, who really did say that “the only thing that ever really frightened me during the war was the U-boat peril“, who wanted to keep Britain fighting, at the very least resisting, until the Americans could, finally, be persuaded to come to the rescue.
Prime Minister Winston Churchill greets Canadian PM William Lyon Mackenzie King, 1941.
Photo from Library and Archives Canada (reference number C-047565) via Wikimedia Commons.Canada’s Prime Minister Mackenzie King did have a grand strategy of his own. It was to do as much as possible while operating with the lowest possible risk of casualties ~ the conscription crisis of 1917 was, always, uppermost in his mind and he was, therefore, terrified of casualties. He mightily approved of the Navy doing a HUGE share in the Battle of the Atlantic ~ especially by building ships in Canadian yards and escorting convoys which he hoped would be a low-risk affair.
Churchill’s grand strategy was based on Britain surviving … there was, I believe, a “worst case” scenario in which the British Isles were occupied and the King and his government went to Canada or even India. But that has always seemed to me to be a sort of fantasy. The United Kingdom, without the British Isles, made no sense.
(While I believe that Rudolph Hess was, as they say, a few fries short of a happy meal, I think that he and several people in Germany believed that it might be possible to negotiate a peace with Britain which many felt was a necessary precursor to a successful campaign against Russia. The Battle of Britain (die Luftschlacht um England, September 1940 to June 1941) was, clearly, not going in Germany’s favour. Late in 1940, the Nazi high command had been forced to send a German Army formation to Libya to prevent a complete rout of the Italians. Malta still held out, meaning that Britain had air cover throughout the Mediterranean. In short, Britain was not going to go down unless it could be starved into submission ~ and in the spring of 1941, the Battle of the Atlantic was going in Germany’s favour. There was, in other words, some reason for Germans to believe that an armistice might be possible ~ freeing up all of Germany’s power to be used against the USSR.)
(But things were changing for the Allies, too. At just about the same time as Hess was flying to Scotland, then Commodore Leonard Murray of the Royal Canadian Navy, who had been in England on other duties, had met with and persuaded Admiral Sir Percy Noble, who liked Murray and had been his commander in earlier years, that a new convoy escort force should be established in Newfoundland and that it should be a largely Canadian force (with British, Dutch, Norwegian and Polish ships under command, too) and that it should be commanded by a Canadian officer. Admiral Noble insisted, to Canada, that Murray, who he liked, personally, and who had written, extensively, on convoy operations in the 1920s and ’30s, must be that commander. The establishment of the Newfoundland Escort Force, which would be more appropriately renamed the Mid Ocean Escort Force in 1942, was a key decision at the much-debated operational level of war which put an expert tactician (Murray) in command of a major force and allowed him (and Noble) to move closer to achieving Churchill’s strategic aim. The Battle of the Atlantic was not won in 1941, but it seemed to Churchill, Noble and Murray that they were a lot less likely to lose it, even without the Americans.)
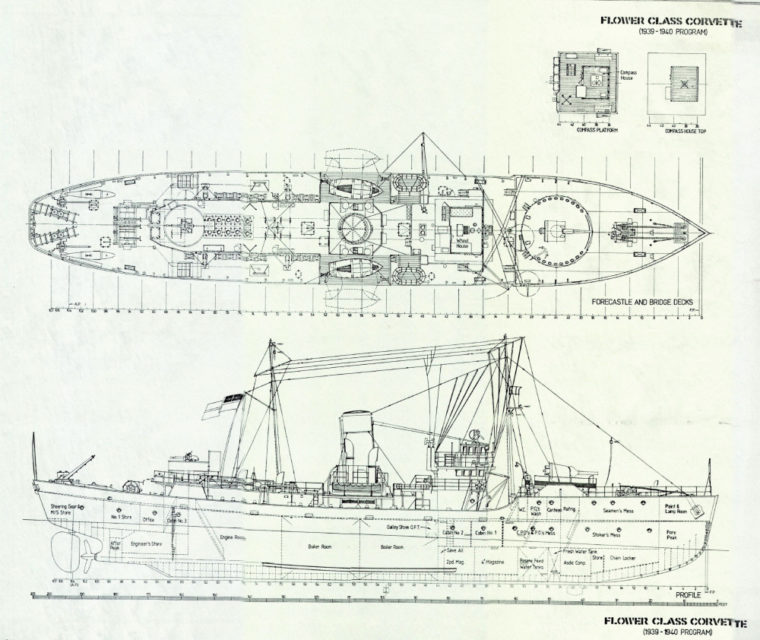
Diagram of the early Flower-class corvettes, via Lt. Mike Dunbar (https://visualfix.wordpress.com/2017/04/12/dreadful-wale-4/)
Anyway, the boundaries of strategy vs. the operational art vs. tactics were as thick and blurry in 1941 as they are today. The decision, taken in 1939, for example, to build little corvettes in the many British and Canadian yards that could not build a real warship was, in retrospect, a key strategic choice, but it was, at the time, totally materialist: just a commonsense, engineer solution to an operational problem ~ lack of ships. Ditto for the eventual decision, which had to be made by Churchill, himself, to reassign some of the big, long-range, Lancaster heavy bombers to Coastal Command. It was, once again, with the benefit of hindsight, a key strategic move, but at the time it would likely have seemed, to Capt(N) Hugues Canuel, the author of that Canadian Naval Review essay, to be materialistic, more concerned with how to use the resources available than with deciding what is needed.
I agree with Capt(N) Canuel that, by and large, Canadians have left strategic and even operational level thinking to first, the British and more recently the American admirals ~ Rear Admiral Murray being known, in the 1930s and early 1940s as a notable exception.